The human papillomavirus (HPV) belongs to subgroup A of the papovirus family (Papoviridae).
HPV has a spherical shape with a diameter of up to 55 nm. A capsid with a cubic type of symmetry, forms a geometric figure - an icosahedron, built of 72 capsomeres. The HPV genome is presented as a cyclically closed double-stranded DNA with a molecular weight of 3-5 mD. Isolated DNA has infectious and transforming properties. One of the DNA strands is considered coding and contains information about the structure of viral proteins. One coding chain contains up to 10 open reading frames, which, depending on the location in the genome, are divided into early and late ones.
The HPV virion contains two layers of structural proteins, denoted by the letter E. The early region includes the E1, E2 genes, which are responsible for viral replication. The E4 gene is involved in the maturation of viral particles. HPVs of high oncogenic risk encode the synthesis of capsid proteins E5, E6 and E7, which are involved in malignant transformation. E6/p53 and E7/Rv1 interactions lead to cell cycle distortion with loss of control over DNA repair and replication. Thus, the polymorphism of the gene encoding p53 is a genetic predisposition for the active development of HPV with subsequent cell malignancy. The late genes L1 and L2 encode proteins of the viral capsid.

Internal proteins associated with DNA are cellular histones, and capsid proteins are type-specific antigens. HPV reproduction occurs in the nuclei of cells, where viral DNA is present in the form of an episome. This is the first feature that distinguishes HPV from other oncogenic DNA-containing viruses that can integrate their genome into the DNA of a transformed cell.
The second feature of HPV is that the viral gene responsible for cellular DNA replication can be transcribed, causing the host cell to divide along with HPV, which leads to a productive type of inflammation, regardless of the ability of the host cell to regulate the expression of the viral genome.
The HPV genome contains hormonal receptors for progesterone and glucocorticoid hormones, which explains the dependence of the course of PVI on the hormonal homeostasis of a woman.

Currently, more than 120 types of papillomaviruses have been identified, of which 70 types are described in detail. It has been established that papillomaviruses have type and tissue specificity, which means that each type is able to infect the tissue characteristic of its localization. For example, HPV type 1 causes plantar warts, HPV type 2 causes common warts, HPV type 3 causes flat warts, and so on.
As a result of large-scale screening studies (De Villiers E.M., 1994), he identified 34 types of papillomas, which are characterized by anogenital localization.
Papillomaviruses are differentiated according to the degree of malignancy into high-risk, low-risk and practically non-oncogenic viruses that affect the skin and other mucous membranes.
|
Types of HPV found in various lesions of the skin and mucous membranes (Villiers E.M., 1989) |
|
| Clinical manifestations | HPV types |
| Skin lesions | |
| plantar warts | 1,2,4 |
| common warts | 2, 4, 26, 27, 29, 57 |
| flat warts | 3, 10, 28, 49 |
| Butcher's warts | 7 |
| Wart epidermodysplasia | 5, 8, 9, 10, 12, 15, 19, 36 |
| Non-warty skin lesions | 37, 38 |
| Lesions of the mucous membranes of the genitals | |
| Condylomata accuminata | 6, 11, 42-44, 54 |
| Non-condylomatous lesions | 6, 11, 16, 18, 30, 31, 33, 34, 35, 39, 40, 42, 43, 51, 52, 55, 56, 57-59, 61, 64, 67-70 |
| Carcinoma | 16, 18, 31, 33, 35, 39, 45, 51, 52, 54, 56, 66, 68 |
| Mucosal lesions other than the genitals | |
| Papilloma of the larynx | 6, 11, 30 |
| Carcinoma of the neck, tongue | 2, 6, 11, 16, 18, 30 |
According to the results of the studies, papillomaviruses were divided into groups of "high" and "low" risk of tumor transformation of HPV-infected epithelium.
Papillomavirus types 16 and 18 are most often associated with cervical cancer in 67 - 93% of cases. Thus, HPV type 16 is most often detected in squamous cell carcinoma, and HPV type 18 is found in glandular cancer tissue. HPV type 16 is detected in 50-70% of cervical cancer cases, type 18 is detected in 10-20%, other types of high-risk HPV are detected much less frequently.
It is known that papillomavirus infection alone is not enough to induce tumor growth, and indicate the role of cofactors (immunodeficiency, smoking, pregnancy, menopause, etc.) in HPV-dependent carcinogenesis. Thus, infection with the papilloma virus is a necessary but not decisive factor in the development of a malignant process.
Anya 2019-12-24 20:14:31
Hello, I have 6.3 Lg VPL 10 ^ 5 cells, please tell me what does this mean?

Good afternoon. This means that the amount of HPV virus in your body is in a clinically significant concentration. This condition requires treatment. For systemic antiviral therapy, the drug Panaviril has proven itself well - intravenous injections No. 5 or rectal suppositories No. 10, one at a time. If there are clinical manifestations, papillomas or changes in the cervix. then it is necessary to remove pathological elements and use Panavir gel locally. Thank you.
Igor 2019-12-19 17:15:12
I have HPV HPV 56 (relative X/KBM 4.6 HPV type 56 (absolute, Lg, copies/sample) 6.5 HPV type 66 (relative X/KBM * 10^5) 3.7 HPV type 66 (absolute, Lg, copies/sample) 5.6 What does it mean, i.e. how critical is it I am a man

Korobkova Elena Vladimirovna Obstetrician-gynecologist answers:
Good afternoon. These types of HPV are highly oncogenic. According to the results of the analyzes, in a clinically significant concentration. You must understand that you are a carrier of this infection and can pass it on to your sexual partner. Because the concentration of the virus is high. You'd better take a course of antiviral therapy - even in the absence of clinical symptoms, the presence of the virus will help reduce immunity, and given the high oncogenicity of the virus, the consequences can be serious. As an antiviral therapy, the antiviral drug Panavir has proven itself well, which also corrects the immune system. For systemic therapy - intravenous administration of the drug 5 ml 1-3-5-8-11 days of treatment, locally to prevent infection Panavir Intim spray, also do not forget about barrier protection during sexual intercourse. Thanks.
Alla 2019-12-08 22:19:39
HPV 53 +++ ???

Korobkova Elena Vladimirovna Obstetrician-gynecologist answers:
This analysis shows the presence of human papillomavirus type 53 in a significant concentration. Thanks.
Julia 2019-11-28 12:13:57
Hello. I have been diagnosed with HPV 2.61 what does this mean?
The human papillomavirus (HPV) can exist in the body for a long time, manifesting itself only when the immune defense is weakened. To identify the infection, various types of tests are used to identify the disease at an early stage and carry out effective treatment.
Referrals for testing for suspected HPV are issued by dermatologists, gynecologists or urologists. Modern medicine can not only detect the presence of a virus in the human body, but also determine whether it belongs to a certain type of strain (dangerous or harmless).
For these purposes, specialists resort to the following methods:
- quantitative analysis.
- PCR (polymer chain reaction).
- Cytology.
- ELISA (enzymatic immunoassay).
- Histology.
Quantitative Analysis, or Digene test, is based on the principle of hybrid DNA capture. For analysis, biological material is taken from the affected area (by scraping or smear). The technique allows you to determine the stage of development of the pathology and the type of strain. Results are provided within 7-10 days.
 PCR study
PCR study PCR- a widely used type of analysis to determine papillomavirus and other common infections. This type of research involves working with liquid media - urine, blood, saliva, amniotic fluid, secretions from the genital tract. This test is highly accurate and expensive. Determines the presence of HPV by the presence of virus DNA in the body already during the day.
For information on how PCR analysis is performed in men, see our video:
 Linked immunosorbent assay
Linked immunosorbent assay Linked immunosorbent assay allows you to identify the quantitative and qualitative content of antibodies in the biomaterial. Traditionally, venous blood donation is prescribed for ELISA. Other environments of the body can also be investigated:
- cerebrospinal fluid;
- urethral discharge;
- cervical mucus.
A response with the results of the examination is prepared and issued to the patient within 3 days.
 Cytological examination
Cytological examination Cytology, also called pap test or pap smear - the study of body cells using a microscope. As a material for analysis, urethral discharge in men and the contents of the urogenital canal in women are used. To obtain highly accurate results, the material must be taken simultaneously from several tissue sites.
How is a Pap test performed in women:
The method allows to determine the presence of benign and malignant strains of papillomavirus. The reliability of the results is 95%. You can get them in 1-2 days, in urgent situations - within one hour.
 Histological examination results
Histological examination results Histology- taking a scraping from the site of papilloma formation for further microscopic examination. This informative diagnostic method allows you to detect the presence of cancer cells with 100% reliability and prevent the development of oncology. Analysis is recommended for patients with papillomas that have changed shape, color, size.
To conduct a histological examination, a biopsy is performed - tissue sampling, which is further processed with medical solutions and studied under a microscope. The answer is issued after 1-2 weeks from the date of taking the biomaterial.
How to prepare for the procedure
To get the most accurate HPV test results, patients will need to follow certain rules. Both women and men are advised to:
- At least 2 weeks before the test, do not take antibiotics and antibacterial drugs.
- On the eve of the delivery of the biomaterial, do not use antiseptic personal hygiene products.
- 2 days before the study, refrain from sexual intercourse.
- Within 3 days prior to the delivery of biological media, do not drink alcoholic beverages.
- Do not urinate 3 hours before the procedure.
Women should not be examined 5 days before and during the same period after menstruation. On the eve of the examination, douching is not recommended. Blood donation should be done in the morning on an empty stomach.
Deciphering - what the results mean
The interpretation of HPV tests is traditionally carried out by a specialist who has the necessary medical knowledge. Simplified, they can be interpreted as follows:
| Quantitative results | Less than 3 units of virus per 10⁵ cells is a safe concentration (norm). |
| 3-5 units per 10⁵ cells - a significant concentration (there is a possibility of neoplasms). | |
| More than 5 units per 10⁵ cells - high concentration (increased risk of developing a malignant process). | |
| PCR results | DNA was not detected - there is no papillomavirus in the patient's blood. |
| Lg less than 3 - insignificant presence (within the normal range). | |
| Lg 3-5 is a significant amount. | |
| Lg 5 or more is an indicator of a high concentration of the virus in the blood. | |
| Cytology | Numbers from 1 to 2 - acceptable rate. |
| Number 3 - additional tests are required. | |
| From 4 to 5 - the presence of malignant cells. |
After screening for human papillomavirus by ELISA, the following results can be obtained:
- IgA - presence of fresh infection;
- IgM - recent infection;
- IgG - long-term presence of the pathogen in the body.
The results of the histological examination are provided in the form of a written conclusion. In the form, you can find an explanation - there are or are no deviations in cells and tissues. Information about the results of the examination is provided in Latin using special medical terminology.
It is important to be aware of the possibility of obtaining erroneous test results. The reasons may be the use of dirty test tubes, illiterate sampling of biomaterial, improper preparation of the patient for the procedure.
A negative response after passing the tests does not become a guarantee of the complete absence of the virus. Such a result can be obtained at a low concentration of the pathogen, with which the body manages to cope on its own.
When receiving incorrect data, in most cases, specialists prescribe a second examination.
This is the amount of HPV per unit volume of blood. This term is used in relation to more dangerous pathogens, such as HIV or hepatitis. The viral load indicator is directly related to the severity of the disease and the risk of complications. It also shows how effectively drugs fight papillomavirus.
There are groups of patients for whom quantitative analysis is extremely important. These include:
- couples planning a pregnancy;
- women with burdened gynecological history;
- people with weakened immune systems;
- patients suffering from multiple papillomatosis of the skin and mucous membranes;
- children born to infected mothers.
In all cases, there is a high risk of HPV complications and the determination of the viral load helps to avoid serious pathologies. The examination is not mandatory, but patients who receive a referral for it should not ignore the doctor's instructions.
Papillomavirus is quite widespread, but most often its negative impact is limited to ugly growths on the skin. It multiplies rather slowly in the cells of the epidermis and mucous membranes, causing minor changes in their metabolism.
According to the degree of danger, viruses of high (cause cancer with a proven frequency) and low oncogenic risk are distinguished. Most types of the virus belong to the second group, but for them the danger of a tumor is not excluded.
Conditions in which the risk of a malignant tumor is maximum:
- warts on areas of the body that are often injured;
- genital warts on the genital tract;
- manifestation of papillomatosis in newborns;
- erosion of the cervix (precancerous condition).
Another reason to treat HPV is that the disease is contagious, and even if the patient does not experience discomfort, it is a source of infection for those with whom the patient lives in the same apartment and for sexual partners.
- What is the human papillomavirus?
- Types of HPV
- Training
- Women
- men
- Research methods
- Rules for donating blood for HPV
- How to pass urine for HPV
- Features of testing women
- What tests should be done for men
- Deciphering quantitative analysis
- Where can it be done and at what cost
- Questions and answers
- Reviews
For many of us, a very urgent problem is how a person is infected with a virus of the papillomavirus group. Doctors say that at least 13% of adults are infected with this virus, of which 40-60% are young men and women who are able to give birth to children.
Human papillomavirus is a type of virus that is often found and can cause various diseases in any particular person and can cause various problems. Some of them can lead to big problems, such as damage to the genitals.
The most popular type is the common wart. These are small round growths that have a convex shape that grow on the arms and face. They are not capable of causing cancer, but bring a lot of inconvenience. How a person perceives a wart infection depends on the person's immunity.

The most dangerous type is the genital wart. They look like pointed or flat warts and grow only on the mucous membrane of the genital organs. Genital warts are almost 100% cancerous.
Types of HPV oncogenic and non-oncogenic
(according to research by McConcl DJ, 1991; LorinczA. T., 1992; Bosch E X. et al., 2002; Kozlova V. I., Pukhner A. F., 2003; Syrjanen S., 2003; Shakhova N. M. et al., 2006;).
- Non-oncogenic HPV types, that is, never causing cancer: 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 10, 28, 49
- Low-oncogenic HPV types (very rarely cause cancer): 6, 11, 13, 32, 34, 40, 41, 42, 43, 44, 51, 72
- Types of average oncogenic risk (percentage of cancerous degeneration is average): 26, 30, 35, 52, 53, 56, 58, 65
- Highly oncogenic types of HPV (the risk of cancerous degeneration is high): 16, 18, 31, 33, 39, 45, 50, 59, 61, 62, 64, 68, 70, 73. This is especially important in women.
By the way, sometimes the classification changes. For example, HPV type 58 in women is no longer highly oncogenic. It began to be attributed to types with an average oncogenicity.
- In 73-90% of cases with cervical cancer, HPV types 16, 18 and 45 are found
- In 77-93% of cases with cervical cancer, HPV types 16, 18, 45, 31 and 59 are found
- In 80-94% of cases with cervical cancer, HPV types 16, 18, 45, 31, 33 and 59 are found
- Precancerous conditions in urology and gynecology are often combined with 61, 62, 68, 70, 73 HPV types.
- human papillomavirus 16 (written HPV 16) - 50%
- human papillomavirus 18 (HPV 18) - 10%
HPV type 16 in women
Human papillomavirus is one of the most common and popular diseases in the world, which affects millions of people. The virus mutates quite quickly, and today scientists have established about 100 types of papillomas, of which only 80 have been thoroughly studied.
Some of their types are not dangerous for humans, while others are 16, 18, 31, 33, 35, 39, 45, etc. can lead to cancer and other serious consequences. Type 16 and 18 papillomas provoke oncological diseases of the small pelvis in women.
HPV types 16 and 18 mean an extremely high risk of oncological diseases such as dysplasia, cancer of the cervix, genital organs, and vagina. It is detected in many women during gynecological screening, which makes it clear to the attending physician about the possible threats and risks of oncology.
The detection of these types of virus does not yet mean cancer itself, but only indicates a high possibility of its occurrence and progression. The papilloma virus of these types progresses on the mucous membranes and in the deep layer of epithelial cells of the genital organs, the cervical canal.
These types of viruses are dangerous mainly for women's reproductive health, and for men, papilloma types 16 and 18 are not such a dangerous disease, since they are most often only transient carriers (short-term carriage that does not last long in the body), therefore, with a joint examination partners or spouses, a similar virus is usually not found in a man, but he probably once was a carrier of the disease.
Causes and symptoms
The main cause of HPV incidence is the onset of sexual activity. Frequent casual relationships, change of partners, unprotected sexual contacts are the main provocateurs of the human papillomavirus.
The domestic route of infection is extremely rare, and some studies deny it altogether, but this cannot be written off. Such infection is possible through certain personal hygiene items (towels, bedding), open wounds and cracks, where the virus easily enters, and also as a result of contact with them by a healthy person.
Another way of infection occurs at the time of childbirth of a woman. When a baby's fetus passes through an infected birth canal, it can become infected with the virus. In a newborn, as a rule, warts form in the throat and on the skin, but all this is curable, and the child will soon be healthy.
Symptoms of HPV types 16 and 18, as a rule, do not manifest themselves for a long time, and the woman does not feel any symptoms at all. When immunity weakens, and the body's defenses decrease, rashes may appear on the skin of the genital organs. This is how a disease called "bovenoid papulosis" manifests itself. It is caused by a type 16 virus.
The disease responds well to treatment, but in certain cases it can turn into skin cancer. For HPV types 16 and 18, it is unusual, but at the same time, the formation of genital warts, warts, or some other growths on the skin and mucous genital organs is not excluded.
Diagnostics
Diagnosis of the virus and oncological changes, as a rule, is not difficult, and the presence of the disease can be detected by several tests and tests:
- PCR analysis for genital infections, where the patient can even determine the type of papillomavirus, as well as its presence or absence;
- Extended colposcopy with biopsy of the cervix, where atypical cancer cells are examined (histology);
- Cytological analysis (PAP test), which determines the presence / absence of cancerous or precancerous cells in the genital tract and cervix;
- DNA analysis for HPV by the “hybrid capture” method, where oncogenic HPV (types 16 and 18) is detected in the epithelial cells of the vagina and cervix.
All these studies mentioned above allow the doctor to establish a complete clinical picture and identify all the risks of the disease in order to start treatment or conduct other examinations on time.
According to statistics, about 75-80% of women at one time or another were carriers of HPV types 16 and 18, but a healthy immunity of the body can most often cope with the virus in time, and especially at a young age, but often HPV lingers in the body for a long time, which leads to unpredictable consequences.
In any case, the doctor conducts a series of tests to accurately know the patient's condition, because it is impossible to immediately establish a diagnosis or the presence of a virus from one analysis, as the results are often contradictory.
It should be noted right away that the identification of HPV types 16 and 18 during analyzes and tests does not mean a death sentence or certainly oncology. If, apart from the presence of an oncogenic virus, no other pathology is detected, then further treatment and constant monitoring by the attending physician is required.
In this case, a woman will need to take tests regularly or once a year, undergo colposcopy and cytological studies in order to identify all changes and malignant processes at an early stage.
Virus type 16 and 18 very often leads to cervical dysplasia or its precancerous condition, which is divided into 3 stages. Without proper treatment, after about 10 years, this disease mutates into cervical cancer or the third stage of dysplasia.
Firstly, do not panic, as you should immediately contact a gynecologist who will conduct an examination and further treatment or conduct additional tests, since PCR tests often have false positive results, so the doctor will double-check the diagnosis anyway.

And then you need to follow the further instructions and recommendations of the doctor, who will then prescribe treatment and tell you what to do next and whether to sound the alarm. If a patient finds warts or other genital warts on her skin, then type 16 or type 18 virus, as a rule, has nothing to do with it, since viruses of other types cause similar clinical manifestations.
They generally have low oncogenicity and do not lead to the formation of malignant tumors. If a woman is pregnant, then the type 16 and 18 virus is not an obstacle to the normal bearing and birth of a child, unless the virus has caused serious changes in the pelvic organs.
Treatment
It is believed that viruses of the 16th and 18th type are treatable and can leave the human body forever, but there are many studies stating the opposite. It should be noted right away that there is no single treatment regimen for any type of HPV. In any case, the doctor independently selects therapy or surgery for treatment.
Many of these methods have been criticized more than once, since the virus still penetrated into the cells of the pelvic organs, or the patients relapsed again.
There are a lot of drugs that can fight the virus, but the doctor must take into account the specifics of the patient's disease, because many of these drugs are simply not advisable to take, since they were originally designed to fight only the external manifestations of the virus.
Basically, doctors use the following treatment methods:
- drug immunostimulating therapy, which strengthens the immune system itself and does not allow the virus to mutate and penetrate into the deep layers of epithelial cells and tissues. These drugs stimulate the production of interferon, which helps fight viruses.
- HPV vaccination certain drugs that produce special antibodies that protect the body from the virus mutating into cancer. Vaccination is used to prevent oncogenic types of HPV, and especially types 16 and 18;
- Antiviral therapy, which is specially represented by drugs that cauterize warts and warts;
- Anti-inflammatory drugs if there is still an inflammatory focus of the urogenital tract;
- Destructive technique, with the help of which the foci of pathology are excised;
- Surgical technique(amputation of the cervix in case of cancer of the initial stages, removal of the tumor along with part of the uterus or the uterus itself, etc.);
- Laser therapy;
- Electrocoagulation;
- Cytostatic drugs for the growth of malignant cells;
- Chemotherapy in case of cancer;
- Radiation therapy;
- Other drugs.
The most popular in the treatment of the virus are immunostimulating drugs that activate the production of interferon, which is necessary to fight any viruses and infections in the body. At the moment, doctors prescribe the following medications to maintain immunity: Viferon, Altevir, Genferon, Intron A, Kipferon, Wellferon, Cycloferon, etc.

All of them have the same effectiveness and have proven themselves in the treatment of HPV of all types. Doctors also use immunotropic drugs, which use various immune activators to treat and prevent all types of HPV. These drugs include Gepon and Isoprinosine.
These are very serious and strong drugs that are used in any immunodeficiency states. Gepon has very positive reviews, and isoprinosine is no less effective in the treatment, but they all have serious side effects.
There are antiviral agents (Solcoderm) on the pharmaceutical market, which are used specifically for the treatment of papillomas, but it should be noted that they are effective only with the external manifestation of the virus, when warts and condylomas appear on the skin. Such drugs simply “cauterize” them, and warts and other growths soon disappear.
The virus of types 16 and 18 usually does not manifest itself outwardly, therefore, in this case, the use of such drugs is considered inappropriate.
Medicines for vaccination against oncogenic types of HPV have received special recognition among the medical community. Vaccination is carried out to prevent cervical cancer and other oncology.
Symptoms and clinic
Symptoms and manifestations of HPV infection are warts, papillomas, dysplasia and cervical cancer. Different types of viruses - different manifestations in patients.
1. Warts
They are caused by the following types of HPV - 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 10, 28, 49.
- youthful (or flat) warts - are caused by types 3 and 5 of the virus. These are small flat elevations on the skin, occur mainly in children. This type of wart is described in detail here.
- spines (or plantar warts) - caused by types 1 and 2 of the virus (you can read more about them here).
- vulgar warts on the fingers - caused by type 2 viruses (detailed article about them here).
These are flat warts on the face.
These are vulgar warts on the arm

Localization: on the genitals, in the anus, in the oral cavity and on the lips (types - 6, 11, 13, 16, 18, 31, 35). Read more about these warts.
These are genital warts
The main mechanism of transmission of this disease in adults is sexual. Very rarely, a contact route of transmission can occur - through common toilet items, through a dirty toilet rim, using a shared bathroom, in a bathhouse, etc.
If a child is born to a mother with genital warts, the child is also infected and may subsequently also develop genital warts or papillomatosis of the larynx and respiratory tract (discussed above).
This is papillomatosis of the larynx
Small, flat wart plaques (somewhat similar to flat warts) appear around the genitals. It often develops in men who constantly change sexual partners. Called by types - 16, 18, 31, 33, 42, 48, 51, 54.
This is bowenoid papulosis.
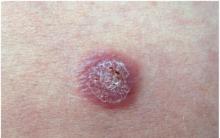
More formidable clinical manifestations of HPV infection in women are cervical intraepithelial neoplasia (CIN, or dysplasia) of the cervix and cervical cancer (see photo). This is the most common type of malignant course of this infection. A more detailed article on CIN and dysplasia can be found here.
Pictured is cervical cancer.
Diagnostics
1. PCR analysis
The main method for diagnosing papillomavirus is the PCR reaction. Using special reagents, the presence of HPV DNA in the material from the patient is determined. The most common types of analysis for HPV are types 16, 18 of the virus, as well as a number of other highly oncogenic types.
Material for analysis is taken from the mucous membrane of the vagina and cervix of a woman. In men - from the mucous membrane of the penis.
Below in the photo is an example of PCR analysis and its interpretation.
PCR can detect the presence of the virus even in a latent (that is, dormant) state. Therefore, it is important to determine the viral load, or the concentration of the virus.

The PCR reaction can also give a false result, both a false positive and a false negative result, especially if the conditions for its conduct are violated (even a push of the table on which the study is being carried out can lead to such a false result).
So, according to modern researchers in the West, up to 20% of all PCR results for papillomavirus were false. And this fact did not depend on the complexity of the equipment and the quality of the reagents.
2. Digene test
A new study gaining popularity in the medical community. This test is used to determine the presence of clinically significant levels of the virus. Thanks to this test, it is possible to identify whether a high degree of oncogenicity in viruses that are in the patient's body, or a low one.
The Digene test is used in combination with a cytological examination of the cervix, and they are also evaluated in a complex manner.
HPV viral load: term, analysis technique, interpretation of results
Viral load in HPV is determined by two methods. Their combination makes it possible to detect the DNA of the pathogen with a probability of 100%, false positive and false negative results are excluded. The technique determines the presence, amount and type of virus. Using the decoding of the analysis, the doctor will be able to decide which treatment will be most effective.
Polymerase chain reaction (PCR) is a technique based on the detection of the genotype of viruses. The peculiarity of carrying out allows artificially increasing the amount of DNA, which makes the accuracy of the analysis exceptionally high.
This test is either qualitative (reveals the fact of infection) and quantitative (viral load). Another analysis method, the Digene test, is even more accurate, since it detects not only whole DNA, but also its fragments.
To determine the degree of risk of complications, biological material is needed:
- blood;
- scraping from the skin or mucous membrane;
- smear from the cervix or urinary tract;
- a tissue sample of a neoplasm (warts, condylomas).
So that the HPV test does not give a false negative result, local antiseptics should not be used for a week before the material is taken. If we are talking about the epithelium of the uterus, penis or urinary system - you can not have a sexual life.
It is human nature to worry, to be nervous for any, even insignificant reasons. And having received from the doctor a referral for analysis for the papillomavirus, the level of expectation of another trouble simply starts to go off scale.
How to understand if the laboratory report indicates an increased HPV viral load? What do the numbers mean as a result of the analysis and can this situation be corrected?
The term viral load is most often used in the diagnosis of hepatitis, HIV, and cetomegalovirus. But this indicator is also applicable to determine the concentration of papillomaviruses in the human body.
The HPV viral load of 100 cells is a measure of the severity of the disease, calculated by evaluating the units of the virus per a certain volume of biological material for analysis.
The measurement of this indicator is used to monitor the dynamics of the patient, predict the course of the disease and the quality of the body's response to antiviral drugs.
To determine which group the detected strain of the virus belongs to, such an indicator as the total HPV viral load is used. This makes it possible to determine the oncogenicity of the strain and more selectively select drugs for the treatment of the disease.
For the diagnosis of HPV, the PCR analysis and the Digene test are currently used. The accuracy of the results is 100%. These studies make it possible to determine the presence or absence of infection, the strain of the virus, and to predict the tactics of patient management.
The indication for an examination is:
- clinical signs of papillomatosis;
- dysplasia and other precancerous conditions of the cervical epithelium;
- control after treatment;
- the patient's desire to be tested for HPV.
Material for research is obtained by scraping the tissues of the urogenital tract. 3 days before the collection of pieces of epithelium, it is forbidden to use local antiseptics and have sex.
What the analysis will show:
- the norm is the absence of viruses;
- general test - will confirm or refute the presence of a pathogen in the body, identify strains of an infectious agent. The disadvantage of this analysis is the inability to determine the total viral load;
- quantitative test - will show the concentration of the virus per 100 thousand cells.
Incredible! Warts / papillomas, wen, lipomas, condylomas can be cured!
- natural remedy
- During the week!
The result of the analysis is not a diagnosis. Be sure to take into account the symptoms, age, history and general condition of the patient. Therefore, the interpretation of the results is the prerogative of the attending physician.
Normally, papillomavirus is not detected. If the result of the analysis showed the presence of a viral load, then the patient should be examined more carefully.
If you see total HPV on the PCR result form, this means that the virus is present in the body. But there is no detail on the types of viral agent. Additional studies should be carried out to determine the strain of the pathogen, its oncogenicity and the degree of damage to the body.
Reference values may have different values in different laboratories. They differ due to the method of processing samples. Therefore, it is desirable to conduct research before and after treatment in one research center.
When a virus is detected, its type is determined and the viral load on the body will be measured. The unit of measurement is the number of DNA and RNA fragments of the virus per 100,000 human cells.
In the result sheet you will see:
- Lg 5 - a critically high level of the pathogen in the body. The risk of neoplasm magnlinization or dysplasia is extremely high.
If neoplasms on the body or genitals are present, and the results of the analysis are negative, then there are 2 options that clarify this situation:
- The patient did not follow the rules for preparing for the material sampling procedure - either urinated before the manipulation, or used local antibacterial drugs.
- The body was able to cope with the virus on its own. And the growths from the skin will have to be removed.
The defeat of low-oncogenic strains of HPV is unpleasant, but safe. The probability of degeneration of a wart or spinule into a malignant neoplasm is extremely low.
The danger is represented by highly oncogenic types of papillomatosis. They provoke the appearance of cervical cancer, oncopathology of the tongue and penis in men.
But even after receiving a result that indicates that you have a high viral load for HPV 66, HPV a7 or 16, this does not mean that you are doomed. The presence of papillomavirus in the body is just the presence of one of the many factors that cause oncopathology.
HPV Treatment Methods
The treatment tactics are chosen by the doctor based on the results of an external examination of the patient and HPV tests. In addition, the presence of symptoms, the size of the growths, the current condition of the patient, the presence or absence of pregnancy are taken into account.
Initially, drugs of conservative therapy with antiviral properties are prescribed. The appointment of interferon-containing agents is shown. The method of administration - oral, rectal, the use of injectables - is chosen by the doctor based on the viral load and external manifestations of papillomatosis.

With a lesion, overgrowth of the genitals shows a general gynecological examination with the collection of a smear from the cervix, colposcopy, and tissue biopsy according to indications. Comorbidities identified by smear results are treated.
Growths are treated with local means - ointments with antiviral components, Epigen spray. The appointment of vitamin complexes and drugs that increase the body's own defenses is shown.
If HPV was found in a pregnant woman, then the question of the use of medications is decided on the basis of the potential benefit to the mother is higher than the potential threat to the child.
In this case, drug therapy is selected more carefully, since many drugs are prohibited during pregnancy. If the activation of the virus occurred in the last weeks of pregnancy, then the question of conducting obstetrics tactics is being decided.
Growth removal techniques:
- Invasive technique with a scalpel.
It is used in rare cases with significant growths. There is a high probability of infection, the appearance of scars.
An electrode is thrown onto the neoplasm and a high-frequency current is passed. The advantage of the technique is the ability to send the growth for histological examination. Cons - soreness, the possibility of infection and scarring. It is not recommended to use this method to remove neoplasms on the face and genitals.
- Photo, laser and radio wave destruction.
The methods are similar. Only the carrier is different. During photodestruction, a light beam of a certain frequency is used to remove neoplasms. With laser removal - a light beam with certain properties, with radio destruction - a radio wave.
All techniques are non-invasive. The papilloma body is evaporated in layers. There is no risk of bleeding, infection of the wound. These techniques are used to remove tumors on any part of the body, including the face and genitals.
- Cryosurgery with liquid nitrogen. This method is recommended for pregnant women and children. The disadvantage is the inability to control the depth of processing.
Whatever result of the analysis for the presence and type of HPV you get, remember that papillomavirus is treated. And a highly oncogenic strain means only the likelihood that a carcinoma will develop. Get treated, see a gynecologist - 2 times a year - as recommended by WHO. In this case, at the first signs of epithelial dysplasia, the doctor will prescribe appropriate therapy.
And you will not only raise your own children, but also see grandchildren.
- Incredible. warts / papillomas, wen, lipomas, condylomas can be cured!
- This time.
- Natural remedy!
- This is two.
- During the week!
- It's three.
Papilight is an antiviral, immunomodulatory, antioxidant and regenerative agent with native concentrates of Caragana jubata. The drug begins to act on the very cause of the HPV virus from the 3rd day of use.
An example of a PCR analysis for HPV
Analysis interpretation

The unit of measurement is the number of genome equivalents (in simple terms, the number of viruses) per 100,000 human epithelial cells (that is, 10 to the 5th power).
Abbreviated: Lg
HPV infection is an insidious disease that can develop in the body for years and eventually lead to serious illness. Its causative agents are papillomaviruses. Some of them are not dangerous, while others, on the contrary, are characterized as highly oncogenic - more likely to provoke cancer.
These strains include 16 and 18. How to confirm the diagnosis of "HPV types 16, 18"? You should contact specialists in this field: a urologist or andrologist, an obstetrician-gynecologist to prescribe a set of studies.
Why you need to treat HPV
After the virus is determined in vitro (i.e. by PCR), it must be eliminated from the body. For this, an integrated approach is used - you need to destroy the pathogen and increase immunity. As a rule, interferon preparations are prescribed in tablets, as well as immunostimulants. The dosage of drugs depends on the patient's condition, viral load and the effectiveness of its reduction.
As additional measures of non-drug support, the doctor recommends walking in the fresh air, a healthy diet and the use of vitamins, and physical activity. These measures strengthen the immune system and harden the body, which helps it cope with the infection on its own, and makes the treatment more effective.
The total effect of drugs and strengthening the immune system leads to the disappearance of most papillomas on the body. Removal of formations is necessary in cases where large warts appear on the face, neck and hands.
Each person in his life is faced with many diseases, in particular infectious diseases. And one such common disease is the human papillomavirus (HPV).

This disease can affect a person at any age, regardless of gender and race.
There are many types of HPV, some of which do not pose a particular danger to the body, while others can lead to the formation of a cancerous condition.
Each papillomavirus group, of which there are about 70, has its own virus DNA, so each group is assigned a specific individual number.
And under each number is a certain type of virus, which has its own characteristics and characteristics.
And among all this variety of infection types, special attention should be paid to HPV type 16 DNA, since this is one of the most terrible genotypes of the virus.
What is HPV, how dangerous is HPV 16, why does it appear, how to cure the disease and what to do if you have been diagnosed with it? You will learn more about this later.
Features of HPV 16

Human papillomavirus type 16 is very common today and occurs most often in female representatives of the age category of 18-30 years.
The infection process is asymptomatic, which makes it difficult to diagnose the disease in the early stages.
Often papillomavirus type 16 is found in a woman during a routine gynecological examination, taking tests for the presence of sexually transmitted diseases.
Most strains of human papillomavirus infection have a low or moderate degree of oncogenicity.
To date, two dangerous strains of the virus can be distinguished - HPV types 16 and 18. Their danger lies in the increased degree of oncogenicity.
Women are more susceptible than men to the human papillomavirus, especially strain 16, which in most cases affects the cervix, resulting in a cancerous condition.

Therefore, if HPV type 16 is detected in women, treatment should be started immediately.
But even if you have been diagnosed with this ailment, there is no need to panic, because worries and stresses will only accelerate the development of the virus.
Papillomavirus type 16 is not a sentence, timely diagnosis and comprehensive treatment can completely save the situation.
You can get HPV type 16 only from another infected person or sexual partner, animals are not carriers of the infection.
In total, 4 ways of transmission of infection from one person to another are known:
- Sexually. Sexual contact is the main mode of transmission of papillomavirus. Therefore, the main category of HPV-infected people are sexually active people who often change sexual partners. Fans of non-traditional types of sex, such as oral or anal contact, may now think that they are safe, but they are not. The HPV 16 virus is transmitted during any sexual intercourse, regardless of its type. And even the usual mutual caresses and kisses put your health and the health of your partner at risk.
- Contact-household method. The virus can be transmitted not only during sexual intercourse, but also when the blood, sweat and saliva of an infected person gets on the damaged skin of a healthy person. It is small wounds, scratches and cuts that allow the infection to penetrate inside. But, it is impossible to get HPV 16 through kitchen utensils.
- Transmission of infection from mother to child during childbirth. If a woman has condylomas on the uterus, then during childbirth, when the baby passes through the infected birth canal, he may also become infected with HPV type 16, which in the child will manifest itself in the form of neoplasms in the oral cavity, respiratory tract or genitals. Fortunately, it is very easy to detect the disease in the first stage in a newborn, since immunity has not yet been fully developed. And early detection will allow faster treatment.
- Self-infection. The probability of contracting papillomavirus independently exists, albeit small. This can happen during careless shaving or hair removal.
It is easy to get infected with the human papillomavirus, although there are certain categories of people who are more than likely to acquire the 16 strain of HPV.
- began to have sex at an early age;
- often change sexual partners;
- prefer non-traditional types of sex;
- have a sexually transmitted disease;
- have some chronic diseases;
- are HIV-infected;
- abuse alcohol and cigarettes, use drugs;
- did artificial termination of pregnancy;
- suffer from diabetes;
- are in stressful situations.
By knowing how HPV is transmitted, you can try to reduce the risk of infection to a minimum. The most susceptible to the effects of papillomavirus type 16 are women under the age of 25-30 years.

The infection enters the body through microcracks in the skin that any person has, so it is quite difficult to protect yourself from infection, but it is possible if you regularly undergo gynecological examinations and lead the right lifestyle and sex life with one proven partner.
Most of the world's population is infected with the human papillomavirus, but in each person the virus manifests itself in different ways, depending on the quality of the immune system.
If the immune system is strong enough, then the infection may not appear, but at the moment of its weakening, the virus begins to activate.
External signs may not appear in every sick person, for example, symptoms of HPV type 16 are observed in only 5% of women.
From the moment of infection to the appearance of the first signs usually takes at least 3 months. The first clear sign of the presence of human papillomavirus in the body is the appearance of papillomas on the skin or mucous membranes.

When infected with HPV type 16, papillomas will have a color similar to skin tone.
Type 16 papillomas can be single, or they can grow, occupying large areas of the skin. And if you do not respond in any way to the appearance of these neoplasms, then the situation will only worsen.
In addition to the formation of small growths on the skin, the following symptoms may occur:
- itching and burning in the genital area;
- the occurrence of pain during urination;
- bleeding from the vagina during or after sexual intercourse.
Often, papillomas that appear as a result of exposure to the body of HPV genotype 16 are localized on the external and internal genital organs in women.
Men, although they can become infected with this strain of the virus, do not pose a serious threat to the male body, unlike women in whom the virus can cause cervical cancer, even if there are no symptoms.
HPV 16 in men also develops without symptoms, but rarely leads to cancer.
The human papillomavirus type 16 often infects the female body, as a result of which every second infected person develops cervical cancer.
And if at the next examination in gynecology such an ailment as HPV type 16 is found, then the question immediately arises: how to live with this and how to get rid of the problem? Do not panic.
Papillomavirus, even such a terrible variety as type 16, is not a sentence. Your life has changed somewhat since your diagnosis, but not radically.
The attending physician will prescribe a course of treatment, thanks to which you can quickly get rid of the external manifestations of diseases.
And besides this, you still have to constantly strengthen the immune system so that it is able to fight the virus.
Annual visits to the doctor and examinations for the presence of oncology will become part of the usual way of life. And even if at the next examination you have type 16 papilloma, then this will be the initial stage of the disease.
Thanks to the timely diagnosis of the tumor, the probability of a speedy recovery will be 100%.
Diagnosis of HPV is one of the main stages, since the sooner the disease is detected, the sooner treatment can begin.
Type 16 papillomavirus usually appears and develops asymptomatically, and the first symptoms may appear only in the later stages, when treatment may no longer help.
Papillomas, of course, remain the main symptom of HPV, but they do not pay attention to them, mistaking them for a pimple or a mole, hoping that they will pass by themselves.
And neoplasms are localized on the internal genital organs, which makes diagnosis more difficult. The only way to diagnose the disease in time is to periodically undergo an examination in gynecology or urology.
After contacting a doctor, HPV type 16 can be detected in women by several methods:
- gynecological examination;
- polymerase chain reaction (PCR analysis). HPV 16 can be easily determined using this popular method for diagnosing the most dangerous types of papillomaviruses. But the method is clearly not distinguished by high accuracy, so the result may be incorrect;
- a colposcopy is performed, with the help of which you can more carefully see the walls of the uterus and other internal genital organs. Allows you to find out the exact location of the infection. HPV type 16 in men is detected by ureteroscopy;
- a vaginal smear is taken, which is sent for histological and cytological examination;
- biopsy. A small piece of infected tissue is given for research for a detailed acquaintance with the nature of the neoplasm and to identify the degree of its oncogenicity and stage of development.
Prevention
Prevention is the best cure. Remember this phrase, especially when it comes to the sexual sphere.
Nature has come up with a wonderful mechanism for healing and prevention for a person, which then helps him not to get sick again. This is the immune system.
If a person has already had warts or papillomas once, then later he develops immunity to this type of virus. Therefore, in adults, juvenile warts, spinules and vulgar warts very rarely appear.
It is on this principle that the method of vaccinating a person against various infectious diseases, including papillomavirus, is built.
That is why it is SO IMPORTANT to keep your immunity at a high level. A detailed article on how to strengthen the immune system - read.
- The vaccine "Gardasil" (Gardasil) manufactured in the USA. This vaccine against types 6, 11, 16, 18 prevents the development of such symptoms of infection as genital warts, neoplasia (dysplasia, or erosion) and cervical cancer, penile skin cancer in men. In many developed countries, HPV vaccination is carried out very actively, starting from the age of 11-12 (link), until the time of the onset of sexual activity, when infection already occurs. Applies to both girls and boys.
- Vaccine "Gardasil 9". This vaccine is nine-valent, that is, it acts against 9 types of the virus: 6, 11, 16, 18, 31, 33, 45, 52 and 58. The effectiveness of preventing cervical cancer is from 98% to 100%.
- Vaccine "Cervarix". This vaccine forms immunity against 2 types of the virus: 16 and 18.
- Personal hygiene measures in public places
- A healthy lifestyle that supports a high immune system
- Proper mode of work and rest
- Moderate physical culture
- Taking vitamins, fruits, juices
- Only one sexual partner (ideally)
- Using a condom during sexual intercourse
And in conclusion - a few videos on the topic of the material recommended for viewing.
Attention: if the doctor did not answer your question, then the answer is already on the pages of the site. Use the search on the site.
Deciphering the HPV analysis is an integral part of the diagnostic study. Based on the data obtained, the doctor decides on the necessary therapeutic tactics. Properly conducted analysis, reliably deciphered results allow you to choose the right treatment.
Human papillomavirus is an infectious disease that cannot be completely cured. Some people experience regular infections that negatively affect their health and quality of life. Such patients are recommended to undergo periodic examination to detect the type of HPV, the nature of its severity and oncogenic degree.
Modern medicine uses several diagnostic methods for the quantitative control of papillomavirus:
- Enzyme immunoassay (ELISA). Examination of the presence of antibodies in the body. Antibodies are specific proteins that are produced as an immune response to the activity of the pathogen. Immunoglobulins are unique to each specific infection.
- Digene-test (Hybrit Capture hybrid capture method) is designed to identify the 18 most dangerous types of HPV. The essence of the method is to stain the biopsy with special fluorescent substances. When a virus is detected in the test materials, highlighting occurs.
- PCR is one of the most informative methods for diagnosing HPV. The analysis is based on an artificial increase in copies of the DNA of the pathogen. It is possible to determine even single viruses, with the highest accuracy.
After conducting a laboratory study, experts begin to decipher the results.
Results interpretation table
When analyzing HPV, the interpretation of the results is summarized in a table, which includes information on quantitative and qualitative indicators.
This table provides general information about possible indicators based on PCR analysis.
The laboratory sheet indicates all types of HPV, for the presence of which the study was carried out. In most cases, these are 12 types - 16, 18, 31, 33, 35, 39, 45, 51, 52, 56, 58, 59 of an average and high oncogenic degree.
The mark "lack of DNA" and the indicator of viral load less than 3 Lg indicates the complete absence of the virus or its insignificant amount. Treatment is not required. The infection may be present in the human body, but does not produce any effect. Growths are not observed.
A concentration of 3-5 indicates the presence of the virus in a small amount. Women in whose body papillomavirus was found need to undergo an additional examination in order to exclude the presence of cervical dysplasia. Patients receive a general immune-boosting treatment. In the presence of genital warts, removal is performed.
A positive test result at a concentration above 5 indicates a danger to humans. The body is infected with a virus. The likelihood of developing cervical dysplasia in women is increased. Additional analyzes are being carried out. Treatment consists in the removal of growths, large-scale antiviral and immunostimulating therapy. You may need to consult an oncologist.
What does result mean
During the research, qualitative and quantitative analysis is taken into account. The former may indicate the presence or absence of a virus. The second is about the concentration of a pathogenic agent in the human body. Only an experienced specialist can decipher the information received, taking into account all the accompanying circumstances. Do not take a positive test result as a sentence. Often, during research, errors are made that affect the indicators, do not make it possible to determine the correct data. In most cases, mistakes are made by patients during the preparation for the upcoming analysis. Reference values must be taken into account.

False positive HPV
False positive HPV test results are common. This happens if:
- the bio sample was contaminated;
- there was an incorrect sampling of materials;
- the patient was treated before the analysis;
- the person did not comply with the norms of preparation for diagnosis.
In order not to get distorted results, it is necessary to take into account some rules. Within 12 hours before the delivery of biological material, it is forbidden to take antiviral, antibacterial and antimicrobial drugs. On the day of the smear, you should take a shower. For the next 2-3 days, it is better to refuse sexual intercourse. A smear for research is not taken during menstruation. Often people are faced with false test results if they tried to treat the infection with antiviral drugs the day before. The virus itself is neutralized, but antibodies remain in the body.

Reference value
The reference values of the indicator (another name is reference) mean the general values obtained in the course of laboratory research on a specific category of the population. These can be young people aged 20-30 years, women who are pregnant, who have given birth, who have not given birth, etc. Such indicators are necessary to obtain an average total indicator of the relative norm.
This is how a quantitative analysis for HPV is determined. An average value of 3-5 Lg, which implies a dubious result, is collected from an assessment of a certain category of papillomavirus carriers. Therefore, reference values cannot be evaluated as the only correct indicator. The concept of the norm may differ depending on the characteristics of the body, age, the presence of concomitant diseases.
In most cases, only the qualitative outcome of the study, which indicates the presence of the virus, matters. In cases of detection of a non-oncogenic type of HPV, its concentration is insignificant.
If the test is positive
A positive HPV test indicates the presence of the virus in the body. You should not worry, according to statistics, 7 out of 10 people are carriers of the papillomavirus. Most people can go their lives without knowing they are infected with HPV. Activation of the symptoms of the disease occurs during a period of weakening of the immune system.
Depending on the identified type of pathogen and the general picture of the disease, the doctor selects the tactics of treatment. In most cases, it includes antiviral and immunostimulating therapy, methods of destruction of neoplasms.
At 56, 16, 31, 18 and other oncogenic strains
Detection of carcinogenic strains of the papillomavirus requires immediate treatment aimed at restoring the body's immune defenses and eliminating formations. HPV types of high oncogenicity are especially dangerous for women, as they cause the development of cervical cancer. The patient needs to undergo an additional study for the presence of erosion or dysplasia. Histological examination of tissues will help to detect malignant changes in cells.
The detection of such strains in the body will not mean the presence of cancer. People with a similar diagnosis need to be attentive to their own health. Regularly examined, take tests.
There are cases when there is a self-healing from the virus. Young people with strong immune defenses are most likely to be healed.
Timely removal of genital warts will help prevent the risk of developing dangerous consequences. All that needs to be done for patients with identified strains is to follow the doctor's recommendations, to be treated, to monitor the state of immunity, attend scheduled examinations, and try not to infect others.
For benign strains
Benign strains of HPV are not dangerous to humans. All that the patient will encounter is the appearance of unpleasant formations on the body. Depending on the quantitative indicator of the virus in the body, the doctor will recommend drug therapy.
More often, healthy young people with a small number of warts on the body are prescribed removal. Strong immunity is able to cope with the infection, and aids are not required. Removal can be done with the help of pharmaceutical preparations or go to the clinic and undergo a hardware procedure.
If growths occur frequently or papillomatosis is diagnosed, antiviral treatment is required. It includes taking drugs that suppress the activity of the infection and the ability to reproduce. Immunostimulants help the immune system to suppress the virus.
It happens that the HPV test is positive, but there are no warts on the body. This indicates a carriage, but the absence of infectious activity. A negative analysis can also be detected in the presence of papillomas on the body. It happens when the immune system is able to independently reduce the activity of the infection. In this case, the concentration of the virus in the blood is constantly changing and may be low at the time of the study.
Regardless of which type of HPV is detected, the patient must discuss all the necessary actions with the doctor. Self-treatment can lead to the development of the disease and increase the risk of undesirable consequences.
Deciphering the analysis for HPV is an informative and important procedure, on which subsequent actions in terms of therapy depend. You should not try to decipher the meanings yourself or with the support of people who lack the necessary qualifications. Only experienced specialists can correctly explain the examination data, which will be based on the numbers, characteristics of the body of a particular patient.









Chantilly Castle - the second in France after Versailles Chantilly Castle how to get from Paris
Amusement park "The Land of Legends Theme Park" in Turkey
Holy places in Greece. Greece Orthodox. Pilgrimage to the feast of St. Nicholas
Picodi: All discounts in one place!
How to get to Dolmabahce Palace