Rotary compressors belong to the volumetric type of compressors and carry out injection by compressing the substance with the help of a rotating rotor. Sometimes this type of compressor is called rotary, but this is erroneous, this error arose, most likely due to incorrect translation of foreign technical literature.
There are rotary compressors with fixed plates, with rotating plates, twin-rotor and with a swinging rotor.
Installation and connection of the air conditioner
It is also important to consider the coolant used. There are several ways to classify the different types of compressors currently on the market suitable for use in refrigeration applications. However, we can create two large groups drawing attention to their technological or operational differences.
Positive displacement machines and aerodynamic machines. . Most suitable choice compressor depends on several factors, and in each case the most suitable one should be used. Among the factors that influence can be identified. All types of compressors can be driven by any known engine, mainly electric or internal combustion engines. It is also possible to use the energy of an alternative engine or a gaseous turbine. Let's take a look at some of the main characteristics and operation of each type of compressor.
Fixed vane compressor
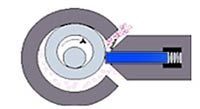
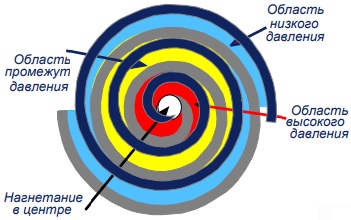
Another name for this compressor is with a rolling rotor (KKR). Structurally, such a compressor is an engine shaft on which a cylindrical rotor is mounted, but the shaft is not in the center of the circle, but eccentrically, that is, it is offset from the center. The rotor also rotates inside a cylindrical body. A gap is formed between the rotor and the housing, the value of which changes during rotation due to the eccentricity of the rotor. Where its value is minimal is the discharge pipe, and where its maximum is the suction pipe. The space between them is blocked by a movable plate, tightly pressed against the rotating rotor by a spring, preventing the flow of the working substance from the high pressure zone to the low pressure zone. This is clearly seen in the figures:
The main advantage is not to contaminate the refrigerant with air, although the flow it displaces is highly variable with pressure fluctuations. They can displace large volumes of refrigerant, typically with low compression ratios. Compression is achieved by accelerating the gas in the rotor, so that increasing the peripheral velocity area increases the compression value. To do this, you need to get high speed values.
Moving vane compressors
For each speed, this type of compressor delivers a predetermined maximum compression ratio. This fact forces us to choose a centrifugal compressor for maximum operation. It does not have the flexibility of other types of compressors. Another factor that affects the compression ratio is the specific gravity of the refrigerant.
Advantages of this type of compressor:
Very simple design
Few moving parts
Reliability
No valves
Less pressure pulsations as the rotor moves continuously
Insufficient oil in the compressor crankcase
They are preferred to be used with heavy refrigerants, so that halogenated liquids are used more against ammonia, which has a lower bulk density. They are usually equipped with a system that allows you to reduce the production of refrigeration equipment by affecting the amount of refrigerant entering the compressor.
The regulation can be set from 10% to 100% in normal automatic mode according to the refrigeration units. Centrifugal machines have one of their primary applications in the low pressure stage of multi-stage chains where large amounts of movement are required, competing with rotary and alternatives.
Excellent weight and size indicators
Small gas dynamic suction losses
Low price due to mass distribution
Flaws:
Flow of gas from the suction area to the discharge area
The presence of a "hot spot", i.e. friction at the point of contact between the rotor and the housing.
Moving vane compressors
The principle of operation of this type of compressor is the same as that of the previous one, with the only difference that the plates are on the rotor and rotate with it. This can be seen in more detail in the figure; for simplicity, only two plates are shown.
Similar to the previous ones, they are mainly used in chemical industry and in air conditioning systems or high volume air compression. It offers smaller dimensions, weight, and greater simplification of ancillary elements due to its lower noise, lower vibration, and greater ease of soundproofing.
They are very much used in the great powers. The movement of rotating machines is round and continuous. They have a direct connection to the motor element and do not have inlet or suction valves, and the gas always circulates in one direction. They allow high compression ratios because the lubricating oil, which must be in excess, also serves as a coolant, subtracting the heat generated by compression.

The advantages and disadvantages of this type are the same as those of the first type, with the exception of:
Possibility to develop more pressure due to more plates
More points of friction
More complex manufacturing
Rotary compressors with two rotors
Toshiba uses such compressors. For what, in fact, it was necessary to complicate the design by adding another rotor?
Functions and types of split air conditioner compressor
The single rotor may be a vane or a rotary piston. In the first case, a cylindrical eccentric piston is placed inside the cylinder with a horizontal axis, generatrix, coinciding with the cylinder. The piston can take futile longitudinal cuts in which the blades move so that when they rest on the cylinder they create a water tightness.
The gas enters through the hole, passes into the space in the form of a crescent and in the next half-turn is compressed, being able to exit through the impulse, provided that the pressure in the chamber corresponds to the amount of condensation. A rotary piston consists of a shaft concentric to a cylinder with a core wrapped in a ring that fits a needle between it and the cylinder. Each of the chambers, as before, communicates with aspiration and drive. In this case, the separating palette remains fixed. They are often used in domestic air conditioners.
Imagine a single-rotor compressor, the rotor on its shaft is located eccentrically, that is, the geometric center is displaced and, accordingly, the center of gravity. Such a design, for example, is used in vibrating phones - an engine with a weight off-center. You can also remember a fan blade with one propeller - during rotation, there are beatings and vibrations. To balance, they came up with the idea of adding another rotor.
Twin rotor compressors can have gears or screw. The latter have two rotors in the form of a spiral, one main and the other auxiliary. The main one has a total of four turns of a circle-like section and an auxiliary six channels that match the profile of the main rotor.
Both turn in the opposite direction. The gas due to the rotation remains enclosed between the spaces of the stator, transported from one end to the other from the gear where the intake and exhaust are located. Here you can see a brief explanation of its operation: with oil injection, the internal tightness of the gear can be maintained significantly, allowing high compression ratios to be achieved. On the other hand, it allows you to reduce the sound level. The capacity of these compressors can be adjusted by openings that allow some of the gas sucked into the suction pipe to be returned before compression begins.
![]()
As a consequence of this:
Reduced vibration and noise
Increased reliability and durability (not only of the compressor itself, but of the entire structure of the refrigeration machine)
Ability to reduce performance up to 15% of the nominal
The last point is important for inverter air conditioners, so it makes it possible not to turn off the compressor, working at low speeds, while saving electricity.
As can be seen, these compressors are valveless and relatively small in size. On the contrary, they require high quality in tolerances, which implies high production costs. They are based on the transformation of rotational motion into an alternative one, similar to internal combustion engines, but in the opposite direction. It can be said that, against all odds, they are indispensable in medium to high capacity installations due to their great flexibility and value for money. Thus, we can talk about alternative compressors based on.
This type of compressor is used by Daikin Corporation, in its SWING terminology. The main reason for the development of this compressor was the transition from R22 refrigerant to other types of refrigerants. When using R22 freon, mineral oil is used for lubrication, and chlorine is present in the freon itself, therefore, when the compressor operates with this type of refrigerant, a protective ferro-chloride film is formed on the surfaces of rubbing parts. This film significantly reduces friction and the risk of corrosion. When using R410a and R407c this film is missing.
Difficulty starting compressors
Construction type Number of effects Its shape Number of compressions Direction of flow. It is clear that each of these five characteristics must be specified in order to identify an alternative compressor, given that the number of possible combinations is large.
From horizontal compressors, vertical placement has been moved to occupy less space, subsequently increasing the rotation speed and reducing the weight of the moving elements. For compressors open type there is a cylinder-piston piston separated from the connecting rod and crankshaft assembly. Tightness was provided by a press tug. In order to eliminate the pressure band, the engine was placed inside the character, resulting in a leak-tight compressor.
The next unpleasant moment when using new refrigerants is pressure loss. These losses occur due to the flow of gas from one zone to another, according to studies, 70% of the flow between the rotor and the housing cylinder, and 30% between the cylinder and the end face of the plate. These losses depend on the presence of an oil film and the tightness of the rotor and plate, which, in turn, cannot be greatly reduced, otherwise the friction force will increase.
Fixed vane compressor
In compressors of an open nature, the two surfaces of the piston were filled, and while one side was compressed, the other was pushed, and vice versa. This is what is called a double effect, with which the displacement was almost doubled. When closed, the piston is empty and only works on one face, which is called a simple effect. valves, mostly reciprocating compressors, are located at the end of the cylinder, and the pairs enter the same way from top to bottom into the inlet and are compressed from bottom to top, i.e. the stream is alternate.
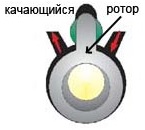
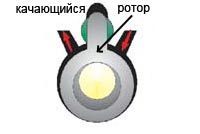
Daikin has developed and patented rotary oscillating compressors. In this compressor, the plate and the rotor are made in the form of a single part, which performs oscillatory and reciprocating movements, which is why the compressor was called "swing rotor", in the English terminology SWING (swing-eng.)
If the suction is through a piston with a cylinder with holes communicating with the suction, during the suction phase the piston creates a recess in the cylinder, opening the suction valve located at the top of the piston, and the steam enters from the bottom to the top. When gas is compressed, it is also performed from the bottom up, and the flow is called continuous.
In general, one stage of compression is performed. There may be cases where two stages are performed on the same machine, i.e. a given number of cylinders suck from the low pressure phase and another number from the intermediate phase. The air conditioner compressor is the so-called "heart" of the air conditioner. Cooling occurs due to the compression of the contents of the refrigerant. Contraction means concentration. This is necessary to liquefy the refrigerant. Then the cold goes to the condenser. When the air conditioner is connected, this process starts again every time and lasts for a while until cold air will not be fed into the vehicle's living room.
As a result, friction between the rotor and the housing cylinder is reduced, and friction losses and overflows between the plate and the rotor are eliminated.
Schematically, it looks like this:
The main area of application of rotary compressors is low-capacity refrigeration machines - from one and a half to ten kilowatts. At the moment, 90% of air conditioners use compressors of this type in hermetic design.
In addition, the air conditioning compressor consumes a large number of energy, so its use is not economical at all. The compressor can work in two ways: from the electric motor or directly from the car engine. Exists different types compressors such as fixed displacement, variable displacement, rotor compressor and reciprocating compressor.
If the air conditioner doesn't work the way it should, or doesn't work at all, it will break down. Another possible cause The problem could be the breakage of the corrugated belt of the air conditioner. This can be checked very quickly by inspecting the air conditioner. If the air conditioner fails, it must be completely replaced. An unavoidable air conditioner replacement is quite expensive in most cases. Repair of a damaged compressor is possible only in very rare cases. However, replacing the A/C compressor is cheaper than replacing the entire air conditioner.
On our website, you can buy from a warehouse in Moscow. We supply original spare parts for equipment according to our authorization (DAIKIN, SAMSUNG, PIONEER air conditioners, CAREL dehumidifiers, DANTHERM humidifiers).
Please contact our specialists for support. Qualification and experience of employees will help you buy a compressor and make right choice compressor and refrigeration equipment.
Causes of Compressor Failure
But the replacement must be carried out in a specialized workshop. The car owner cannot handle this task without previous experience. You can save money by purchasing spare parts outside of the workshop. In addition, we have brake linings, horns, steering knuckles, spark plugs, mudguards, ribbed belts, fuel filters and other spare parts. Air conditioner compressor failure.
The belt is damaged or worn; refrigerant leak; the clutch of the component is broken; solenoids are worn as a result of mechanical action; partial valves are stuck; wiring is shorted or damaged. Signs that the air conditioning compressor is not working.
Air conditioning compressor - purpose, types, modifications ...
Purpose of the compressor
The air conditioner compressor draws in refrigerant vapors from the evaporator, compresses them and pumps them into the condenser, ensuring that the liquid refrigerant in the evaporator boils, the vapor condenses in the condenser and the refrigerant circulates through the pipes of the refrigeration circuit. From the evaporator, low-pressure gaseous freon 3–5 bar enters the compressor, where it is compressed to a pressure of 15–25 bar, after which it enters the condenser.
When activated and actuated, air conditioning has little effect on noise; air temperature cannot be regulated; strange smells in the cabin. Causes of failure in the air conditioning compressor. Planned Maintenance carried out at the wrong time; air conditioning system components are used incorrectly; low quality components are used; the schema is reset; the piece operates under conditions of high humidity and temperature changes; low quality refrigerant is used; lack or excess of fat in the compressor; the air conditioner pipe is damaged; The motor fan is broken. The condition of the object is diagnosed in a special bank or in a car.
Manufacturers are constantly improving the design of the main elements and components of the compressor - thrust bearing, scroll elements, built-in protection against unstable voltage, which reduces vibration and mechanical losses, increases reliability. As a result, the air conditioner consumes less energy and generates less noise and vibration. In addition, the innovative motor design ensures the compact dimensions of the device and low weight.
Compressors by type
By type, compressors are divided into voluminous and dynamic. In positive displacement compressors, working processes - suction, compression, expansion, etc. - occur due to a periodic change in the volume of working cavities. This type includes rotary, scroll, piston and screw compressors. In dynamic type compressors, working processes are carried out by converting the kinetic energy of the flow into potential pressure energy. This type includes centrifugal and axial compressors. Their use is effective in refrigerating machines of high capacity from 5 to 10 thousand kW and more, therefore, centrifugal and axial compressors are not found in domestic air conditioning systems.
Compressors by design
According to their performance, compressors are divided into hermetic, semi-hermetic and open. Hermetic compressors, together with the electric motor, are located in a sealed, welded, non-separable casing, which is why they are unrepairable and, in case of failure, are only subject to replacement. The suction and discharge pipes, as well as the contacts for connecting the electric motor, are located on the outer side of the casing, and its bottom acts as an oil bath. In semi-hermetic compressors, the drive is located in the compressor crankcase, which, if necessary, allows servicing the internal components of the compressor with the drive. Open compressors have an external electric motor connected to the compressor directly or through a transmission.
Most air conditioners use hermetic compressors that cannot be repaired.
Rotary compressors
The change in the volume of the cavities and the working processes occur during the rotation of the rotor. There are two modifications of rotary compressors: with a rotating rotor and with a rolling rotor, and only compressors with a rolling rotor are found in air conditioners. The main elements of a rotary rolling compressor are the rotor and the pressure plate that separates the high and low pressure areas.
Rotary compressors have enough simple design, low pressure pulsations and good balance, but large power losses to overcome friction forces make it possible to use them effectively only in household air conditioners with low refrigeration power - up to 10 kW. Rotary compressors for air conditioners are reliable in operation. They have a small size, hermetic design with a liquid separator directly on the outer wall of the casing. Low power allows the use of single-phase electric motors for the drive.
Rotary compressors varieties
The scope of rotary compressors is very wide. They can be used for air conditioners, heat pumps, dehumidifiers and other refrigeration applications. Rotary compressors are most successfully used in low power air conditioners (household air conditioners such as window, mobile and split systems). The main advantages of this type of compressors are compactness and low noise level.
Rotary compressors

Compressor with fixed plates, in which the refrigerant is compressed using an eccentric mounted on the engine rotor. When the rotor rotates, the eccentric rolls along inner surface compressor cylinder and the refrigerant vapor in front of it is compressed and then pushed out through the compressor outlet valve. The plates separate the areas of high and low refrigerant vapor pressure inside the compressor cylinder.
 Some manufacturers (Mitsubishi Electric, Panasonic, Sanyo, etc.) use rotary compressors in their split systems. with two rotors. Two rotors rotate eccentrically on the compressor shaft, each of which compresses the refrigerant in its cylinder. The rotors rotate in antiphase, thus compensating for the beat.
Some manufacturers (Mitsubishi Electric, Panasonic, Sanyo, etc.) use rotary compressors in their split systems. with two rotors. Two rotors rotate eccentrically on the compressor shaft, each of which compresses the refrigerant in its cylinder. The rotors rotate in antiphase, thus compensating for the beat.
Such compressors are used in applications where low noise and vibration are especially important.
The cylinders of a two-rotor compressor are interconnected by a bypass pipe (bypass) with a control valve, which allows you to effectively control the performance when using compressors of this type in split systems.
Daikin has introduced a new type of rotary compressor - swing rotor. In a swing compressor, when the shaft rotates, the plate rigidly connected to the rotor performs a complex movement (reciprocating and oscillatory at the same time). Since the blade and rotor are a single unit, friction losses are reduced and there is no local heating zone (“hot spot”). In addition, there is no refrigerant leakage between the plate and the rotor, which reduces the overall pressure loss in the compressor.
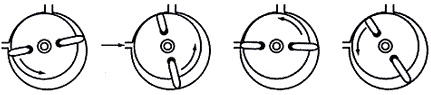
Compressor with rotating plates, in which the refrigerant is compressed by means of plates mounted on a rotating rotor. The axis of the rotor is offset relative to the axis of the compressor cylinder. The edges of the plates fit snugly against the surface of the cylinder, separating the areas of high and low pressure. The diagram shows the cycle of suction and compression of steam.
inverter compressors
Recently, inverter technology has been increasingly used, which makes it possible to regulate the refrigerant flow by changing the speed of a rotary compressor. This technology allows you to change the frequency of the compressor supply voltage from 30 to 120 Hz. The performance value is controlled more precisely than in traditional systems. After starting, the compressor operates at maximum capacity to quickly reach the required temperature of the cooled object, and then its cooling capacity is reduced to the value necessary to accurately maintain the set temperature. Most of the time, the compressor runs at low capacity, which significantly reduces the energy consumption of the system.
A feature of all compressors is the obligatory presence of an oil separator. Its purpose is to return the oil that enters the vapor of the injected refrigerant back to the compressor. The use of an oil separator maximizes the performance of the air conditioning unit and prolongs the life of the compressor.
Rotary compressors analogue selection
What to do in those cases when the air conditioner is to be repaired, it is not possible to find spare parts for which? What to do if it is not possible to use the original compressor due to its absence from the supplier's warehouse? Is it possible to use existing rotary compressors with the same cooling capacity and thermodynamic parameters, but from a different manufacturer?
Analogue selection
When choosing an analogue of the original compressor, you need to pay attention to the following main parameters:
- cold performance
– supply voltage and power consumption,
- on what freon and with what oil it is used,
– for dimensional and geometric compatibility.
When evaluating the compatibility of the layout scheme, the volume of the compressor, the angle of rotation of the dryer and the coincidence of the seats are taken into account.
The height of the compressor, its diameter and the diameter of the dryer from different manufacturers, as a rule, are close and small deviations are permissible when installing an analogue - the connecting pipes can always be cut or extended.
The mismatch of the angle of rotation of the battery causes great inconvenience, because. will result in a rework of the entire harness or in the manufacture of new landing studs.
Traditionally, a 3-point base in the form of an equilateral triangle is used to mount a rotary compressor in outdoor units. The table, prepared according to information from compressor manufacturers, shows data on the diameters of the bases of rotary compressors for air conditioners.
| brand | Series | btu/h | Platform diameter, mm |
| Samsung | Series 39-44 | 5000-12000 | 150 |
| Samsung | Series 48-55 | 18000-30000 | 176 |
| Hitachi | SG Series (G) | 4800-10500 | 160 |
| Hitachi | SH-Series (H) | 11800-23200 | 176 |
| Matsushita | R-P Series | 5000-13500 | 150 |
| Matsushita | K-series | 11900-26500 | 176 |
| Matsushita | J-series | 15500-35000 | 196 / 210 |
| L'Unite Hermetique | RGA Series | 6800-9450 | 150 |
| L'Unite Hermetique | RK/trK Series | 6550-14300 | 176 |
| SIAM (Mitsubishi Electric) | RH-series | 7500-15700 | 176 |
| SIAM (Mitsubishi Electric) | RH-series | 15700-24000 | 196 |
| SIAM (Mitsubishi Electric) | RH-series | 15700-34000 | 210 |
| Reichi Precision | Series 39-44 | 4500-10830 | 150 |
| Reichi Precision | Series 48 | 6800-15000 | 176 |
| Sanyo | C-R33F Series | 6780-9200 | 150 |
| Sanyo | C-R50F Series | 9680-12500 | 176 |
| LG Electronics | QB series | 4980-9250 | 150 |
| LG Electronics | QK-QJ series | 9200-18300 | 176 |
| Daewoo Carrier | EA-EB Series | 5000-11000 | 150 |
| Daewoo Carrier | EC-ED Series | 11500 -21500 | 176 |
Thus, for equipment with low capacity (5000–9000 btu/h), compressors with a base diameter of 160 or 150 mm are mainly used. For models with a capacity of 12000 btu / h and above, manufacturers use a base with a diameter of 176 mm.
In practice, it is more often not the radius or diameter of the platform that is used, but the distance between the landing studs or between the centers of the holes in the landing plate for the studs. By simple geometric calculations, it can be calculated that for a platform diameter of 150 mm, the distance between the studs will be 129.9 mm, and for a diameter of 176 mm - 152.42 mm, respectively.
Conclusion
As an alternative to the original, you can use a compressor from any manufacturer with a similar performance. For installation in an external compressor unit with a different rotation of the battery relative to the mounting plate, engineers either use an adapter plate or make new mounting studs on their own.
Manufacturers rotary compressors and location of factories
| Manufacturers | Japan | Korea | China | Thailand | Other countries |
| Hitachi | |||||
| Toshiba Carrier (Meizhi) | |||||
| Panasonic | |||||
| Mitsubishi Electric | |||||
| Sanyo | |||||
| MHI | |||||
| Daikin | |||||
| Fujitsu General | |||||
| LG | |||||
| Samsung | |||||
| Daewoo | |||||
| Teco | |||||
| Rechi | |||||
| Tecumseh | |||||
| Qing'an | |||||
| Gree | |||||
| Chunlan |
All compressor plants have a unified quality control system. Products are randomly tested to control performance parameters:
– Checking on the calorimeter
– Checking the cylindrical shape
– Checking the spherical shape
– Noise and vibration measurement
– Behavior when the shaft is blocked
– Behavior during high and low pressure cycling
– Operation of built-in protection
– Electronic material analysis
– Performance as part of the air conditioner
– Life tests
Need rotary compressors for air conditioners - contact us!
Scroll compressors
 The scroll compressor is a positive displacement type single shaft compressor. Its working bodies are two spiral plates (movable and fixed spirals), which are inserted one into the other. When the compressor is running, the movable scroll moves in a circular orbit relative to the axis of the fixed scroll, but the movable scroll does not rotate around its axis. This movement is provided by a special anti-rotation device and an eccentric shaft that rotates in only one specific direction. This ensures a continuous decrease in the volume of working cavities, and, consequently, uniform steam injection and a constant moment on the motor shaft (which contributes to an increase in its service life). There is a floating seal to reduce the starting torque. Scroll compressors for air conditioners are fully balanced, but very difficult to manufacture and expensive. They have a sealed design and are used in chillers of small and medium capacity.
The scroll compressor is a positive displacement type single shaft compressor. Its working bodies are two spiral plates (movable and fixed spirals), which are inserted one into the other. When the compressor is running, the movable scroll moves in a circular orbit relative to the axis of the fixed scroll, but the movable scroll does not rotate around its axis. This movement is provided by a special anti-rotation device and an eccentric shaft that rotates in only one specific direction. This ensures a continuous decrease in the volume of working cavities, and, consequently, uniform steam injection and a constant moment on the motor shaft (which contributes to an increase in its service life). There is a floating seal to reduce the starting torque. Scroll compressors for air conditioners are fully balanced, but very difficult to manufacture and expensive. They have a sealed design and are used in chillers of small and medium capacity.
The undisputed market leader in scroll compressors is Copeland (Emerson). Catalog of scroll compressors COPELAND SCROLL download
Scroll compressors device and principle of operation
The device and principle of operation of the scroll compressor
A scroll compressor is a type of positive displacement compressor (pump) in which the working medium is compressed by the interaction of two spirals. One spiral remains motionless, and the other makes eccentric movements without rotation, which ensures the transfer of the working medium from the suction cavity to the discharge cavity.
The compressor consists of two involute or Archimedean spirals, a shaft with an eccentric, a housing and other elements designed to provide a given movement and proper interaction of the compressor parts. Spirals do not have touch points, minimal gaps remain between them. This determines the durability of the spirals, but at the same time sets strict requirements for the accuracy of manufacturing the entire structure.
The refrigerant vapors ahead of the touch line are compressed and pushed out into the central hole in the compressor cover. Touch points are located on each turn of the inner scroll, so vapors are compressed more smoothly, in smaller portions, than in other types of compressors.
As a result, the load on the compressor motor is reduced, especially at the time of compressor start-up. The refrigerant vapor enters through the inlet in the cylindrical part of the housing, cools the engine, then is compressed between the scrolls and exits through the outlet in the upper part of the compressor housing.
The frequency of movement of the movable spiral reaches several tens of thousands of cycles per minute. Such compressors are quite efficient and have a long service life without a significant reduction in efficiency.
A bit of history
The idea of a spiral has been known to mankind for more than 3 thousand years. Spirals (from the Greek speira - coil) are curves twisting around a point on a plane (flat spirals), for example, an Archimedean spiral, a hyperbolic spiral, a logarithmic spiral, or around an axis (spatial spiral), for example, a helix. But technically, humanity was able to bring the idea to life only by the end of the 20th century.
It all started in 1905, when the French engineer Leon Croix developed the design of a scroll compressor and received a patent for it. However, at that time this technology could not be implemented, because. lacked the necessary production base. Therefore, the design of a working prototype had to wait until the second half of the twentieth century, because. for effective functioning, in a scroll compressor, it is necessary to ensure a small structural gap in the mating parts (scrolls). Such accuracy was only possible with precision machining developed during the second half of the twentieth century, which explains the relatively recent introduction of the scroll compressor to the high-tech market.
The concept of scroll compressors was revived by the physicist Nils Young in 1972. Young gave the idea to the employees of Arthur D. Little (USA). Arthur D. Little management saw the high potential of this concept and began developing a possible model in January 1973. Major manufacturers of refrigeration and petrochemical equipment were very interested in developing a compressor in principle new design to achieve significant efficiency. Already during testing of the prototype scroll compressor, it was revealed that it has the ability to create a high compression ratio and the highest efficiency that existed in the early 70s. refrigeration compressors, and also has high performance characteristics(reliability, low noise level, etc.).
Then Arthur D. Little made a major effort in late 1973 to develop a working model of a refrigeration scroll compressor for American corporation Trane. A little later, many large companies, for example, "Copeland" (USA), "Hitachi" (Japan), "Volkswagen" (Germany), start intensive research and improvement of the design of the refrigeration scroll compressor, mastering the technology of manufacturing parts and the scroll compressor as a whole.
Application area
Scroll compressors are increasingly being used in refrigeration and air conditioning systems every year. This is due to the fact that they are more reliable in operation, contain 40% less details, than piston, produce less noise and have a longer service life.
Scroll compressors have found application in all major air conditioning systems, including split and multi-split models, floor standing versions and in chillers, roof tops and heat pumps. A typical application is air conditioning in apartments, ships, factories and large buildings, also in automatic telephone exchanges, in refrigeration processes and in transport.
Refrigeration scroll compressors are widely used in condensing units, supermarket “remote refrigeration” systems, industrial refrigeration and transport applications, including containers. The cooling capacity limits for scroll compressors are constantly increasing and are currently approaching 200 kW when using a multi-compressor station.
The popularity of scroll compressors is very high due to the wide range of applications, which is explained by their reliability and versatility.
Major Scroll Compressor Manufacturers and Factory Locations
| Manufacturers | USA | China | Japan | Thailand | Other countries |
| Copeland | |||||
| Danfoss | |||||
| Bitzer | |||||
| Hitachi | |||||
| Daikin | |||||
| Panasonic | |||||
| Mitsubishi Electric | |||||
| Sanyo | |||||
| Toshiba Carrier | |||||
| MHI | |||||
| LG |
Copeland (Emerson) is the market leader in scroll compressors. V various systems refrigeration, millions of Copeland compressors are in operation around the world, featuring high quality and advanced design. Every year, up to 4 million scroll compressors are manufactured at nine factories located on 3 continents. Copeland Engineering Support Centers are located in Europe, Asia and the USA.
Need scroll compressors for air conditioners - contact us!
Piston compressors

In reciprocating compressors, working processes are determined by a change in the volume of working cavities during the reciprocating movement of the pistons in the cylinders. Hermetic reciprocating compressors are more commonly used for air conditioners with low cooling capacity - from 1.5 to 50 kW.
Piston compressors for air conditioners are relatively easy to manufacture and cheap, but the presence of reciprocating pistons in their design is the cause of such difficult-to-remove drawbacks as unbalance, refrigerant flow pulsations in the lines and, as a result, increased noise and vibration. Recently, piston compressors have been replaced by rotary, scroll and screw compressors.
Tecumseh, Bitzer, Dorin, Bock, Danfoss, Cubigel are leaders in the segment of commercial and industrial refrigeration. Share in the air conditioning segment reciprocating machines accounts for only 3% of the total number of compressors used in this area. The main manufacturers of reciprocating compressors for air conditioning systems are Tecumseh, Bristol, Copeland.
Screw compressors
 Screw compressors are fully balanced, have high efficiency and reliability, as well as simple and effective capacity control, but the complexity of manufacturing screws causes their high cost. Screw compressors are used in medium and large chillers from 50 to 5000 kW, such as chillers.
Screw compressors are fully balanced, have high efficiency and reliability, as well as simple and effective capacity control, but the complexity of manufacturing screws causes their high cost. Screw compressors are used in medium and large chillers from 50 to 5000 kW, such as chillers.
There are two modifications of screw compressors: twin screw and single screw.
In the case of a twin-screw compressor, the leading and driven rotors are placed, rotating in rolling bearings. On the middle part of the rotors, the teeth of the driving and driven screws are cut, which are mutually engaged like gears. The role of the cylinder - the working volume - is performed by the cavities between the teeth of the screws, covered by the walls of the housing. The increase in gas pressure is achieved by reducing the closed (at the end of the suction process) volume of gas.
Main structural elements of a single-screw compressor are a leading rotor with grooved screws located on the same shaft with an electric motor and two driven gate rotors made in the form of a star with teeth. The driven rotors are exactly placed opposite each other on opposite sides of the main rotor in such a way that the axes of rotation of the gates and the propeller are strictly perpendicular.
Major Screw Compressor Manufacturers and Factory Locations
| Manufacturers | Japan | China | USA | Germany | Other countries |
| Twin screw compressors | |||||
| Hitachi | |||||
| Kobelco | |||||
| Mayekawa | |||||
| Ebara | |||||
| York | |||||
| Trane | |||||
| carrier | |||||
| Hartford | |||||
| Bitzer | |||||
| GEA (Grasso) | |||||
| RefComp | |||||
| Frascold | |||||
| FuSheng | |||||
| Hanbell | |||||
| Dalian Bingshan | |||||
| Chongqing Jialing | |||||
| Yantai Moon | |||||
| Single screw compressors | |||||
| Finetec Century | |||||
| McQuay | |||||
| Vilter | |||||
| Daikin | |||||
| Mitsubishi Electric | |||||
Need screw compressors for DAIKIN air conditioners - contact us!
The main malfunctions of compressors
The life of the air conditioner, as a rule, is 7-10 years and is determined precisely by the resource of the compressor. Various factors can significantly reduce the operating time of the air conditioner. This is an inaccurate calculation of heat gains in the room and, as a result,
deliberately incorrect selection of equipment in terms of performance, poor-quality installation, performed with
using non-certified tools and components, lack of regular seasonal maintenance or violation of the operating conditions of the split system. For example, using an air conditioner negative temperatures or non-compliance with the standards of the supply voltage of the network.
Almost all compressors for air conditioners cannot be repaired and, if they fail, they need to be replaced. The main malfunctions of hermetic compressors in small refrigeration units (air conditioners) include mechanical and electrical defects.
Mechanical defects of compressors
Mechanical defects
One of the mechanical defects is compressor jamming. This defect accounts for 20% of all faults. For some compressors with a single-phase electric motor, it is up to 40%.
The main causes of compressor seizures are as follows:
1. Flow of liquid refrigerant into the compressor crankcase
When the compressor is stopped, liquid refrigerant may accumulate in the compressor crankcase. When starting the compressor oil pump in the first moments of time, instead of oil, it will supply a liquid refrigerant that does not have good lubricating properties.
As a result, jamming or severe wear of the moving parts of the compressor is possible. To prevent the negative consequences of refrigerant leakage, it is recommended:
– control overheating of the suction vapors of the refrigerant in order to avoid excessive cooling of the compressor during operation;
– eliminate any possibility of oil retention in the compressor suction line;
– use an electric compressor crankcase heater to maintain the oil temperature when the compressor is stopped.
2. Insufficient amount of oil in the compressor crankcase
The reasons leading to rapid wear of the compressor are poor return or foaming of oil in the compressor crankcase.
A small amount of oil during compressor operation is carried into the discharge line and circulates mixed with the refrigerant through the system. Oil circulation is considered normal in an amount of approximately 1% by weight of the circulating refrigerant. For a compressor with a capacity of 1.1 kW, this is 1 kg / h. The standard oil charge of such a compressor is 1.2 kg.
Manufacturers choose oil in an amount sufficient to ensure good solubility and unhindered circulation. When designing a refrigeration system, conditions must be provided for the return of oil to the compressor, namely, the optimal speed of the refrigerant in the pipelines and their rational location.
Refrigerant flow rates
Recommended minimum flow rates are as follows:
- for horizontal and inclined pipelines in the direction of movement of the refrigerant, at least 4 m/s;
- for vertical pipelines with the movement of the refrigerant up at least 8 m / s.
To avoid high hydraulic resistance and noise, the maximum speed should not exceed 16–48 m/s.
In pipelines longer than 30 m, it is desirable to have siphons; in horizontal sections - a slight inclination in the direction of movement of the refrigerant (at least 12 mm per running meter). At the same time, it is necessary to ensure proper oil filling in accordance with the manufacturer's recommendations and provide oil lifting loops on the pipelines.
3. Oil foaming in the compressor crankcase
The phenomena that occur in the compressor crankcase at start-up are described above, as well as their consequences. A sign of oil outgassing can be a very low noise level during compressor start-up, since the oil-vapor emulsion has soundproofing properties. Therefore, it is necessary to constantly monitor the oil level indicator.
4. Penetration of liquid refrigerant into the compressor cylinders
If liquid refrigerant or oil enters the compressor cylinders, valve failure, gasket destruction, jamming, and sometimes the simultaneous occurrence of these damages can occur. As a result of the migration of liquid refrigerant when the compressor is stopped, it can accumulate in the compressor discharge cavity up to the valves. At start-up, this leads to a sharp increase in the load on the compressor pistons and bearings. Therefore, in order to avoid these defects, it is necessary to constantly monitor the condition of the valves and sealing gaskets.
5. Fouling of the refrigeration circuit
If solid particles enter the system, they can cause wear and seizing of the moving parts of the compressor. Therefore, it is necessary to carefully monitor the cleanliness of the system, especially during the preparation and installation of pipelines and apply a filter on the suction line to the compressor.
6. Presence of unconditioned gases in the compressor
This defect occurs in about 5% of cases. The ingress of air into the compressors for air conditioners occurs when the sealing of the compressor is violated in contact with environment or due to a leak in the suction line. Especially dangerous is the ingress of air with high humidity into the system. The result is oil decomposition (hydrolysis), overheating of the electric motor and valves, destruction of compressor components and parts. Oil hydrolysis produces acids that destroy the motor winding.
The presence of air in the system leads to an increase in pressure and temperature of the end of compression, overheating of the valve group, oil carbonization, destruction of gaskets, and overheating of the motor windings.
For the purposes of prevention, it is necessary to prevent the contact of the internal cavities of the compressor with the environment, monitor the condition of the pipelines, and the magnitude of the pressure on the suction and discharge lines. If these pressure values deviate from those specified, air may be present in the system. Therefore, in this case, it is necessary to stop the compressor, evacuate the system and restore the tightness of the system.
7. Malfunction of valves and gaskets, destruction of the discharge pipeline
The compressor housing inside the casing has a safety spring suspension. The discharge pipe is also equipped with a vibration damper.
Under difficult transport conditions and when operating with frequent starts and stops, refrigerant leakage may occur in the discharge pipe. Sometimes this can happen with a broken compressor spring suspension. In the presence of these malfunctions, it is necessary to replace the destroyed parts.
The reasons for the appearance of increased noise are poor fastening of pipelines, operation in conditions not intended for this refrigeration system, incorrect electrical connection, liquid ingress into the compressor, etc.
Difficulty starting compressors
Difficult starting occurs with small compressors in both refrigeration and air conditioning systems. The electric motors of these compressors are very sensitive to voltage fluctuations in the mains, as well as to changes in pressure levels at the time of start-up, which can occur when the ambient temperature deviates from the permissible one. In the event of increased noise, it is necessary to turn off the installation and first check the fastening of pipelines and electrical wiring.
With increased operating noise outdoor unit domestic air conditioner attention should be paid to the correct installation of the compressor on rubber shock absorbers and their condition. Rubber loses elasticity over time and is pressed under the weight of the compressor. It is noticed that silicone shock absorbers show the best properties. When replacing the compressor, as a rule, the starting capacitor and rubber bands are changed. After replacement, it is important to properly fix the shock absorbers, do not overtighten, but provide a gap between the rubber bushing and the nut.
Electrical defects of compressors
Electrical defects
1. Sparking in electrical connections
This defect is about 20% of all electrical defects, i.e., about 6% of all faults. It occurs when voltage is applied to the electric motor, if the compressor is under vacuum, especially during sudden changes in voltage in the mains. Sparking is carried out between the terminals or between the terminals and the motor housing, as well as in its windings, which is explained by the occurrence of a corona discharge.
Therefore, voltage should not be applied when the compressor is under vacuum. Voltage supply is possible only after the compressor has been filled with refrigerant to a pressure above atmospheric pressure. You can verify the completeness of filling by the readings of pressure gauges.
2. Combustion of the starting winding of the electric motor.
This defect accounts for about 80% of all electrical faults (for single-phase motors), or 22% of all compressor faults. Burnout of the starting winding occurs either due to overheating due to prolonged operation of the electric motor, or due to high strength current drawn by the motor. The reasons for this malfunction are:
- incorrect connection of the motor windings
Improper connection of the motor windings can damage the starting capacitor. Moreover, the combustion of the winding and damage to the capacitor can occur simultaneously in a very short time.
To avoid this malfunction, it is necessary to carefully monitor the correct connections of the motor windings.
An indication of a bad connection may be elevated level noise and vibration during compressor start-up.
- incorrect installation of the current relay or its malfunction
If the current relay is incorrectly installed, with large (over 15 °) deviations from the vertical position, the relay does not work and the starting winding and capacitor are constantly energized, which leads to their burnout. Therefore, the relay must be located in the electrical box and have a clear fixation of its location. The voltage relay is less sensitive to changes in its position, however, its operation, i.e., the frequency of switching on and off, may be affected by a deviation from the normal position.
– increased frequency of compressor starts per hour
When the compressor is started, a large current flows through the starting winding of the electric motor, causing it to heat up. Therefore, the time between compressor starts must be sufficient to cool the starting winding. According to the operating instructions, it is allowed to perform no more than 10–12 cycles per hour, work with 5–7 cycles is considered normal. To prevent burning of the starting winding during frequent start-stops of the compressor, it is recommended to use a timer to delay the start of the compressor.
– the start relay is not suitable for this type of compressor
When replacing a current or voltage relay, only the relay recommended by the manufacturer for this type of compressor should be used. The values of the on and off voltages depend on the parameters of the winding and the electrical network. Voltage fluctuations in the electrical network directly affect the operation of the current or voltage relay.
– mains voltage mismatch
Increased voltage compared to the nominal one can cause permanent operation of the starting winding of the electric motor, and low voltage leads to the impossibility of starting the compressor, or to a quick shutdown of the compressor immediately after starting. The voltage relay, designed, for example, for a voltage of 110 V, will not turn off when the mains voltage is 220 V after starting the compressor. As a result, the starting winding and capacitor will be constantly energized, which will cause the system to trip. automatic protection.
Undervoltage in the network in most cases is the main cause of burnout of the compressor motor windings. At low voltage, the motor operates in critical conditions, a current greater than that for which it is designed flows through the armature winding of the electric motor, and with any prolonged operation, the failure of the electric motor is only a matter of time. Low supply voltage several times reduces the service life of the electric motor, and then - the replacement of the compressor with an electric motor.
An indirect sign of problems in the mains supply is the frequent burnout of incandescent lamps and blinking visible to the human eye.
3. Burnout of the main winding of the electric motor
This defect accounts for about 3.5% of all electrical faults in compressors with single-phase motors.
The causes of burnout of the main winding are as follows:
- Wrong compressor motor
The selected compressor motor must provide efficient work compressor on a certain refrigerant in a given temperature range with the required parameters of the electrical network. Deviations lead to compressor overheating, an inefficient heat exchange process.
The capacity of the compressor must match the ability to remove heat from the condenser. Increased compressor capacity increases the condensing temperature and pressure. In the event of a dangerous increase in the condensing temperature, an oil cooler and a condenser fan should be used in the refrigeration system.
– contaminated or insufficient heat exchange surface of the condenser
Poor heat removal in the condenser occurs when the condenser heat exchange surface is contaminated, its heat exchange surface is insufficient (if the condenser is selected incorrectly), the condenser fan malfunctions, and the condenser-compressor unit is improperly installed. As a result of these reasons, it is possible not only to burn out the main winding of the electric motor, but also the appearance of intermediate defects, such as burning oil in the valves, frequent activation of the automatic compressor protection system, which reduces its service life.
The need to repair or replace the compressor may become clear not only if the compressor is no longer working, but even earlier for a number of reasons. For example, according to the results of the analysis of the compressor oil, when a violation of the tightness of the refrigerant circuit is detected, when moisture is detected in the refrigerant circuit.
In these cases, if you do not take urgent measures and leave the compressor running, then soon there will be a malfunction and failure of the compressor.
Loop leakage
Violation of the tightness of the refrigerant circuit can be caused by various reasons and does not always lead to a breakdown. It depends on the location of the leak, the amount of refrigerant that has leaked out, the time interval between the occurrence and detection of a leak, the mode of operation of the air conditioner, and a number of other factors. When a refrigerant leaks, its mass flow through the compressor, which is cooled by the refrigerant, decreases. Also, with an insufficient amount of freon, the return of oil to the compressor crankcase worsens. Due to the low amount of refrigerant, the compressor overheats and the discharge temperature rises. In addition, with a significant freon leak, air may enter the refrigeration circuit.
Signs of a refrigerant leak are as follows: darkening of the compressor insulation; periodic operation of the thermal protection of the compressor, due to overheating of the compressor; abnormal increase in steam superheat; decrease in pressure in the evaporator; no subcooling in the condenser; dark oil with a burning smell; and finally, the presence of bubbles in the sight glass, if any.
It is possible to reliably determine the lack of refrigerant only when it is completely evacuated, followed by weighing and comparing with the filling data in the passport or on the factory tag (nameplate). During normal charging of the refrigeration circuit, other reasons for the appearance of the listed symptoms should be looked for.
If the leak is detected in time and the refrigerant has not completely leaked from the circuit, then the repair of the air conditioner in the workshop is not necessary. It is necessary to analyze the oil, eliminate the leak, refuel the air conditioner, having previously evacuated it, run the air conditioner in cooling / heating modes with control of all necessary parameters (suction and discharge pressures, refrigerant overheating, air temperature difference at the inlet and outlet of the indoor unit, current characteristics of the compressor).
The percentage of leaks caused by the destruction of pipelines is very small. More often, leaks occur through leaks on the rolling joints. To determine the places of leaks, it is necessary to carry out pressure testing of the system and check for the absence of a possible leak with a leak detector of all connections.
Moisture in the circuit
Moisture usually enters the refrigerant circuit with wet atmospheric air(which is a mixture of dry air and water vapor) if the installation of the air conditioner is not carried out in accordance with the rules. Vacuuming the freon line during installation is always necessary in order to remove moist air from the mounted line. Purge of the mounted line with refrigerant, which is sometimes performed instead of evacuation, is unacceptable, since it does not guarantee 100% removal of air from the system.
The percentage of leaks caused by the destruction of pipelines is very small. More often, leaks occur through leaks on the rolling joints.
The danger of the presence of moisture in the refrigerant circuit of the air conditioner lies in the fact that the moisture remaining in the system, which is in a vapor state at positive temperatures, often does not manifest itself in any way until the compressor fails. However, by indirect signs, it is possible to determine the presence of moisture in the air conditioner.
One of the signs of moisture in the refrigerant circuit is a greenish tint to the oil and a positive acidity test.
Another sign is a change in the color of the moisture indicator in the sight glass. If these signs are detected, urgent intervention is required to save the compressor from failure. If the air conditioner is operating in heating mode at sufficiently low outdoor temperatures, and the evaporating temperature of the outdoor unit heat exchanger drops below 0 °C, moisture turns into ice and clogs the capillary tube or expansion valve. As a result, the suction pressure of the air conditioner drops, the compressor temperature rises, and the thermal protection trips. This cycle is repeated until the compressor burns out.
Oil analysis
The dark color of the oil and the smell of burning indicate that the air conditioning compressor has overheated. The causes of overheating can be varied: refrigerant leak from the air conditioner; operation of the air conditioner for heating at negative temperatures outside; insufficient performance of the expansion valve; premature throttling; compressor defects (loss of valve tightness); steam leaks from the discharge side to the suction side, for example, when the stem-spool of a four-way valve is jammed; high discharge pressure.
The oil then loses its lubricating properties and decomposes to form resinous substances that cause the A/C compressor to fail. Filtration does not completely restore the properties of oil that has undergone thermal decomposition. Therefore, it must be replaced.
The greenish hue of the oil indicates the presence of copper salts in it. The reason is the presence of moisture in the refrigeration circuit of the air conditioner. The acidity test of such oil is usually also positive.
A clear oil with a slight odor, similar in color to new oil, indicates that the compressor does not need an immediate oil change, as long as it is free of acid and moisture.
conclusions
Given some of the above compressor malfunctions, it must be remembered that the air conditioner is complex. technical device, which requires timely service. Compliance general rules installation and commissioning of equipment, the timing of service maintenance and timely troubleshooting significantly increase the service life of the air conditioner.










Mixed Personality Disorder: Causes, Symptoms, Types and Treatments
GTA 4 control settings
FAQ on Smuggling in GTA Online
LSPDFR - welcome to the police
The huge map of Grand Theft Auto San Andreas and its secrets