Currently, in Russia, a disease such as syphilis is quite common, so it is distinguished as a socially significant pathology that threatens the life and health of people. According to medical statistics, the incidence rate is only increasing every year. Those who have not encountered this disease should familiarize themselves with it in detail, considering what it is. syphilis, symptoms and treatment, photo prevention.
Syphilis - what is it? syphilis is a serious illness, which is characterized by the fact that the pathological process affects the skin, mucous membranes and internal organs of the patient.
The causative agent of syphilis is a microorganism called pallidum spirochete. It looks like a curved spiral, can move in different ways, and is able to divide in a transverse way.
Favorable conditions for the development of this bacterium are in the lymphatic tracts and nodes of a person, so it is there that it begins to multiply rapidly. It is possible to detect the presence of such microorganisms in the blood at the stage of the secondary type of the disease.
Bacteria can stay in a warm and humid environment for quite a long time, the most optimal temperature is 37°C. In addition, they are resistant to low temperatures. Pathogenic microorganisms die in case of drying, heating to 55°C-100°C, treatment with disinfectants, acid or alkaline solutions.
Household syphilis, symptoms and treatment, prevention, photo can lead to many negative consequences for human health, even end very tragically. But the prognosis depends on whether this dangerous disease is detected in a timely manner.
Incidence

Symptoms diseases directly depends on the stage at which it proceeds. Moreover, clinical manifestations in different sexes may differ. Experts distinguish 4 degrees of development of the disease, which begin with an incubation period and end with a tertiary type. The first signs of syphilis disturb a person only when the incubation period ends, which passes without causing any sensations. Parsing syphilis, symptoms and treatment, prevention, photo all stages of infection should be considered.
primary stage
The initial symptom of the disease is appearance on the female labia or the head of the male genital organ hard chancre which is characterized by pain.
Occurs in those places where pathogenic microorganisms penetrated into the body. Therefore, rashes can appear on other parts of the skin, but most often they occur on the patient's genitals. This is due to the fact that in most cases the infection process occurs through sexual contact.

1-2 weeks after the rash has formed, there is an increase in the lymph nodes located near it. This suggests that pathogenic bacteria with the help of the circulatory system diverge throughout the body, affecting the internal organs of the patient.
After the onset, it disappears without the use of medications after 20-40 days. But this does not mean at all that the disease has receded, because in fact the pathology is only developing.
When the primary stage ends, the patient may feel weakness throughout the body, lack of desire to sleep and eat, headache, fever, soreness in muscle tissues and joints.

secondary stage
The first period of development ends, the secondary one begins to develop, which is slightly different. The clinical manifestations in this case are rashes.

It may appear on the hands and other parts of the body. It is not accompanied by any discomfort, but is considered the initial symptom of this stage. It begins to disturb the patient 8-11 weeks after the very first rashes appeared on the patient's body.
Most often, skin manifestations occur on those parts of the body that are more exposed to mechanical stress, for example, on the folds, inguinal folds, mucous membranes.

Some patients note that their hair falls out very much, and neoplasms appear in the genital area.

In the event that the patient does not treat the pathology at this stage of development, then gradually the skin manifestations will go away on their own, but the infection will not disappear, but will turn into a latent type that can last up to 4 years. After some time, a relapse of the disease will occur.

Tertiary stage
Fortunately, now it is quite rare to detect this stage of the course of the disease only if the therapy was not carried out on time. Then, after a few years from the date of infection, the tertiary stage may occur. With it, damage to internal organs is observed, the appearance of foci of infection on the skin, mucous membranes, heart, lungs, liver, organs of vision, brain, bones. The surfaces of the nasal cavity are capable of sinking, and in the process of eating food can enter the nose.
Clinical manifestations are associated with the fact that the nerve cells of the brain and spinal cord die, so the patient often develops dementia, progressive paralysis. In no case should you start the disease before this period, if you find the first signs in yourself, you should immediately consult a doctor. Otherwise, the consequences will be dire.

At the first stage, small rashes with a red color are observed. Over time, they transform into small sores. They have a compacted base, smooth edges and a brown-red bottom. Disappear a few weeks after infection.

Many are interested in the question Does syphilis itch men and women? No, such a manifestation was not observed.
At the second stage of development, small tubercles appear on the skin, which have a pale pink tint. Gradually, they begin to change their color, after which brown or bluish spots form. Sometimes doctors observe the appearance of pustules on the patient's body.

At the third stage, the skin, legs, back and other areas of the human body does not appear so significantly. Small tubercles are found that have a red-blue tint, but there are very few of them. After all, the main symptom is damage to the body from the inside.

To say unequivocally what does syphilis look like it is impossible, because the nature of skin manifestations can be different. Rashes differ depending on what character they have, in what quantity they appear, they can occur singly or multiple.

Almost always syphilis in women and men, or rather, its symptoms, manifested on the skin, gradually disappear. Instead of themselves, they leave small scars and scars. However, this does not mean at all that the disease has receded. Outwardly, it may not cause any sensations, but inside the body is increasingly endangered.
Photo of syphilis

Now the most reliable method of research is blood test for syphilis - Wasserman reaction. The purpose of this examination is to detect the antibodies of the immune system that the body produces if it does not contain pathogens that cause this dangerous disease.
Where biomaterial is taken how long is the procedure? Removal of the required amount of blood not from a finger, but from a vein. Sometimes it is taken from the blood vessels that are located on the hands or forearms.
Special training not required prior to analysis. The only thing needed donate blood on an empty stomach, for this you need not to eat 6-8 hours before the procedure. This will help to obtain the most reliable information during the laboratory study.
If the result is negative, then there is no pathology if it is positive, then an infection develops in the body. However, there are some exceptions in which the result of the survey may be false. That is, even if the analysis showed a negative result, the patient can still be infected, and vice versa. This is possible if:
- At the time of the examination, the person had been infected for only a few days.
- A person suffers from a secondary and tertiary stage of the disease, in which the content of protective antibodies becomes less.
If a positive result is obtained, the specialists mandatory laboratory testing to make sure the results are correct. After all, false reactions are quite common.

How is syphilis transmitted?
There are several ways how can you get syphilis. These include:
- Sexual act of any kind.
- Blood, so often drug addicts who share syringes become infected. Also, the infection can be transmitted through a razor blade, which is used by several people.
- Breast milk, due to which the pathology is transmitted to the child.
- The intrauterine route, in which the baby is born already infected.
- Bacteria transmission household way, for example, when the patient and other people use the same towel or utensils.
- Saliva, which rarely acts as a carrier of infection, usually, if such contamination occurs, among dentists who work without gloves.
How does syphilis manifest itself? after infection?
Unfortunately not. Therefore, to feel that the presence of infection is impossible immediately. In this regard, if unprotected sexual contact has occurred, then to prevent infection no later than 2 hours later, the following must be done:
- Wash the genitals and the surface of the thighs with soap.
- Treat these parts of the body with a solution of antiseptics such as Chlorhexidine, Miramistin. Women should inject the drug into the vagina, and men into the urethra.

This method is guaranteed not to prevent the penetration of pathogenic microorganisms, reduce the risk of infection transmission only by 70%. In addition, this method will not always work, so it is best to use condoms. Even if sexual contact occurred with a trusted partner, you should still not neglect the treatment of the genitals with antiseptic agents.

Also, after casual sexual intercourse, it is advisable to undergo an examination by a venereologist to make sure that there is no infection in the body. To detect syphilis, go to the doctor in just a few weeks after the sexual act, because before he does not show himself in any way.
All manifestations on the skin and mucous membranes are highly contagious, so even short-term contact with a sick person leads to the transmission of bacteria. Blood is also considered dangerous. If she got on medical or cosmetic instruments, and then a healthy person was injured by them, then the infection is guaranteed to pass to him.
In order to prevent family members from becoming infected with the virus, it is necessary to reduce the likelihood of transmission of infection in the household as much as possible. The patient should have personal dishes, hygiene items, should try not to come into contact with healthy people.

All sick patients are primarily concerned with the question, and is syphilis curable? A favorable prognosis is possible, but the most important is the timely detection of pathology. Your further recovery depends on this. How to treat syphilis, a dermatovenereologist who specializes in this area knows.
Treatment time this disease is long enough. If he was discovered at the primary stage, then therapy takes 2-3 months, and if - at the secondary stage, it will last about 2 years. During treatment, the patient is strictly forbidden to live sexually, and his family members are recommended to take preventive measures.
The patient is in most cases treated in a hospital under the supervision of a physician. Therapy regimen It does not depend on what symptoms a person has, but based on the results of laboratory tests. The doctor prescribes drugs for the treatment of syphilis, the most efficient of which are penicillins. They are administered by injection every 3 hours. Such the course is 24 days.
The causative agent of the infection has a rather strong sensitivity to these drugs, but sometimes they are ineffective or cause an allergic reaction in the patient. Then the specialist recommends such means as fluoroquinolones, macrolides, or teracyclines. Immunostimulants and vitamin therapy are also prescribed.

If a woman wishes to have a child
But in the past she suffered this dangerous disease, how to plan a conception? In order to prevent the birth of a baby with an acquired disease, expectant mothers are repeatedly examined. It is possible to conceive a child to a person who has had this infection, but it will be necessary to carry out diagnostics and take preventive measures.

Talking about syphilis, symptoms and treatment, photo prevention it should be said that no traditional medicine recipes and therapy without the help of a doctor can help in the fight against this disease. This is in principle unacceptable, because not only is it absolutely not beneficial, it can also be dangerous. Therefore, with a possible infection or the manifestation of the first symptoms, you should immediately consult a doctor. The sooner the disease is detected, the better the prognosis for recovery.
We reviewed the disease syphilis. Symptoms and treatment, prevention, photos help fight disease. Have you observed this? Leave your opinion or feedback for everyone on the forum.
Character, which is mainly transmitted through sexual contact, including oral and anal sex. In some cases, infection is possible through a kiss or even just close physical contact with a person who has this disease.
It has long been known that the disease "syphilis" is transmitted through direct contact with the resulting ulcers. But it is worth noting that most of these ulcers go unnoticed by humans.
Very often, a person already infected with this disease does not even imagine it. The worst thing is that due to such ignorance of his condition, he will unknowingly infect his sexual partner. And if there are several of them ... Can you imagine the scale of the problem?
In addition, infection can occur from mother to child. That is, if a pregnant woman is infected, while still in the womb, the fetus can also be infected. This form of syphilis is called congenital and in some cases leads to very serious defects in the development of the baby. Sometimes a child may not even survive.
Why does syphilis appear? It occurs due to the causative agent of the disease - pale treponema, which originates from the genus spirochetes.
How widespread is syphilis?
It has a chronic course and often leads to severe complications. These include arthritis, brain damage, blindness, and more. Not so long ago, syphilis was a huge danger to the people around, because there was no reliable treatment.
This situation lasted until 1940, before the invention of an antibiotic called penicillin, which fought well against this disease.
To date, fewer people are suffering from syphilis. Although from time to time there are individual outbreaks of the disease.
Symptoms of syphilis
This disease usually occurs in three stages:
- Primary or early syphilis. During this period, characteristic only for this one, which are called "hard chancre", appear on the skin. These sores are firm, almost painless, and appear about 10 to 90 days after infection occurs. If you do not carry out treatment, syphilis will not go anywhere, although the ulcers will disappear in a month and a half (and on their own), without leaving any scars and scars.
- Secondary syphilis. This stage most often lasts from one to three months. On the body there are pockets of a pinkish rash. Its characteristic location is the soles of the feet and palms. In addition, there may be moist warts located in the groin, white spots inside the mouth, an increase in the size of the lymph nodes, weight loss and fever. Like the primary stage, the secondary also goes away on its own without any treatment.
- Tertiary syphilis. Everything is different here: if this form is not started to be treated, serious complications can arise in the work of the brain and spinal cord, heart and nervous system. In addition, the third stage of syphilis can cause paralysis, blindness, deafness, dementia, impotence, and, worst of all, death.
Latent (or latent) syphilis is isolated separately. This period is characterized by the absence of any symptoms.
How to treat syphilis?
If less than a year has passed since you became infected, then one dose of penicillin is most likely enough to get rid of the disease. If you have an allergic reaction to this antibiotic, it can be replaced with doxycycline or tetracycline.
When the disease "syphilis" has passed into a later stage, much larger doses of the drug will be needed and a rather long period of time for a cure.
Syphilis is a serious disease that is characterized by damage to the skin, mucous membranes and internal organs of a person.
It is classified as a classic sexually transmitted disease. Unprotected intercourse with an unreliable or random sexual partner can cause syphilis.
The symptoms of syphilis are very diverse, and the manifestations of the disease largely depend on its period. Previously, this infection was considered incurable, but in our time it is successfully treated with antibiotics.
How is syphilis transmitted?
In most cases, syphilis is transmitted through sexual contact in the vagina, mouth, or rectum. Treponema enters the body through small defects in the mucous membrane of the genital tract.
However, there are cases of infection by household means - the disease is transmitted from one partner to another through saliva during a kiss, through common objects on which there is a dry discharge containing pale treponema. Sometimes the cause of infection can be a transfusion of infected blood.
Pathogen
A mobile microorganism from the order of spirochetes, pale treponema is the causative agent of syphilis in women and men. It was discovered in 1905 by German microbiologists Fritz Schaudin (German: Fritz Richard Schaudinn, 1871-1906) and Erich Hoffmann (German: Erich Hoffmann, 1863-1959).
Incubation period
On average, it is 4-5 weeks, in some cases the incubation period of syphilis is shorter, sometimes longer (up to 3-4 months). It is usually asymptomatic.
The incubation period may increase if the patient has taken some antibiotics for other infectious diseases. During the incubation period, the test results will show a negative result.
Symptoms of syphilis
The course of syphilis and its characteristic symptoms will depend on the stage of development at which it is located. However, the symptoms in women and men can be very diverse.
In total, it is customary to distinguish 4 stages of the disease - starting from the incubation period, and ending with tertiary syphilis.
The first signs of syphilis make themselves felt after the end of the incubation period (it proceeds without symptoms), and the beginning of the first stage. It is called primary syphilis, which we will discuss below.
Primary syphilis
The formation of a painless hard chancre on the labia in women or the head of the penis in men is the first sign of syphilis. It has a dense base, smooth edges and a brown-red bottom.
Ulcers form at the site of penetration of the pathogen into the body, it may be other places, but most often chancres form on the genitals of a man or woman, since the main route of transmission of the disease is through sexual intercourse.
7-14 days after the onset of a hard chancre, the lymph nodes closest to it begin to increase. This is a sign that triponemes are spread throughout the body with blood flow, and affect the internal organs and systems of a person. The ulcer heals on its own within 20-40 days after the onset. However, this cannot be regarded as a cure for the disease; in fact, the infection develops.
At the end of the primary period, specific symptoms may appear:
- weakness, insomnia;
- headache, loss of appetite;
- subfebrile temperature;
- pain in muscles and joints;
The primary period of the disease is divided into seronegative, when standard serological blood tests are negative (the first three to four weeks after the onset of hard chancre) and seropositive, when blood tests are positive.
Secondary syphilis
After the end of the first phase of the disease, secondary syphilis begins. Symptoms that are characteristic at this moment are the appearance of a symmetrical pale rash all over the body, including the palms and soles. It doesn't cause any pain. But it is the first sign of secondary syphilis, which occurs 8-11 weeks after the appearance of the first ulcers on the patient's body.
If the disease is not treated even at this stage, then over time the rash disappears and syphilis flows into a latent stage that can last up to 4 years. After a certain period of time, a relapse of the disease occurs.
At this stage, there are fewer rashes, they are more faded. The rash often occurs in areas where the skin is subjected to mechanical stress - on the extensor surfaces, in the inguinal folds, under the mammary glands, in the intergluteal fold, on the mucous membranes. In this case, hair loss on the head is possible, as well as the appearance of flesh-colored growths on the genitals and in the anus.

Tertiary syphilis
Today, fortunately, infection in the third stage of development is rare.
However, if the disease is not treated in a timely manner, then after 3-5 years or more from the moment of infection, the tertiary period of syphilis begins. At this stage, the infection affects the internal organs, foci (threshing floors) are formed on the skin, mucous membranes, heart, liver, brain, lungs, bones and eyes. The bridge of the nose can sink, and during meals, food enters the nose.
Symptoms of tertiary syphilis are associated with the death of nerve cells in the brain and spinal cord, as a result, dementia, progressive paralysis may occur in the advanced third stage. The Wasserman reaction and other tests may be weakly positive or negative.
Do not wait for the development of the last stage of the disease, and at the first alarming symptoms, immediately consult a doctor.
Diagnostics
Diagnosis of syphilis will directly depend on the stage at which it is located. It will be based on the symptoms of the patient and the tests received.
In the case of the primary stage, hard chancres and lymph nodes are subject to examination. At the next stage, the affected areas of the skin, papules of the mucous membranes are examined. In general, bacteriological, immunological, serological and other research methods are used to diagnose infection. It should be borne in mind that at certain stages of the disease, the results of tests for syphilis can be negative in the presence of the disease, which makes it difficult to diagnose the infection.
To confirm the diagnosis, a specific Wasserman reaction is performed, but it often gives false results of the analysis. Therefore, for the diagnosis of syphilis, it is necessary to simultaneously use several types of tests - RIF, ELISA, RIBT, RPGA, microscopy, PCR analysis.

Treatment of syphilis
In women and men, the treatment of syphilis should be comprehensive and individual. This is one of the most formidable sexually transmitted diseases, leading to serious consequences if not properly treated, so under no circumstances should you self-medicate at home.
The basis of the treatment of syphilis is antibiotics, thanks to them, the effectiveness of treatment has approached 100%. The patient can be treated on an outpatient basis, under the supervision of a doctor who prescribes a comprehensive and individual treatment. Today, penicillin derivatives in sufficient doses (benzylpenicillin) are used for antisyphilitic therapy. Premature termination of treatment is unacceptable, it is necessary to complete the full course of treatment.
At the discretion of the attending physician, they may prescribe additional treatment with antibiotics - immunomodulators, vitamins, physiotherapy, etc. During treatment, any sexual intercourse and alcohol are strictly contraindicated for a man or a woman. After the end of treatment, it is necessary to pass control tests. These may be quantitative non-treponemal blood tests (for example, RW with cardiolipin antigen).
Consequences
The consequences of treated syphilis usually include a decrease in immunity, problems with the endocrine system, and chromosome damage of varying severity. In addition, after the treatment of pale treponema, a trace reaction remains in the blood, which may not disappear until the end of life.
If syphilis is not detected and treated, it can progress to the tertiary (late) stage, which is the most destructive.
Late stage complications include:
- Gummas, large ulcers inside the body or on the skin. Some of these gums “dissolve” without leaving any traces; syphilis ulcers form in place of the rest, leading to softening and destruction of tissues, including the bones of the skull. It turns out that a person simply rots alive.
- Damage to the nervous system (hidden, acute generalized, subacute (basal), syphilitic hydrocephalus, early meningovascular syphilis, meningomyelitis, neuritis, spinal cord, paralysis, etc.);
- Neurosyphilis, which affects the brain or the membrane that covers the brain.
If the infection with treponema occurred during pregnancy, then the consequences of the infection may occur in a child who receives pale treponema through the mother's placenta.
Prevention
The most reliable prevention of syphilis is the use of a condom. It is necessary to conduct a timely examination when in contact with infected people. It is also possible to use antiseptic preparations (hexicon, etc.).
If you find yourself infected, it is important to tell all your sexual partners about it so that they also undergo the appropriate examination.
Forecast
The prognosis of the disease in most cases is favorable. Timely diagnosis and adequate treatment leads to a complete recovery. However, with a long-term chronic course and in cases of infection of the fetus in the womb, persistent irreversible changes develop, leading to disability.
Definition of illness. Causes of the disease
Syphilis- a chronic infectious disease caused by pale treponema (Treponema pallidum), with a course in the form of active manifestations, alternating with latent periods, which is transmitted mainly sexually and is characterized by a specific systemic lesion of the skin, mucous membranes, nervous system, internal organs and musculoskeletal system .
According to WHO data, there were 18 million cases of syphilis in the world in 2012, with an incidence of 25.7 cases per 100,000 population. Syphilis has been associated with 350,000 adverse pregnancy outcomes, including 143,000 stillbirths, 62,000 neonatal deaths, 44,000 preterm infants, and 102,000 infected infants. In 2015, 34,426 new cases of syphilis were registered in the Russian Federation, with an incidence rate of 23.5 per 100,000 population.
The cause of the disease is infection with pale treponema (Treponema pallidum) - a small spiral-shaped microorganism that, under natural conditions, can exist and multiply only in the human body. Pale treponema almost instantly dies in the external environment due to drying, is easily destroyed by boiling and exposure to antiseptics and ethyl alcohol. In addition to the typical spiral shape, it exists in the form of cysts and L-forms, into which it reorganizes to survive in an unfavorable environment for it.
The infection is transmitted sexually (including through oral and anal sex), transplacental, transfusion, and rarely - by household contact. Cases are described when bites, kisses, vaginal-finger contact led to infection with syphilis. Children can become infected with syphilis through close household contact if adult family members have the disease. The contact-household method of infection also includes a professional one - infection with syphilis, mainly by medical personnel when performing diagnostic and therapeutic procedures.
Three conditions under which infection occurs:
There are two points of view on the contagiousness of syphilis. According to some authors, infection occurs in 100% of cases, according to others - only in 60-80%, which is facilitated by a number of factors: intact skin and acidic pH of its surface, viscous vaginal and urethral mucus, competing microflora of the genital organs, phagocytosis and others. local defense mechanisms of the body.
The contagiousness of syphilis depends on the stage of the disease: as a rule, primary and secondary forms are especially contagious, latent syphilis can spread transplacentally and transfusionally.
If you experience similar symptoms, consult your doctor. Do not self-medicate - it is dangerous for your health!
Symptoms of syphilis
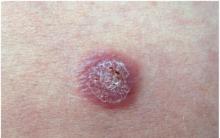
Primary syphiloma (hard chancre)- a symptom of the primary period of syphilis, a sign of which is erosion or an ulcer that occurs at the site of the introduction of pale treponema into the skin or mucous membranes. The formation of a chancre begins with the appearance of a small red spot, which after a few days turns into a nodule with a crust, when it is rejected, an erosion or ulcer of an oval or round shape, painless on palpation, with clear boundaries, is exposed.
By size, hard chancres are distinguished:
- ordinary - 1-2 cm in diameter;
- dwarf - from 1 to 3 mm;
- giant - from 2 to 5 cm.
More often, the chancre is solitary, but with repeated sexual intercourse with an infected partner, multiple rashes may appear. Multiple chancres include "bipolar" chancre, in which ulcers occur simultaneously on different parts of the body, and "kissing" chancre on adjacent surfaces.

In 90-95% of cases, the chancre is located in any area of the genital organs. The fact that it is often found at the base of the penis indicates that the condom is not fully effective in preventing syphilis. Very rarely, chancres can appear inside the urethra, in the vagina and on the cervix. An atypical form of chancre in the genital area is an indurative edema in the form of an extensive painless compaction of the foreskin and labia majora.
Outside the genitals, chancres are most often found in the mouth (lips, tongue, tonsils), less often in the fingers (chancre-panaritium), mammary gland, pubis, navel. Casuistic cases of the appearance of chancres in the chest and eyelids are described.
Folmann's syphilitic balanitis- this is a clinical variant of a hard chancre, a sign of which are spots with scales on the glans penis, combustiform chancre - resembling a superficial burn, herpetiform - in the form of a group of point microerosions, hypertrophic - simulating skin carcinoma.
Syphilitic lymphadenopathy- swollen lymph nodes - is a symptom of the primary and secondary periods of syphilis.
Syphilitic roseola (spotted syphilis)- a manifestation of the secondary, early congenital and less often tertiary period of syphilis, which occurs in 50-70% of patients.
Late roseola (erythema) Fournier is a rare manifestation of tertiary syphilis, usually occurring 5-10 years after infection. It is characterized by the appearance of large pink spots, often grouped into bizarre figures. Unlike roseola, with secondary syphilis, it flakes off and leaves behind atrophic scars.

A symptom of secondary and early congenital syphilis appears with a recurrence of the disease in 12-34% of cases. It is a rash of isolated dense nodules (papules) of a hemispherical shape with a smooth surface from pink-red to copper or cyanotic color. There is no itching and pain, but if you press on the center of the papule, patients notice a sharp pain (Yadasson's symptom).

Wide condyloma observed in 10% of patients. The warty surface of the papules, which almost always merge into large conglomerates, is weeping, eroded and often covered with a gray, fetid coating. There is a sharp pain during sexual intercourse and the act of defecation. In rare cases, wide warts can be located under the armpit, under the mammary glands, in the folds between the toes, in the deepening of the navel.
Pustular syphilis most often found in patients who abuse alcohol and drugs, infected with HIV and with hemato-oncological diseases.
Syphilitic alopecia (baldness)- this characterizes untreated secondary and early congenital syphilis. Usually appears in 4-11% of cases a few weeks after the onset of the primary rash (fresh roseola) and spontaneously regresses after 16-24 weeks.

Pigmentary syphilide- discoloration of the skin - a manifestation of secondary syphilis in the first 6-12 months after infection. Clinically, it is an alternation of pigment and depigment spots (network form), and at first only hyperpigmentation of the skin is noted. Depigmented (white) rounded spots with a diameter of 10-15 mm in the neck area (spotted form) are traditionally called the "necklace of Venus", and in the forehead area - the "crown of Venus". Without treatment, within 2-3 months, the rash spontaneously regresses. More rare is the "marble" or "lace" form.
Syphilitic angina- a symptom of secondary syphilis, a sign of which is the appearance of roseola and (or) papules on the mucous membrane of the mouth, pharynx, soft palate. If the papules are localized on the vocal cords, a characteristic "hoarse" voice appears. Sometimes syphilitic tonsillitis is the only clinical manifestation of the disease, and then it is dangerous in terms of the possibility of sexual (during oral sex) and domestic infection due to the high content of treponema in the elements of the rash.
Syphilitic onychia and paronychia occur at all stages and with early congenital syphilis.
Tubercular syphilide (tertiary papule)- the main symptom of the tertiary period of syphilis, which may appear as early as 1-2 years after infection. But usually occurs after 3-20 years. It is characterized by the appearance of isolated brownish-red seals up to 5-10 mm in size, which rise above the level of the skin and have a smooth and shiny surface. The outcome of the existence of the tubercle is always the formation of a scar.
Syphilitic gumma (gumous syphilide) characterizes the tertiary period and late congenital syphilis. When this occurs, a mobile, painless, often single node with a diameter of 2 to 5 cm in the subcutaneous tissue. Gummas can occur in muscle and bone tissue, on internal organs. Most often, they are localized in the oral cavity, nose, pharynx and pharynx, as a result, perforation of the hard palate occurs with food entering the nasal cavity and a “nasal” voice, deformation of the cartilaginous and bony parts of the nasal septum with the formation of a “saddle-shaped” and “lorgnette” nose.
Symptoms of neurosyphilis:
Symptoms from the internal organs (visceral syphilis) are observed in patients with visceral syphilis and depend on the localization of the process. Yellowness of the skin and sclera occurs with syphilitic hepatitis; vomiting, nausea, weight loss - with "gastrosyphilis"; pain in muscles (myalgia), joints (arthralgia), bones - with syphilitic hydrarthrosis and osteoperiostitis; cough with sputum - with syphilitic bronchopneumonia; pain in the heart - with syphilitic aortitis (mesaortitis). Characteristic is the so-called "syphilitic crisis" - paroxysmal pain in the area of the affected organs.
Symptoms of early congenital syphilis:
- syphilitic pemphigus;
- syphilitic rhinitis;
- diffuse papular infiltration;
- osteochondritis of long tubular bones;
- Parro's pseudoparalysis is a symptom of early congenital syphilis, in which there is no movement of the limbs, but nerve conduction is preserved;
- Sisto's symptom - the constant cry of a child - is a sign of developing meningitis.
Symptoms of late congenital syphilis:
- Parenchymal keratitis is characterized by clouding of the cornea of both eyes and is observed in half of the patients;
- Clutton's joint (syphilitic drives) - bilateral hydrarthrosis in the form of redness, swelling and enlargement of the joints, more often the knees;
- The buttock-shaped skull is characterized by an increase and protrusion of the frontal and parietal tubercles, which are separated by a longitudinal depression;
- Olympic forehead - an unnaturally prominent and high forehead;
- Symptom of Avsitidia - thickening of the sternal end of the right clavicle;
- Dubois symptom - shortened (infantile) little finger;
- Saber shin - a characteristic symptom of late congenital syphilis in the form of an anterior bend of the tibia, resembling a saber;
- Getchinson's teeth - dystrophy of the permanent upper middle incisors in the form of a screwdriver or a barrel with a semilunar notch on the free edge;
- Diastema Gaucher - widely spaced upper incisors;
- The tubercle of Corabelli is the fifth accessory tubercle on the chewing surface of the first upper molar.
The pathogenesis of syphilis
The introduction of pale treponema occurs in damaged areas of the skin and mucous membranes of a person. With the help of the adhesin protein, T. Pallidum, interacting with fibronectin and other cell receptors, “sticks” to various types of host cells and migrates throughout the body through the lymphatic system and blood. Penetration into tissues is facilitated by the induction of the formation of matrix metalloproteinase-1 (MMP-1) by treponema, which is involved in the destruction of collagen, as well as its helical shape and high mobility. Fixing in the lesions, treponema causes endarteritis of the blood vessels with the participation of lymphocytes and plasma cells, which are replaced by fibroblasts during the development of the disease, causing scarring and fibrosis. The antigenic structure of treponemas consists of protein, polysaccharide and lipid antigens. The response of the body to the introduction of the pathogen is realized by cellular and humoral systems. Macrophages are involved in the implementation of the cellular response, carrying out phagocytosis of spirochetes, T-lymphocytes - directly destroying the pathogen and contributing to the production of antibodies, and B-lymphocytes responsible for the production of antibodies. During the development of the infection, fluoresceins (IgA) are first produced, then antibodies to protein antigens, then reagins (IgM), and by the time the disease develops, immobilisins (IgG). An important feature is the ability of pale treponema, due to its unusual molecular architectonics, to “avoid” the humoral and cellular immune response.

After the introduction of the spirochete, a latent (incubation period) begins - the period of time between the primary infection and the appearance of the first clinical symptoms, lasting from 9 to 90 days (average 21 days). The lengthening of the incubation period, first of all, is facilitated by taking antibiotics in doses insufficient for a cure.
In 90-95% of cases, at the end of the incubation period, a primary focus appears at the site of treponema introduction - a syphilitic hard chancre. In 5-10% of cases, the disease proceeds initially hidden - without its formation (headless syphilis). After 7-10 days of the appearance of the chancre, regional lymph nodes begin to increase. After 1-5 weeks, the chancre spontaneously regresses. The interval between the appearance of the chancre and its disappearance is commonly called the primary period of syphilis.
1-5 weeks after the formation of the primary chancre, due to the spread of treponema throughout the body, a skin rash appears, which persists for 2-6 weeks, after which it spontaneously disappears. After a certain time, the rash may recur. Such an undulating course of syphilis is associated with the activation of treponema or the inhibition of their reproduction due to the body's immune response. The interval between the first appearance of a rash and the appearance of tertiary syphilis is commonly called the secondary period of syphilis, and the intervals between relapses are called the latent period of syphilis. Secondary syphilis with relapses occurs in 25% of patients.
It should be noted that in a sufficient number of cases, syphilis may initially exist in a latent form, pass into it after the primary period or after the first episode of secondary syphilis, and proceed asymptomatically. In such cases, early latent syphilis with a disease duration of less than two years and late latent disease with a disease duration of more than two years after infection are distinguished. Secondary and latent syphilis can continue for several years and even decades.
Approximately 15% of patients with untreated syphilis develop a skin rash in the form of tuberculous or gummous syphilides 1-45 years after infection, indicating the transition of the disease to the tertiary period. As with secondary syphilis, the rash may disappear and recur.
Neurosyphilis
In 25-60% of cases, the nervous system is already affected in primary and secondary syphilis. Neurosyphilis detected in the first 5 years after the onset of the disease is called early. In 5% of cases, it occurs with symptoms - damage to the cranial nerves, meningitis, meningovascular disease, in 95% of cases no symptoms are observed. Neurosyphilis detected after 5 years after the onset of the disease is called late. In 2-5% of patients, it occurs in the form of progressive paralysis, in 2-9% - in the form of dryness.
Visceral syphilis
With early visceral syphilis (up to 2 years from the moment of infection), only functional disorders develop, and with late (over 2 years) - destructive changes in internal organs, bones and joints. In 10% of patients with late visceral syphilis, 20-30 years after infection, cardiovascular syphilis occurs, which is the main cause of death from this disease.
congenital syphilis
It occurs as a result of infection of the fetus through the umbilical vein and lymph nodes of the umbilical cord from a sick mother. Infection is possible already from 10-12 weeks of pregnancy. May be latent or clinical.
Classification and stages of development of syphilis
The International Classification of Diseases of the 10th revision divides syphilis into:
1. Early congenital syphilis:
- early congenital syphilis with symptoms
- early congenital syphilis latent;
- early congenital syphilis, unspecified;
2. Late congenital syphilis:
- late congenital syphilitic eye disease;
- late congenital neurosyphilis (juvenile neurosyphilis);
- other forms of late congenital syphilis with symptoms;
- late congenital syphilis latent;
- late congenital syphilis, unspecified;
3. Congenital syphilis, unspecified;
4. Early syphilis:
- primary syphilis of the genital organs;
- primary syphilis of the anal area;
- primary syphilis of other localizations;
- secondary syphilis of the skin and mucous membranes;
- other forms of secondary syphilis;
- early syphilis latent;
- early syphilis, unspecified;
5. Late syphilis:
- syphilis of the cardiovascular system;
- neurosyphilis with symptoms;
- asymptomatic neurosyphilis;
- neurosyphilis, unspecified;
- gumma (syphilitic);
- other symptoms of late syphilis;
- late or tertiary syphilis;
- late latent syphilis;
- late syphilis, unspecified;
6. Other and unspecified forms of syphilis:
- latent syphilis, not specified as early or late;
- positive serological test for syphilis;
- syphilis, unspecified.
Complications of syphilis
There are the following complications in primary syphilis:
At secondary syphilis there may be complications in the form of nodular syphilis, manifested by multiple nodes, and malignant syphilis, which is most common with HIV infection and is characterized by multiple pustules, ecthymas and rupees.
A serious complication of syphilis is abortion- 25% of pregnant women have fetal death, in 30% of cases - death of newborns after childbirth.
HIV infection- Patients with syphilis are several times more likely to become infected with HIV.
Death from syphilis occurs as a result of damage to internal organs. The most common cause is aortic rupture due to syphilitic aortitis.
Diagnosis of syphilis
Microscopic, molecular, immunohistochemical, serological and instrumental methods are used to diagnose syphilis.
Material for research:
- discharge from erosions, ulcers, eroded papules, blisters;
- lymph obtained by puncture of the lymph nodes;
- blood serum;
- cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) obtained by puncture of the spinal cord;
- tissues of the placenta and umbilical cord.
Indications for examination:
Microscopic methods are used to diagnose early forms and congenital syphilis with clinical manifestations. Two methods are applied:
- A study in the dark field determines the live treponema in the discharge from erosions and ulcers and differentiates it from other treponemas.
- The method of silvering according to Morozov - allows you to identify treponema in biopsy specimens of tissues and lymph.
Molecular Methods based on the detection of specific DNA and RNA of the pathogen by molecular biological methods (PCR, NASBA) using test systems approved for medical use in the Russian Federation.
Serological diagnostic methods aimed at detecting antibodies produced by the body to antigens of pale treponema (non-treponemal and treponemal tests).
False-positive serological tests for syphilis- positive results of serological reactions in persons who are not ill and have not had syphilis before.
- Acute false-positive reactions are observed up to 6 months and are associated with pregnancy, vaccination, infectious diseases, menstruation, some dermatoses, endemic treponematoses, Lyme disease.
- Chronic are observed for more than 6 months and are most often associated with oncological, autoimmune diseases, diseases of the liver, lungs, cardiovascular and endocrine systems. They can also be observed in drug addiction and in old age.
False-negative serological tests for syphilis observed in secondary syphilis due to the "prozone phenomenon" and in persons with severe immunodeficiency and certain infections (HIV, tuberculosis).
Clinical assessment of serological reactions
For the diagnosis of syphilis, a complex of serological reactions is used, which must necessarily include one non-treponemal test (more often RMP) and two confirmatory treponemal tests (in Russia it is more often ELISA and RPHA). By the presence of a combination of positivity of these three tests, the diagnosis is made or rejected.
The study of cerebrospinal fluid performed to diagnose neurosyphilis and shown:
- patients with syphilis with clinical neurological symptoms;
- persons with latent and late forms of infection;
- patients with secondary recurrent syphilis;
- with suspicion of congenital syphilis in children;
- in the absence of negative non-treponemal serological tests after a full-fledged specific treatment.
The diagnosis of neurosyphilis is considered confirmed if the patient has syphilis, proven by serological tests, regardless of its stage, and a positive result of bladder cancer with CSF.
Seror resistance it is considered the absence of negative or decrease in the titers of non-treponemal tests within a year in persons who have received adequate treatment for primary or secondary syphilis, and within 2 years in persons who have received adequate treatment for latent early syphilis.
Treatment of syphilis
In the treatment of syphilis, benzylpenicillin and its derivatives are used. If intolerance to the drug is detected, alternative ones are prescribed: semi-synthetic penicillins (ampicillin, oxacillin), erythromycin, doxycycline and ceftriaxone
Syphilis (syphilis) refers to infectious diseases, transmitted in most cases sexually. The causative agent of syphilis is a spiral-shaped microorganism Treponema pallidum(pale treponema), is very vulnerable in the external environment, multiplies rapidly in the human body. Incubation period, i.e time from infection to first symptoms, approximately 4-6 weeks. It can be shortened to 8 days or lengthened to 180 with concomitant sexually transmitted diseases (,), if the patient is weakened by an immunodeficiency state () or took antibiotics. In the latter case, the primary manifestations of syphilis may be absent altogether.
Regardless of the length of the incubation period, the patient at this time is already infected with syphilis and is dangerous to others as a source of infection.
How can you get syphilis?
Syphilis is transmitted mainly through sexual contact - up to 98% of all cases of infection. The pathogen enters the body through defects in the skin or mucous membranes of the genitals, anorectal loci, mouth. However, approximately 20% of sexual partners who have been in contact with patients with syphilis remain in good health. Risk of infection significantly reduced if there are no conditions necessary for the penetration of infection - microtrauma and a sufficient amount of infectious material; if sexual intercourse with a patient with syphilis was single; if syphilides (morphological manifestations of the disease) have a small contagiousness(the ability to infect). Some people are genetically immune to syphilis because their body produces specific protein substances that can immobilize pale treponema and dissolve their protective membranes.
It is possible to infect the fetus in utero or in childbirth: then congenital syphilis is diagnosed.
The everyday way - through any objects contaminated with infectious material, handshakes or formal kisses - is realized very rarely. The reason is the sensitivity of treponemas: as they dry, the level of their contagiousness drops sharply. Get syphilis through a kiss it is quite possible if one person has syphilitic elements on the lips, oral mucosa or throat, tongue containing a sufficient amount of virulent (that is, live and active) pathogens, and another person has scratches on the skin, for example, after shaving.

The causative agent of syphilis is Treponema pallidum from the Spirochete family.
Very rare routes of transmission of infectious material through medical instruments. Treponemas are unstable even under normal conditions, and when sterilized or treated with conventional disinfectant solutions, they die almost instantly. So all the stories about syphilis infection in gynecological and dental offices most likely belong to the category of oral folk art.
Transmission of syphilis with blood transfusions(blood transfusions) almost never occurs. The fact is that all donors must be tested for syphilis, and those who have not passed the test simply will not be able to donate blood. Even if we assume that there was an incident and there are treponemas in the donor blood, they will die during the preservation of the material in a couple of days. The very presence of a pathogen in the blood is also rare, because Treponema pallidum appears in the bloodstream only during treponemal sepsis» with secondary fresh syphilis. Infection is possible if enough virulent pathogen is transmitted with direct blood transfusion from an infected donor, literally from vein to vein. Given that the indications for the procedure are extremely narrowed, the risk of contracting syphilis through the blood is unlikely.
What increases the risk of contracting syphilis?
- Liquid secretions. Since treponemas prefer a humid environment, mother's milk, weeping syphilitic erosions and ulcers, sperm discharged from the vagina contain a huge number of pathogens and are therefore the most infectious. Transmission of infection through saliva is possible if there is syphilides(rash, chancre).
- Elements of dry rash(spots, papules) are less contagious, in abscesses ( pustules) treponema can be found only along the edges of the formations, and in pus they are not at all.
- Disease period. With active syphilis, nonspecific erosions on the cervix and head of the penis, herpetic rash vesicles and any inflammatory manifestations leading to defects in the skin or mucous membranes are contagious. In the period of tertiary syphilis, the possibility of infection through sexual contact is minimal, and papules and gummas specific for this stage are actually not contagious.
With regard to the spread of infection, latent syphilis is the most dangerous: people are unaware of their illness and do not take any measures to protect their partners.
- Accompanying illnesses. Patients with gonorrhea and other STDs are more easily infected with syphilis, since the mucous membranes of the genitals are already damaged by previous inflammations. Treponemas multiply rapidly, but the primary lues is "masked" by the symptoms of other venereal diseases, and the patient becomes epidemically dangerous.
- The state of the immune system. People who are debilitated by chronic diseases are more likely to contract syphilis; AIDS patients; in alcoholics and drug addicts.
Classification
Syphilis can affect any organs and systems, but the manifestations of syphilis depend on the clinical period, symptoms, duration of illness, age of the patient, and other variables. Therefore, the classification seems a little confusing, but in reality it is built very logically.
- depending from time span, which has passed since the moment of infection, early syphilis is distinguished - up to 5 years, more than 5 years - late syphilis.
- By typical symptoms syphilis is divided into primary(hard chancre, scleradenitis and lymphadenitis), secondary(papular and pustular rash, spread of the disease to all internal organs, early neurosyphilis) and tertiary(gummas, damage to internal organs, bone and joint systems, late neurosyphilis).

chancre - an ulcer that develops at the site of introduction of the causative agent of syphilis
- primary syphilis, according to blood test results, may be seronegative And seropositive. Secondary according to the main symptoms are divided into stages of syphilis - fresh and latent (recurrent), tertiary are differentiated as active and latent syphilis, when treponemas are in the form of cysts.
- By preference damage to systems and organs: neurosyphilis and visceral (organ) syphilis.
- Separately - fetal syphilis and congenital late syphilis.
Primary syphilis
After the end of the incubation period, the characteristic first signs appear. At the site of penetration of treponema, a specific rounded erosion or ulcer is formed, with a hard, smooth bottom, “tucked” edges. The sizes of formations can vary from a couple of mm to several centimeters. Hard chancres can disappear without treatment. Erosions heal without a trace, ulcers leave flat scars.

Disappeared chancres do not mean the end of the disease: primary syphilis only passes into a latent form, during which the patient is still contagious to sexual partners.

in the figure: chancres of genital localization in men and women
After the formation of a hard chancre, after 1-2 weeks begins local enlargement of lymph nodes. When palpated, they are dense, painless, mobile; one is always larger than the others. After another 2 weeks it becomes positive serum (serological) reaction to syphilis, from this point on, primary syphilis passes from the seronegative stage to the seropositive stage. The end of the primary period: the body temperature may rise to 37.8 - 380, there are sleep disturbances, muscle and headaches, aching joints. Available dense swelling of the labia (in women), head of the penis and scrotum in men.
Secondary syphilis
The secondary period begins about 5-9 weeks after the formation of a hard chancre, and lasts 3-5 years. Main symptoms syphilis at this stage - skin manifestations (rash), which appears with syphilitic bacteremia; wide warts, leukoderma and alopecia, nail damage, syphilitic tonsillitis. Present generalized lymphadenitis: the nodes are dense, painless, the skin above them is of normal temperature ("cold" syphilitic lymphadenitis). Most patients do not notice any special deviations in well-being, but the temperature may rise to 37-37.50, runny nose and sore throat. Because of these manifestations, the onset of secondary syphilis can be confused with a common cold, but at this time, lues affects all body systems.

syphilitic rash
The main signs of a rash (secondary fresh syphilis):
- The formations are dense, the edges are clear;
- The shape is correct, rounded;
- Not prone to merging;
- Do not peel off in the center;
- Located on visible mucous membranes and over the entire surface of the body, even on the palms and feet;
- No itching and soreness;
- Disappear without treatment, do not leave scars on the skin or mucous membranes.
accepted in dermatology special names for morphological elements of the rash that can remain unchanged or transform in a certain order. First on the list - spot(macula), may progress to stage tubercle(papula) bubble(vesicula), which opens with the formation erosion or turns into abscess(pustula), and when the process spreads deep into ulcer. All of the listed elements disappear without a trace, unlike erosions (after healing, a stain first forms) and ulcers (the outcome is scarring). Thus, it is possible to find out from trace marks on the skin what the primary morphological element was, or to predict the development and outcome of already existing skin manifestations.
For secondary fresh syphilis, the first signs are numerous pinpoint hemorrhages in the skin and mucous membranes; profuse rashes in the form of rounded pink spots(roseolaе), symmetrical and bright, randomly located - roseolous rash. After 8-10 weeks, the spots turn pale and disappear without treatment, and fresh syphilis becomes secondary. hidden syphilis flowing with exacerbations and remissions.

For the acute stage ( recurrent syphilis) is characterized by a preferential localization of the elements of the rash on the skin of the extensor surfaces of the arms and legs, in the folds (groin, under the mammary glands, between the buttocks) and on the mucous membranes. The spots are much smaller, their color is more faded. The spots are combined with a papular and pustular rash, which is more often observed in debilitated patients. At the time of remission, all skin manifestations disappear. In the recurrent period, patients are especially contagious, even through household contacts.
Rash with secondary acute syphilis polymorphic: consists simultaneously of spots, papules and pustules. Elements group and merge, forming rings, garlands and semi-arcs, which are called lenticular syphilides. After their disappearance, pigmentation remains. At this stage, the diagnosis of syphilis by external symptoms is difficult for a non-professional, since secondary recurrent syphilis can be similar to almost any skin disease.
Lenticular rash in secondary recurrent syphilis

Pustular (pustular) rash with secondary syphilis
Pustular syphilis is a sign of a malignant ongoing disease. More often observed during the period of secondary fresh syphilis, but one of the varieties - ecthymatous- characteristic of secondary exacerbated syphilis. Ecthymes appear in debilitated patients approximately 5-6 months from the time of infection. They are located asymmetrically, usually on the shins in front, less often on the skin of the trunk and face. Syphilides number 5 - 10, rounded, about 3 cm in diameter, with a deep abscess in the center. A gray-black crust forms above the pustule, below it there is an ulcer with necrotic masses and dense, steep edges: the shape of the ecthyma resembles funnels. After that, deep dark scars remain, which eventually lose their pigmentation and become white with a pearly tint.

Necrotic ulcers from pustular syphilides, secondary-tertiary stages of syphilis
Ecthymes can go into rupioid syphilides, with the spread of ulceration and disintegration of tissues outward and deep. Centered rupees multilayer "oyster" crusts are formed, surrounded by an annular ulcer; outside - a dense roller of a reddish-violet color. Ecthymas and rupees are not contagious, during this period all serological tests for syphilis are negative.
Acne syphilides - abscesses 1-2 mm in size, localized in the hair follicles or inside the sebaceous glands. Rashes are localized on the back, chest, limbs; heal with the formation of small pigmented scars. Smallpox syphilides are not associated with hair follicles, they are lentil-shaped. Dense at the base, copper-red color. syphilis similar to impetigo- purulent inflammation of the skin. It occurs on the face and scalp, pustules are 5-7 mm in size.
Other manifestations of secondary syphilis
Syphilitic warts similar to warts with a wide base, often formed in the fold between the buttocks and in the anus, under the armpits and between the toes, near the navel. In women - under the breast, in men - near the root of the penis and on the scrotum.
Pigmentary syphilide(spotted leukoderma literally translated from Latin - "white skin"). White spots up to 1 cm in size appear on the pigmented surface, which are located on the neck, for which they received the romantic name "Venus' necklace". Leukoderma is determined after 5-6 months. after infection with syphilis. Possible localization on the back and lower back, abdomen, arms, on the front edge of the armpits. The spots are not painful, do not peel off and do not become inflamed; remain unchanged for a long time, even after specific treatment for syphilis.
Syphilitic alopecia(alopecia). Hair loss can be localized or cover large areas of the scalp and body. Small foci of incomplete alopecia are often observed on the head, with rounded irregular outlines, mainly located on the back of the head and temples. On the face, first of all, attention is paid to the eyebrows: with syphilis, the hairs first fall out from their inner part, located closer to the nose. These signs marked the beginning of visual diagnostics and became known as " omnibus syndrome". In the later stages of syphilis, a person loses absolutely all hair, even vellus.
Syphilitic angina- the result of damage to the mucous membrane of the throat. Small (0.5 cm) spotty syphilides appear on the tonsils and soft palate, they are visible as bluish-red foci of sharp outlines; grow up to 2 cm, merge and form plaques. The color in the center quickly changes, acquiring a grayish-white opal shade; the edges become scalloped, but retain the density and original color. Syphilides can cause pain during swallowing, a feeling of dryness and constant tickling in the throat. Occur along with a papular rash during the period of fresh secondary syphilis, or as an independent sign of secondary exacerbated syphilis.

manifestations of syphilis on the lips (chancre) and tongue
Syphilides on the tongue, in the corners of the mouth due to constant irritation, they grow and rise above the mucous membranes and healthy skin, dense, the surface is grayish in color. May become covered with erosions or ulcerate, causing pain. papular syphilis on the vocal cords initially manifested by hoarseness of voice, later a complete loss of voice is possible - aphonia.
syphilitic nail damage(onychia and paronychia): papules are localized under the bed and at the base of the nail, visible as reddish-brown spots. Then the nail plate above them becomes whitish and brittle, begins to crumble. With purulent syphilis, severe pain is felt, the nail moves away from the bed. Subsequently, depressions in the form of craters form at the base, the nail thickens three or four times compared to the norm.
Tertiary period of syphilis
Tertiary syphilis is manifested by focal destruction of the mucous membranes and skin, any parenchymal or hollow organs, large joints, and the nervous system. Main features - papular rashes and gummas degrading with rough scarring. Tertiary syphilis is rarely defined, develops within 5-15 years if no treatment has been carried out. Asymptomatic period ( latent syphilis) can last for more than two decades, is only diagnosed by serological tests between secondary and tertiary syphilis.

what can affect advanced syphilis
Papular elements dense and rounded, up to 1 cm in size. They are located in the depths of the skin, which becomes bluish-red above the papules. Papules appear at different times, grouped into arcs, rings, elongated garlands. Typical for tertiary syphilis focus rashes: each element is determined separately and in its stage of development. The disintegration of papular syphilomas begins from the center of the tubercle: rounded ulcers appear, the edges are sheer, there is necrosis at the bottom, and a dense roller along the periphery. After healing, small dense scars with a pigmented border remain.
Serpinginous syphilides are grouped papules that are in different stages of development and spread to large areas of the skin. New formations appear along the periphery, merge with the old ones, which at this time already ulcerate and scar. The sickle-shaped process seems to crawl to healthy areas of the skin, leaving a trail of mosaic scars and pigmentation foci. Numerous tubercular seals create a colorful picture true polymorphic rash, which is visible in the late periods of syphilis: different sizes, different morphological stages of the same elements - papules.

syphilitic gumma on the face
syphilitic gumma. At first it is a dense knot, which is located in the depth of the skin or under it, mobile, up to 1.5 cm in size, painless. After 2-4 weeks, the gumma is fixed relative to the skin and rises above it as a rounded dark red tumor. A softening appears in the center, then a hole forms and a sticky mass comes out. In place of the gumma, a deep ulcer is formed, which can grow along the periphery and spread along the arc ( serping gummy syphilis), and in the "old" areas there is healing with the appearance of retracted scars, and in the new ones - ulceration.
More often syphilitic gummas are located alone and are localized on the face, near the joints, on the legs in front. Closely located syphilides can merge to form gum pad and turn into impressive ulcers with compacted, uneven edges. In debilitated patients, with a combination of syphilis with HIV, gonorrhea, viral hepatitis, gum may grow in depth - mutilating or irradiating gumma. They disfigure the appearance, can even lead to the loss of an eye, testicle, perforation and death of the nose.
gummas in the mouth and inside the nose disintegrate with destruction of the palate, tongue and nasal septum. Defects appear: fistulas between the cavities of the nose and mouth (nasal voice, food can get into the nose), narrowing of the orifice(difficulty swallowing), cosmetic problems - failed saddle nose. Language first increases and becomes bumpy, after scarring it wrinkles, it becomes difficult for the patient to talk.
Visceral and neurosyphilis
At visceral tertiary syphilis, organ damage is observed, with the development neurosyphilis- symptoms from the central nervous system (CNS). During the secondary period, early syphilis of the central nervous system appears; it affects the brain, its vessels and membranes ( meningitis And meningoencephalitis). In the tertiary period, manifestations of late neurosyphilis are observed, these include atrophy of the optic nerve, dorsal tabes and progressive paralysis.

Dorsal tabes– Manifestation of syphilis of the spinal cord: the patient literally does not feel the ground under his feet and cannot walk with his eyes closed.
progressive paralysis It manifests itself as much as one and a half to two decades after the onset of the disease. The main symptoms are mental disorders, from irritability and memory impairment to delusional states and dementia.
optic nerve atrophy: with syphilis, one side is first affected, a little later vision deteriorates in the other eye.
Gummas affecting the head brain are rarely observed. According to clinical signs, they are similar to tumors and are expressed by symptoms of brain compression - increased intracranial pressure, rare pulse, nausea and vomiting, prolonged headaches.

bone destruction in syphilis
Among the visceral forms predominates syphilis of the heart and blood vessels(up to 94% of cases). Syphilitic mesaortitis- inflammation of the muscular wall of the ascending and thoracic aorta. It often occurs in men, accompanied by an expansion of the artery and phenomena of cerebral ischemia (dizziness and fainting after exercise).
Syphilis liver(6%) leads to the development of hepatitis and liver failure. The total proportion of syphilis of the stomach and intestines, kidneys, endocrine glands and lungs does not exceed 2%. Bones and joints: arthritis, osteomyelitis and osteoporosis, the consequences of syphilis - irreversible deformities and blockade of joint mobility.
congenital syphilis
Syphilis can be transmitted during pregnancy, from an infected mother to her baby at 10-16 weeks. Frequent complications are spontaneous abortions and fetal death before delivery. Congenital syphilis according to time criteria and symptoms is divided into early and late.
early congenital syphilis
 Children with a clear lack of weight, with wrinkled and flabby skin, resemble little old people. Deformation skull and its facial part ("Olympic forehead") is often combined with dropsy of the brain, meningitis. Present keratitis- inflammation of the cornea of the eyes, loss of eyelashes and eyebrows is visible. Children aged 1-2 years develop syphilitic rash, localized around the genitals, anus, on the face and mucous membranes of the throat, mouth, nose. A healing rash forms scarring: scars that look like white rays around the mouth are a sign of congenital lues.
Children with a clear lack of weight, with wrinkled and flabby skin, resemble little old people. Deformation skull and its facial part ("Olympic forehead") is often combined with dropsy of the brain, meningitis. Present keratitis- inflammation of the cornea of the eyes, loss of eyelashes and eyebrows is visible. Children aged 1-2 years develop syphilitic rash, localized around the genitals, anus, on the face and mucous membranes of the throat, mouth, nose. A healing rash forms scarring: scars that look like white rays around the mouth are a sign of congenital lues.
syphilitic pemphigus- a rash of vesicles, observed in a newborn a few hours or days after birth. It is localized on the palms, the skin of the feet, on the folds of the forearms - from the hands to the elbows, on the trunk.
Rhinitis, the causes of its occurrence are syphilides of the nasal mucosa. Small purulent discharges appear, forming crusts around the nostrils. Breathing through the nose becomes problematic, the child is forced to breathe only through the mouth.
Osteochondritis, periostitis- inflammation and destruction of bones, periosteum, cartilage. It is most often found on the legs and arms. There is local swelling, pain and muscle tension; then paralysis develops. During early congenital syphilis, destruction of the skeletal system is diagnosed in 80% of cases.
late congenital syphilis
late form manifests itself in the age period of 10-16 years. The main symptoms are visual impairment with the possible development of complete blindness, inflammation of the inner ear (labyrinthitis), followed by deafness. Skin and visceral gummas are complicated by functional disorders of organs and scars that disfigure the appearance. Deformation of teeth, bones: the edges of the upper incisors have semilunar notches, the legs are bent, due to the destruction of the septum, the nose is deformed (saddle-shaped). Frequent problems with the endocrine system. The main manifestations of neurosyphilis are tabes dorsalis, epilepsy, speech disorders, progressive paralysis.
Congenital syphilis is characterized by a triad of signs Getchinson:
- teeth with an arched edge;
- cloudy cornea and photophobia;
- labyrinthitis - tinnitus, loss of orientation in space, hearing loss.
How is syphilis diagnosed?
Diagnosis of syphilis is based on clinical manifestations characteristic of different forms and stages of the disease, and laboratory tests. Blood take to conduct a serological (serum) test for syphilis. To neutralize teponems in the human body, specific proteins are produced - which are determined in the blood serum of an infected or sick person with syphilis.
RW analysis blood test (Wassermann reaction) is considered obsolete. It can often be false positive in tuberculosis, tumors, malaria, systemic diseases and viral infections. Among women- after childbirth, during pregnancy, menstruation. The use of alcohol, fatty foods, and certain drugs before donating blood for RW can also be the cause of an unreliable interpretation of the analysis for syphilis.
It is based on the ability of antibodies (immunoglobulins IgM and IgG) present in the blood of those infected with syphilis to interact with antigen proteins. If the reaction has passed - analysis positive, that is, the causative agents of syphilis are found in the body of this person. Negative ELISA - no antibodies to treponema, no disease or infection.

The method is highly sensitive, applicable for the diagnosis of latent - hidden forms - syphilis and checking people who have been in contact with the patient. positive even before the first signs of syphilis appear (according to IgM - from the end of the incubation period), and can be determined after the complete disappearance of treponema from the body (according to IgG). ELISA for the VRDL antigen, which appears during alteration (“damage”) of cells due to syphilis, is used to monitor the effectiveness of treatment regimens.
RPHA (passive hemagglutination reaction)- bonding of erythrocytes that have antigens on their surface Treponema pallidum with specific antibody proteins. RPHA is positive in case of illness or infection with syphilis. Remains positive throughout the patient's life even after complete recovery. To exclude a false positive response, RPHA is supplemented with ELISA and PCR tests.
Direct Methods laboratory tests help to identify the causative microorganism, and not antibodies to it. With the help, you can determine the DNA of treponema in the biomaterial. Microscopy a smear from a serous discharge of a syphilitic rash - a technique for visual detection of treponema.
Treatment and prevention
Treatment of syphilis is carried out taking into account the clinical stages of the disease and the susceptibility of patients to drugs. Seronegative early syphilis is treated more easily, with late variants of the disease, even the most modern therapy is not able to eliminate consequences of syphilis- scars, organ dysfunction, bone deformities and disorders of the nervous system.

There are two main methods of treatment for syphilis: continuous(permanent) and intermittent(course). In the process, control tests of urine and blood are required, the well-being of patients and the work of organ systems are monitored. Preference is given to complex therapy, which includes:
- Antibiotics(specific treatment of syphilis);
- Restorative(immunomodulators, proteolytic enzymes, vitamin-mineral complexes);
- Symptomatic drugs (painkillers, anti-inflammatory, hepatoprotectors).
Assign nutrition with an increase in the proportion of complete proteins and a limited amount of fat, reduce physical activity. Prohibit sex, smoking and alcohol.
Psychotrauma, stress and insomnia adversely affect the treatment of syphilis.
Patients with early latent and contagious syphilis undergo the first course of 14-25 days in the clinic, then they are treated on an outpatient basis. Treat syphilis with penicillin antibiotics- intramuscularly injected sodium or potassium salt of benzylpenicillin, bicillins 1-5, phenoxymethylpenicillin. A single dose is calculated according to the weight of the patient; if there are inflammatory signs in the cerebrospinal fluid (spinal fluid), then the dosage is increased by 20%. The duration of the entire course is determined according to the stage and severity of the disease.
permanent method: the starting course for seronegative primary syphilis will take 40-68 days; seropositive 76-125; secondary fresh syphilis 100-157.
course treatment: tetracyclines are added to penicillins ( doxycycline) or macrolides ( azithromycin), preparations based on bismuth - bismovrol, biyoquinol, and iodine - potassium or sodium iodide, calcium iodine. Cyanocobalamin (vit. B-12) and solution coamide enhance the action of penicillin, increase the concentration of the antibiotic in the blood. Injections of pyrogenal or prodigiosan, autohemotherapy, aloe are used as means of non-specific therapy for syphilis, which increase resistance to infection.
During pregnancy, syphilis is treated only with penicillin antibiotics, without drugs with bismuth salts.
Proactive(preventive) treatment: carried out as in the case of seronegative primary syphilis, if sexual contact with the infected was 2-16 weeks ago. One course of penicillin is used for medical prophylaxis of syphilis if the contact was no more than 2 weeks ago.
Prevention of syphilis- Identification of the infected and the range of their sexual partners, preventive treatment and personal hygiene after sexual intercourse. Surveys for syphilis of people belonging to risk groups - physicians, teachers, staff of kindergartens and catering establishments.
Video: syphilis in the program “Live healthy!”
Video: syphilis in the encyclopedia of STDs









Chantilly Castle - the second in France after Versailles Chantilly Castle how to get from Paris
Amusement park "The Land of Legends Theme Park" in Turkey
Holy places in Greece. Greece Orthodox. Pilgrimage to the feast of St. Nicholas
Picodi: All discounts in one place!
How to get to Dolmabahce Palace