Wood carving has existed for many centuries, new directions, types and subspecies of carving appear, but there is no single classification of carving types. We have summarized the classic and new types of carving. A special place in the classification of thread types is occupied by house carving. It practically concentrates all types and subspecies of thread.
1. House carving: the origins of wood carving can be traced back to ancient times. With the development of the Russian state, the art of woodcarving also develops. Carvings were used to decorate palaces, temples, churches, icons, houses, wooden buildings, interior items, furniture, household items, musical instruments, toys, souvenirs, amulets. The reign of Peter 1 turned out to be favorable for the development of woodcarving in Russia. Under Peter 1, shipbuilding was most developed, since wood in those distant times was the main material for creating the Russian fleet. The bows of the ships were decorated with figures - images of animals and birds - a dragon, an elephant, the head of a lion or a horse. These images symbolized the power, strength and courage of sailors. The skillfully carved prow figure is not only a worthy decoration of the ship, but also, as it was believed, a symbol of good luck for sailors. Such a carving is called ship or baroque. "Coming ashore" wood carving has found wide application in wooden architecture, the manufacture of wooden utensils, in home decoration and various decorations.
House (ship) carving was most developed in the late 19th and early 20th centuries. At the same time, the carving was not of the same type, it was performed using different techniques - which made the decor of the decorated products more figurative, richer and more picturesque.
2. Saw carving: in the second half of the 20th century, saw carving, made with a thin jigsaw file, became widespread in wooden buildings in the countryside and in the city. Of the variety of types of thread - it is the most common and affordable. Saw thread has several subspecies: through, consignment note, openwork. In all subspecies, the background is cut out or removed.
3. Flat thread and its subspecies: the most common, affordable, not requiring special premises and large material costs is a flat-cutting thread and its subspecies.
4. Contour carving: the name itself suggests that in this carving technique a contour, a contour drawing is performed. Contour carving is used to perform not strict geometric shapes, but free patterns, which, as it were, are drawn on the workpiece with a cutting tool. In this case, various lines can be used: straight lines, curves - arbitrary curvature, wavy, spiral, etc.
5. Geometric thread: the main subspecies of a flat-cut thread, which is based on two components - a plane and a recess made on it. It is called geometric because it is based on all kinds of geometric elements - triangles, polygons, circles, rhombuses, squares, ovals. Combining the simplest geometric shapes, you can get an amazing pattern, where every element, every stroke is accurately drawn. Complex elements of carving are formed from geometric figures: ladders, windings, beads, snakes, lights, spikes, various combinations of which with each other create geometric carving motifs, and the combination of motifs forms a geometric ornament.
6. Staple thread: Staple thread is based on a staple notch or staple cutting, shaped like a fingernail. Therefore, bracketed threads are often called nail threads. Staple carving is a kind of flat carving and, in combination with other types of carving, is used to decorate caskets, cutting boards, decorative panels, and household spatulas.
7. Wrinkled carving: used for finishing and decorating flat carvings. A feature of this carving is the decoration of the surface of the product of the executed motif with wrinkles-rays. Each ray is an acute-angled groove that originates from a center point. From the center, the groove smoothly passes into an extended wrinkle, reaching the greatest width and depth of the outer end of the ray. There is a way to immortality for wood carving: to keep the skill, experience, carving techniques. Teach the young to carve wood. In villages and cities. After all, they build houses from wood, from logs. This is in the traditions of Russians - to build from wood, cut lace on wood, decorate their houses with carved architraves, porches. Folk art is a true value. Woodcarving is an integral part of it. Russians must not forget how to cut wood. Creating beauty with your own hands is in the blood of our crafty people.
Used materials and tools
For wood carving, different types of wood are used. The choice of one or another breed depends on the purpose and shape of the decorated product and the type of carving. From deciduous trees, linden is often used for carving. Linden wood is easily and cleanly cut, little prone to cracking and warping. Due to its low hardness, linden is not used to make furniture, so its use is limited to small household items. Alder wood is also easy to cut, warps little, accepts finishes well and imitates other species, such as mahogany. All this makes it suitable for all kinds of work. An excellent material for carving is birch wood. It is harder than linden and alder and is more difficult to cut, but the quality of the carving is better. Birch wood is well stained and finished. Its disadvantages are the ability to easily absorb and release moisture, as well as the tendency to warp and crack, which does not allow it to be used in large products. From birch, you can make overhead carved decorations and details of furniture and other products. For carving on small items - dishes, souvenirs - poplar and aspen wood is used.
Oak has long been used for large decorative carvings and the manufacture of carved furniture. Oak carving is complex and laborious due to the high hardness of the wood and the tendency to chip, but it is very expressive and decorative.
Beech wood is close to oak in hardness, but gives fewer chips, as it is more uniform. Beech is well stained with aqueous solutions of dyes and finished. Beech is mainly used for small carvings. Walnut wood is the best material for carving. It cuts beautifully in all directions, rarely chipping and allows for the most precise carving. Walnut wood is well finished and especially polished. It is used in the manufacture of furniture both for carving on solid wood and for applied carving in combination with other species. For highly artistic small carvings and sculptures, walnut wood is also considered the best material. For small items decorated with carvings, rarer types of wood are also used: apple, cherry, etc. From coniferous species, wood of pine, spruce, cedar, yew is used for carving. From ancient times, decorations for architraves, icons, cornices, and gates were carved from pine. This carving is large, so the unevenness in the density of the layers of early and late softwood does not complicate the work. Spruce cuts lighter than pine, but it has more knots and is very hard, so it is less often used for carving. Harvesting of wood for carving should be done from October to January, when the movement of juices in the trunk stops and the risk of wood cracking and damage by fungi and insects decreases. Boards intended for carving are dried to a moisture content of 8-10%, making sure that cracks and warping do not form. Boards intended for carving are first cut into blanks on circular saws, then they are cut to size on planer and thicknesser machines. Wide blanks are obtained by gluing individual bars or planks with a PVA dispersion. In this case, it is necessary to select wood plots so that the cut and direction of the layers are the same. An incorrectly glued blank made of bars with the opposite direction of the layers of wood makes it difficult for the carver to work, reduces the artistic value of the carving, and when stained with water-based dyes, bars of different shades are obtained. Before carving, the surface of the workpiece is leveled by scraping. The surface is not sanded with sandpaper, as abrasive grains can get into the pores of the wood, which will quickly dull the tool.
Any wood is very sensitive to changes in environmental humidity. This property is one of the disadvantages of timber.
At high humidity, wood easily absorbs water and swells, and in heated rooms it dries out and warps. Drying wood is a very long and troublesome business. It is very difficult to dry hard wood that has a core. Even dead wood after sawing into short logs and barking is covered with numerous cracks. The core is especially valued, the wood of which is harder and drier, and its pores are filled with a special preservative substance. When the ridge dries, the sapwood first cracks, and then the core. To preserve the valuable wood of the core, the sapwood is cut off with an ax and the ends are smeared with putty. Without sapwood, heartwood dries quite well, with almost no cracks. Steaming speeds up the drying of the wood. Raw wood is placed in a vat of suitable size, a little water is poured into the bottom, covered and placed in a heated oven of a gas or electric oven, tightly covering it with a damper. Steamed wood not only resists cracking, but also acquires a deep brownish-golden color. Boiling in oil. Small pieces of wood are boiled in cottonseed oil, drying oil or any vegetable oil.
Cookware made from wood steamed in oil is very water-resistant and does not crack even with everyday use. Boiling in saline speeds up the drying of small pieces of hardwood. Raw wood is placed in a saucepan or boiled water, poured with a saturated solution of table salt and simmered for about 3-4 hours. After that, it is dried at room temperature for about 2-3 weeks. This method is particularly suitable for hardwoods. Drying finished products in sand can achieve an interesting decorative effect. A layer of clean river sand is poured into a suitable container, the product is laid and covered with a new layer of sand. In this case, the product should not touch the walls. After that, a container without a lid is placed on a flooded Russian stove. The drying effect is achieved by the optimal distance of the container in relation to the fire. Drying in grain in Russia was well known. In the spring, a few weeks before sowing, the workpiece or product was buried in the seed grain, which absorbed moisture from the wood. Then the workpiece was taken out and dried at room temperature.
Drying on cement or concrete floor based on the ability of cement stone to intensively draw moisture into itself. Wet wood is laid on a dry concrete floor and after 2-3 hours it is turned over so that alternately one or the other face is adjacent to the cement floor. Drying in manure, shavings, polyethylene and air is also used.
The natural type of drying is atmospheric, airy. It is necessary to dry the wood in the shade, under a canopy and in a draft. It is better to choose a place for drying at the attic of the house, a barn or a specially arranged canopy. When dried in the sun, the outer surface of the wood heats up quickly, while the inner remains damp. Due to the difference in stresses, cracks form, the tree quickly warps. After atmospheric drying in warm, dry weather, the moisture content of wood is 15-20%. Blanks intended for interior decoration can be transferred to a heated room and dried. When drying products, cracks often occur. The best way to seal a large crack is to insert a piece of the same wood into it. If it is not possible to select a piece of wood from the same blank, then a piece of the same color is selected, located far from the core of the trunk and oriented in the same way towards the center. After the glue dries, the junction is planed and cleaned with a planer. Small cracks are usually sealed with sawdust-based putty.
Tools For successful work, a woodcarver needs a well-equipped workplace, appropriate tools and fixtures. For the work of cutters, a dry, bright room with a constant temperature and humidity is necessary. The walls and ceiling of the room should be painted in light colors. The equipment of the carver's workplace depends on the nature of the carving work performed. In the manufacture of small products, carving can be done on a regular table. For products big size suitable workbench.
The workbench or table is placed so that the light falls from the front and left. The best
lighting - natural, without direct sunlight. At artificial lighting the light should come from two or three sources so that there are no sharp shadows on the workpiece. The workshop needs one carpenter's workbench for preparing material for carving, as well as a grinding machine and a table for sharpening and straightening tools. For woodcarving, various shapes, chisels or chisels are used. Straight chisels with a web width of 3-30 mm are used mainly for cleaning the background in relief carving, sometimes they are used in contour carving. Oblique chisels, also called cutters, are the main tool for making geometric carvings. They are used both when performing rough work (cutting wood with a full blade), and when stripping threads with the tip of a knife. It is desirable to have several knives with different tip shapes: from sharp (30°) to rounded. Clucarzy chisels are distinguished by a short blade 2-15 mm wide and a long, curved neck near the blade. The shape of the canvas may be different. Use them when doing relief carving, as well as for cutting in hard-to-reach places. Straight cranberries clean the background in relief carving. Semicircular chisels with a web width of 3-
30 mm, depending on the radius of curvature, there are the following types:
Sloping with a large radius of curvature;
Medium or semicircular;
Steep with a small radius of curvature.
This is the main tool for all types of carving, except for geometric, where these chisels are used only for cutting semicircular holes. Corner chisels with a web width of 5-15 mm are used when sampling narrow groove lines. In cross section, the chisel forms an angle of 50-70°. Such chisels can be made in the form of a cranberry. Tserazik chisels, dense 2-3 mm wide, are close in shape to steep semicircular chisels, but their profile is deeper. Ceraziki is used to cut through narrow veins. Semicircular shavings are used to work on wood in hard-to-reach places. Rasps are used for surface treatment. Chassines are metal rods, at one end of which there are notches in the form of a grid, dots, stars. They are used for chasing the background, mainly in Kudrinskaya carving. In addition to the main cutting tool, the cutter also needs an auxiliary one: a marking tool, tools for drilling, sawing. Auxiliary tools also include:
Mallets for striking the handle of a chisel when cutting out a background, cutting a relief in a large carving;
Rotisserie or drill with a set of drills for drilling holes in slotted thread and drilling deep places in relief;
Jigsaw and files for sawing out the background in a slotted thread.
In addition, the cutter may need carpentry tool when preparing parts for threading: planer, jointer, scrapers, etc.
The main technological methods and operations of woodcarving
The manufacturing process of carved products can be divided into the following stages:
Project development;
Procurement and preparatory operations;
Direct carving;
Finishing carved product;
The design development phase may include the process of creating an artistic intent and the process of modifying or refining some finished sample. This also includes the development of sketches, drawings and the like. Often the carver has to think over the design of the product, the manufacturing and assembly technology, as well as design the necessary devices.
All this also applies to the design stage. Prepared and preparatory operations include, for example, the following types of work:
Wood harvesting;
Drying wood;
Material selection;
Processing of blanks and manufacturing of products for thread;
Marking blanks for threading;
Tool sharpening, etc.
Sketching and modeling: the development of sketches and modeling of future carvings occupy an extremely important place in the carver's robot. Of course, not all people can draw like artists, but often this is not required. In addition, it has been noted that drawing abilities can develop, you just need to show patience and perseverance. At first, in carving, you can get by with ready-made samples, gradually starting to make your own changes and improvements to them. Then, with the accumulation of skills and experience, move on to completely independent works. The carver needs to study the issues of composition and perspective, the techniques of geometric constructions, various types of proportions. To do this, read the relevant literature and get acquainted practically. When performing complex types of carving, one pattern is not enough. Sometimes, to clarify the shape of the relief, the figure shows details in section. However, this does not always help. In such cases, it is recommended to make a model of the future carved product in a material that is easier to process - clay, plasticine, gypsum.
The model makes it possible to feel the volume, to clarify the ratio of details between themselves and with the background, to clarify the carving technique, to determine which tool is needed for work. At home, it is most convenient to use plasticine for modeling - it does not dry out, it is always ready to work, and does not give dirt. The model can be performed in a generalized form, without detailed details. It is enough if it conveys the main, most important elements of the future product.
Enlargement and reduction of the sketch. Quite often, a carver needs to rescale a sketch he has made or an illustration in a book. To do this, the following main methods can be used:
Resizing "by cells";
Redrawing a picture with a pantograph;
Photocopying.
Translation and rescaling of the drawing is very easy to do with photocopying. In modern conditions, this is the cheapest, easiest and fastest way.
Woodworking technology already in the X - XII centuries. was quite developed. Most of the buildings and wooden carvings, showing the considerable skill of carpenters, carvers, turners and joiners, have come down to us already from the 19th century. Thread types
- House (ship) carving
In the 20-30s of the XIX century. in the peasant architecture of the Gorky region and the Middle Volga region, the so-called deaf relief carving spread. This is a carving with an uncut (deaf) background and a high relief of the pattern. She moved to the huts from the Volga ships.
House (ship) carving has a free character. A richly and freely developed floral pattern is usually located throughout the board, the leaves curl in steep counter spirals, they are connected and at the same time separated by images of a multi-petalled flower, visible as if from above, so that all the petals are arranged in a circle or fit into a circle.
Blind relief carving in the 19th and first half of the 20th century. used to decorate furniture - cabinets, tables, mirror frames, cases for floor and wall clocks.
The master carver must be proficient in all types of carving, including those that are used extremely rarely.
- openwork carving
In the middle and in the second half of the XIX century. in Russian wooden buildings, both in rural and urban areas, openwork, sawn carving, performed with a thin file - a jigsaw, became widespread.
Openwork sawn carving adorns the pediments of houses, covers window trims, framing entrances, etc.
openwork carving very effective, it is like wood lace. Many ornamental and decorative motifs of Russian deaf, embossed carving have passed into openwork carving. There are also conditional, generalized, geometrized images of female figures in sawn carving, very similar to images in Russian folk embroidery and lace.
Houses with openwork carvings preserved from the last century can be found in many cities of our country. There are especially many old buildings with carved decoration in the Siberian city of Tomsk.
Folk craftsmen have always had a sense of proportion, therefore, only certain parts of the building were decorated with openwork carvings: window and door frames, chapels, end boards. On sunny days, when the shadow from the slotted architraves covers the smooth walls of houses with dark lace, expressiveness openwork carving intensifies. But even on cloudy days, the details of the carving stand out in a clear pattern against the general background of the wooden structure.
But not only for the sake of beauty, carpenters sewed all kinds of overhead parts to the house. Each of them has a specific practical purpose. For example, a prichelina is a board that covers the ends of the roofs sticking out from under the roof to their ends. moisture did not penetrate, destroying the tree.
The end board, which was nailed to the ends, has the same purpose. log cabin. The window platband closes the joint between the window sash trim and logs. In northern Russian huts, the junction of two chapels was covered with a so-called brush, the lower end of which was decorated with openwork carvings. The so-called towels were also carved - the lower ends of the chapels protruding from under the roof.
Nowadays openwork house carving continues to be used to decorate rural wooden houses, country houses, arbors, sheds, towers on playgrounds.

The main tool used for drilling holes in the board is a brace. They usually drill large holes. This is a reliable, proven carpentry tool. A ratchet with a ratchet is more convenient, which allows you to lock the cartridge by turning the ring and change the direction of its rotation when clamping or releasing from the drill.
Wood drilling tools:
- brace,
- drill and flat center drills,
- holder with interchangeable flat drills
Holes with a diameter of 10 mm or more are drilled using special flat drills - perok. In addition to ordinary perks, there are universal ones with removable cutting plates on sale. The kit includes 7 drills with a width of 14, 16, 18, 20, 22, 25 and 32 mm. If it is not possible to purchase flat drill bits for wood in a store, you can make them yourself. Make plates with cutting edges from an old saw blade 1.5-2 mm thick, which can be processed quite easily with a file.
When cutting, the canvas is broken according to the applied deep risks. The risks are applied with a scraper, file or some other tool from solid metal. Make a holder from a bolt or rod with a diameter of 8 mm.
Having fixed the rod in a vice, make a cut from the side of the end with a hacksaw for metal. Drill a hole perpendicular to the cut. Punch a hole in the plate at an appropriate distance from the top edge.
Connect the plate to the holder with a rivet. If you want to make the holder universal, cut a thread in its hole and select the appropriate lock screw. The universal holder is constantly clamped in the chuck, and when drilling holes of different diameters, only drill-plates are changed. Before drilling, the center of the future hole is marked with an awl.
Small holes are drilled with a drill or drill. If you are unfamiliar with a drill, look at the picture where it is shown.
Often, openwork carving is called sawn carving, since its technique is based on sawing figured openings in the board. Saws for sawing curved blanks along the outer contour are called rotary or circular. The width of the blade of the circular bow saw is from 4 to 15 mm.
Narrow blades are used when cutting blanks with steep bending lines, and wider blades are used in large ones with smooth, slightly curved or straight contours. Unlike a conventional joiner's bow saw, the blade must be rotated. This makes it possible to make cuts in different directions, almost without changing the position of the saw machine.
The circular bow saw machine can be made by yourself from birch or beech wood. Depending on the size of the workpieces you are sawing and the length of the blades you have, bow saws can have a wide variety of sizes. The circular saw consists of two racks that are inserted into the eyes hollowed out in the thickened ends of the strut. Holes are drilled in the lower parts of the racks, into which the pegs machined on a lathe are inserted. The handles should rotate with some effort.
On the opposite side, at the end of each handle, longitudinal cuts are made into which the canvas is inserted. The tension of the canvas occurs due to the twisting of the bowstring, which tightens the upper ends of the spacers. The bowstring is made from 10-1 2 turns of hemp or linen twine. Instead of twine, a rod with a thread cut at both ends is also used to tighten the upper ends of the racks.
The rod is passed through the holes in the racks and, having put on metal washers, the wing nuts are screwed on both sides. The stands of a homemade circular saw are usually made elongated - this makes it possible to cut curved lines at a considerable distance from the edge of the board. And the saw blade, along with the spacer, is shortened. Such a saw is much more convenient to work with than a standard saw.
All saws basically have three types of teeth: isosceles, rectangular and oblique. If the saw is intended for sawing wood across the fibers, then its teeth should be isosceles triangles, if along, then inclined.
Circular saw, moving along curved lines, crosses the wood fibers at a variety of angles. What kind of tooth shape should a circular saw have? The most versatile was a saw with a rectangular tooth shape, when one of its edges is located at a right angle to the blade. To increase the maneuverability and ease of movement of the circular saw, the set of teeth must be made quite large.
Curvilinear blanks from boards with a thickness of not more than 10 mm are cut with a small round saw or jigsaw.
The main tool for sawing out internal openings in the workpiece is hacksaws with narrow wedge-shaped blades, the so-called triggers. Triggers can also cut blanks along the outer contour. In addition to the usual triggers of different sizes, universal ones with removable canvases are used.
The thickness of the blades of the triggers is 1.5 mm, the length is 325-530 mm, the width at the handle is 20-40 mm, the shape of the teeth is rectangular. The saw is bred through one tooth: even teeth to the right, and odd teeth to the left. They sharpen at random, that is, first through one tooth on one side, and then, turning the canvas, on the other side.
If the hammer could not be bought, it is made by hand from an ordinary hacksaw or an old saw blade 1.5 mm thick. The hacksaw blade is cut so that an elongated sharp wedge is obtained.
If the teeth of the hacksaw you are using have rectangular shape, then the excess metal is cut off from the side of the butt, but if they are of a different shape, then you need to cut off that part of the web on which the teeth are located in order to cut out new teeth on this edge later. You can cut the canvas as follows.
Clamp the blade in a vise between two planks so that only the part that needs to be cut protrudes. Run the tip of the scraper several times along the edges of the boards on the canvas until a sufficiently deep risk is formed. Apply the same risk on the other side of the canvas.
Then, with hammer blows, bend the protruding part of the canvas. Usually the canvas breaks easily exactly at the risk. Align the resulting rough fracture with a file.
Strengthen the canvas with clamps on the workbench. In order not to inadvertently touch the teeth with a file, nail a metal plate 3-4 mm thick along them on a workbench.
First, with several passes of the file, remove the metal from one side of the blade, and then from the other. Usually, before planing, the cross-section of the saw has the shape of a rectangle, and after it, it has the shape of an acute triangle or a highly elongated trapezoid.
When sawing, the butt of such a blade is not clamped by wood fibers and the saw moves easily in the cut. The wider the cut formed by the saw, the easier it is to change the direction of the blade. This is especially necessary when cutting sharp bends. To get a wide cut, the saw blade is well bred.
For openwork carving use boards 15-25 mm thick from aspen, pine, birch and alder. Since birch wood is affected by fungi in the open air, carved from it openwork patterns must be covered with a protective layer oil paint. When choosing a material, it is necessary to harvest well-dried boards without cracks, warping and with a minimum number of knots. The smooth surface of the boards is obtained by planing.
Usually, any saw pattern consists of several repeating elements. For each of them, you need to cut a full-size template from thick thick cardboard, textolite, plywood. Soak a cardboard template several times with drying oil and dry for a day. Our drawing shows a pattern of a 5-shaped curl - the most characteristic element of house carving.
When sawing lines with different steepness, different sections of the canvas alternately participate in the work. Very steep lines with a small radius of curvature are cut with the tip of the hammer, that is, its narrowest part.
As the steepness of the line decreases, the middle part of the saw enters the work, and if the line being cut is almost straight, the wide part of the saw located closer to the handle is included in the work. After cutting out the openings on the carved board, eliminate all sorts of flaws and inaccuracies with a narrow-bladed knife and chisels.


- Geometric carving
Geometric carving is diverse in its techniques and the visual effect that it produces. Here, the most used trihedral - notched carving is distinguished, the very name of which suggests that it is based on notches of various sizes, each of which has three faces.
It is followed by a nail-like thread, in the form of recessed holes, and a contour thread. All the variety of cutting on one or another object was achieved by endless combination and variation of these basic techniques.
Currently, geometric carving has switched to new items: caskets, boxes, ladles.

Geometric carving- one of the most ancient types of wood carving, in which the depicted figures have a geometric shape in various combinations. Such a carving is carried out in the form of rectilinear and arcuate elements with a jamb knife and semicircular chisels. This type of carving is popular because of the ease of execution, a small set of tools used in the work. At the same time, this carving does not require, as with relief carving, special knowledge of the theory of drawing. Another advantage of geometric carving is the shallow depth. carved pattern, which does not violate the composition of the product itself.
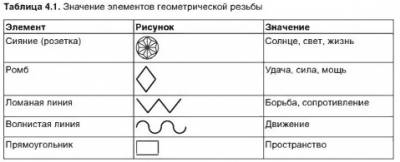
The main types of patterns in geometric carving:
a. Chain
b. snake
v. Honeycombs (squares)
Zigzag snake
d. Honeycombs (diamonds)
e. Christmas trees
- relief carving
Second the most important carving, very ancient in origin and widespread, was flat-relief carving. The very name of the thread shows that it is based on a flat relief.
This means that a pattern, usually free vegetative, is revealed on the surface of a board or household item by choosing, i.e. deepening the background around the future pattern. The background deepens slightly (0.5-1 cm), the drawing itself remains on the same level with the board.
To give it more liveliness and softness, the edges of the pattern thus revealed, mainly images of leaves, berries, birds and animals, are slightly rounded or oval.



- sculptural carving
Along with flat-relief and high-relief carving (house carving, ship carving), volumetric, sculptural carving has become widespread.
In the old days, carvers were carved by craftsmen - carvers, usually from a whole wooden block, beehives in the form of human or animal figures.
Sculpture- one of the types of fine art, the task of which is to recreate the images of people, animals, significant social and historical events in plastically expressive forms.
- Slotted wood carving
For many centuries, Russian craftsmen with the help of a knife and an ax built wooden palaces, churches, peasant huts, created household utensils decorated with carved patterns. As a result, certain traditions, types and techniques of woodcarving have developed. The most widespread, due to its relative simplicity, was slotted thread.
Slotted wood carving is a carving with a fully selected background. It can be geometric, contour, oval, with good and clean execution it gives the product openwork and lightness, especially platbands, cornices and fences.

Slotted wood carving can be performed both in the technique of flat-relief carving (with a flat ornament) and in the technique of relief carving. Flat slotted carving was often used to decorate antique Russian furniture. When using such a thread in lockers and screens, a bright fabric is placed under it as a background.
The background in the slotted thread was previously removed with a chisel or saw, but now they have been replaced by an electric jigsaw. In the latter case, the thread is called sawn. Since this operation is mechanized, saw thread is used in the mass production of furniture.
A slotted carving with a relief ornament is called openwork. Such carvings were widely used to decorate baroque and rococo furniture in the late 17th and 18th centuries.
It is easier to cut out an ornament of a slotted or laid on thread than to choose a background with notched contours in a blind thread. The edges of the ornament do not always turn out to be even and clean, therefore, they are rounded off by cutting off a narrow chamfer along the edges or choosing narrow fillets-recesses. House carving does not require especially careful execution, since it often looks from afar.
House carving is mainly performed by sawing and drilling. The traces left by the tool are rarely cleaned, wood scratches are often not taken into account. However, many carpenters try to make such carvings as clean as possible.
Holes in the workpiece or in the part are drilled or cut with round chisels, small and large, depending on where the part should be. To protect the part from chipping, its back side should be pressed tightly against some smooth board.
Saw through the parts in this order. First of all, a hole is drilled, then a jigsaw or a hacksaw is inserted into it and sawed through according to the risks. The workpiece can be laid on a workbench and sawn from top to bottom, but it is better to arrange a special stand made of a thick board about a meter long.
Overhead wood carving- this is an ornament made with a slotted carving and glued or nailed onto a finished background, for example, on a platband board or on another detail.
Laid-on threads with this method of execution are clearer than blind threads and look much better. In this case, slotted threads should be made as clean as possible. It is not recommended to chamfer reverse side details, as it may give the impression that the thread is torn off from the main background.

sawmill wood carving It became widespread in folk art in the 19th century. due to the spread of the production of thin factory-made sawboards used for finishing work. The process of sawing carving includes the following operations: preparing the board, applying a template, cutting or drilling holes, rough cutting the thread contour, finishing the contour, working out the relief and cleaning the surface.
Until now, in Russian villages and villages, as well as small provincial towns, you can see old houses with lacy wooden decoration, preserved from the last century. Only separate parts of the house were decorated with openwork sawn carvings: window and door frames, chapels, end boards. Overhead carved details on houses, in addition to aesthetic, had practical significance. So, carved boards along the slopes of the roof - prichelina - covered the ends of the slats sticking out from under the roof. Their purpose is to protect the slegs from moisture penetration so that they do not collapse. The same function was performed by end boards, which were nailed to the ends of a log cabin. Window casings covered the joints between the window frame and logs. In northern Russian huts, the junction of two chapels was covered with a patterned towel, and the lower ends of the chapels protruding from under the roof were also decorated with carvings. Such carvings were also used to decorate cornice valances, brackets, attics, fillings in attic windows, backs of chairs, beds, etc.
Sawing carving or sawing is a patterned through wood carving based on a planar through ornament with zoomorphic and plant elements. In the case of fixing an openwork thread on the planes of entrance gates, gates, etc., such a thread is called a cut-overhead thread, regardless of the method of its fastening.
The widespread use of sawn carving in folk art is associated with the development of the lumber industry in the 19th century, thanks to which thinner and cheaper sawboards began to be produced, which were used for Finishing work. The process of sawing carving includes the following operations: preparing the board, applying a template, cutting or drilling holes, rough cutting the thread contour, finishing the contour, working out the relief and cleaning the surface.
Pine and larch wood has always been used and continues to be used for openwork carving. For elements decorating housing, birch, aspen and linden wood could also be used. Dried boards (as a rule, ¾ vershok (33 mm) thick) were smoothly planed in layers. Templates or stencils created by the craftsmen themselves were used to apply the pattern to the blank. Therefore, it is so difficult to find repeating ornaments in the decor of wooden houses. After drawing the pattern, the blank was fixed on a workbench with a preliminary laying of a tight-fitting board or shield under it. With a large thickness of the workpiece, holes were drilled with a perk drill using a brace. Drilled not immediately through the entire thickness of the part. As soon as the tip of the drill reached the lower mouth of the workpiece, it was turned over and a hole was drilled with on the other side, which prevented the appearance of chips on the underside of the part.The workpiece was sawn out with a bow saw or hammer along the outer contour.Then, holes were drilled with a brace where the edges of the board coincided with the contours of the opening. in work alternately used different sections of the saw blade. Very steep lines with a small radius of curvature were sawn out of its narrowest part. As the steepness of the line decreased, the middle part of the saw began to work, and if the sawn line was almost straight, then the wide part of the saw, located closer to the handle, was included in the work. A jigsaw was also used to cut the thread contour, leaving a small allowance for further processing. If circular or curvilinear elements are embedded in the pattern of the ornament, then they were either sawn out with a saw only if the radii of curvature allowed. In other cases, they were filed in black with broken straight lines in order to then give the desired shape with the help of straight, semicircular, sloping and curved chisels and various types of skins.
The outline was cut clean with a cutter, straight or semicircular chisels. To make smooth cuts, the chisel was held at an angle to the surface and cut with light sliding cuts. In narrow places, the material was removed with a Bogorodsk knife.
Finished the work by cleaning the threads with rasps or sandpaper, the edges of the ornament were sometimes slightly oval, visually softening the contour.
Nowadays, sawn house carving continues to be used to decorate rural wooden houses, country houses, arbors, shady canopies, towers on playgrounds.
(Annex 1)
Situation
Schoolchildren had to create household items, such as decorative and applied wood products with artistic processing.
When doing this work, the students sawed out parts for their products from plywood, but they did not know what to do next, what kind of artistic processing to choose.
The children needed to solve this problem.
Task: Find the best solution for this situation and how to implement it.
Specification of the task:
Determine the main types artistic processing wood.
· Justify what type of artistic wood processing is the simplest and most acceptable for this task.
Job context:
Select and study slotted thread information, necessary tools and fixtures, as well as about the methods of slotted threads.
Additional Information.
1. Artistic wood processing – ancient craft. In wooden architecture, people found usefulness and beauty. He decorated the house with carved wooden products, and the house decorative carving, made toys, wooden utensils and souvenirs.
http://pandia.ru/text/78/016/images/image002_4.jpg" align="left" width="293" height="207 src=">.jpg" align="left" width="372 "height="320 src=">
http://pandia.ru/text/78/016/images/image006_3.jpg" align="left" width="139" height="204">
http://pandia.ru/text/78/016/images/image008_2.jpg" alt="(!LANG:Picture 128 of 14126" align="left" width="108" height="172 src=">!}  .jpg" align="left" width="312" height="240 src="> different kinds mosaics: inlay, intarsia, marquetry, beautifully decorating furniture with it.
.jpg" align="left" width="312" height="240 src="> different kinds mosaics: inlay, intarsia, marquetry, beautifully decorating furniture with it.
Woodworking" href="/text/category/derevoobrabotka/" rel="bookmark">wood processing along with sawing and turning).
There are many types of carving. Among them, the most widespread are:
- flat notched; geometric; slotted.
a) FLAT THREAD It is characterized by the fact that its basis is a flat background, and the carving elements go deep into it, that is, the lower level of the carved elements lies below the background level.
http://pandia.ru/text/78/016/images/image014_2.gif" width="216" height="177">
There are several subspecies of such a thread:
align="left" width="132" height="130 src=">The main element of the thread is a bracket (outwardly it looks like a trace left by a fingernail when pressing on any soft material, hence the name nail-shaped) - a semicircular notch on a flat background. Such a notch is made with a semicircular chisel in two steps: first, the chisel is deepened into the tree perpendicular to the surface, and then at an angle at some distance from the first notch. The result is the so-called bracket.
b) GEOMETRIC CARVING- is also a type of flat notched thread.
This is one of the most ancient and widespread types of woodcarving. Due to the ease of implementation, in the second half of the 17th century in Russia, it was most widely used. It is made in the form of various notches that form a geometric ornament on the plane, hence its name "geometric".
http://pandia.ru/text/78/016/images/image019_0.jpg" alt="(!LANG:Photo" align="left alt="width="50 height=130" height="130">.jpg" alt="Photo types of woodcarving" align="left" width="189" height="112"> рис. 2!}
Wooden houses" href="/text/category/derevyannie_doma/" rel="bookmark">carved wooden houses. wooden houses of any income, conquered with filigree ligature self made, intricately woven into such amazing patterns that it is difficult to even imagine that they are really created by human hands. Until now, individual samples of wood carving, reminiscent of lace plexuses, have survived and come down to us.
http://pandia.ru/text/78/016/images/image024_2.jpg" align="left" width="276" height="184 src="> slotted or Propilnaya (through openwork) thread - view decorative processing wood, in which the patterns outlined on a flat surface are cut with a jigsaw or twist saw. In sawn carving, decorativeness is achieved by an openwork mesh. The patterns of sawn wooden strips decorating the facades of houses are beautiful. Curls of a through floral or geometric ornament look great against the background of the wall.
Saw thread - is the simplest. This work does not require large material costs, and in terms of simplicity and ease of execution, it is the most accessible craft for any student.
Many beautiful products can be made from plywood and decorated with sawn carvings: furniture, kitchen utensils, candlesticks, shelves, boxes, etc.
http://pandia.ru/text/78/016/images/image026_2.jpg" align="left" width="221" height="164 src=">.jpg" align="left" width="165 "height="216 src=">
http://pandia.ru/text/78/016/images/image030_2.jpg" align="left" width="156" height="98 src=">
http://pandia.ru/text/78/016/images/image032_1.gif" alt="2" align="left" width="212" height="184 src="> Sawing carving on plywood is usually cut with a jigsaw , which consists of a frame with a handle, upper and lower clamping screws.A narrow and thin steel file is stretched and fastened between the clamping screws with the teeth tilted towards the handle.
An eccentric clamp is used to tighten the frame before attaching the file. After fixing the file with screws, the eccentric clamp is removed. The file is stretched under the action of the frame.
http://pandia.ru/text/78/016/images/image034_2.jpg" alt="(!LANG:lobzik_1" align="left" width="244" height="180 src="> Так же для работы необходим специальный выпиловочный столик, который крепят в заднем зажиме верстака.!}
Performance of work" href="/text/category/vipolnenie_rabot/" rel="bookmark"> performance of work, the movement of the file must be carried out for its entire length.
If the file jams in the part, you need to slightly turn the file to the side and remove the delay, or release the upper end of the file and remove it from the cut.
To cut out the inner contours of the pattern, a hole is drilled in plywood, in
which is inserted freed from the upper clamp, the end of the file. To insert the free end of the file into the prepared hole, it is necessary to fix one arc of the jigsaw in a vice, then pass the end of the file into the hole of the part, and, squeezing the arcs of the jigsaw, secure the file with a clamp. Do this carefully so as not to break the nail file. After sawing a hole, the nail file is removed in the same way.
(also carving is one of the types of artistic processing of wood along with sawing, turning), as well as art in general (this is an old folk craft).
Encyclopedic YouTube
-
1 / 5
It does not have a strict classification, since the same product can combine different types threads.
It is conditionally possible to distinguish the types of thread:
- through thread (this includes saw and slotted thread)
- blind thread (all subspecies of embossed and flat notched thread)
- sculptural carving
- house carving (it is a separate direction, since it can combine all three of the above types).
- Chainsaw carving (Performing mostly sculptural carving with only a chainsaw.)
The conditional classification of thread types is as follows:
through thread
through thread is divided into proper end-to-end and consignment note, has two subspecies:
- Slotted carving - (through sections are cut with chisels and chisels)
- Saw thread (actually the same, but such sections are cut with a saw or jigsaw).
A slotted or sawn thread with a relief ornament is called openwork.
Flat serrated thread
Flat carving is characterized by the fact that its basis is a flat background, and the elements of the thread go deep into it, that is, the lower level of the carved elements lies below the background level. There are several subspecies of such a thread:
- contour thread - the simplest, its only element is a groove. Such grooves-grooves create a pattern on a flat background. Depending on the chosen chisel, the groove can be semicircular or triangular. The semicircular one is cut with a semicircular chisel, and the triangular one is cut with a corner cutter, an angular chisel or a knife in two steps.
- stapled (nail-like) carving - the main element is a bracket (outwardly it looks like a trace left by a nail when pressed on any soft material, hence the name nail-like) - a semicircular notch on a flat background. Such a notch is made a semicircular chisel in two steps: first, the chisel is deepened into the tree perpendicular to the surface, and then at an angle at some distance from the first notch. The result is the so-called bracket. A set of such brackets of different sizes and directions creates a picture or its individual elements.
- geometric carving:
- trihedral thread
- two-sidedwashing thread
- four-sided washout thread
- black lacquer carving - the background is a flat surface covered with black lacquer or paint. How grooves are cut in the contour carving on the background, from which the drawing is built. Different groove depths and their different profiles give interesting game chiaroscuro and contrast of the black background and light cut grooves.
relief carving
Relief carving is characterized by the fact that the carving elements are above the background or on the same level with it. As a rule, all carved panels are made in this technique. There are several subspecies of such a thread:
- flat-relief carving with a pillow background - can be compared with contour carving, but all the edges of the grooves oval, and sometimes with varying degrees of steepness (more sharply from the side of the picture, gradually, gently sloping from the side of the background). Due to such littered contours, the background seems to be made of pillows, hence the name. The background is on the same level as the drawing. Relief carving with selected background - the same carving, but only the background is selected with chisels one level lower. The contours of the picture are also oval.
- Abramtsevo-Kudrinskaya carving (Kudrinskaya) - originated in the Abramtsevo estate near Moscow, in the village of Kudrino. Vasily Vornoskov is considered the author. The carving is distinguished by a characteristic "curly" ornament - curly garlands of petals and flowers. The same characteristic images of birds and animals are often used. As well as flat-relief, it happens with a pillow and a selected background.
sculptural carving
A distinctive feature is the presence of sculpture - images of individual figures (or groups of figures) of people, animals, birds or other objects. In fact, it is the most difficult type of carving, since it requires the carver to have a three-dimensional vision of the figure, a sense of perspective, and maintain proportions.
It is considered a separate subspecies. Bogorodskaya carving. Also, a kind of sculptural carving can be considered the art of carving with a chainsaw, which is becoming increasingly popular among both carvers and connoisseurs of beauty. The popularity is easy to explain. Carving with a chainsaw is, first of all, an action, a performance, a show. Increasingly, festivals, competitions, and demonstration performances by masters of chainsaw carving at public events, presentations, and exhibitions began to be held. Unlike other genres of wood carving, the viewer not only sees the end result of the master's painstaking and long work, but also visually participates in the process of creating a sculpture. Recently, the creation of sculptures on various copy-milling machines has also become increasingly popular, the most affordable of which is the Duplicarver.











Chicken in kefir - recipes for marinated, stewed and baked poultry for every taste!
Simple Chicken Recipe in English (Fried) Recipes in English with translation
Chicken hearts with potatoes: cooking recipes How to cook delicious chicken hearts with potatoes
Recipes for dough and fillings for jellied pies with mushrooms
Stuffed eggplant with chicken and mushrooms baked in the oven with cheese crust Cooking eggplant stuffed with chicken