More than 80,000 real tasks of the Unified State Exam 2020
You are not logged into the system "". It does not interfere with viewing and solving tasks Open bank of USE tasks in mathematics, but to participate in the competition of users to solve these tasks.
The result of the search for USE assignments in mathematics on request:
« A bicycle left point A of the circular track.» - 251 jobs found
(impressions: 606 , answers: 13 )
A cyclist left point A of the circular track, and after 10 minutes a motorcyclist followed him. 2 minutes after departure, he caught up with the cyclist for the first time, and 3 minutes after that, he caught up with him for the second time. Find the speed of the motorcyclist if the length of the track is 5 km. Give your answer in km/h.
Job B14()(impressions: 625 , answers: 11 )
A cyclist left point A of the circular track, and after 20 minutes a motorcyclist followed him. 5 minutes after departure, he caught up with the cyclist for the first time, and 10 minutes after that, he caught up with him for the second time. Find the speed of the motorcyclist if the length of the track is 10 km. Give your answer in km/h.
The correct answer has not yet been determined
Job B14()(impressions: 691 , answers: 11 )
A cyclist left point A of the circular track, and after 10 minutes a motorcyclist followed him. 5 minutes after departure, he caught up with the cyclist for the first time, and 15 minutes after that, he caught up with him for the second time. Find the speed of the motorcyclist if the length of the track is 10 km. Give your answer in km/h.
Answer: 60
Job B14()(impressions: 613 , answers: 11 )
A cyclist left point A of the circular track, and after 30 minutes a motorcyclist followed him. 5 minutes after departure, he caught up with the cyclist for the first time, and 47 minutes after that, he caught up with him for the second time. Find the speed of the motorcyclist if the length of the track is 47 km. Give your answer in km/h.
The correct answer has not yet been determined
Job B14()(impressions: 610 , answers: 9 )
A cyclist left point A of the circular track, and after 20 minutes a motorcyclist followed him. 5 minutes after departure, he caught up with the cyclist for the first time, and 19 minutes after that, he caught up with him for the second time. Find the speed of the motorcyclist if the length of the track is 19 km. Give your answer in km/h.
The correct answer has not yet been determined
Job B14()(impressions: 618 , answers: 9 )
A cyclist left point A of the circular track, and after 20 minutes a motorcyclist followed him. 2 minutes after departure, he caught up with the cyclist for the first time, and 30 minutes after that he caught up with him for the second time. Find the speed of the motorcyclist if the length of the track is 50 km. Give your answer in km/h.
The correct answer has not yet been determined
Job B14()(impressions: 613 , answers: 9 )
A cyclist left point A of the circular track, and after 30 minutes a motorcyclist followed him. 5 minutes after departure, he caught up with the cyclist for the first time, and 26 minutes after that he caught up with him for the second time. Find the speed of the motorcyclist if the length of the track is 39 km. Give your answer in km/h.
The correct answer has not yet been determined
Job B14()(impressions: 622 , answers: 9 )
A cyclist left point A of the circular track, and after 50 minutes a motorcyclist followed him. 5 minutes after departure, he caught up with the cyclist for the first time, and 12 minutes after that, he caught up with him for the second time. Find the speed of the motorcyclist if the length of the track is 20 km. Give your answer in km/h.
The correct answer has not yet been determined
Task B14 (More than 80,000 real tasks of the Unified State Exam 2020
You are not logged into the system "". It does not interfere with viewing and solving tasks Open bank of USE tasks in mathematics, but to participate in the competition of users to solve these tasks.
The result of the search for USE assignments in mathematics on request:
« a cyclist left point a of the circular track and after 30 minutes following him» - 106 jobs found
(impressions: 613 , answers: 11 )
A cyclist left point A of the circular track, and after 30 minutes a motorcyclist followed him. 5 minutes after departure, he caught up with the cyclist for the first time, and 47 minutes after that, he caught up with him for the second time. Find the speed of the motorcyclist if the length of the track is 47 km. Give your answer in km/h.
Job B14()(impressions: 618 , answers: 9 )
A cyclist left point A of the circular track, and after 20 minutes a motorcyclist followed him. 2 minutes after departure, he caught up with the cyclist for the first time, and 30 minutes after that he caught up with him for the second time. Find the speed of the motorcyclist if the length of the track is 50 km. Give your answer in km/h.
The correct answer has not yet been determined
Job B14()(impressions: 613 , answers: 9 )
A cyclist left point A of the circular track, and after 30 minutes a motorcyclist followed him. 5 minutes after departure, he caught up with the cyclist for the first time, and 26 minutes after that he caught up with him for the second time. Find the speed of the motorcyclist if the length of the track is 39 km. Give your answer in km/h.
The correct answer has not yet been determined
Job B14()(impressions: 628 , answers: 9 )
A cyclist left point A of the circular track, and after 30 minutes a motorcyclist followed him. 10 minutes after departure, he caught up with the cyclist for the first time, and 40 minutes after that, he caught up with him for the second time. Find the speed of the motorcyclist if the length of the track is 40 km. Give your answer in km/h.
The correct answer has not yet been determined
Job B14()(impressions: 611 , answers: 8 )
A cyclist left point A of the circular track, and after 30 minutes a motorcyclist followed him. 5 minutes after departure, he caught up with the cyclist for the first time, and 39 minutes after that he caught up with him for the second time. Find the speed of the motorcyclist if the length of the track is 39 km. Give your answer in km/h.
The correct answer has not yet been determined
Job B14()(impressions: 628 , answers: 8 )
A cyclist left point A of the circular track, and after 30 minutes a motorcyclist followed him. 15 minutes after departure, he caught up with the cyclist for the first time, and 54 minutes after that, he caught up with him for the second time. Find the speed of the motorcyclist if the length of the track is 45 km. Give your answer in km/h.
The correct answer has not yet been determined
Job B14()(impressions: 639 , answers: 8 )
A cyclist left point A of the circular track, and after 30 minutes a motorcyclist followed him. 10 minutes after departure, he caught up with the cyclist for the first time, and 44 minutes after that, he caught up with him for the second time. Find the speed of the motorcyclist if the length of the track is 33 km. Give your answer in km/h.
The correct answer has not yet been determined
Job B14()(impressions: 899 , answers: 7 )
A cyclist left point A of the circular track, and after 30 minutes a motorcyclist followed him. 10 minutes after departure, he caught up with the cyclist for the first time, and 30 minutes after that he caught up with him for the second time. Find the speed of the motorcyclist if the length of the track is 30 km. Give your answer in km/h.
The correct answer has not yet been determined
Job B14()(impressions: 591 , answers: 7 )
A cyclist left point A of the circular track, and after 30 minutes a motorcyclist followed him. 5 minutes after departure, he caught up with the cyclist for the first time, and 49 minutes after that, he caught up with him for the second time. Find the speed of the motorcyclist if the length of the track is 49 km. Give your answer in km/h.
Sections: Maths
Type of lesson: iterative-generalizing lesson.
Lesson Objectives:
- educational – repeat methods for solving various types of word problems for movement
- developing - develop students' speech through the enrichment and complication of its vocabulary, develop students' thinking through the ability to analyze, generalize and systematize material
- educational - the formation of a humane attitude among students to participants in the educational process
Lesson equipment:
- interactive whiteboard;
- envelopes with tasks, thematic control cards, consultant cards.
Lesson structure.
The main stages of the lesson |
Tasks to be solved at this stage |
||
| Organizational moment, introductory part |
|
||
| Preparing students for active work (review) |
|
||
| The stage of generalization and systematization of the studied material (work in groups) |
|
||
| Checking the performance of work, adjusting (if necessary) |
|
||
| Summing up the lesson. Parsing homework |
|
Forms of organization of cognitive activity of students:
- frontal form of cognitive activity - at stages II, IY, Y.
- group form of cognitive activity - at stage III.
Teaching methods: verbal, visual, practical, explanatory - illustrative, reproductive, partially - search, analytical, comparative, generalizing, traductive.
During the classes
I. Organizational moment, introductory part.
The teacher announces the topic of the lesson, the objectives of the lesson and the main points of the lesson. Checks the readiness of the class to work.
II. Preparing students for active work (review)
Answer the questions.
- What kind of movement is called uniform (movement at a constant speed).
- What is the path formula for uniform motion ( S=Vt).
- From this formula, express the speed and time.
- Specify units of measure.
- Conversion of speed units
III. The stage of generalization and systematization of the studied material (work in groups)
The whole class is divided into groups (5-6 people in a group). It is desirable that in the same group there are students of different levels of training. Among them, a group leader (the strongest student) is appointed, who will lead the work of the group.
All groups receive envelopes with assignments (they are the same for all groups), consultant cards (for weak students) and thematic control sheets. In the thematic control sheets, the group leader assigns marks to each student of the group for each task and notes the difficulties that students have in completing specific tasks.
Card with tasks for each group.
№ 5.
No. 7. The motorboat passed 112 km against the current of the river and returned to the point of departure, having spent 6 hours less on the way back. Find the speed of the current if the speed of the boat in still water is 11 km/h. Give your answer in km/h.
No. 8. The motor ship passes along the river to the destination 513 km and after parking returns to the point of departure. Find the speed of the ship in still water, if the speed of the current is 4 km/h, the stay lasts 8 hours, and the ship returns to the point of departure 54 hours after leaving it. Give your answer in km/h.
Sample of thematic control card.
| Class ________ Full name of the student ___________________________________ | ||
job number |
Comment |
|
Consultant cards.
| Card number 1 (consultant) |
| 1. Driving on a straight road |
| When solving problems of uniform motion, two situations often occur. If the initial distance between the objects is equal to S, and the speeds of the objects are V1 and V2, then: a) when objects move towards each other, the time after which they will meet is equal to . b) when objects move in one direction, the time after which the first object will catch up with the second is equal to, ( V 2 > V 1) |
Example 1. The train, having traveled 450 km, was stopped due to a snow drift. Half an hour later the path was cleared, and the driver, having increased the speed of the train by 15 km/h, brought it to the station without delay. Find the initial speed of the train if the distance traveled by it to the stop was 75% of the total distance.
X= -75 is not suitable for the condition of the problem, where x > 0. Answer: The initial speed of the train is 60 km/h. |
| Card number 2 (consultant) |
2. Driving on a closed road |
| If the length of the closed road is S, and the speeds of objects V 1 and V 2 , then: a) when objects move in different directions, the time between their meetings is calculated by the formula ; |
| Example 2 At competitions on the ring track, one skier completes the circle 2 minutes faster than the other and after an hour has bypassed him exactly on the circle. How long does it take each skier to complete the lap? Let be S m is the length of the ring road and x m/min and y m/min are the speeds of the first and second skiers, respectively ( x > y) . Then S/x min and S/y min - the time for which the first and second skiers pass the circle, respectively. From the first condition we obtain the equation . Since the speed of removal of the first skier from the second skier is ( x- y) m/min, then from the second condition we have the equation . Let's solve the system of equations.
Let's make a replacement S/x=a And S/y=b, then the system of equations will take the form:
60(a + 2) – 60a = a(a + 2)a 2 + 2a- 120 = 0. The quadratic equation has one positive root a = 10 then b= 12. So the first skier completes the lap in 10 minutes, and the second skier in 12 minutes. Answer: 10 min; 12 min. |
| Card number 3 (consultant) |
3. Movement on the river |
| If an object moves along the river, then its speed is equal to Vstream. =Voct. +
Vtech. If an object is moving against the current of the river, then its speed is Vagainst the current =V oct. – Vtech. The object’s own speed (speed in still water) is equal to The speed of the river is The speed of the raft is equal to the speed of the river. |
| Example 3 The boat went downstream for 50 km and then went back 36 km, which took him 30 minutes longer than downstream. What is the speed of the boat if the speed of the river is 4 km/h? Let the boat's own speed be X km/h, then its speed along the river is ( x + 4) km / h, and against the current of the river ( x- 4) km/h. The time of the boat's movement along the river is equal to hours, and against the flow of the river, hours. Since 30 minutes = 1/2 hour, then, according to the condition of the problem, we compose the equation =. Multiply both sides of the equation by 2( x + 4)(x- 4) >0 . We get 72( x + 4) -100(x- 4) = (x + 4)(x- 4) x 2 + 28x- 704 \u003d 0 x 1 \u003d 16, x 2 \u003d - 44 (we exclude, since x> 0). So, the own speed of the boat is 16 km/h. Answer: 16 km/h. |
IV. Problem solving stage.
Problems that caused difficulties for students are analyzed.
No. 1. From two cities, the distance between which is equal to 480 km, two cars simultaneously left towards each other. In how many hours will the cars meet if their speeds are 75 km/h and 85 km/h?
- 75 + 85 = 160 (km/h) – closing speed.
- 480: 160 = 3 (h).
Answer: the cars will meet in 3 hours.
No. 2. From cities A and B, the distance between them is 330 km, two cars simultaneously left towards each other and met after 3 hours at a distance of 180 km from city B. Find the speed of the car that left city A. Give your answer in km / h.
- (330 - 180) : 3 = 50 (km/h)
Answer: The speed of a car leaving city A is 50 km/h.
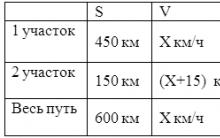
No. 3. From point A to point B, the distance between which is 50 km, a motorist and a cyclist left at the same time. It is known that a motorist travels 65 km more per hour than a cyclist. Determine the speed of the cyclist if it is known that he arrived at point B 4 hours 20 minutes later than the motorist. Give your answer in km/h.
Let's make a table.
Let's make an equation, given that 4 hours 20 minutes =
,It is obvious that x = -75 does not fit the condition of the problem.
Answer: The speed of the cyclist is 10 km/h.
No. 4. Two motorcyclists start simultaneously in one direction from two diametrically opposite points of a circular track, the length of which is 14 km. In how many minutes will the motorcyclists catch up for the first time if the speed of one of them is 21 km/h more than the speed of the other?
Let's make a table.
Let's make an equation.
where 1/3 hour = 20 minutes.Answer: After 20 minutes, the motorcyclists will line up for the first time.
No. 5. From one point of the circular track, the length of which is 12 km, two cars started simultaneously in the same direction. The speed of the first car is 101 km/h, and 20 minutes after the start it was one lap ahead of the second car. Find the speed of the second car. Give your answer in km/h.
Let's make a table.
Let's make an equation.
Answer: The speed of the second car is 65 km/h.
No. 6. A cyclist left point A of the circular track, and after 40 minutes a motorcyclist followed him. 8 minutes after departure, he caught up with the cyclist for the first time, and 36 minutes after that he caught up with him for the second time. Find the speed of the motorcyclist if the length of the track is 30 km. Give your answer in km/h.
Let's make a table.
Movement to the first meeting |
|||
cyclist |
No. 9. From pier A to pier B, the distance between which is 168 km, the first ship set off at a constant speed, and 2 hours after that, the second one set off after it, at a speed of 2 km / h more. Find the speed of the first ship if both ships arrive at point B at the same time. Give your answer in km/h. Let's make a table, based on their conditions, that the speed of the first ship is x km / h. Let's make an equation: Multiplying both sides of the equation by x ,Answer: the speed of the first ship is equal to the river 12 km/h V. Summing up the lesson.During the summing up of the lesson, once again, students should pay attention to the principles of solving problems on movement. When giving homework, give an explanation of the most difficult tasks. Literature. 1) Article : Mathematics of the Unified State Examination 2014 (a system of tasks from an open bank of tasks) Koryanov A.G., Nadezhkina N.V. - published on the website | ||











Living and dead water: myth or reality, what is the power of living and dead water?
Craniosynostosis, or premature fusion of the bones of the skull Frontal crest in a child
Beautiful hair How to achieve hair density at home: useful tips
Why mosquitoes bite some people, but not others
How to achieve beautiful hair