The simplicity of the design of reciprocating compressors contributed to their popularization and distribution. Today, piston compressors have found the widest application in different areas human activities, from the aeration of aquariums to industrial engineering. Brilliant in its simplicity, the invention has a lot of advantages and high functionality. For example, the supply of air or gas under pressure of more than 20 atmospheres is a task that even more sophisticated devices could not cope with. However, the most advanced mechanisms need timely prevention of malfunctions and competent repairs.
This system is mainly located behind the air conditioning heat exchanger. This is the so-called thermistor type of heating. The heat generated by these thermistors is released using a finned aluminum strip and air supplied inside the car.
The temperature of thermistors is automatically controlled by their thermal characteristics, as they electrical resistance increases as the temperature rises, and electricity proceeds according to Ohm's law. The exhaust heat exchanger helps transfer heat from the exhaust gases to the coolant. In this way, at least part of the unused thermal energy of the exhaust gas is obtained and used to heat the interior more quickly to the required temperature.
Varieties of compressors
Compressors are used not only for air injection, for example, in chemical industry and in geology - they pump various gases under pressure: chlorine, nitrogen, oxygen, hydrogen, helium, ethylene and some mixtures. In industry and other areas of human activity, compressor stations and turbochargers, low and high pressure piston compressors are used, and these mechanisms are most common today.
The fuel heater contains a small combustion chamber through which engine coolant flows. The heated refrigerant then flows through the heat exchanger of the heating system, where the air supplied inside the car is heated. The fuel heater may be located directly in the engine cooling cooler.
Air conditioning has become almost an integral part of the car. Compared with the past, the glazed surface has increased significantly in modern cars, the greenhouse effect- a significant increase in the air temperature in the room. High air temperatures adversely affect driver attention and therefore driving safety. Travel comfort is also an important aspect as people spend more and more time on the road. Soaked clothes or unpleasant sensations of heat are a thing of the past.
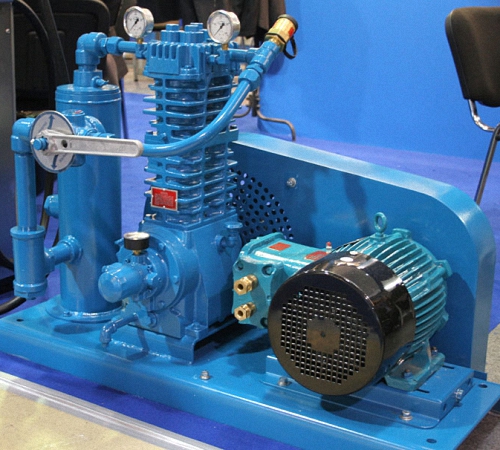
Modern compressors differ from many other mechanisms in their concise simplicity, and the design itself guarantees their almost uninterrupted operation for a long period, including the provision of inexpensive maintenance and repair.
Pressurized air supply is the principle of operation of most compressors, many of which are capable of operating in difficult climatic conditions, as well as with the supply of contaminated gas mixtures without the risk of damage to the mechanism. However, to extend the life of reciprocating compressors, it is still worth taking care of quite acceptable conditions for their operation.
The following requirements are set for the air conditioning system. Quickly cool the inside of the car to the required temperature, maintain the required temperature in any weather and driving mode, provide the required temperature for each passenger in the car, if possible, purify and improve indoor air quality, the air conditioner should be easy to operate and environmentally friendly environment Wednesday. To meet the above requirements, the air conditioning system must supply air and then clean, cool and remove excess moisture.
Polluted air or mixtures pumped into the cylinders of compressors, including reciprocating ones, carry an additional load on all components, and this leads to their wear. Some types of compressors are capable of supplying purified air (gas) without oil impurities, and their housing gives a minimum noise level. Most modern compressors periodically need replacement parts for their smooth operation, and in the event of a breakdown, it is best to contact the nearest service center for maintenance.
Engine does not start
In order to operate the air conditioner in a conventional internal combustion engine vehicle, the engine must first be started as it drives the compressor via a belt. Electronics in modern systems will initially run the control mechanism to see if all conditions for action are met. In the constant power versions this is done by means of an electromagnetic clutch, in the variable power versions it is done through a special valve which significantly reduces the refrigerant flow through the compressor.
Varieties of piston compressors
Mechanisms for pumping air under pressure differ in the engine, for example, there are electric and steam compressors operating on a steam drive, and there are those operating on an internal combustion engine.
Compressor mechanisms have different performance, which is conditionally estimated by the volume of gas passing under pressure per unit of time:
The exception is hybrid vehicles with an electric motor compressor compressor, so it works even when the electronics shut off the internal combustion engine. The refrigerant volume in the system currently averages 500 grams, and the trend is to further reduce this volume.
For example, on a medium-sized car made 10 years ago, it took more than 900 grams.
- Manual air conditioner.
- Temperature controlled air conditioner.
- Fully automatic air conditioning.
- Mini-compressors are used in medicine, instrument making, aquaristics - productivity up to 3*10ˉ² m³/s.
- Laboratory mini-compressors and transport units with air pumping from 3*10ˉ² to 0.01 m³/s.
- Devices of medium productivity - within 0.1 to 1 m³ / s, compressor stations of mines, factories, plants and mines are used.
- High-performance compressors with a pressure of more than 1 m³ / s are chemical plants and compressor stations.
Compressors operating on volatile compounds and light inert gases are additionally sealed. AT maintenance many other mechanisms are needed, including piston compressors. The simplicity of the design of reciprocating compressors does not mean that there are no costs for repairing a reciprocating compressor. And their relative cheapness does not eliminate the need to purchase spare parts for a piston compressor or its service.
The selected temperature of the interior of the car is maintained at a constant level, where the distribution and amount of air can be adjusted manually. The internal temperature is kept electronically constant by default. The distribution and amount of air are regulated fully automatically. In this way, the airflow from the individual exhausts is optimally distributed for the maximum comfort of the vehicle's occupants.
Pressing a number button or turning the A/C manual control on the car's control panel activates the electronics, which checks the system and, if OK, starts the compressor. Of course, the refrigerant enters the compressor in the gas phase. Cooling is carried out either by natural movement or by moving air. In other words, if the natural cooling rate is low, the electronics turn on the fans in front of the condenser to increase airflow and lower the temperature of the refrigerant.
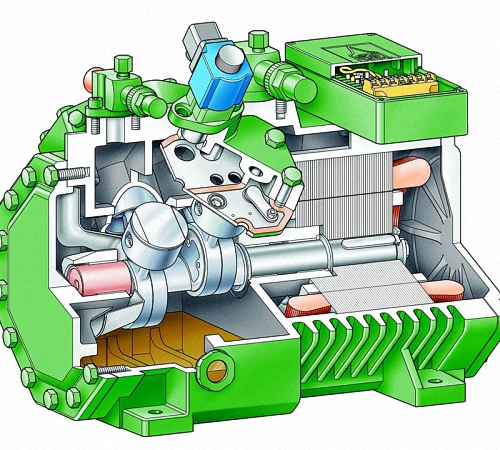
Technical parameters of reciprocating compressors
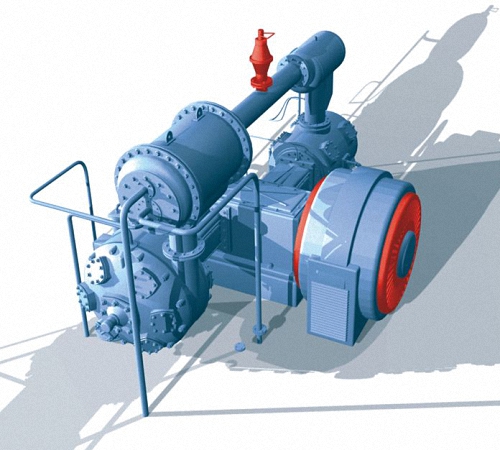
Reciprocating compressors, the principle of operation of which is based on the injection and pumping of gases or air under high pressure, are able to change the parameters of the gas volume. All types of compressors operate on the basis of the principle of piston movement between valves in a reciprocating pattern.
Thus, the refrigerant transfers its temperature environment into the surrounding air. The cooling rate itself is estimated based on information from the pressure sensor in the system. The liquefied refrigerant flows from the condenser to the filter and dehydrator. It also functions as a reservoir for liquid refrigerant. Here, the refrigerant removes any moisture that may be in the system. The fans then pass through the evaporator and through ducts leading to the exhaust gases in the cab.
What is the air conditioning system?
The evaporated refrigerant is sucked back into the compressor and the whole process begins to resume. Air circuit, air supply and distribution with heater and fan.
- Cooling circuit.
- Temperature control system.
The device of each type of this device is dictated by the conditions of use, functionality and scope of their use. For example, angular compressors are the most common type of compressor units, since they have a relatively low weight and compact dimensions, they can be mounted in small areas. Cylinders can be placed on both sides of the base or on one side only. The vertical type of reciprocating compressors has the same layout as the horizontal ones, which are designed for a higher load, but they are smaller and have a different capacity.
- Supply fresh air from outside - open circuit.
- Internal air circulation is a closed circuit.
From there, it is directed through control valves and exhausts to the right places inside the car. Closed circuit - internal air circulation. In this operating state, air is drawn in almost completely from inside the vehicle, cleaned in a dust filter, treated in a condenser and heat exchanger, and then returned to the inside of the vehicle. The internal circulation is activated by a switch and serves to prevent the entry of polluted air, traffic jams or fog.
There are several types constructive solutions compressor devices, which are conditionally combined into subgroups.
1. Horizontal, vertical and angular.
2. Multi-stage, 1-stage and 2-stage.
3. Single and double acting compressors.
4. Multi-cylinder, 1-cylinder and 2-cylinder compressors.
5. Crosshead compressors (with head) or without crosshead.
Recently, much attention has also been paid to the purity of the intake air. Modern air conditioners are equipped with an air quality sensor that measures the concentration of certain pollutants, unburned hydrocarbons. The sensor is located in the air intake manifold. As the concentration of contaminants increases, the resistance of the sensor decreases, thereby increasing the current flow. This current value is compared to a set reference value, which determines how much harmful air quality can be found inside the car.
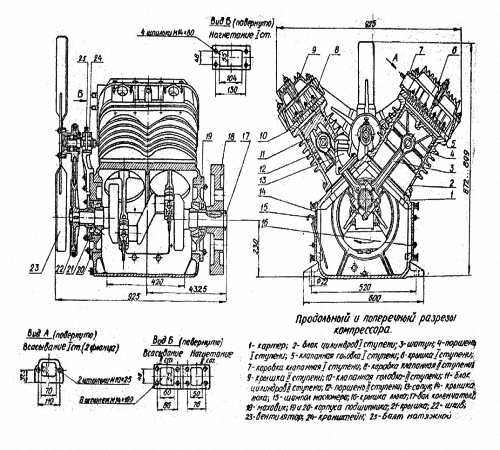
According to the type of placement of cylinders relative to the axis of the unit, the device of an angular type piston compressor is V-shaped, rectangular and W-shaped. Each type of this type of compressor structurally has much in common - they consist of the main components, as shown in the diagram of a reciprocating compressor, figure:
If the concentration of pollutants in fresh air above the set limit, the air conditioning ECU automatically switches to closed loop, up to 100% internal air circulation. Subsequently, the control unit focuses on measuring the air quality inside the car and compares it with the quality of the outside air. If the sensor detects that the indoor air quality is worse than the outdoor air quality, the air conditioner switches to 100% fresh air.
Cooling circuit The cooling circuit consists of the following parts. Compressor, condenser, refrigerant tank with drying filter - dryer, expansion valve, evaporator, regulation and control devices, hose and pressure pipe system, refrigerant. This is the device that circulates the refrigerant in the air conditioning system. The compressor operates only when the air conditioner is turned on and sucks in and then compresses only the gaseous refrigerant. The compressor is lubricated by the oil contained in the refrigerant.
- cylinder and piston units, sealing elements,
- movement mechanisms - compressor crankcase, main shaft, connecting rods and crossheads,
- auxiliary components - filters, coolers, receivers, lubrication units, moisture and oil separators, protection and adjustment systems.
Schematically, the principle of operation of a vertical piston compressor is performed in 2 stages:
Why is the compressor down
Currently, a drum compressor is used, but there is also a piston, scroll or blade. In terms of regulation, compressors are divided into regulated or unregulated. For unregulated compressors, the amount of refrigerant transported is controlled by turning on and off the electromagnetic clutch in the compressor drive. With controlled compressors, the electromagnetic clutch is disabled. The amount of refrigerant is regulated by a control valve, which assists with an additional control valve if necessary.
1. The air or gas contained in the expanding cavity of the cylinder gradually expands as the piston moves along the axis away from the cylinder head. At the same time, inside the cylinder, the air pressure decreases relative to external parameters, and this leads to its batch suction through the valve.
2. Next, air (gas) is compressed or injected during the movement of the piston, which is performed in the opposite direction - the pressure in the cylinder increases in proportion to its compression, after which the compressed air is released with force through the discharge valve.
Thus, the refrigerant control ranges from 0 to 100%. In short, it is written that the compressor is “not running” all the time, but only when the medium is not cooling. Then disconnect the solenoid clutch or control valve. Older constant power compressors take an average of 4-5 kW, with variable power compressors, the sampling rate is from 0 to 5 kW. On average, however, we can expect a subscription of around 1.5-2 kW.
During this cooling, it passes from a gaseous state to a liquid state - it condenses. Rapid cooling occurs in such a way that the heat from the condenser is transferred to the flowing air, either by natural attack or by a fan. A coolant tank with a filter for drying - the so-called dehydrator.
The scheme of a piston compressor for most designs is fundamentally the same - it is a cylinder, a piston, valves (suction and discharge), a crank mechanism (crosshead, crank and connecting rod) and a rod. Compressors are also evaluated by such parameters as piston force, amplitude and power, shaft speed, air pumping volume and others.
This part serves as a container for feeding and leveling. The amount of refrigerant required for proper operation depends on various conditions operation of the air conditioner, and the refrigerant tank can cover various volumes of its volumes. The drying filter is designed to absorb - to receive water and impurities in the refrigerant. According to the design, it can store 6 to 12g of water.
The expansion valve controls the amount of refrigerant entering the evaporator. The regulation of the amount of refrigerant is important from the operating state, since the amount of refrigerant in the evaporator, depending on the instantaneous operating state, must be such that it passes everything from liquid to gaseous state. The amount of refrigerant in the evaporator depends on the pressure, the temperature of the coolant behind the evaporator.
The scheme of operation of a reciprocating compressor is associated with changes in the temperature of the gas (air), the occurrence of vibrations, therefore, they need cooling and reliable support, which is already incorporated in their design. However, long-term operation and maintenance of reciprocating compressors causes breakdowns, reduced productivity and clogging.

Reciprocating Compressor Troubleshooting
Let us consider in detail the causes of problems and possible solutions. For example, if the flywheel does not turn, then a larger gap is made between the piston base and the valve plate, in the range of 0.2-0.6 mm. The cause of the problem is the stop of the piston in the plane of the valve.
When passing air through the dehumidifier, flush or replace the valve. Possible causes - destruction or clogging of the valve. If air is detected in the discharge tube after stopping, the valve must be cleaned, most likely, the check valve is clogged there.
With an increase in the heating of the compressor head, it is necessary to tighten according to the norm, replace the piston rings with a detected defect, clean the contaminated surfaces, change the oil to the one indicated in the technical documentation. The probable causes of overheating are the use of oil that does not correspond to that specified in the data sheet, insufficient time for its cooling; Possibly an overdue oil change. Connecting rod bolts can be overtightened, which make it difficult for oil to reach the liners, or the thermal clearance at the junction of the piston rings is too small, it is important to check the loosening of the fastening studs.
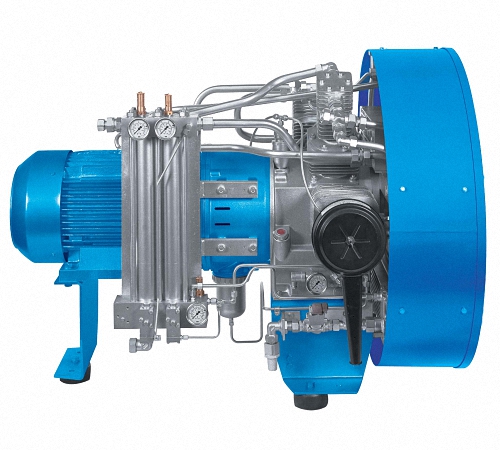
With a slow set of revolutions, or when the mechanism does not start under pressure, change the valve, grind the body and revise the belts. Possible causes are loose drive belts or clogged check valve.
If an oil leak is detected along the crankshaft from the crankcase, the oil seal must be replaced and the breather clearance must be cleaned. Possible reason- clogging of the breather hole and general wear of the stuffing box.
If the performance of a reciprocating compressor decreases, it is necessary to flush or replace the filter, change worn piston rings, locate the leak to eliminate it, clean and change defective valve plates, or level the contact plane of the direct-flow valve. The most likely causes of reduced piston performance are stuck or broken valve plates, air leakage due to a loose connection or depressurization, as well as a clogged air filter or general wear of the piston rings.
When the cylinder knocks, it is necessary to change the oil, replace defective piston rings and worn parts, bore the cylinder or replace the piston. The most likely causes of knocking are broken piston rings or seizing due to soot and unsuitable oil, as well as general wear on the piston or its cylinder, the connecting rod bushing or piston pin.
With excessive formation of soot, all components are cleaned of soot, oil is changed, it is important to further ensure that there is no excess oil in the crankcase. The probable reason is the use of low-quality oil and the appearance of its excess in the crankcase.
If a knock occurs in the crankcase, it is necessary to revise and tighten the connecting rod bolts, change the bearings or process the connecting rod journals to the repair size, and replace the liners. Probable causes are worn out crankshaft bearings, connecting rod journals and liners, weakened fastening of the connecting rod bolts.
If the pressure in the receiver and the dispensing valve decreases, it is necessary to clean the check valve, since the most likely cause is a breakdown or clogging of the check valve.
The best solution to bring the compressor back to working order is to contact the specialists of the local service center. However, before repairing any technical unit or unit, it is important to make a complete diagnosis in order to identify the exact cause of the malfunction, then repair and replacement Supplies will be carried out most efficiently. When diagnosing reciprocating compressors, competent specialists will not only find the cause of a malfunction or defects, but also eliminate all its shortcomings and causes of failure.
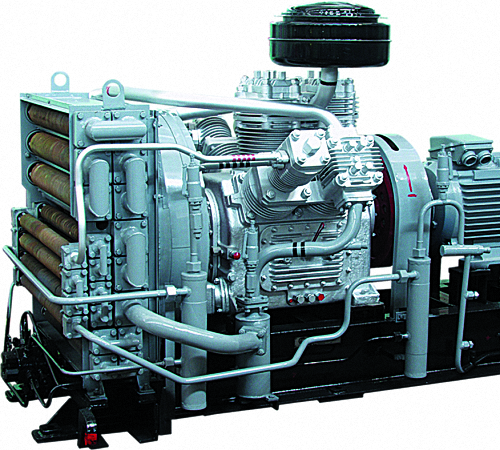
Maintenance of reciprocating compressors
With any depreciation, slight or increased, any equipment wears out, and the compressed air or gas mixture pumped by a reciprocating compressor has impurities, oils and suspension. Often this is what leads to a decrease in the performance of its main components or even valve depressurization. Piston compressors, like any other technical devices, periodically need a preventive inspection of all its components, as well as a change in consumables and worn out components.
Sometimes a factory defect, a violation of the operating rules or its excessive load is possible, due to which a decrease in work efficiency occurs and there is a need for repair of reciprocating compressors. It is very important not to miss the moment when it would be quite enough to replace parts in time or adjust them so as not to lead to a complete breakdown of the compressor.
Often, service center personnel are faced not so much with a clear breakdown of air injection devices, but with their unreliability or unstable operation, small defects, and when these causes are eliminated, the compressors again work smoothly.
The reasons may be different, for example, frequent overheating, knocking, excessive carbon deposits, a decrease in its efficiency, etc. Some symptoms indicate the need to replace components, others lead to its inevitable breakdown. There are several symptoms when piston compressor it is necessary to stop even before its complete or partial breakdown and stop.

1. This is an indicator of pressure - its decrease in the cooling system or when blowing the engine, a decrease in gas pressure when suction is below normal, or when the pressure in the compressor lubrication circulation system decreases.
2. These are temperature indicators - an increase in the temperature of the main bearing shells of more than 70 ° C or a high temperature of the leaving water.
3. This is a spontaneous shutdown of the engine lubrication of cylinders and seals, extraneous noise or other failures.
Among the defects in the diagnosis of a reciprocating compressor, such problems are most often found.
1. Depreciation: oil seals or their insufficient lubrication, as well as counterweights, high-pressure cylinder bushings with cracks.
2. Corrosion of any element of the compressor or its components in places of greatest stress, for example, at cylinders and crossheads.
3. Fault safety valve and other nodes.
4. Contamination or oil leakage.
5. Broken connecting rod bolts.
6. Inaccuracy in the centering of the stem or its bending, for example, due to one-sided heating in the stuffing box.
7. Loss of cast piston plugs into the cylinder.
8. Looseness on the piston seat rod.
9. Broken or defective piston rings, coupling, crankshaft parts, valve springs or lift stop.
10. Rod surface defect or wear cracks on connecting rods.
11. Excessive bolt tension.
12. Overheating of the crank.
13. Damaged crosshead or stem connections.
14. Bolt falling out or nut loosened.
15. Extraneous uncharacteristic noises - work with a knock for a long period due to violation of the clearances of the connecting rod bearings.
16. Inaccuracies in the laying of the shaft and the fit of the bolt head and nut to the surface of the connecting rod.
Piston compressors, like any other mechanism, may experience malfunctions during their operation due to one reason or another. In order to understand typical faults, it is necessary to classify them.
They are:
- Mechanical.
- Operational
- Electrical.
The first type includes:
Intake air filter clogged
The nature of the fault: superficial and internal pollution filter element
Reason: violation of the requirements for the premises, the place of installation of the compressor. The presence of dust, paint, etc. in the air.
Consequences: reduced compressor performance, overheating, premature wear, cylinder - piston group.
Mechanical damage to the suction air filter
The nature of the fault: absence of a filter assembly, absence of a filter element, violation of the integrity of the filter or filter element (breaking, cracks, breakdown)
Cause: Careless operation, storage, transportation.
Consequences: Penetration of dust particles, paint aerosols into the valve assembly and into the compressor cylinders. Wear and contamination of valves, valve group channels, wear of cylinders, pistons, coking and subsequent loss of ring mobility (deposition), oil contamination (oil oxidation and aging). Compressed air pollution.
Violation of the lubrication regime.
The nature of the fault: Overheating, compression reduction, catastrophic wear of the cylinder-piston group.
Consequences: mechanical breakdowns of the cylinder-piston group. Scuffing on the surfaces of the cylinders, wear of plain bearings (liners), overheating, breakage of rings, jamming of pistons, connecting rods, breakage of connecting rods. Increased loads on the motor bearings.
Here attention should be paid to lubrication features of reciprocating compressors:
a) the oil must be compressor oil - this oil has an order of magnitude (10 times) less ash content compared to engine oils;
d) change the oil, exactly as written in the technical manual of the compressor.
The second type of fault is negligent operation (non-observance of the compressor operating mode):
Compressor operation mode - intermittent, with duty cycle (PV) up to 60%, with the duration of one cycle from 6 to 10 minutes. Continuous operation of the compressor is allowed for no more than 15 minutes, but not more than once within 2 hours. From this it follows that the total operating time of the compressor should not exceed 36 minutes. This applies to industrial air-cooled reciprocating compressors. For household compressors PV less than 60%. And the useful time does not exceed 30 minutes. at one o'clock.
Typical faults: External pollution of all compressor nodes, a common thing is where we paint and store the compressor. Breakage of pipeline fittings, plastic protective housings of the compressor, pressure switches (pressure switches) of the protective casings of the fan and the fan impellers themselves, we forget to drain the condensate from the receiver, mechanical failure of pressure regulators, pressure gauges, self repair and reconfiguration of complex compressor units, etc.
Electrical faults divided into two main types: mechanical and actually electrical.
Mechanical accidents- this is a deformation or breakage of the rotor shaft, loosening of the stator core to the frame, loosening of the crimping of the rotor core, melting of babbit in plain bearings, destruction of the separator, ring or ball in rolling bearings, breakage of the impeller, deposition of dust and dirt in moving elements, etc.
Most mechanical accidents are caused by radial vibrations due to the asymmetry of the supply network (the so-called phase imbalance), mechanical overloads on the motor shaft, defective components or defects during assembly. Up to 10% of all BP accidents are of mechanical origin. At the same time, 8% are accounted for by accidents associated with phase asymmetry and only 2% by accidents associated with mechanical overload. The proportion of accidents due to marriage is small and therefore can be ignored in this review.
electrical accidents, in turn, are divided into three types:
Network accidents (voltage accidents) associated with accidents in the power supply network;
Current accidents associated with breakage of conductors in the windings of the stator, rotor or cable, interturn and phase-to-phase short circuit of windings, broken contacts and destruction of connections made by soldering or welding; accidents leading to insulation breakdown as a result of heating caused by the flow of overload or short circuit currents;
Accidents associated with a decrease in insulation resistance due to its aging, destruction or moisture.
Below is a table of the main malfunctions that may occur, their symptoms, causes and remedies.
| Name of the malfunction, its manifestation and symptoms | Probable Cause | Remedy | |
| Reduced compressor performance | Clogged air filter | Clean or replace filter element | |
| Violation of the density of connections or damage to the air ducts | Determine the location of the leak, seal the connection, replace the air duct | ||
| Belt slippage due to insufficient tension or contamination | Tighten the belt, clean from dirt | ||
| Air leakage from the receiver into the discharge air duct - constant "hiss" when the compressor is turned off | Ingress of air from the receiver into the discharge air duct due to wear or clogging of the check valve seal | Unscrew the hex head of the valve, clean the seat and seal or replace | |
| Motor overheating and compressor stop during operation | Insufficient oil level in the compressor crankcase | Check oil quality and level, top up if necessary | |
| Continuous operation of the compressor at maximum pressure and air consumption - protection operation | Reduce the load on the compressor by reducing the air consumption, restart the compressor | ||
| Compressor stop during operation | Power supply disturbances | Check the power circuit | |
| Vibration of the compressor during operation. Uneven engine hum. After stopping when restarting, the engine hums, the compressor does not start | There is no voltage in one of the phases of the power circuit | Check and provide power to the circuits | |
| Excess oil in compressed air and receiver | The oil level in the crankcase is above average | Bring the level up | |
| Note - If other faults are found, contact the manufacturer's representative (seller). | |||
Pnevmomagazin.ru











Chocolate biscuit: the secrets of cooking in a slow cooker and oven
Chemical composition and nutritional value
Apple chips at home
Braised cabbage with white beans, recipe
How to reduce the ass, hips and stomach at home?