The concept of kyphosis comes from the Greek word "hump" or "bent", which determines the type of pathology of the organ.
Kyphosis of the neck is a pathological curvature of the spine that develops in this area, which belongs to the category of rare diseases.
Deformation of the neck makes the shape of the spine arched, curved back.
Features of pathology in the cervical region
The spine is the backbone of the human body. Due to the existing natural kinks, it provides the skeleton with cushioning properties. If the back bends forward in the lumbar region and neck, then we are talking about a disease called lordosis.
The protrusion of her thoracic and sacral region is diagnosed as kyphosis. If the natural deflection of the cervical region gradually straightens, becoming flat, then this indicates the development of a pathology of the neck.
Curvature of the vertebral neck back is a rare occurrence. In this case, blood circulation is disturbed as a result of a change in the shape of the spine, in which its structural elements are squeezed.
The brain lacks oxygen and blood supply. Blood pressure is disturbed, hands go numb, a hump forms in the neck.

Causes and risk factors
The disease can manifest itself in people of different age groups - from an infant to an elderly person.
At birth, the cause is recognized as the presence of a weak muscular corset or diseases of the bone tissues, making them fragile.
At an older age, kyphosis of the cervical spine develops due to neck injuries and concomitant diseases.
There are several main reasons for the development of pathology.
Congenital pathology
It happens due to underdeveloped elements of the spine, most often the vertebral body itself or the intervertebral disc. The hereditary factor influences when several generations have abnormal development of the vertebrae.
The congenital cause of the disease is rickets in children (lack of vitamin D in the body) at 1 year of age, which provokes the development of kyphosis due to weakening of the ligaments and muscles of the skeleton.
Anomalies of the fetus inside the womb and its postpartum trauma are also a risk for the development of the disease.
Acquired pathology
The causes of this disease are:

Degenerative-dystrophic changes in the spine
Occur in the elderly due to a violation of the muscle tone of the neck. With age, the cervical vertebrae deform in people under the influence of daily stress and diseases.
Classification and degrees of pathology
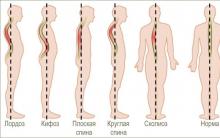
There are 2 types of cervical kyphosis - angular, manifested by a pronounced angle at the highest point of curvature of the spine and arched.
By origin, such a deformation is divided into pathological and physiological.
Depending on age, the disease happens:
- infant (rachitic);
- children's;
- adolescent or youthful.
Children's kyphosis manifests itself in a bone or muscle form. Bone deformity occurs due to damage to the vertebral body or a systemic disease.
The muscular form of the disease occurs as a result of poor physical development, a serious illness.
The stages of development of the disease are divided as follows:
- minimal 1st degree with a curvature angle not exceeding 30°;
- average 2nd degree with a curvature angle of 30-60°;
- severe 3rd degree curvature at an angle of more than 60 °.
Symptoms of the disease
The main and obvious symptom is a violation in the cervical region and spine.
 The first sign of the disease is the appearance of a headache in the neck, which occurs due to the fact that many nerves and blood vessels pass through the openings of the spinal cord.
The first sign of the disease is the appearance of a headache in the neck, which occurs due to the fact that many nerves and blood vessels pass through the openings of the spinal cord.
In addition to pain, dizziness, jumps in blood pressure, auditory and visual disturbances are noted. Decreased motor activity in the neck, muscle spasms, numbness of the hands, tingling in the lower jaw and neck also create a general feeling of discomfort.
In addition to these signs of the disease, there is a stoop and the formation of an occipital hump due to protruding spinous processes.
Due to the unnatural position of the cervical vertebrae, pain is noted not only in the place of curvature, but also in other areas of the body.
The patient becomes numb in certain parts of the neck and shoulders, a pain syndrome appears. Due to compression of the nerve roots in the spinal cord, a problem with urination may begin, and peripheral paralysis may occur.
Establishing diagnosis
It is enough for an experienced specialist to look at the patient to determine the curvature. Such a patient has a stooped back, lowered shoulders forward and down, a round back. But to make a final diagnosis in order to determine the degree of the disease, it is possible only after research:
- radiography in 2 projections, direct and lateral (to confirm the diagnosis and assess the degree of development of pathology);
- magnetic resonance and computed tomography (for a detailed examination of pinched nerves);
- spinal radiographs.
Treatment Methods
Kyphotic deformity of the neck appears for various reasons, therefore, treatment is prescribed after the diagnosis is made individually for each patient.
The characteristics of the human body, its general condition, the severity of the disease are taken into account.
Treatment usually lasts a long time and requires a lot of effort on the part of the patient, only scrupulous adherence to the doctor's recommendations gives a complete cure for cervical kyphosis.
The treatment consists of the following sequence of events:

A good result in certain cases is given by acupuncture, massage, reflexology.
Treatment is carried out by a doctor who works with his hands on the damaged parts of the spine and surrounding tissues.
The result of such manipulations are the following changes in the body:
- occipital and spinal pains stop;
- vertebrae, joints, intervertebral discs are placed in their natural place;
- blood pressure returns to normal due to improved blood supply, dizziness disappears;
- muscles become less tense, and the muscular corset gains strength.
Only qualified verterbrologists have the right to engage in manual treatment. The number of procedures is prescribed by the attending physician (usually every other day). Depends on the general condition of the patient and concomitant diseases in him.
Like all diseases of the spine, cervical kyphosis is treated with physical exercises, because only they are able to return the curved area to its previous state.
Therapeutic gymnastics allows you to strengthen the ligaments and muscles that support the spine, which allows you to improve blood circulation in it, and also restores flexibility to the joints. The course of exercises is selected by the doctor individually for each patient.
No less important condition for recovery is the correct posture, which must be maintained constantly. One of the exercises for this is touching the wall with four points of the body.
In severe cases, surgical treatment or prosthetics is prescribed using metal plates, which are installed in the area of the pathology on neighboring vertebrae, and removed after a certain time.
Such treatment ends with physiotherapy, gymnastics, swimming.
Complications and consequences
Kyphosis of the neck is actually not a disease of the spine, it is rather a symptom of it, the beginning of the occurrence of serious pathologies in the body.
If you ignore these kyphotic manifestations, then you can get problems and complications.
What can happen:

The most serious complication is deformity due to deformation of the cervical region or the onset of complete paralysis.
Easier to prevent than to cure
Regular exercise, active lifestyle, swimming, aerobics, yoga are excellent prevention of pathology.
Equally important is the observance of the correct body position when walking, sitting, standing.
To avoid cervical kyphosis, it is necessary to perform a certain set of preventive exercises, which is recommended by doctors.
Exercises performed with this pathology are carried out when the pain syndrome is eliminated. They are a good preventive measure for many diseases.
The disease responds well to conservative treatment at an early stage of development. The main thing is not to forget that each disease must be examined at its first signs by qualified doctors in order to avoid the development of pathological processes.
The curvature of the cervical spine is no exception to the rule.
Treatment of a compression fracture of the lumbar spine
 Various situations, whether it is sports training, a fall from a height or a bad jump into the water, can often lead to discomfort in the back. And if they do not go away for a long time, then it can be assumed that a compression fracture of the spine has occurred there. This condition is fraught with certain complications, so you need to know how to correctly identify it at the initial stage and in what ways it can be treated.
Various situations, whether it is sports training, a fall from a height or a bad jump into the water, can often lead to discomfort in the back. And if they do not go away for a long time, then it can be assumed that a compression fracture of the spine has occurred there. This condition is fraught with certain complications, so you need to know how to correctly identify it at the initial stage and in what ways it can be treated.
- Types of compression fractures
- Diagnostics
- Signs and symptoms of a compression fracture of the spine
- Treatment
- Conservative treatment
- Surgery
- Complications
- Conclusion
Features of a compression fracture
Many people are susceptible to this injury, and it occurs due to the simultaneous pressing and bending of the spinal column. Experiencing compression, the vertebra is compressed, deformed and cracks occur. In most cases, a compression fracture has to be diagnosed in the lumbar and lower thoracic regions.
- Compression fracture of the thoracic region. The highest level of pressure is felt in the area of 11 and 12 vertebrae, which receive maximum damage with this type of fracture.
- Compression fracture of the lumbar. In this area, compression fractures affect the first vertebra, and this leads to compression of the nerve roots.
Less common are situations where compression fractures occur in the cervical spine. This can be facilitated by car accidents, unsuccessful jumps from a height, or strong blows to the head.
Types of compression fractures
Depending on the degree of damage to the spine, there are several types of compression fractures:
- 1 degree. The vertebra loses in height no more than half of its initial size.
- 2 degrees. With this type of damage, the height of the vertebra is reduced by 2 times.
- 3 degrees. In such a situation, the vertebra loses more than half of its original height.
Also, depending on the presence or absence of complications, compression fractures are divided into the following types:

Diagnostics
The appearance of pain in the back does not allow us to state with high accuracy that we are talking about a compression fracture. This symptom can be observed in other pathologies.
To differentiate this disease from other dangerous ailments and timely start treatment, the patient will have to undergo a comprehensive examination, which involves the following procedures:
- Radiography of the spine. Based on its results, it is possible to obtain data on the presence of damage, its location, the degree of fracture of the lumbar spine and the presence of complications.
- CT scan. Doctors resort to this method of diagnosis after an x-ray. With this procedure, you can get more detailed information about the damaged area.
- Myelography. A diagnostic method aimed at a thorough examination of the spinal cord, allowing to determine its condition after a compression fracture.
- Neurological examination. Allows you to establish the state of the spinal cord, nerve roots and peripheral nerves.
- MRI. This diagnostic method is resorted to only when there is a suspicion of damage to the structures of the spinal column.
- Densitometry. This procedure is prescribed by specialists at their own discretion, with its help it is possible to differentiate a compression fracture from osteoporosis.
Based on the results of these diagnostic procedures, a specialist can make a correct diagnosis, as well as determine the risk of a compression fracture, as well as the degree of its effect on the spinal cord, and choose the most effective method of treatment.
Signs and symptoms of a compression fracture of the spine
 Unfortunately, a compression fracture of the lumbar spine has to be observed in a large number of patients, and most often it is found in people with an underdeveloped spinal column, which are often disturbed by musculoskeletal diseases. Common causes of vertebral injury are sudden movements, mechanical damage, and heavy lifting.
Unfortunately, a compression fracture of the lumbar spine has to be observed in a large number of patients, and most often it is found in people with an underdeveloped spinal column, which are often disturbed by musculoskeletal diseases. Common causes of vertebral injury are sudden movements, mechanical damage, and heavy lifting.
If the diagnosis is carried out by an experienced doctor, then on the basis of the existing symptoms of a fracture, as well as the results of the examination, he can make an accurate diagnosis and select an effective treatment.
Specialists distinguish a number of symptoms that are observed with a compression fracture of the lumbar spine:
Pain that has a different localization. They can be found in the back, on the legs and arms. It is by pain that one can assume the presence of a fracture of the lumbar spine, at the initial stage it manifests itself weakly, but gradually begins to intensify.
General malaise. With a fracture of the lumbar spine, the patient often experiences dizziness, fatigue and weakness.
High compression of the spinal cord. This symptom is most characteristic of a severe fracture of the lumbar spine, and subsequently the patient complains of acute pain in the back.
Treatment
The very fact of the presence of pain is a sufficient reason to make an appointment with a doctor and begin treatment of the damaged area of the spine. taking into account the degree of damage, the presence or absence of complications, doctors decide on treatment using conservative methods or through surgical intervention.
Conservative treatment
 This option is most often chosen by specialists for the treatment of the consequences of a compression fracture. It is a very effective method of therapy and involves taking medications, as well as limiting physical activity. As part of this treatment, specialists prescribe kyphoplasty and vertebroplasty.
This option is most often chosen by specialists for the treatment of the consequences of a compression fracture. It is a very effective method of therapy and involves taking medications, as well as limiting physical activity. As part of this treatment, specialists prescribe kyphoplasty and vertebroplasty.
Conservative treatment is a long process and takes about 3 months. During this course, the patient must be constantly observed by the doctor, undergoing an examination, so that one can understand how successfully the fusion of the damaged area is going.
Pain syndrome treatment. To relieve back pain, patients are shown medications. They are expected to help relieve pain.
Activity restriction. To splice joints, it is necessary to follow the recommendations of the attending physician, which involve limiting physical activity, reducing the time spent in a sitting and standing position, and refusing to perform actions that lead to an increase in the load on the spine. Patients in the older age group of 50 years and older need to adhere to strict bed rest, as at this age it takes longer for bones to fuse. Limiting activity increases the likelihood of a speedy cure, and violation of this recommendation is fraught with the appearance of unpleasant neurological complications, one of which is paralysis.
Fixation. Fixing the spine in one position helps to cure the disease faster. To do this, you have to use a fixing orthopedic corset. With this device, you can give the body the correct position, as well as remove part of the axial load from the spine. Only a custom-made corset is allowed to be used, as it must exactly fit the shape of the body.
minimally invasive methods. Several decades ago, two new treatments for compression fractures became available to physicians. These are kyphoplasty and vertebroplasty.
 The main task of vertebroplasty is to restore the integrity of the spine and repair damage. This is one of the popular methods of therapy for compression fractures, which is used in European clinics.
The main task of vertebroplasty is to restore the integrity of the spine and repair damage. This is one of the popular methods of therapy for compression fractures, which is used in European clinics.
The essence of this treatment is to create a small puncture in the skin, which is used to insert a metal rod into the vertebral body. Through it, a special solution is introduced into the cavity of the affected vertebra, which helps to increase the strength of the structure of the affected part. This procedure requires the use of local anesthesia, and its duration is approximately one hour. X-ray control is mandatory during the procedure.
Practice shows that when this procedure is carried out in European clinics, a positive effect is achieved in 90% of cases. Patients need a minimum of time for rehabilitation in order to return to a normal lifestyle. In the treatment of vertebroplasty, the rehabilitation period takes only 2 hours, during which the patient must comply with strict bed rest. Over the next 24 hours, he is required to limit physical activity. But sometimes the doctor has to decide on the appointment of painkillers.
The goal of kyphoplasty is to fully or partially restore the height of a vertebra, as well as change its position, if necessary. The procedure is performed using local anesthesia. Its essence is to create two small incisions in the skin, which are used to introduce a balloon placed in the vertebral body. To give the vertebra its previous height, the balloon is inflated to the desired size, after which bone cement is injected into it, which ensures reliable fixation of the position and size of the vertebra.
None of these considered procedures allows the damaged vertebra to become whole again, but something else is required of them - to remove pain and discomfort, and also to help the person return to a normal lifestyle.
Surgery
Not in all cases, conservative methods are effective enough. Sometimes there is a danger of neurological complications, and therefore the doctor has to make an unpopular decision - to perform an operation. During the surgical intervention, the specialist has to resect parts of the vertebra that have a destructive effect on the nerve roots of the spinal cord, and after removing them, metal implants are placed there.
Complications
 The high level of development of modern medicine, combined with the experience of specialists, does not allow to completely minimize the risk for the spine, since during the operation there is a risk associated with the proximity of the spinal cord and nerve roots. This method of treatment of vertebral compression fractures can lead to complications such as the appearance of segmental instability, neurological disorders, and kyphotic deformity.
The high level of development of modern medicine, combined with the experience of specialists, does not allow to completely minimize the risk for the spine, since during the operation there is a risk associated with the proximity of the spinal cord and nerve roots. This method of treatment of vertebral compression fractures can lead to complications such as the appearance of segmental instability, neurological disorders, and kyphotic deformity.
Kyphotic deformity is dangerous because it can provoke the appearance of a pointed or hollow hump in the thoracic spine. A similar phenomenon is often observed in older people who are overweight. Conducive to the development of this disease is a compression fracture of the spine and osteoporosis. Often kyphosis is accompanied by acute pain, often there are disturbances in the work of the cardiovascular system, lungs and stomach. Patients with a similar diagnosis have chronic fatigue, fatigue, shortness of breath, as well as dysfunction of the digestive system.
segmental instability. The most susceptible to this disease are people whose vertebra has lost more than a third of its original height as a result of degenerative effects. In a normal state, the spinal column successfully copes with its main functions - it helps to correctly distribute the axial load, provides the necessary support and allows you to perform all the necessary movements. The occurrence of a compression fracture leads to irreversible disorders, which, in addition to dysfunction of the spine, are accompanied by pain that the patient feels in any state - both during movement and at rest. Instability is a factor that provokes the occurrence of degenerative-dystrophic processes in the spine.
neurological complications. The risk of their occurrence is highest if bone fragments have occurred as a result of a fracture. Because of them, the back of the brain and nerve roots are subjected to high compression. Such a condition requires careful attention of specialists because neurological complications can appear immediately after the injury or after a while. It is possible to determine the presence of disorders associated with neurology by the presence of pain that occurs during exertion and at rest, numbness of the limbs.
Conclusion
 A compression fracture of the spine is one of those dangerous conditions that cannot be determined only by the clinical picture. An accurate diagnosis can only be made based on the results of the diagnosis, so it is wrong to expect that the pain that occurs in the back does not represent anything serious. With delayed treatment, there is a possibility that conservative treatments will not be effective, and then surgery will have to be considered. Naturally, this method is not popular, because it can seriously injure the spine. Therefore, it is best not to bring yourself to such a state.
A compression fracture of the spine is one of those dangerous conditions that cannot be determined only by the clinical picture. An accurate diagnosis can only be made based on the results of the diagnosis, so it is wrong to expect that the pain that occurs in the back does not represent anything serious. With delayed treatment, there is a possibility that conservative treatments will not be effective, and then surgery will have to be considered. Naturally, this method is not popular, because it can seriously injure the spine. Therefore, it is best not to bring yourself to such a state.
The spine of a healthy person has natural physiological curves, however, if the curvature in the thoracic region increases significantly, the so-called “round back” is formed, then this is a direct sign of kyphotic deformity. At the same time, the shoulder girdle moves forward, and the chest narrows, and its anteroposterior size increases.
What are the main reasons for the development of this condition?
The causative factors of the disease include the following:
- Genetic predisposition, congenital weakness of the ligamentous apparatus of the musculoskeletal system;
- Traumatic injuries of the spinal column;
- Damage to the intervertebral cartilage discs by such a pathological process as osteochondrosis;
- Weakness of the muscular corset of the back;
- A history of poliomyelitis, bone tuberculosis, radiculitis or radiculopathy;
- Incorrect posture while sitting and walking, lifting weights and other increased stress on the spine.
How does kyphosis of the thoracic spine manifest itself clinically?
The clinical signs of kyphosis of the thoracic spine include:
- posterior curvature of the spine in the sagittal plane;
- Tilt the shoulder girdle forward and down;
- Reducing the volume of the chest and abdominal cavities;
- Visible stoop, the appearance of a hump in the thoracic region;
- Difficulty breathing, the appearance of shortness of breath with moderate physical exertion and even at rest, which occurs due to a significant decrease in chest excursion, the active participation of the auxiliary respiratory muscles, which also requires a large amount of oxygen for its functioning;
- The appearance of various diseases of the internal organs, which are innervated by the roots that emerge between the vertebrae of the thoracic spine.
What are the therapeutic measures aimed at reducing and eliminating kyphotic deformity?
Treatment of this disease, which is terrible for its complications, it is advisable to start at the earliest stages. In this situation, a comprehensive and systematic approach is needed, which is based on the following therapeutic measures and procedures: physiotherapy exercises, massage, physiotherapy techniques, medications, a balanced diet with an increased amount of vitamins and minerals consumed, as well as wearing a special corset that strengthens the muscles of the back.
If you believe many qualified doctors, then the methods of therapeutic exercises help best in the early stages of kyphosis.
Here are some examples of simple exercises:
- To begin with, take a knee-elbow position, straighten the spine in the cervical and thoracic regions, spread your elbows to the sides as much as possible. In this position, start moving forward (approximately 50 steps);
- Take a gymnastic stick, lying on your stomach, put it on your back in the area of the shoulder blades and grab it tightly with your hands. Tilt your head back, try to rise up, and then take the starting position. Try to complete ten such repetitions in one session;
- Lie on your back, place your arms bent at the elbow joints along the torso. During a deep breath, try to bend as much as possible in the thoracic spine, while the points of contact with the floor will be the heels, buttocks, elbows and back of the head. Try to perform as many repetitions as possible, each time returning to the starting position;
- Squat with a gymnastic stick. To perform this exercise, you need to stand up with your feet shoulder-width apart, take a gymnastic stick and bring it over your head onto your back, and then start squats, trying to constantly keep your back as even as possible, each time returning to its original position.
The neck is the most vulnerable part of the spinal column, which is easy to injure, often amenable to curvature and the effects of various dystrophic processes. Kyphosis of the cervical spine is a rare disease caused by outward curvature of the vertebrae.
This pathology causes a number of problems: headaches, increased blood pressure, discomfort and pain along the spine, impaired sensitivity and motor activity, changes in the structure of cartilage and destruction of intervertebral discs. Cervical kyphosis is diagnosed in people of different age categories, so it is very important not to forget about preventive measures.
Possible reasons
At birth, the child's spine does not have curvatures, only after some time physiological curves (kyphosis and lordosis) begin to form. The protrusion of the spinal column back in the thoracic and lumbosacral region is called pathological kyphosis. Kyphotic deformity of the cervical spine is a pathology that is very rare. Doctors divide all possible causes into two categories: acquired and congenital.
Acquired causes include:
- Advanced age, at which the destruction of cartilage and bone tissue is observed.
- Concomitant diseases of the spinal column (spondylosis, osteoporosis, osteochondrosis).
- Violation of posture in the form of scoliosis, increased load on the spine, or, conversely, their complete absence.
- Back injury, which includes damage to the muscles, ligaments and the vertebrae themselves.
- Damage to the vertebrae or other tissues by infectious agents (for example, tuberculosis of the spine).
- Progressive inflammatory processes in severe form, which have a sharp negative effect on the entire body.
- Oncological neoplasms in the spine and tissues adjacent to it.
Congenital causes include:
- Intrauterine abnormal development of the child.
- Damage to the cervical vertebrae during passage through the birth canal or during childbirth.
- Genetic predisposition, characteristic of several generations at once.
Kyphosis of the neck leads to numerous negative consequences. If you notice the disease in time and take all possible measures to combat it, then you can avoid complications and its further development.
Classification
Doctors divided kyphosis into two types: arcuate (in the form of a short strongly elongated arc) and angular (in the form of a round tug, the apex of which is one or more processes of the vertebrae). In the second situation, in the absence of measures to combat the disease, patients develop a hump.
Several forms of kyphotic deformity are distinguished by etiology:
- Postural develops most often in people under 30 years old, and mainly among the female half of the population due to stretched spinal ligaments.
- Paralytic is formed as a result of the onset of paralysis of the muscles of the back for various reasons.
- Postoperative associated with a violation of the technique of operations on the spinal column, as well as non-compliance with the recommendations of a specialist in the postoperative period.
- Post-traumatic makes up about 35% of all kyphosis and develops very quickly. Occurs after fractures of the spine, injuries of ligaments and muscles.
- Senile (senile) is associated with age-related changes and is also common among women.
- Degenerative develops as a result of concomitant diseases of the spine, for example, osteochondrosis.
- Rachitic is typical for young children from 6 months of age with a diagnosis of rickets.
- Scheuermann-Mau disease or juvenile form of kyphosis. Curvature of the spine is observed during the period of active growth and is almost always combined with scoliosis.
As a result of diagnostic procedures, it is possible to identify not only the form of the disease, but also the severity of pathological processes in the cervical vertebrae.
Characteristic symptoms
Pathological kyphosis of the cervical or cervicothoracic spine is manifested by many symptoms. Patients suffering from this disease complain of restrictions in the mobility of the neck, crunching and discomfort when turning the head, frequent dizziness and headaches of varying intensity in the back of the head, impaired posture, the appearance of stoop, and subsequently a hump, increased blood pressure at rest.
Patients are concerned about the violation of the sensitivity of the upper limbs (the tips of the fingers go numb and tingle), the skin of the face and neck, the spasm of the skeletal muscles of the cervical region from behind, the deterioration of vision and hearing, the functional pain syndrome in the affected area, passing to the shoulders and lower part of the head.
The greater the angle of curvature of the spinal column, the more pronounced signs of the disease are observed in patients
Diagnosis and treatment
Usually, if kyphosis is diagnosed in the early stages, then it responds well to drug treatment and requires physiotherapy support. To determine the degree of bending angle, the following procedures are carried out:
- Radiography of the spine in the lateral projection with the maximum extension of the spinal column.
- Magnetic resonance imaging to identify the degree of curvature and changes in the structure of cartilage tissue.
- Contrast myelography (obtaining an image of the subarachnoid space after the introduction of a contrast agent into it) if it is impossible to perform an MRI.
If necessary, they conduct a study of other organs and systems to see how much their work is impaired. Treatment of kyphosis of the cervical spine directly depends on the initial cause of its appearance. In addition, general well-being, the state of the body, the degree of the disease, and the individual characteristics of each person are taken into account.
Therapy usually takes a lot of time and effort. Only under the condition of the ideal fulfillment of all the prescriptions of a specialist is it possible to achieve a complete cure for cervical kyphosis. The main measures in the fight against the disease are:
- Therapeutic gymnastics, the exercises in which are selected for each patient individually.
- Taking medications (analgesics, antispasmodics, non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, etc.).
- Neck and neck massage.
- Manual and physiotherapy.
- Wearing specially designed collars that are able to keep the neck in a fixed, level position.
- Conducting surgery.
Gymnastics with cervical kyphosis
What is kyphosis and how to treat it - figured it out. Before doing any exercise, you should consult your doctor. There are simply cases when carrying out any procedures is contraindicated. The main exercises that help to cope with kyphosis in the neck are the following.
Starting position - standing, hands behind the back holding a gymnastic stick, feet shoulder-width apart. On a deep breath, sit down as low as possible, while exhaling, stand up. Perform 10-15 repetitions smoothly, without sudden movements. Starting position - standing, arms lowered. On inhalation, the arms stretch up and the head is slightly thrown back. You need to stay in this position for 5-10 seconds. As you exhale, lower your arms and relax.

A positive effect can be achieved after acupuncture
Starting position - lying on your back, elbows pressed to the floor. Slowly and gently, the head rises up along with the chest as you inhale, and as you exhale, it lowers. 10-15 repetitions for 1 approach. Starting position - standing on your elbows and knees, head down, buttocks raised up. Walking in this position should include at least 50 steps, gradually increasing the load.
Starting position standing or sitting. The palms rest against the forehead, and at this time the forehead must be resisted by the palms. The duration of the exercise is from 10 seconds with a further increase in time. The effect of gymnastics will be maximum if it is supplemented by wearing a special collar. It is not recommended to use gymnastics if there is a temperature, high blood pressure, mental disorders, acute infectious diseases.
The information provided is not intended for self-medication. Its accuracy and applicability in your case is not guaranteed. Contact medical specialists!
As we said in the article containing, kyphosis as such is more of a symptom than a disease. However, it is a completely independent launching pad for many ailments.
Among the latter there are those that can make a person an invalid until the end of his days.
What does neglected kyphosis lead to?
Let's start with elementary things that help to understand the main risks.
The curvature of posture is nothing but violation of the anatomical structure chest (and sometimes - and the upper part of the lumbar zone).
The most typical consequences
A change in the shape and position of the vertebrae is necessarily reflected in the position of the ribs. Over time, their mobility is significantly limited.
The ribs are squeezed placed inside the organs. The most significant pressure is on the lungs, a key element of the respiratory system. Their constant stay in constraint over time provokes the development of pulmonary insufficiency. This is the first complication of kyphosis, the most typical.
We argue further. Well, what else is in the chest? That's right, heart. His work also requires normal physiological conditions. Cardiac is often added to pulmonary insufficiency in a person with a kyphotic posture.
But these are far from all possible surprises.
Other complications of kyphosis
With a strong thoracolumbar deformity and with compensatory lordosis, the abdominal cavity is compressed. The result is the development of chronic diseases of the digestive organs - the stomach and intestines.
The liver also suffers.
An additional negative factor is the insufficient supply of oxygen to the mentioned organs, which is explained by inconvenient conditions for the proper functioning of the heart.
We will not say that every patient with a diagnosis of "kyphosis" is threatened with gastritis or colitis. You just need to understand that even a prerequisite for acquiring such ailments can be the last straw, adding to other reasons for the development of a particular disease.
The worst
Finally, let's think about the most frightening type of complications of kyphotic spinal deformity - the violation of motor functions. It is possible when the modified vertebrae begin to push against the spinal canal, which contains the spinal cord.
Alas, sometimes incorrect posture leads to paresis and paralysis. Occasionally, pressure on the spinal cord sets the stage for inflammatory diseases - for example, for.
For some, the most terrible complication may not even be paralysis, but deformity. Angular kyphosis gradually turns into a real hump.
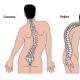
The human spine is never perfectly straight, even in the absence of pathologies. Natural curves in the thoracic, cervical and lumbar regions provide flexibility and smooth out stress. Normally, the neck has a slight forward concavity - a physiological lordosis that is characteristic of all people.
Collapse
What it is?
- concavity of the spine back. Normally, such a bend occurs in a person in the thoracic and sacral regions. If for some reason the neck arches back, then the patient is diagnosed with pathological kyphosis of the cervical spine.
Causes
Kyphotic deformity of the cervical spine can either be present in a person from infancy or be acquired throughout life.
One of the causes of the disease in infants is heredity. The probability of encountering this pathology is significantly higher if there were people in the family with diseases of the spine (especially the upper sections). The appearance of kyphosis is affected by the weak development of the muscles and vertebrae of the cervical region. This may be due to childhood rickets or problems that arose in the womb.
There are many factors that cause acquired kyphosis. The cause may be pathology of the spine. Much more likely to suffer from kyphosis are people who move little, receive an insufficient amount of physical activity, and are in a sitting position for a long time. In such cases, the muscles weaken, the correct posture is not respected. The situation is aggravated by the presence of scoliosis.
Symptoms and signs
Externally, the disease affects the patient in the form of stoop, the presence of a hump, which can be arched or have an acute angle. These characteristic external features are clearly visible in the photo of kyphosis of the cervical spine:

Symptoms of kyphosis of the cervical spine are divided into 4 groups:
- extravertebral group,
- vertebral symptoms (insufficient mobility);
- myosfacial group of symptoms;
- spinal cord compression.
Not all extraverberal symptoms occur in the area of the curvature. The activity of some organs and systems of the body is difficult. The patient suffers from the following symptoms:
- Pain in the occipital region. The pain can be of varying intensity.
- deterioration of vision and hearing;
- problems with coordination;
- nausea.
Verterbral leads to the fact that the patient cannot move the neck normally. Difficulty moving both horizontally and vertically. The neck crunches and creaks when turning and tilting. The symptoms are aggravated by movement.
The myofascial group includes the following symptoms:
- constant feeling of fatigue, decreased performance;
- the muscles of the neck are constantly tense, a seal is formed in them.
Compression is associated with impaired nervous activity. The deformation of the cervical region leads to pinching of the vertebral artery, as a result of which the brain receives an insufficient amount of oxygen. This complication can lead to serious consequences. Compression myelopathy has the following symptoms:
- numbness in the neck, shoulders, jaw and arms;
- decreased muscle tone;
- facial skin loses sensitivity (with damage to the trigeminal nerve);
- upper limbs trembling and cold;
- twitching of fascia - connective tissue membranes covering organs, nerves and blood vessels.
In some patients, urination and defecation may be disturbed. Often worsens memory and thinking. Some patients complain of changes in blood pressure.
Classification
By origin, kyphosis happens:
- Paralytic. Develops due to paralysis of the spinal muscles.
- Rachitic. In children, this form of the disease can occur as early as six months of age.
- Postural. It is manifested due to incorrect posture, more common in women.
- Infectious.
- Congenital.
- Degenerative-dystrophic. It is formed due to the presence of other pathologies of the spine.
- Senile (due to age-related changes).
There are four stages of the development of the disease:
- The angle of curvature is less than 40 degrees.
- Curvature of 41-50 degrees.
- Deformation at 51-70°.
- The angle exceeds 71 degrees.
Diagnostics
The kyphotic setting of the cervical spine is usually clearly visible already during the initial visual examination. But in order to accurately determine the diagnosis, the following measures are taken:
- Direct and lateral radiography.
- X-ray in two projections. Allows you to get a complete picture of the state of the vertebrae and tissues.
- MRI. This type of examination provides the most accurate information about the degree of development of the disease.
- Contrast myelography (if the patient for some reason cannot undergo an MRI).
- Examination and examination by a neurologist, as the curvature of the neck can affect the spinal cord, affecting nerve activity.

Treatment
Treatment of kyphosis of the cervical spine involves both alleviating the symptoms and eliminating the curvature itself. In order to return the spine to its natural angle of bend, a medical corset is used. But the effect is achieved only with special exercises, physiotherapy, medicines and massage. Treatment should be taken seriously, all necessary actions and procedures should be performed regularly and on time, and only then will it be possible to get rid of kyphosis.
Exercises
Therapeutic exercises make the neck muscles stronger, promote better blood circulation. You need to practice every day. Exercise helps in both treatment and prevention. There are different complexes of therapeutic exercises. For greater efficiency and safety, it is best to first consult with your doctor and ask to prescribe the complex on an individual basis.
How to warm up your neck
When curving, you always need to be careful not to damage the nerves and tissues. All exercises must be performed smoothly, make sure not to overwork. How to warm up the neck before training with kyphosis? To begin with, it is better to do a couple of light warm-up exercises. Sitting, slowly and gently pull your head forward without tilting it down. In a standing position, gently turn your head to the sides 5-10 times. Then do a light warming massage of the neck muscles to prepare yourself for gymnastics.
Complex
The following exercises will help reduce pain and discomfort, relieve tension and relax muscles.
- The starting position is all fours. The head is pulled back, the body bends down, then you need to crawl in this way for about twenty meters.
- The patient lies on the floor (belly down). You need to take a stick, put your hands behind your head, and arching strongly, then return to the starting position.
- Lie on your back, stretching your arms along the body and bending your knees. Then, inhaling, bend over, resting your elbows and the back of your head. Exhaling, straighten up again and lie down.
- Standing position. On inspiration, the patient stands on his toes, raises his arms to the side of the body, then takes the starting position. The exercise is repeated 10 times.
- The patient lies with his stomach up, arms along the body. In the same position, raise your arms up and stretch. Repeat 10-12 times.
Yoga
Under medical supervision, you can try to alleviate your well-being with yoga classes. But only with caution, because not all exercises are suitable for people with spinal curvature. Some of them are quite complex and the patient can overwork, causing harm to himself. When practicing yoga, it is important to monitor the condition and stop doing exercises if pain and other unpleasant symptoms appear.
Physiotherapy
With the help of physiotherapy, blood circulation can be improved by relieving pressure on tissues and nerves. Therapeutic procedures help relieve symptoms, reduce pain, and improve overall well-being. The following methods are applied:
- acupuncture,
- ultrasonic impact,
- electrophoresis,
- magnetotherapy.
In the treatment of kyphosis, massage is often used, which gives the muscles strength and elasticity, and makes the patient feel better.
Preparations
Patients are prescribed drugs aimed at stimulating blood supply, relieving inflammation. This role is played by:
- muscle relaxants (Mefedol, Sibazon, Mydocalm),
- chondroprotectors (Teraflex, Dona, Artra),
- anti-inflammatory drugs (Voltaren, Diclofenac).
B vitamins are also prescribed.
Operations
Surgical intervention is rarely resorted to if other means and methods do not help. A persistent pain syndrome is forced to carry out operations, which cannot be eliminated with medication and with the help of physiotherapy. Such extreme measures have to be resorted to when the nerve roots are compressed and nothing can be done about it. The symptoms resulting from compression cannot be suppressed by any other methods. The need for surgical intervention is also associated with the severity of disease progression and the severity of complications.
2 methods are used:
- Osteotomy. Fixation of the vertebrae in a normal position with the help of plates.
- Kyphoplasty. It is used if there is a fracture or injury of the vertebrae. A special capsule is inserted into the vertebra, which is filled with a cementing substance.
Complications
Untreated kyphosis can lead to the following consequences:
- The back takes on an arched appearance, greatly spoiling the appearance of a person, and is accompanied by pain.
- With the progression of the disease, the vertebrae degrade and shift.
- Hernias and other pathologies of the spine are formed.
- Headache, tinnitus and dizziness due to impaired blood circulation.
- Problems with coordination and mental abilities.
As a result of neglected kyphosis, a person may even remain disabled. Therefore, it is so necessary to quickly and timely treat this disease.
Output
In order to avoid severe symptoms and long-term treatment, it is better to follow preventive measures: engage in recreational exercises, lead an active lifestyle, maintain proper posture, and diet. Also, check with your doctor on time.








The influence of the Internet on a person
Types of seizures Tonic-clonic seizures in children
Profession Internet project manager
best remedy for prostatitis
Symptoms and treatment of mastopathy of the mammary glands