It is rather difficult to determine the type of radiator suitable specifically for a particular heating system, without knowing its main characteristics. There are devices installed in private houses with an autonomous heating system, as well as radiators, the installation of which is possible only in a city apartment.
Bimetallic heating radiators - types, specifications
If we compare aluminum radiators with bimetallic ones, then the latter compare favorably with the former in terms of their technical characteristics. Despite all its positive qualities, aluminum appliances have a number of serious drawbacks, which do not allow their use in multi-storey buildings residential buildings. Bimetallic analogues are quite capable of coping with all the technical limitations associated with installation in city apartments connected to the central heating network.
The device of bimetallic devices
 In appearance, a bimetallic radiator does not differ in any way from aluminum, because both are made of the same metal. The whole "secret" is in the internal structure of the battery.
In appearance, a bimetallic radiator does not differ in any way from aluminum, because both are made of the same metal. The whole "secret" is in the internal structure of the battery.
The bimetal radiator has internal stainless steel inserts that provide reliable protection aluminum from the harmful effects of all kinds of impurities contained in the water. It is thanks to the built-in steel sections, the outer case of the bimetallic device does not directly contact the coolant. In addition, steel is more resistant to the destructive effects of acids and alkalis, which are present in large quantities in central heating systems, and does not enter into chemical interaction with copper elements of urban communications (pipes, heat exchangers, etc.).
The use of steel inserts for the passage of water also provides other useful properties of bimetallic heating devices:
- Durability. Due to the fact that the internal steel cavities are resistant to destruction and corrosion, the manufacturer can set a fairly long service life of the device - up to 20 years.
- Strength. The body of the product can withstand pressure up to 30-40 atmospheres. Such a heating radiator is not afraid of even the strongest water hammer.
- Economy. Narrowed water supply channels provide an optimal combination of the device's thermal inertia and energy consumption for heating.
Adding here all the positive qualities that have passed from aluminum counterparts, such as compactness, high heat dissipation and a presentable appearance, it can be stated with certainty that today bimetallic devices are the best option heating of multi-storey buildings.
Heating radiator: dimensions
When choosing a bimetallic heating device, the dimensions of the product are of great importance.
In order to create a thermal curtain for cold air penetrating through the glass, heating devices are usually installed under the window. Therefore, the device should easily fit in a niche under the windowsill and provide the necessary level of heat transfer.
In height, all bimetallic radiators have standard indicators. The distance between the vertical channels varies depending on the modification of the device and is 200 mm, 350 mm and 500 mm.
However, it should be noted that the distance between the vertical channels is not yet the full height of the device, but only the size of the segment between the centers of the output and input manifolds. The real height of the device is determined as follows: center distance + 80 mm. So, for example, a radiator marked 500 will take about 580 mm, and the 350th model will take about 420 mm. The width of the device is determined by the number of sections.
The number of sections for all types of heaters is calculated the same.
According to the technical requirements for heating residential buildings in middle lane countries, a power equal to 1 kW is intended for heating 10 square meters. meters of area.
The manufacturer usually indicates the power value of one section for each battery. Knowing the value of the heat output of the section, you can calculate the number of required elements using the formula:
N \u003d S * 100 / Q, where Q is the power of one section, S is the area of \u200b\u200bthe room and N is the desired amount.
Most Models bimetallic radiators have a standard section width of 80 mm, so the power of a conventional 500 mm section is about 180 watts. In accordance with this, the total number of sections is determined. So, for example, for heating a room with an area of 20 m2, you will need 12 sections, the width of such a battery will be about 1 m.
Design features
As mentioned earlier, a bimetallic radiator differs from aluminum in that there are steel tabs inside it that protect the body from corrosion.
These tabs can be installed in various parts device:

Construction types

- Monolithic. The radiator consists of non-separable steel pipes. It has a fixed number of sections that cannot be changed. The main characteristic of a cast radiator is increased reliability. The device is recommended for use in systems where frequent pressure surges are observed.
- collapsible. The number of sections is determined independently, depending on the area of \u200b\u200bthe room. Sections are interconnected by metal threaded pipes.
The choice of one or another design depends on the type of heating system. So, for autonomous heating, it is better to purchase a collapsible model, for a city apartment - a cast one.
Capacity
 The presence of steel inserts inside the device helps to reduce the capacity of the section. On the one hand, this is good: the amount of thermal inertia and the coolant itself is reduced, which allows you to significantly save energy and provides comfortable control. But on the other hand, too narrow water supply channels quickly become clogged with all sorts of debris that is inevitably present in modern central heating networks.
The presence of steel inserts inside the device helps to reduce the capacity of the section. On the one hand, this is good: the amount of thermal inertia and the coolant itself is reduced, which allows you to significantly save energy and provides comfortable control. But on the other hand, too narrow water supply channels quickly become clogged with all sorts of debris that is inevitably present in modern central heating networks.
The capacity of the section is determined by the distance between the vertical channels.
For a device with a distance of 500 m - a capacity of 0.2-0.3 l;
for a 350 mm battery - 0.15-0.2 l;
for 200 mm - 0.1-0.16 l.
As you have already noticed, the capacity of bimetallic radiators is really small. For instance, the popular RIFAR device, 80 mm wide and 350 mm high, holds only 1.6 liters. Despite this, the radiator is able to heat a room up to 14 square meters. m. True, the weight of the device reaches 14 kg, since the bimetallic radiator is 1.5-2 times heavier than aluminum ones.
A bimetallic heating battery is better suited for a city apartment. If you are the owner of a private house that has its own heating boiler, it is better to purchase an aluminum radiator.
When choosing a bimetallic parting, you need to pay attention to the following parameters:

So, having calculated the number of radiators, the required number of sections included in them and setting the required power of the device, you can proceed with the installation of the heating system.
It should be remembered that the heat balance in the room directly depends on the dimensions of the device. So, if the width of the radiator is small, you should increase its height or the number of sections.

It must be borne in mind that even the most expensive, high-quality and suitable bimetallic radiator for your heating system must be installed in compliance with all installation rules. Only in this way will he be able to maintain his positive qualities and ensure maximum heat transfer with minimal energy costs.
A bimetallic radiator is a heating device in which the coolant circulates through a steel core placed inside an aluminum housing. Batteries of this type belong to sectional heating devices and operate on the principle of combined (convective and radiant) heat exchange.
Technical characteristics of bimetallic heating radiators include a number of parameters and design features, allowing you to evaluate the heater and compare it with other models of the same size.
How to compare bimetallic radiators with each other?
Everyone who thoroughly approaches the choice of heating batteries for his house or apartment strives to purchase products with optimal performance and performance specifications. To correctly select the most suitable radiator, the compared models must be of the same size. In the reference data, the parameters are given for one section, so you need to compare not the devices as a whole, but their structural parts. The main parameter by which the division into standard sizes takes place is the center distance.
The center distance is the size between the axis of the upper and lower collectors. Like all-aluminum models, bimetallic radiators are produced mainly with center distances from 200 to 800 mm. Models with great value center distance, and as a result, with an increased height of the sections (but a smaller width of the entire radiator), are rare. They are used if the interior features of the room do not allow placing a horizontally located device.

Geometric parameters
The main geometric characteristics of a bimetallic radiator are its height, as well as the width and depth of the section. The height, as a rule, is 60 - 80 mm higher than its center distance.
Most manufacturers produce models with a section width of 80 mm. Knowing the number of sections, you can easily determine the total width of the device.
The depth of the section is 80 - 100 mm. The radiator can be either of constant depth or variable in height, like the stylish and elegant device of the DreamLiner series from Royal Thermo.

Installation of a heating radiator on a wooden wall.
Thermal power
This parameter allows you to determine how many radiator sections of a particular model are needed to heat a room of a certain area. Thermal power is measured in watts and is at the center distance:
- 500 mm - from 170 to 200 W;
- 350 mm - from 120 to 140 W;
- 300 mm - from 100 to 145 W;
- 200 mm - about 100 watts.
In their information, technical materials (instructions, manuals, catalogs), manufacturers indicate tables showing the number of sections that are optimal for heating rooms of various sizes.

The steel core is the basis of the structure.
Volume (capacity) of one section
In bimetallic radiators, the coolant circulates through steel cores. The core is an H-shaped welded structure, consisting of an upper and lower collector, interconnected by a vertical tube (heat pipe). Each manifold has two side holes with internal threads, thanks to which the sections can be connected using steel nipples. This design completely eliminates the contact of the coolant with aluminum.
Unlike aluminum radiators, where the heat conductor has an oval cross section, only round tubes are used in the steel cores of bimetallic models, which provides for a smaller capacity of each section. Thus, the bimetallic Rifar Base 500 has a section capacity of 0.20 liters, while the aluminum model Rifar Alum 500 of the same size has a volume of 0.27 liters.

Section weight
Bimetallic radiators have a larger mass than similar models of aluminum radiators. This is due to the use of steel cores in their design, the density of which (and hence the mass) exceeds that of aluminum. For example, the bimetallic radiator Varmega Bimega 500/80 weighs 1.75 kg, and the aluminum radiator Almega 500/80 from the same manufacturer weighs 1.2 kg.
Pressure
The working pressure of bimetallic radiators is 16 - 40 atm (1.6 - 4.0 MPa). According to regulatory documents, devices must be tested by pressure testing the heating system with a pressure that is 1.5 times higher than the working value. The documentation also indicates the value of the maximum pressure, upon reaching which it can begin to collapse.

Connection of sections.
Comparative technical characteristics of bimetallic radiators
For a convenient comparison of various models, tables 1-3 contain data on the main characteristics of products from 11 manufacturers. The information is given both for the most common size 500 mm and for radiators with a center distance of 350, 300 and 200 mm, which are present in model range only a few manufacturers.
Table 1 - Comparison of the characteristics of models with a center distance of 500 mm.
| Manufacturer and model | Overall dimensions, mm | Section volume, l | Section weight, kg | Pressure, atm | Thermal power, W | |||
| height | width | depth | working | test | ||||
|
Bilux plus R500 |
563 | 80 | 85 | 0,21 | 1,82 | 20 | 30 | 182 |
|
Industry Pasotti elegance |
565 | 80 | 100 | 0,19 | 2,06 | 35 | 52 | 176 |
|
Global Style Extra 500 |
566 | 81 | 80 | 0,21 | 1,87 | 35 | 52,5 | 170,7 |
|
Konner Bimetal 80/500 |
563 | 80 | 80 | 0,40 | 2,18 | 30 | 45 | 190 |
|
Rifar Base 500 |
570 | 79 | 100 | 0,20 | 1,92 | 20 | 30 | 204 |
|
Royal Thermo Biliner 500 |
574 | 80 | 87 | 0,205 | 2,01 | 30 | 45 | 171 |
|
Tenrad BM500 |
550 | 80 | 75 | 0,22 | 1,45 | 24 | 36 | 161 |
|
Varmega Bimega 500/80 |
565 | 80 | 80 | 0,3 | 1,75 | 30 | 45 | 190 |
|
Santechprom RBS-500 |
560 | 80 | 95 | 0,23 | 2,34 | 16 | 24 | 185 |
|
Sira Industry RS Bimetal 500 |
572 | 80 | 95 | 0,199 | 2,03 | 40 | 60 | 201 |
|
Scola JB-SA 500 |
565 | 78 | 80 | 0,28 | 1,85 | 30 | 40 | 188 |

Variety of standard sizes.
Table 2 - Comparison of the characteristics of models with a center distance of 350 mm.
| Manufacturer and model | Overall dimensions, mm | Section volume, l | Section weight, kg | Pressure, atm | Thermal power, W | |||
| height | width | depth | working | test | ||||
|
Global Style Extra 350 |
416 | 81 | 80 | 0,17 | 1,42 | 35 | 52.5 | 119.6 |
|
Konner Bimetal 80/350 |
413 | 80 | 80 | 0,30 | 1,28 | 30 | 45 | 140 |
|
Rifar Base 350 |
415 | 80 | 90 | 0,18 | 1,36 | 20 | 30 | 136 |
|
Royal Thermo Biliner 350 |
424 | 80 | 87 | 0,175 | 1,52 | 30 | 45 | 118 |
|
Tenrad BM350 |
400 |
80 | 75 | 0,15 | 1,18 | 24 | 36 | 120 |
|
Varmega Bimega 350/80 |
412 |
80 | 80 | 0,22 | 1,43 | 30 | 45 | 140 |

Table 3 - Technical characteristics of bimetallic radiators with a center distance of 300 and 200 mm.
| Manufacturer and model | Overall dimensions, mm | Section volume, l | Section weight, kg | Pressure, atm | Thermal power, W | |||
| height | width | depth | working | test | ||||
|
Center distance 300 mm |
||||||||
|
Bilux plus R300 |
365 | 80 | 85 | 0,17 | 1,29 | 20 | 30 | 142 |
|
Santechprom RBS-300 |
360 | 80 | 95 | 0,178 | 1,67 | 16 | 24 | 121 |
|
Sira Industry RS Bimetal 300 |
372 | 80 | 95 | 0,165 | - | 40 | 60 | 145 |
|
Scola JB-SA 300 |
365 | 78 | 80 | - | 1,45 | 30 | 40 | 106 |
|
Center distance 200 mm |
||||||||
|
Bilux plus R200 |
550 | 80 | 75 | 0,22 | 1,45 | 24 | 36 | 161 |
|
Rifar Base 200 |
565 | 80 | 80 | 0,3 | 1,75 | 30 | 45 | 190 |
Applicable materials
The core of the bimetallic radiator section is made of steel pipes. For batteries of normal strength (working pressure 16 - 20 atm), the core is made of carbon steel grade St.3 or its foreign analogues(e.g. Tenrad radiators). The core (frame) of high-strength models is welded from stainless pipes. High-strength devices with a stainless steel core (for example, Biliner from Royal Thermo) can withstand burst pressures of more than 100 atm.
The outer part of bimetallic radiators is made of die-cast aluminum. The extrusion method used in the production of some aluminum models cannot be used in this case, since a core must be placed inside the workpiece before shaping begins. O-rings are made from heat-resistant silicone rubber.

ribbing
The fins serve to increase the total heat transfer area of the heater. IN modern models apply various Constructive decisions which make the finning more efficient.
The efficiency of heat transfer is increased due to the introduction of additional ribs into the structure, as well as the profiling of convection channels between the ribs. In Tenrad radiators, the channels form a confuser, due to which the air flow speed increases, which increases the intensity of convective heat transfer. The outer edges of the ribs are rounded to increase safety.

Section connection method
In bimetallic radiators, the sections are connected to each other using steel threaded nipples. In the manufacture of radiators of the Monolit series from Rifar, a different type of connection is used - welding. This model of heaters can withstand high pressures (operating up to 100 atm) and temperatures (up to 135 ° C versus 110 ° C for nipple models).

Bimetallic radiators are the most technically advanced heating device for water heating systems. Combining high efficiency and good performance, devices of this type are optimal for use in domestic conditions. Knowing specifications bimetallic heating radiators of various models, you can choose the heater that best suits the working conditions in a particular room.
The owners of apartments in houses with centralized heating have been waiting for a long time for manufacturers to create batteries that can withstand all its shortcomings: high pressure, low-quality coolant and powerful water hammer that can destroy weak aluminum or steel radiators.
The combination of these two metals made it possible to produce bimetallic radiators that are completely unique in their technical characteristics.
Feature of bimetallic devices
When a steel coil was placed inside the aluminum case, fixing the entire structure tightly by welding, several problems were solved at once:
Consumers who have already tested bimetallic structures in their apartments say that their only drawback is their high cost. But, as a rule, quality, safety, beauty and economy are just those properties for which it is not a pity to pay any money.
Types of aluminum-steel radiators
Manufacturers, following the lead of consumers, are trying to reduce the cost of production of bimetallic structures without changing their device as a whole. Now on the market you can find several types of batteries of this type:

If the radiators are to be installed in a room with autonomous system heating, it makes no sense to invest a lot of money in expensive models. In this case, it is enough to calculate the power and determine optimal dimensions bimetallic heating radiators (10 sections - this is the standard type, although you can choose a different type of device).
Types of radiators
Unlike the Soviet era, when the batteries had the same standard accordion look, today there are different types radiators, and bimetallic ones are no exception in this regard.
Monolithic models are a one-piece section consisting of steel pipes that cannot be disassembled. Such a design cannot be changed in size, increase or decrease the number of sections. If the power required for the room is calculated correctly, then a better and more reliable "friend" for a system with strong pressure drops cannot be found. Cast bimetallic radiators are able to withstand pressure up to 100 atmospheres and are the most expensive on the market.
Collapsible or, as they are also called, sectional models, allow you to independently determine what size sections of a bimetallic heating radiator are needed for each particular room.
In order for the apartment to be truly warm, it is necessary to determine in advance how much power the radiator should have, taking into account all heat losses. The capacity of the device depends on the size of the device, and the smaller it is, the more economical it works.
Standard battery dimensions
 The dimensions of bimetallic radiators are exactly the same as other types of heaters. They are determined by the center distance between the lower and upper horizontal collectors. Do not consider these parameters as the size of the entire structure. To calculate the height of a bimetallic radiator, add 80 to the center index indicated on the product. There are three center distances - 200, 350 and 500 mm, but these are not the only parameters of these devices.
The dimensions of bimetallic radiators are exactly the same as other types of heaters. They are determined by the center distance between the lower and upper horizontal collectors. Do not consider these parameters as the size of the entire structure. To calculate the height of a bimetallic radiator, add 80 to the center index indicated on the product. There are three center distances - 200, 350 and 500 mm, but these are not the only parameters of these devices.
- the length of the standard section is 80 mm;
- depth - from 75 to 100 mm;
- height - 550-580 mm.
To calculate how high they are, for example, standard radiators bimetallic 500 mm, you need to add 80 to this indicator, and the resulting 580 mm is its true size, which should be taken into account when determining the place where it will stand.
In addition to standard models, there are so-called design options for bimetallic radiators.
tall structures
When the interior of an apartment or office requires a special approach to the arrangement, then the heaters should harmoniously fit into it. So, if indoors panoramic windows, then it is possible to install bimetallic radiators, the dimensions of which are 880 mm or more in height, with a section length of 80 mm and a depth of 95 mm.
As a rule, these are cast reliable devices that can be mounted on walls. They can not only heat the room, but also decorate it, as they are produced in a fairly rich color scheme. In extreme cases, you can order the manufacturer a model of the desired shade or with a specific pattern.
Low batteries
 Another design solution is low bimetallic heating radiators. They can be installed under large windows where standard models do not fit in height. Bimetallic radiators with a minimum center distance of 200 mm, while their characteristic feature is the same strength, reliability, ability to withstand high pressure and the level of heat transfer as in standard models.
Another design solution is low bimetallic heating radiators. They can be installed under large windows where standard models do not fit in height. Bimetallic radiators with a minimum center distance of 200 mm, while their characteristic feature is the same strength, reliability, ability to withstand high pressure and the level of heat transfer as in standard models.
This is due to the fact that the design of these heaters does not change depending on the size. True, there are manufacturers who are "cunning", saying that the price of their products is lower due to their dimensions. In this case, in fact, bimetallic radiators (300 mm, 400 mm or 200 mm does not matter) have a different structure. They do not have a steel horizontal core, and only vertical collectors are made of this metal. You can identify a fake by the data sheet, which indicates a pressure level of 20-40 atmospheres that is not usual for "real" bimetallic heaters, but only 12-15, which is unusual for these devices.
It is not worth buying such a product in an apartment with a centralized type of heating, but in an autonomous system they will be in place.
The ratio of power and size of radiators
As long-term practice of using heating devices has shown, the width of the sections of a bimetallic radiator (like any other), its length and height are reflected in the power, and this is understandable: the larger the area of \u200b\u200bthe radiator, the higher its heat transfer.
If we compare the heat transfer, mass, capacity, size and pressure level of a bimetallic structure with an aluminum counterpart, we will see what is the difference between them.
- Bimetal radiators 350 mm (center distance):
- Heat dissipation 136 W (aluminum - 139)
- Pressure level (working) 20 bar (15 bar for aluminum)
- Crimping index 30 Bar (20-25 Bar respectively).
- Section capacity 0.18 l (0.19 l)
- The weight of one section is 1.36 kg (aluminum - 1.2 kg).
- Bimetal radiators 500 (80 deep):
- Heat dissipation from one section 204 W (180 W aluminum with similar dimensions).
- Working pressure 30 bar (20 respectively).
- Crimping pressure 40-50 bar (30 bar).
- Section capacity 0.2 l (0.27 l).
- The weight of one element is 1.90 kg (1.45 kg).
As can be seen from the above parameters, the power varies depending on the size of the radiator, as well as its pressure level, and weight, and volume.
When choosing which type of batteries to install, you need to start from the real needs of the room in the amount of heat, and not from the style and quality of interior design. Fortunately, modern manufacturers produce models of any level - low bimetallic heating radiators are in stores next to high counterparts.
Knowing how much power the device should have, it is enough to look at the table provided by either sellers or manufacturers for each product and find the corresponding size indicator. When installing a sectional model, it can always be increased to increase power, but if the radiator does not fit under the window, then designer heater options should be chosen.
Aluminum- lightweight material that is widely used.
Among other things, heating batteries are made from it.
In their creation is very important characteristics calculation.
Influence of aluminum radiator size

Aluminum batteries are made in a wide range of sizes. Length has a primary effect on power.
Accordingly, in order to achieve the required heating, it is necessary increase the number of sections. The total length of the battery depends on the calculations.
Depth and height also change the metrics because they affect volume. Unlike length, these two values- Variable, due to which there are many different models.
The next indicator is center distance. It is responsible for the heating rate of the radiators, since it means the gap between the supply and return pipes.
The manufacturing method also affects performance:
- Outflow from metal increases the strength and durability of the device. In this case, each section is an integral unit from which the device is assembled. This is done in a certain sequence: first the upper parts are welded, then the lower ones.
- extrusion method involves forcing heated aluminum through a metal lattice plate. Thanks to this, a profile of a given shape is obtained, which is divided into parts and assembled into a radiator.
Attention! Such heaters are rare, and are usually made to order. It's connected with inability to make changes into the design after the end of production.
center distance
The indicator represents the gap between the axes of the radiator. They are arranged symmetrically one above, one below. Pipes adjoin them, through which inclusion in the heating circuit is carried out.

Photo 1. Aluminum radiator model 350/80, center distance 350 mm, manufacturer - "Oasis", China.
The value varies depending on the manufacturer. in the range of 150-2000 mm. For most devices, this indicator is equal to 500. This is related to heating systems in apartment buildings: in old buildings, calculations are made for cast-iron radiators. When replacing batteries, the costs of digesting the pipeline are undesirable.
Reference! The name of most models contains number indicating the center distance.
Depth
Depends on the material from which the battery is made. The minimum value is 52 mm. It is enough to create a high power of small sections. The maximum indicator - 180 mm. It is quite rare and requires strength. There are models with greater depth, but their use is impractical due to insufficient heating.
Determination of section volume

To calculate, you need to know the value described above, as well as the length and height. First value, visually - width.
She is 80 or 88 mm, what is indicated in the passport.
Second- variable. Usually the vertical component of the section dimensions is 570 mm.
To find the volume, it is enough multiply three numbers.
Section calculation method
To determine the required number of elements, you need to determine the power. There are several rounded values computed for room with ceiling height 2.7 meters:
- For a standard room 100 watts.
- For each window add by 10.
- If it is angular, the value multiply by 1.2.
- If the ceilings are higher or the windows are larger than usual, add 10%.
- The heating is weakened from the upper floors to the lower ones, so each should be add another 2%.

Received rated power multiply by the area of the room. The result is a total value calculated with a margin.
The number is then divided by passport indicator of one section, rounding up. An example calculation looks like this:
- (100 + 10) * 1,2 * 1,04 = 137,28 , where the extreme factor is chosen for the flat third from top floor.
- 137.28 * S = 151 * 18 = 2471 where S (18)- area.
- 2471 / 190 = 13. In this case, with power one section of 190 watts will need 13 pieces.
Radiator weight
Aluminum is a light metal. Products made of this material have a small mass, which facilitates their movement, reduces the required installation strength. It should be noted that in the manufacture of batteries, metal is alloyed with silicon. This slightly increases the severity.
The average weight of one section is 1.25 kg. The value varies between from 1 to 1.35, which depends on the dimensions and wall thickness. For example, for mounting a radiator of 10 units with a small margin, enough fasteners for 15 kg.
Important! Of all types of aluminum radiators the lightest. This makes it easy to transport them.
Height and width of a custom-shaped radiator
There are batteries unusual look. From metals you can create a device up to three meters high, up to two wide.
Read in the article
Dimensions of heating radiators
The standard height of the most popular models of heating devices with a center distance along the eyeliners is 500 millimeters. It was these batteries that in most cases could be seen about two decades ago in city apartments.
Cast iron radiators. A typical representative of these devices is the MS-140-500-0.9 model.
The specification for it says: dimensions cast iron radiators:
- length of one section - 93 mm;
- depth - 140 millimeters;
- height - 588 millimeters.
It is not difficult to calculate the dimensions of a radiator from several sections. When the battery consists of 7-10 sections, add 1 centimeter, taking into account the thickness of the paronite gaskets. If the heating battery is to be installed in a niche, it is necessary to take into account the length of the flushing valve, since cast-iron radiators with side supply always require flushing. One section provides a heat flow of 160 watts at a temperature difference between the hot coolant and the air in the room equal to 70 degrees. The maximum working pressure is 9 atmospheres.
Aluminum radiators. For aluminum heaters on the market today, with the same interaxal spacing of the connections, there is a significant variation in the parameters (in more detail: “Dimensions of aluminum heating radiators, section volume, preliminary calculations“).
Typical are the following dimensions of aluminum heating radiators:
- the length of one section is 80 millimeters;
- depth 80-100 millimeters;
- height - 575-585 millimeters.
The heat transfer of one section directly depends on the area of its fins and depth. Usually it is in the range from 180 to 200 watts. The working pressure for most models of aluminum batteries is 16 atmospheres. Heating devices are tested with a pressure one and a half times greater - this is 24 kgf / cm².
Aluminum radiators have next feature: the volume of coolant in them is 3, and sometimes 5 times less than in cast iron products. As a result, the high speed of movement of hot water prevents silting and the formation of deposits. Bimetal radiators. The steel core in such devices in no way affects their appearance and dimensions of heating radiators, but the maximum working pressure increases significantly. Unfortunately, the increase in the strength of the bimetallic battery leads to a high cost. And the price of such a product is already inaccessible to a wide range of consumers.
Bimetallic heating radiators section dimensions are as follows:
- length 80-82 mm;
- depth - from 75 to 100 millimeters;
- height - a minimum of 550 and a maximum of 580 millimeters.
In terms of heat transfer, one bimetallic section is inferior to aluminum about 10-20 watts. The average value of the heat flux is 160-200 watts. Due to the presence of steel, the working pressure reaches 25-35 atmospheres, and during testing - 30-50 atmospheres.
When arranging the heating structure, pipes should be used that are not inferior in strength to radiators. Otherwise, the use of durable devices loses all meaning. For bimetallic radiators, only steel eyeliner is used.
Overview of the main features of radiators
So that you can see all the information in the most visual form, you are presented with a table - a comparison of heating radiators is presented in it on a scale from one to four pluses, depending on how this or that feature is inherent in a particular option
| Cast iron batteries | Aluminum options | Bimetallic batteries | Steel panel products | Steel tubular elements | Convectors | |
| small mass | + | +++ | +++ | +++ | +++ | +++ |
| Corrosion resistance | +++ | + | +++ | + | ++ | +++ |
| Heat transfer indicators | + | +++ | +++ | +++ | ++ | ++++ |
| pressure resistance | +++ | ++ | +++ | + | ++ | +++ |
| Attractive look | + | +++ | +++ | ++ | ++++ | +++ |
| Thermal inertia | +++ | + | + | + | + | + |
| Ease of maintenance | ++ | ++ | ++ | +++ | +++ | + |
| Price | +++ | ++ | + | ++++ | + | ++ |
Based on this data, you can see the strengths and weaknesses of a particular option, the table shows that ideal option does not exist, each has its own strengths and weaknesses, so the choice is up to you.
Important!
If you have chosen a specific solution, it is important to purchase quality products, so choose products from brands that have been on the market for a long time and have proven themselves among buyers. .
It is important to choose best solution from one or another group of radiators
Dimensions of cast iron radiators
Standard Soviet batteries of this type had a height of 580 mm, a rib width of 94 mm and a thickness of 140 mm. Many owners of houses and apartments still consider such models the most reliable. Therefore, cast-iron radiators are still in demand today. Manufacturers, of course, noticed this and began to supply the market with retro-style cast-iron radiators, which have a very attractive design. If desired, for the home, you can, of course, buy such batteries. Their sizes can be different. There are low, standard and high models of this type on the market. The approximate dimensions of cast iron heating radiators of different types can be found in the table below.
Dimensions of cast iron batteries
Very often, stylish cast iron retro radiators have small legs. In this case, the height is calculated, of course, taking them into account.

If you are looking for stylish batteries made from cast iron of a domestic manufacturer, then it is better not to find STI new. Their main parameters:
- The cast-iron radiator Nova 500 can withstand pressure up to 18 atmospheres. Crimping pressure of 16 atmospheres allows you to survive the water hammer of a centralized heating system.
- The thermal power of the structure is 150 W, which is quite enough to provide heat to a room of 15 m2.
- Externally, the heating radiator Nova 500 (cast iron) looks as stylish as its aluminum counterparts.
If you believe the reviews of consumers, then this type of heating device is distinguished by quality, reliability and interesting design.
Advantages and disadvantages
All advantages of steel radiator:
- due to the design characteristics, the service life is practically eternal, having a strong resistance to various injuries, size 2 cm;
- you can install such heating equipment manually yourself, this type of work does not require unique skills and abilities, you just need to install everything according to an existing template or on the manufacturer's website;
- have a unique design and will fit into various designer interiors.

Original design with steel batteries
All the disadvantages of steel radiators for the heating system of a house and apartment:
- the main disadvantage of steel batteries is instability at humid temperatures, because in this case the systems deteriorate and even in some cases cannot be repaired, and corrosion also appears. Also, some of their partial terrain should by no means be kept without water, because they will deteriorate;
- uniquely strong susceptibility to chemical stops on mounted welds;
- poor-quality paintwork leads to peeling and the original appearance of the batteries is lost within 3 years.
Knowing about all the shortcomings of this steel equipment, it still becomes worthy for all heating devices. According to consumer reviews, the design has many excellent technical criteria and working moments.
Considering the cost factor, as well as design and other positive features devices, moreover, at a very cheap cost, then such heating may well become the main device for heating your entire room.
Cast iron batteries Konner
Another "favorite" of the public is Konner, which was able to find its place in the Russian market. A fairly wide variety of models, their price and reliability have made her famous.
Main product parameters:
- Thermal power ranges from 120W to 180W depending on the size. For example, a 300 mm cast-iron radiator from this company produces 120-130 W of heat.
- Water heating +110 degrees.
- The working pressure is 12 atmospheres, with a test head - 20 atmospheres.
Dimensions and stylish look allow you to install batteries of this type not only under windows, if the design of the room requires it.
There are dozens of manufacturers of cast iron batteries on the market today. All of them correspond to the parameters of the domestic heating network, have an affordable price, are reliable in operation and look great in the interior.
Types and types
There are two types of steel radiators, the most common being the panel radiator. less popular tubular radiator. Panel type radiators are panels mounted on a floor surface or on a wall. This type of steel radiator has a high level of aesthetics, as well as higher heat supply factors.
The production of panel radiators takes place according to a certain technique: two plates welded together, and a heat flow is produced between them. The thickness reaches 2 cm, spot welding in this production is the main welding and production moment. The advantage of the system in choosing right size. Pluses are also in connecting radiators. such a connection is different, the most famous are only three: installation from the side, from below, standard.

Panel steel radiator
What should be the dimensions of the radiators
The choice of dimensions of heating devices is not based on aesthetic considerations. Heat dissipation plays a key role here. This is especially true if a model is selected for installation under a window. It is necessary to choose a model in such a way as to meet several requirements at once:
- along the length, the radiator must cover at least 70-75% of the width of the window opening;
- the distance from the floor should be 80-120 mm;
from the window sill 60-120 mm.
When choosing the dimensions of the radiator, you need to select them depending on how high the window sill is located.
Only under such conditions will the heat transfer of the heater you have chosen be normal: it will produce the number of watts declared by the manufacturer.
Types of radiators
Heating radiators, which you will find in our catalog, are high-quality domestic and foreign appliances. various kinds. Depending on your preferred type of connection, you can choose models with bottom or side connectors for attaching pipes. We offer to purchase heating radiators, the price of which will save the family budget.
Steel radiators
- Panel. They consist of two sheets of steel and are compact. However, this type of product has certain vulnerabilities that you should pay attention to. These radiators are sensitive to water hammer. That is why panel radiators are recommended to be installed in those houses that are equipped with a closed individual heating system.
- Tubular. Such radiators are made without a housing. Their design is pipes in which the coolant circulates. Color and shape can be different, which gives a wide scope for creating design solutions in any room.
Aluminum radiators
These are quite popular systems that compare favorably with their steel counterparts in their cost. At the same time, aluminum is characterized by more high rates heat transfer. Two types of products are made from this metal - extrusion and cast. The sections of the former consist of three elements connected to each other, while the latter are separately manufactured sections, which are considered to be more fragile. You can buy aluminum heating radiators for any type of premises.
Bimetal radiators
They combine the advantages of steel and aluminum products. These batteries are characterized by high resistance to corrosion, excellent heat dissipation, low weight and exceptional structural strength. In addition, bimetallic products cope well with water hammer, withstand pressures up to 40 atm and temperatures of 90 ° C.
Cast iron radiators
Despite the fact that a large number of aluminum and steel products are presented on the modern market, cast iron batteries do not lose their relevance. However, now they have moved into a different price category, becoming an elite product, which is sold to create a unique interior in the style of "retro" or "classic".
It is very convenient to buy heating radiators in the Garantkomfort.ru online store - add the product you like to the "Basket" and place an order. The purchase can be delivered in Moscow within one day.
Standard sizes of radiators
IN GOST 26645-85 tolerances are described with nominal intervals.
The radiator has three linear dimensions, responsible for the volume of the section.
Width: thin or thick

This is the distance between the outer walls of the battery. Pretty variable.
The depth is usually 75-140 mm depending on material and manufacturer.
In rare cases, larger items are found.
Length
Visually - length. This is the gap from the left to the right side wall. The indicator is taken equal to 80 mm when creating an order 95% appliances. In other cases, a little more, maximum - 88 mm. Any other radiators are made to order. This does not apply to cast iron devices: they are wider.
Minimum Height

The most variable value, which is the vertical component of the section.
Usually it is 380-420 or 540-580 mm.
There is special types batteries, the length of which is in the interval two to three meters.
Similar devices are placed in bathrooms.
Important! Axial distance is often mentioned. This is the gap between the connection points of the supply and return pipes.
Standard sizes - 350 and 500 mm. But there are also other options, especially among aluminum products.
Low batteries
Radiators with a small center distance have the following advantages:
- they can be placed under a low window sill;
- they have the maximum heat transfer per unit area.
Cast iron radiatorsThe dimensions of the sections of heating radiators MS-140M-300-0.9 are:
- length 93 mm;
- depth - 140 millimeters;
- height - 388 millimeters.
heat dissipation of cast iron radiators

Aluminum radiators
As for the thermal power, it varies from a minimum of 50 watts per section to a maximum of 160 watts. The determining factor is the finning area of one section. At the same time, a change in dimensions does not significantly affect the working pressure - low aluminum devices are designed for 16 atmospheres, and when tested for 24 atmospheres.
Bimetal radiatorsBimetallic low radiators, such as in the photo, have two nuances:
- among heaters, there are batteries not with solid steel cores, but with steel tubes placed between aluminum collectors. Their operating pressure, specified by the manufacturers, is usually 12 or 16 atmospheres;
- they often do not have vertical channels and, in the case of lateral connection, can be heated from collectors due to the thermal conductivity of aluminum. The circulation of the coolant is provided by the last section, since it is flowing.
Manufacturer's choice
The best steel heating radiators can be seen in almost different places of residence, not only in individual real estate, but also in shopping centers, because these products can be purchased and installed at the best price with a unique design. If you need to make a choice in favor of any manufacturer of radiators, you should find out what material the device was made of.
A specific scheme for creating equipment prefers a certain production: painting, design, packaging and other materials.
The price of steel radiators is formed on the basis of technical characteristics, at the expense of the manufacturer, and they may also differ according to criteria such as brand, size. Domestic steel battery systems will be cheaper than foreign ones, but the operating parameters are almost the same, so is there any point in overpaying.
To do right choice in acquisition heating radiator. you need to see the following points:
- uniformity of heating depends on the depth and height of the heater; equipped with a Mayevsky tap, which serves as an air vent for the heating system. It will also help prevent various dangerous situations, accidents in which this crane will come in handy. Also the need for hook descent of water;
- if the installation is under the windows, then the size is shorter than the window opening within 70%;
- if there is a desire in the practicality of the equipment, you need to purchase a device with the option of a temperature regulator. This criterion is enabled either manually or automatically for the heatsink temperature.
Dimensions of steel radiators
General overview of types of radiators and their dimensions
There are several main groups of heating batteries, which differ in design features:
- Sectional.
- Panel from steel and bimetallic.
- Convector.
- Author's models, made to order, having unlike shapes, but performing their functions.

In the photo - the original heater
The material used and the design features of heating devices determine:
- resistance to water hammer;
- corrosion;
- clogging and scaling;
- heat transfer intensity and other components of success.
As for the size, the difference in height between the upper and lower collectors (centre distance) affects the possibility of installing a heater. Most often they are installed in niches under windows, if the window opening is large enough, then a high battery simply does not fit.

The diagram shows the center distance
This parameter is especially important for systems with natural circulation. The fact is that the pressure in the system is created due to the difference in height between the water supply to the battery and the boiler, the larger this value, the greater the natural pressure in the pipes.
Note!
For example, it makes sense to choose a center distance of 250 mm for heating radiators only for very low window sills.
In this case, it will be possible to install batteries even under a window sill 50-60 cm high.

An example of a battery in a room with large windows
Panel heaters are an all-welded structure with a heat carrier coil between two finned panels with a gap of up to 1 cm between them. Such a surface increases the heated surface area and its heat transfer - radiation plus convection. The meager capacity contributes to rapid heat transfer - the efficiency reaches 75%, but they also cool down quickly.
The disadvantage of panel products is:
- in their vulnerability to water hammer, which makes them unsuitable for use in central heating systems;
- corrode from acidic water;
- water cannot be drained for a long time due to the same corrosion, but already in contact with oxygen.
Sectional batteries are good for the possibility of their constructive change - an increase / decrease in the number of sections to change power or repair. The traditional brittle but durable cast iron with high inertia has been replaced by bimetallic devices.

In the photo - a bimetallic heater device
In them, the coolant passes through steel tubes with aluminum fins with high thermal conductivity.
A bimetallic battery is the embodiment of two advantages in one product, namely:
- steel withstands unstable pressure and aggressive environment;
- aluminum reacts with lightning speed to temperature changes.
Note!
Of the shortcomings, one can only note the cost.
The price of a bimetallic radiator can be 2-3 times higher than an analogue made of cast iron or steel.
When choosing bimetallic batteries you also have to take into account the diameter of the vertical and horizontal channels, and not just the center distance. As for the dimensions, the models with a difference between the nipple holes of 500 mm can be considered the most popular (while the total height of the heater is 570 mm).
The photo shows the horizontal and vertical channels, if the quality of the coolant is poor, they should not be too narrow
But in vacuum batteries, the concept of "center distance" simply does not exist. The fact is that they use only 1 flow pipe through which the coolant circulates, and uniform heating of the surface is achieved due to the evaporation of a low-boiling liquid.
Tubular batteries - registers, are superior to sectional ones in terms of compactness and variety of shapes. The absence of leaks at the joints is ensured by welding of the fragments, they withstand a working pressure of up to 15 atm., But thin walls do not hold water hammer well. It is quite possible to make registers with your own hands by choosing an arbitrary step between the pipes.
Device Popularity
Most people before installation are wondering how to choose the right heating radiators. what is the main task in choosing them? IN modern world There is a wide range of such systems. This is great, because there is variety in the choice, but this variety causes a feeling of uncertainty in the buyer. After all, most of these products are made by many manufacturers, they differ in design, colors and other special categories.
Steel types of radiators are now recognized as the most popular type among heating structures,
Steel heating radiators are a device for insulating and warming apartments and houses, the equipment has a pair of stainless steel sheets welded together, having a water space, or a place for water. Steel batteries should not be placed in places with a humid temperature; this equipment cannot be installed in baths and bathrooms, as it will deteriorate.

Steel radiator device
Types of aluminum-steel radiators
Manufacturers, following the lead of consumers, are trying to reduce the cost of production of bimetallic structures without changing their device as a whole. Now on the market you can find several types of batteries of this type:
- The device of the "classic" radiator is such that the basis on which the coolant flows is a steel collector, "packed" in an aluminum casing. This is done so that steel takes over the entire load in contact with water, and aluminum, which has the highest level of heat transfer, heating up from it, transfers heat to the room. The simplified models that have appeared, no matter what the size of the bimetallic radiator section, are equipped with steel vertical channels, while the horizontal collectors remain aluminum. This really significantly reduced their cost and increased the degree of heat transfer, but also made them vulnerable to the quality of the coolant and the level of pressure in the network.
- The second type is a typical expensive "classic" that can be installed in heating systems with the most unstable pressure.
If the installation of radiators is supposed to be in a room with an autonomous heating system, then it makes no sense to invest a lot of money in expensive models. In this case, it is enough to calculate the power and determine the optimal dimensions of bimetallic heating radiators (10 sections is the standard type, although you can choose another type of device).
Specifications
Robert Zender became the developer of this heating system, this device was originally prepared as a cooling base for the motor components of motorcycles, but with the development of technology and the passage of time, this equipment became heating. Decades later, these products began to be used in industry and in this area of human activity.
It is necessary to identify certain unique criteria and technical characteristics of steel radiators.
- for the production of such heating, high-quality metal is used, and hard metals, which can give resistance to various shocks and loads. Such equipment is most suitable for private building plans, the service life in this case increases, since in individual buildings there are less stops and loads than in multi-storey buildings;
- apply simple technologies and methods, thanks to this, the price of such products is optimal, which allows you to acquire any type at your discretion, which is suitable for various types of buildings;
- possession of stability to various attacks, because welding takes place openly, without various chemicals, therefore, hydraulic loads are not terrible; the outer shell is the main distinguishing feature of such batteries, since iron can be painted in various color scheme, which is sold in stores, can be compacted in sections; thanks to steel, it can heat a building of various sizes;
- universal tool, can be mounted on any fasteners, however, they are present in the kit, so this equipment can be independently quickly and accurately mounted.
Steel panel radiators types and definition of power
Steel panel radiators are a competitor to conventional sectional type heaters. They are attractive in that compared to all sectional models with smaller dimensions they have a higher heat transfer coefficient. They consist of panels in which the coolant moves along the formed passages. There can be several panels: one, two or three. The second component is corrugated metal plates, which are called fins. It is due to these plates that a high level of heat transfer of these devices is achieved.

Steel panel radiators have different sizes and power
To obtain different thermal power, panels and fins are combined in several versions. Each option has a different power. To choose the right size and power, you need to know what each of them is. By structure, steel panel batteries are of the following types:
- Type 33 - three-panel. The most powerful class, but also the most overall. It has three panels, to which three finning plates are connected (which is why it is designated 33).
- Type 22 - two-panel with two fins.
- Type 21. Two panels and between them one plate with corrugated metal. These heaters, with equal dimensions, have a lower power compared to type 22.
- Type 11. Single panel steel radiators with one finned plate. They have even less thermal power, but also less weight and dimensions.
- Type 10. This type has only one heating medium panel. These are the smallest and lightest models.
All these types can have different heights and lengths. Obviously, the power of panel radiators depends on both the type and dimensions. Since it is impossible to calculate this parameter on their own, each manufacturer compiles tables in which he enters the test results. According to these tables, radiators are selected for each room.

Types of steel panel radiators
Tall and narrow
High radiators even in the usual version look unusual. And if you paint it in a non-standard color, give it an unusual shape, combine it with a mirror or a shelf, it turns out in general, it looks more like a designer thing than a banal heating device.
We’ll immediately upset fans of cast iron: the highest cast-iron radiator is around a meter. Not seen above. The same can be said about bimetallic ones - they cannot be higher than a meter. And in general, all that is in the bimetal is 760-860 mm or so.
Steel panel radiators are standard in heights up to 900 mm. But there are also special models that can reach two meters or more. For example, Kermi has two models Verteo Plan and Verteo Profil - they can be up to 2.2 m maximum. Purmo also has giants: Kos V, Faros V, Tinos V, Narbonne V and VT, Paros V. They differ in the type of front panel (smooth or profiled) and depth. But all of them have only a bottom connection.
Steel tubular radiators are available up to 3000 mm high. Moreover, if necessary, some manufacturers can do higher. There are high models from any manufacturer: everyone who is present on the market offers such non-standard options “on order”. Here we list only the most interesting in terms of design: Entreetherm, Planterm for Arbonia, Dekor series for Kermi, Harmony for the Russian KZTO, Charleston for Zender.
There are no tall radiators in other types. Choice and so, I must say, considerable. Wouldn't get lost.
Temperature deviation of the reducer housing from 20 С
∆t2º
= 20 –20 = 0.
Guaranteed
transmission side clearance
j n min
= 0.06 + 112 (11.5 10-6 15
— 10.5 10-6 0) 2 sin20
= 0.073 mm.
Define the view
conjugation by . For
gear wheel with m≥1
mm, a w
= 112 mm and j n min
\u003d 0.073 mm (73 microns) - type of conjugation C.
Choose an indicator
providing guaranteed lateral
gap on - f ar
(deviation of center distance).
By type of conjugation
determine limit deviations
center distance ±f a
w
= 112 ± fa
= (112 ± 0.045) mm.
4. Measurement schemes
all assigned parameters.
4.1. local
kinematic error of gear
wheels can be controlled
on instruments for measuring kinematic
accuracy, in particular by defining
its harmonic component is the largest
differences between local neighbors
maximum and minimum values
kinematic error of the gear
wheels in one turn. kinematic
error of gears 1 and 6 (one
of the wheels is exemplary, and the other is verifiable)
controlled on devices with glass
limbs 2 and 5 with radial strokes
with division value 2′. Moving Strokes
causes current pulses in the photodiodes.
The phase shift of the pulses caused by
kinematic error in the gear
pair and rotation mismatch
gears, determined by the phase meter
3 and recorder 4.

4.2. Accumulated
step error can be controlled
on the device, the scheme of which is given
below, in which with continuous rotation
gear wheel 5 in the electronic unit
2 receive pulses from the circular
photoelectric converter
4, installed on the same axis with
measuring wheel, issuing
command pulse at a given position
tooth. When a command impulse appears
recorder 3 fixes the ordinate of the error
wheel pitch.

4.3. Measurement
spur tooth direction errors
wheels is carried out on devices, at
which there exists a caret with exact
longitudinal guides and measuring
the tip moves along the axis
measured wheel.

1 - table with longitudinal
moving together with the checked
wheel; 2 - transverse carriage; 3
- spindle; 4 - checked wheel;
5 - measuring unit; 6-
microscope; 7 - a ruler that can be
accurately set to the desired angle.
4.4. Measurement
center distance fluctuations
one revolution in double gearing
can be performed on the MTs-400 device for
center distance measurements. On the
mandrels 4 and 5 push controlled
6 and exemplary 3 gears. Mandrel
5 located on a fixed carriage
7, the position of which can be changed
only when adjusted to the required
center distance. Mandrel 4
located on a fixed carriage 2,
which is compressed by a spring so that
gear pair 3-6 is always in
close contact on both
sides of the tooth profiles. When rotating
gear pair due to inaccuracies
its manufacture measuring interaxal
distance is measured, what is fixed
measuring or recording instrument
1.

5. We carry out the working
gear drawing. rules
execution of cylindrical drawings
gears according to GOST 2.403-75 (design
and the shape of the wheel must match
task).
Features of mounting radiators
The dimensions of bimetallic heating radiators, as well as cast iron or aluminum ones, should therefore be selected as carefully as possible. Whatever dimensions, however, the battery has, it must, of course, be installed correctly. heating radiators are usually mounted on brackets to the wall. Before installing them, markup is mandatory. Radiators are mounted either strictly horizontally, or with a slight slope in the direction of the coolant current. In the latter case, it is easier to remove air plugs from the sections. Batteries can be connected to the battery lines in three ways: from below, diagonally and from the side. In any case, an individual valve should be installed on each radiator. This allows you to repair the battery without having to turn off the entire heating system as a whole. Also, a Mayevsky crane (or some of its modern analogues) is also installed on each radiator without fail.
What is it like to be a virgin at 30? What, I wonder, women who did not have sex until almost reaching middle age.

What does the shape of your nose say about your personality? Many experts believe that by looking at the nose, you can tell a lot about a person's personality.
Therefore, at the first meeting, pay attention to the nose is unfamiliar.

9 famous women who fell in love with women Showing interest in someone other than the opposite sex is not unusual. You can hardly surprise or shock someone if you admit it.

13 Signs You Have the Best Husband Husbands are truly great people. What a pity that good spouses do not grow on trees. If your significant other does these 13 things, then you can.

How to look younger: the best haircuts for those over 30, 40, 50, 60 Girls in their 20s don't worry about the shape and length of their hair. It seems that youth was created for experiments on appearance and bold curls. However, already

10 Adorable Celebrity Kids Who Look Very Different Today Time flies and one day little celebrities become unrecognizable adults Pretty boys and girls turn into s.
How to choose the right size of radiator sections
Determining the dimensions of sections and their number - most important step in the creation of a classical heating system.
With standard position

The power that they are able to develop depends on the size of the batteries and the material.
The length is almost always the same and is 80 mm. First determine the height. To do this, choose the installation location, on which the available space depends.
And design also plays a big role. These parameters determine the vertical component. Usually decided between 350 and 500 millimeters.
Depending on the characteristics of the room, you can purchase devices from 200 mm. If a radiator is purchased for a bathroom or a bathroom, a narrow model is recommended that can completely close the space between the floor and the ceiling. Altitude devices have different variations from one and a half to three meters.
Having defined two linear characteristics and material, move on to calculating the depth and number of sections. The number of the latter is usually taken equal to 10 , but there are others. The thickness is found from the volume. The cubic value is divided by the length and height. The definition of power is also closely related to these indicators: knowing the required one, you can find the number of sections.
With original interior

To create a design, manufacturers often donate technical specifications.
First of all This applies to cast iron products. Domestic radiators look serious, while they are simply covered paint.
European ones are sleeker, but weaker in heating. In any case, you need to find out from the documentation about the power that they are able to develop, since you need to choose devices for heat transfer.
Reference! There are batteries in the style of "retro". They have a pleasant appearance, but are expensive.
Aluminum have the same shape, except for custom-made, but differ in a variety of colors. In addition, a wide range of dimensions helps to fit them into almost any part of the room.
Bimetallic radiators, unlike analogues, are not only straight, but also curved. Because of this, they look good in rooms with smooth corners.

Regardless of the material chosen, before buying, you should read the technical documentation and find out the dimensions internal parts sections containing the coolant.
This will help determine the batteries, not only by external signs, but also by the ability to heat.
Should be mindful of combinations. So, if a certain device fits the design, but its power is not enough, you can install additional heating by hiding it behind the side panel. Or combine radiator heating with underfloor heating.
good option for guest rooms will become fireplace installation. Although the latter more often plays a decorative role, it is also able to reduce the number or size of sections installed in the room. Sometimes it's better to sacrifice beauty than to freeze every winter.
If there was a desire create a special design, contact the battery manufacturer. They will help you do the calculations. Thanks to this, the finished product will look beautiful and perform its direct function.
How to choose the size of a heating radiator
The selection of the battery size is as follows. After making sure that the products of the manufacturer that suits you are suitable in height and depth, you need to find out the number of sections for each room. To do this, we calculate the required thermal power of heating devices using the algorithm:
- in a room with one outer wall and 1 window receives 100 W of heat per 1 m2 of its area;
- if there are two walls facing the outside, then you need to take 120 W per 1 m2 of the room;
- when there are 2 walls and 2 windows, then 130 W/m2.
Note. The algorithm will give the correct result for rooms up to 2.5-2.7 m high. If the ceilings are higher, it is recommended to take 40 W of heat per 1 m3 of room volume.
Multiplying these figures by the area of the rooms, we obtain the required thermal power, by which we determine the dimensions of the battery, taking the heat transfer of 1 section as a basis. Below, as an example, are tables showing all dimensions, center distances and heat transfer of GLOBAL aluminum and bimetallic radiators:

As a rule, the values of the thermal power of the sections are indicated taking into account that the difference between the average temperature of the coolant and the room air is 70 ˚С (in the passport they write: at DT=70). This means that at +22 ˚С in the room, the supply water temperature should be about 100 ˚С, while in a private house it is rarely 70 ˚С.

And at this temperature, the battery section will give off 30% less heat, which should be taken into account.
Advice. In order not to be mistaken, it is necessary to subtract 30% from the power indicated in the product passport, and preferably 50.
Having determined the real power of 1 section, it becomes clear how to find their number: divide the heat consumption found earlier by this value. But after that, you may encounter a situation where the heater assembly is not included in the window sill niche, or vice versa, it looks too unpresentable in it, as shown in the photo:

How to choose the battery size in such cases? If it does not fit under the window, then the solution is simple: you need to divide the number of sections into 2 parts, instead of one device, two will come out. The length of the first will be 75% of the window opening, and the second will be all that remains. This part can be placed near the side wall, bringing pipelines to it. In the opposite situation (as in the photo), you need to take sections with a smaller center distance and height. Their heat transfer is less, which means that the total length of the heater will increase after recalculation, and as a result it will look great.
Types of radiator connection
If connecting the bottom way to connect the radiator. it will be equipped with a special valve for thermal control, which will immediately provide certain temperature necessary.
With the side connection of a steel radiator, a standard heat circulation scheme in the room is used, and such a connection is cheap and not at all remarkable, not noticeable.
Making multiple panels will result in more heat input. A variety of metal alloys can also be mounted to them, as a result, the size of the base will increase, which gives heat transfer.
Types of battery connection
However, these heating systems also have features, for example, weight. According to this criterion, they can reach the weight level of cast-iron installations, which are quite heavy. Also, the volume of water will be a minus, which means that thermal control will be lower and, accordingly, heat transfer too. The thickness of the radiator can reach 160mm, which is superior to the thickness of cast irons. In addition, the inner shell of such batteries is difficult to clean dirt.
Products from pipes help to remember the times of cast-iron batteries. they are similar in external parameters. They are in most cases, the installation of cast-iron batteries is carried out in administrative buildings and residential buildings of the Stalinist period. Resistant to strong atmospheric pressure reaching up to 10, they can reach more than a hundred cm in length, the maximum width is 2 cm. They can also be sectional and non-sectional.
General indicators of cast iron radiators
In truth, it is from this metal that heating devices are most adapted to “survival” and long-term operation in conditions of centralized heating. Starting in 1857, when cast iron radiators were invented, they carried heat to the homes of people from different countries. Currently, Western countries have stopped using this metal for heating housing, but in the CIS, most houses built in the 60-70s are still heated with their help.
The parameters of modern cast-iron batteries are the same in some respects, although they and old models have their own advantages and disadvantages.
- The level of heat transfer and power are the first points that consumers pay attention to when choosing heating appliances for their homes. In many ways, these indicators are influenced by the size of cast-iron heating radiators, but the average power of one section is 140-160 watts.
- Low inertia provides uniform heat radiation and long-term cooling of the structure when it is turned off.
- The size of a cast iron radiator section affects its weight. There are elements that weigh 3 kg, and there are those that weigh 7 kg.
- The average dimensions of cast iron heaters have become a classic standard. So the width of the cast-iron radiator section is 80-100 mm, the height is from 370 mm to 570 mm, and the depth is from 70 mm to 120 mm.
- The volume of old types of radiators is 1.5 liters, for domestic models of the new generation 0.7-0.8 liters, and for foreign analogues - 0.4-0.6 liters.
- Operating pressure is another important factor, which should be taken into account when installing radiators. So for Soviet samples, it was 6-9 atmospheres, and the wall thickness and size of the new type of cast-iron battery can withstand loads up to 12 atmospheres. Some manufacturers are cunning when they indicate that their cast iron products have a working pressure of 15-18 atmospheres. This is actually the pressure that each battery is subjected to at the factory to test its water hammer strength.
- The stated warranty period for cast iron radiators is 20-35 years, although there are companies that give their products 50 years of operation, and this is not surprising. Such a long active "life" of these devices is due to the presence of a wide channel through which the coolant passes without difficulty, leaving no debris at the bottom, but corrosive scale on the walls.
These are the main indicators that are inherent in many models, but since there are manufacturers from different countries on the market today, the size of the cast-iron radiator section may differ, and its weight, and other parameters.
4 Preliminary basic dimensions of the wheel.
- dividing
diameter: 
- wheel width:
,
where but- wheel width coefficient, but =0,4.
accept standard
meaning b 2 = 56mm.
3.5 Transmission module
Transmission module:

where coefficient
K m is taken for chevron wheels: K m = 5.2.
T FE \u003d K Fd T 2 -
equivalent
moment on the wheel
where  - coefficient of durability. Here
- coefficient of durability. Here
N FG =4106-
base number of cycles. At N108 we accept K Fd =1.0.
That. equivalent
moment on the wheel T FE \u003d T 2 \u003d 238.3
N.
The module accepts
meaning: 
Accept module
gears equal to m = 1 mm.
3.6 Total number
teeth and angle.
Minimum Angle
inclination of teeth of chevron wheels min = 25;
Total number
teeth
z =2
a w cos min /m.
z =2140cos
25/1 = 253
We define
actual angle value
=
arccos ( z m
/ 2a w).
=
arccos (2531/ 2140)
= 25.4.
3.7 Number of gear teeth
and wheels.
Number of teeth
gears
z 1 =z /(u±l)z 1min.
For chevron
wheels z 1min = 17cos3= 13;
z1
=253/(6.3+l)
= 35 > z 1 min .
Number of teeth
wheels: z 2 \u003d z - z 1 \u003d 253 - 35 \u003d 218.
3.8 Actual
ratio
Actual
gear ratio u f \u003d z 2 / z 1
= 218 / 35 = 6,23.
Deviation from
given gear ratio is not
exceeds the allowed 4%.
3.9 Wheel diameters.
Dividing
diameters, d:
gears d 1 =z 1 m/cos= 351
/ cos 25.4= 38.1 mm;
wheels d 2 \u003d 2a w - d 1 \u003d 2140
- 38.1 \u003d 241.9 mm .;
Circle diameters
peaks d a and troughs d f of the teeth:
d a1 =d 1
+2(1 +x 1 -
y)m = 38.1 + 211
= 40.1 mm;
d f1 =d 1
- 2 (1.25 - x 1) m \u003d
38,1 — 21,251
= 35.6 mm;
d a2 =d 2
+2(1 +x2
— y)m= 241.9 + 211
= 243.9 mm;
d f2 =d 2
- 2 (1.25 - x 2) m \u003d
241,9 — 21,251
= 239.4 mm;
3.10 Workpiece dimensions
wheels.
To obtain
during heat treatment accepted for
calculation of mechanical characteristics
wheel material, it is required that
the dimensions of the wheel blanks did not exceed
maximum allowable values: D zag D prev; C zag, S zag S before;
Values Dzag ,
S zag, C zag (mm) calculate
according to the formulas:
for cylindrical
gears D zag \u003d d a +6 mm \u003d 40.1 + 6
= 46.1 mm80 mm;
For wheel with
grooves take the smaller of
values Dzag \u003d 0.5b 2 \u003d 0.556 \u003d 28 mm.125 mm; and S zag \u003d 8m \u003d 8mm 80mm.
3.11 Forces in engagement
circular F t \u003d 2T 2 / d 2 \u003d 2238.3 / 0.2419 \u003d 1970.2 N;
radial
F r \u003d F t tg / cos \u003d 1970.20.364 / cos 25.4 \u003d 793.9 N.
(for standard
angle =20° tg=0.364);
axial F a =
F t tg= 1970.2tg
25.4= 935.5 N.
3.12 Checking the teeth
wheels by bending stresses.
Rated stress
bending in the teeth of the wheel:
F2 =K Fa K F K Fv Y Y F2 F tE /(b 2 m)
[] F2
For wheels with >0°
accept for the 9th degree of accuracy
K Fa=1.
Degree of accuracy
transfers are accepted depending on
circumferential wheel speed (m/s)
degree of accuracy
9th.
Coefficient
load concentration K F ,
accept for running-in wheels
at variable load K F =K0 F (1-X)+X,
where is the initial concentration coefficient
load K0 F =1.635.
That. K F =1.3175.
Coefficient
dynamic load accept
according to peripheral speed K Fv =
1,07.
Coefficient Y is calculated by the formula Y =1-°/140=0.965.
Shape factor
tooth Y F2 = 3.6, Y F1 = 3.7.
F tE = K Fd F t
-
equivalent circumferential force.
Durability factor K Fd =
1. I.e. F tE = 1970.2 N.
As a result, we have:
F2 =11.31751.070.9653.61970.2/(0.0560.001)
= 172.3 MPa< 256
condition is met
Rated stress
in gear teeth:
F1 = F2 Y F1 /
Y F2 [] F1 ,
F1 =172.33.7
/ 3,6 = 177,1<294МПа.
condition is met
Calculation of heating radiators
In conclusion, it is necessary to focus on the question of how to calculate the number of heating radiators per room or other room. . The required number of sections can be determined in several ways:
The required number of sections can be determined in several ways:
- Based on the area of the room. This method is suitable for rooms with low ceilings (within 3 m). To do this, you need to multiply the number of square meters of room area by the required amount of heat per meter, according to SNiP this is 100 watts. For example, 20 sq.m will require 20x100 \u003d 2000 watts. Then the required amount of heat is divided by the heat output of one section of the radiator, indicated in the technical data sheet. The resulting number of sections of the heater is rounded up to a whole number.
- Based on the volume of the room. This method is relevant when calculating radiators for rooms with high ceilings or staircases, and in addition, it is more accurate than the above method. According to regulatory documents for heating 1 cu. m. of air in the room requires 41 W of thermal power. Accordingly, by multiplying the volume of the room by 41, the required amount of heat is obtained, which is then also divided by the heat transfer power of one section and the resulting value is rounded up to an integer. For buildings equipped with modern double-glazed windows, a lower heating power is required - 34 W / m3. It should be borne in mind that manufacturers are often cunning and indicate heat transfer indicators at the maximum temperature of the coolant, therefore, when calculating, it is necessary to build on the minimum parameters of the heater.
- A more accurate calculation is only possible for specialists, since this takes into account many parameters, coefficients and tabular values \u200b\u200bspecified in the regulatory documentation. These include: the amount of heat for the room depending on its location and value, the area of the room, the coefficients of glazing and thermal insulation of enclosing structures, coefficients that take into account the number of external walls, the height of the ceilings, the type of higher and lower rooms, the outdoor temperature in the coldest week and five days and much more. Therefore, in order to obtain such an accurate heat engineering calculation, it is necessary to contact an organization specializing in these services.
 As can be seen from the materials of this article, the choice of radiators of the required size and thermal power is an important measure to ensure a comfortable stay in the house. If you do not pay due attention to this procedure, then later you can forget about the comfort in the room.
As can be seen from the materials of this article, the choice of radiators of the required size and thermal power is an important measure to ensure a comfortable stay in the house. If you do not pay due attention to this procedure, then later you can forget about the comfort in the room.





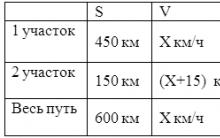

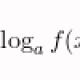



Living and dead water: myth or reality, what is the power of living and dead water?
Craniosynostosis, or premature fusion of the bones of the skull Frontal crest in a child
Beautiful hair How to achieve hair density at home: useful tips
Why mosquitoes bite some people, but not others
How to achieve beautiful hair