Varietal types of raspberries
Raspberries can be divided into 4 groups (types):
Common garden raspberry- These are traditional varieties of the last century, with berries up to 4 g in size. Previously, there were no raspberries with large berries. Harvest from a bush no more than 2 kg. The best varieties of ordinary raspberries
large-fruited raspberries- the weight of the berries of these raspberry varieties is up to 12 g (for forest raspberries, berries are 0.3-0.5 g). The bush is relatively low, thick. Truth from the drought large-fruited varieties may go unharmed. The best varieties of large-fruited raspberries.
standard raspberry- The best varieties of standard raspberries.
Annual (remontant) raspberry- gives a harvest in the first year, that is, one summer passes from germination to harvest (that's why it is called annual), the period of consumption of raspberries is right up to October 10-20. In terms of yield, taste, and size of berries, it surpasses ordinary raspberries. Tapestries are not required. The best varieties of annual remontant raspberries.
The best varieties of traditional summer fruiting
Everyone loves to eat raspberries at the beginning of summer. Here you can’t do without modern summer varieties that bear fruit on the shoots of last year.
‘Kuzmin’s News’, ‘Early Sweet’, ‘Sweetie’, ‘Malakhovka’, ‘Shosha’, ‘Caprice of the Gods’, ‘Sorceress’, ‘Balm’.
Lyashka, Lashka (Laszka)
Lyashka - variety early ripe with a long fruiting period. Polish industrial variety, medium or vigorous up to 2.5 m.
The stems are rigid, curved in the upper part, with small, almost not prickly thorns. Fruit twigs are formed on two-year-old shoots and in large numbers.
It has a high yield, about 17-20 t/ha. Dense berries with good transportability.
Drought tolerant and winter hardy. Requires protection from fungal diseases. Valued for large berries with a dessert taste, and for an extended period of fruiting. Very suitable for home and commercial gardening.
Glen Fine
 New mid-early Scottish variety. Most fruitful summer raspberry. In industrial plantings it gives up to 30-35 t/ha. The bushes are medium-sized - 1.5-2 m. The shoots are smooth. Forms fruit clusters of 20-25 berries each. A very long period of fruiting - bears fruit for a month and a half. The berries are red-raspberry, medium-large, excellent sweet taste, tolerate transportation well. Disease resistant.
New mid-early Scottish variety. Most fruitful summer raspberry. In industrial plantings it gives up to 30-35 t/ha. The bushes are medium-sized - 1.5-2 m. The shoots are smooth. Forms fruit clusters of 20-25 berries each. A very long period of fruiting - bears fruit for a month and a half. The berries are red-raspberry, medium-large, excellent sweet taste, tolerate transportation well. Disease resistant.
Glen Fine - very suitable for home growing. Recognized as the best summer variety in England in 2009.
Cascade Delight
 Medium maturity new American variety. Begins fruiting later than the Glen Fine variety for 7-10 days. The bushes are powerful, low. Shoots are vertical, almost smooth. The berries are large, sweet, fragrant, with a caramel aftertaste.
Medium maturity new American variety. Begins fruiting later than the Glen Fine variety for 7-10 days. The bushes are powerful, low. Shoots are vertical, almost smooth. The berries are large, sweet, fragrant, with a caramel aftertaste.
The variety forms a powerful root system, resistant to root rot. It adapts to different growing conditions, tolerates both heat and rainy weather.
Productivity is high - 4-5 kg per bush. Fruiting 3-3.5 weeks.
Cascade Delight is suitable for amateur and industrial gardening.
Tulamin
 Variety medium late deadline maturation (from mid-July), bred in Canada. The bush is vigorous, the shoots are small-thorned. Great taste of large fragrant berries- the ideal of raspberry flavor in Europe. The berries are large 5-7 g, elongated, red-crimson, shiny, beautiful and very tasty.
Variety medium late deadline maturation (from mid-July), bred in Canada. The bush is vigorous, the shoots are small-thorned. Great taste of large fragrant berries- the ideal of raspberry flavor in Europe. The berries are large 5-7 g, elongated, red-crimson, shiny, beautiful and very tasty.
Tulamin is disease resistant. Tolerates frost well. Berries tolerate transportation.
Octavia (Octavia)
 New grade of raspberry of English selection. Long fruiting period. Shoots are medium-sized, not prickly. Ripens two weeks after Glen Ample. High-yielding, up to 25 t/ha. The berries are large (average weight 6-8 g), bright red, dense, round-conical, tolerate transportation, with excellent taste and aroma. Lasts longer than Glen Ample.
New grade of raspberry of English selection. Long fruiting period. Shoots are medium-sized, not prickly. Ripens two weeks after Glen Ample. High-yielding, up to 25 t/ha. The berries are large (average weight 6-8 g), bright red, dense, round-conical, tolerate transportation, with excellent taste and aroma. Lasts longer than Glen Ample.
Octavia is a winter-hardy variety, tolerates frosts down to -30 °. Resistant to diseases of the vegetative organs.
Benefis (Benefis)
Medium-late variety, obtained at the Institute of Horticulture in Poland. It bears fruit on two-year-old shoots. Shoots vigorous, rigid, curved at the top, thornless. The berries are large and very large, cone-shaped, dark red with a slight bloom, with dense pulp. Winter-hardy, quite resistant to fungal diseases. Berries tolerate storage and transportation.
Glen Ample
A mid-late raspberry variety with an extended fruiting period, bred in Scotland, one of the most common in Europe. The main crop is harvested in summer on biennial shoots, bears fruit from the end of June (for middle lane).
Vigorous shrub up to 2-3.5 m. Rigid shoots without thorns. On each shoot, 20-30 fruit branches are formed, on which up to 20 berries are formed.
Berries weighing 5-6 g, up to 10 g, round-conical, dense, transportable, dull red, juicy, fragrant, sweet and sour with a tasting score of 9 points.
The yield of one shoot is 1.2-1.6 kg. With industrial cultivation and planting with an interval of 0.5 m between plants and 3 m between rows, the yield is approximately 22 t/ha.
Winter hardiness and drought resistance were rated 9 points, disease resistance - 8 points, pest resistance - 7-8 points. Susceptible to viruses. Aphids are not damaged.
Glen Prosen
Variety of medium ripening, English selection. Shoots are high, erect, powerful, without thorns. It bears fruit on two-year-old shoots. The berries are bright red, round or round-conical, dense, pleasant taste, transportable. The yield on each shoot is up to 1 kg per season, about 15 tons / ha. Winter-hardy, resistant to major diseases. Drought resistant.
Hussar
New mid-early, non-repairable, high-yielding grade.
The bush is upright, powerful, up to 3 m high, does not require support, the shoots are sprawling, almost thornless, there is little overgrown.
The berries are dark crimson, truncated-conical, large (3.5-5 g), transportable, juicy with sweet and sour dessert taste, fragrant, rich in vitamin C and sugars.
Withstands long summer drought and winters with little snow and frosts down to 25-30°C. Resistant to fungal diseases and pest damage.
The average yield and varietal quality gives under adverse growing conditions. Under the most favorable conditions, the yield will triple, and the average size berries up to 10 g. In this case, the shoots under the weight of the crop will sag and you cannot do without a trellis.
Volnitsa
New medium-early, large-fruited, fruitful, non-repairable winter-hardy variety, bred at the Kokinsky strong point. From one bush, the yield is up to 4 kg, the total productivity is 113 centners / ha.
The berries are cone-shaped, slightly pubescent, bright red, large (3.5-4 g), sweet and sour, but practically without a characteristic raspberry aroma. Tasting score 4 points.
The bush is sprawling, medium-sized, requiring a garter, prone to overgrowth, the amount of overgrowth is moderate. Shoots upright, light brown, covered with thorns. The leaves are large, wrinkled, dark green, devoid of pubescence.
Quite resistant to fungal diseases.
Meteor
super-early, semi-repaired grade. Harvested in the first half of June. In favorable weather, it forms an autumn crop on the tops of annual shoots.
Bushes erect, up to 2 m high, slightly sprawling. The ability to shoot formation is average. Shoots are weakly thorny.
The berries are transportable, medium-large (up to 3-3.5 g), hemispherical, ruby in color, dessert taste with aroma, attractive. Ascorbic acid in the pulp up to 24 mg%, vitamin P - 60 mg%, anthocyanins - 162 mg%, dry matter - 10.4%, sugars - 8.2%, acids - 1.1%. Productivity from 1 bush is about 2.0 kg, or up to 110 kg / ha. Differs in amicable return of a harvest.
Resistant to fungal diseases, raspberry mite, tolerant to purple spotting, winter-hardy.
Materials used: hozvo.ru/news/garden/Letnyayamalina/
Liked the post? Share with friends!
Raspberry category menu
The best varieties of large-fruited raspberries
‘Red Guard’, ‘White Guard’, ‘Chief Marshal’, ‘Beloved’, ‘Patricia’, ‘Pride of Russia’, ‘Beauty of Russia’, ‘Generalissimo’, ‘Taganka’.
Patricia
 The variety is large-fruited, medium-late summer ripening, non-repairable (traditional), standard.
The variety is large-fruited, medium-late summer ripening, non-repairable (traditional), standard.
Bushes up to 1.8 m high, semi-spreading, annually form 6-10 replacement shoots and 5-7 root suckers. Annual shoots of medium thickness, straight, pubescent, light to medium waxy, without thorns.
fruitful(250 kg per hundred or 4-7 kg per bush). Differs in friendly ripening of berries. Transportability is poor. Dessert appointment. Berries are large 4-12 g, truncated-conical, with a velvety surface, medium density, well removed from the fruit, with a few small seeds. When fully ripe, they do not crumble for a long time. The taste is sweet with raspberry flavor. Tasting score 4.0 points.
The leaves are large and medium, flat, slightly wrinkled, the edges are crenate, light green, mostly five-leafed. Reddish-brown when blooming.
Patricia is resistant to major diseases. Winter hardiness is moderate, bending down is required for the winter shoots.
Taganka
Variety new remontant, different high yield(at least 5 kg per bush). The bush is medium tall (up to 2 m), there are a lot of shoots: coppice - 4-5 stems, replacement shoots at least 8-12. One of the very best
repairing
varieties of large-fruited type. On annual shoots, the thorns are short and small, black-violet, plastic (not piercing). Ripening dates - early and medium early. The berries are large (from 4 to 10 g), red, slightly pubescent, blunt, easily removed from the fruit, but do not crumble for a long time. The variety is resistant to pests and fungal diseases.
The best varieties of standard raspberries
‘Patricia’ is an ideal variety for a gardener; ‘Divine’, ‘Charm’, ‘It’s time to go North’ - it is grown even north of the Arctic Circle.
Tarusa
Variety medium-late, large-fruited non-repair standard, with strongly thickened shoots, hard and tough.
Bushes do not require supports, about 1.5 m high.
The berries are large (4-12 g), obtuse, bright red, shiny, easily removed from the fruiting bed, dense and withstand transportation, smooth with a "raspberry" aroma.
The yield is high - about 200 kg per hundred square meters or 3-4 kg per bush, and when manure is applied, the yield is twice as large.
Bushes about 1.5 m high, form 8-10 replacement shoots and 4-5 root suckers that do not spread over the site. Annual shoots are upright, thick, hard, internodes are shortened. Shoots non-running with a rosette of leaves at the top, covered with pubescence, with a waxy coating, without thorns,
Twigs have up to 2-3 orders of branching, thickened, strong, medium length, they have 15-20 or more berries. The leaves are large, dark green, have a corrugated surface, their edges are bearded.
Does not freeze at frosts down to -30°С; in more severe frosts, bending under the snow is required. It is better to bend the shoots in advance, when they are not yet brittle and bend well (at the end of September).
Resistant to diseases and pests, in the presence of diseases, the yield does not decrease.
Arbat
Variety medium-early, large-fruited, non-repairable.
Bushes 1.5-2.0 m high, sprawling, form 8-12 replacement shoots and 5-8 root suckers, almost not spreading over the site. Annual shoots are thick, strong, thin at the top, non-lodging, without pubescence, with a wax coating, without thorns. Internodes 3-5 cm. Fruit twigs are thickened, have 2-4 branching orders, form 15-20 berries or more. The leaves are large, dark green, with a corrugated surface, the edges are bearded.
Berries weighing 4-12 g, elongated (up to 4 cm), conical, dark red, shiny, dense, transportable, sweet with a "raspberry" aroma.
The yield is about 20 t / ha or 4-5 kg per bush, when manure is applied, the yield is twice as high. Bears fruit annually. It works better than other large-fruited varieties in dry years.
It does not freeze in frosts down to -30°C; in more severe frosts, bending under the snow is required.
abundant
Variety medium-early, large-fruited, non-repairable, productive.
Bushes up to 2 meters high, compressed, semi-spreading. Shoots are elastic and strong, without thorns. Replacement shoots 8-10, root suckers 4-5; not prone to overgrowth, but need removal of excess shoots. It is better to leave no more than 10 fruiting shoots on a bush. The leaves are large with a sparse arrangement. Fruit twigs are not brittle, prone to strong branching. The berries strongly bend the stems, so garters required.
Ripening berries friendly, begins in the first decade of July, ends by the end of the month. To remove the berries, 4-5 collections are required, the most significant are the second and third. high yielding(4-5 kg and even more than 7 kg per bush). The berries are large (4–10 g), conical, bright red, shiny, dense, easily removed from the fruit. The taste is not inferior to forest raspberries. Dessert appointment. Transportability is good.
Doesn't freeze in frosts down to -30 ° C, in more severe frosts, bending under the snow is required.
Is different heat resistance, giving high yields during prolonged heat, when more than 30 ° C in the shade.
Resistance to diseases and pests is good, in the presence of diseases the yield does not decrease.
The best varieties of annual remontant raspberries
Varieties of the XXI century
Raspberry varieties included in the State Register of the Russian Federation
The State Register includes about 90 varieties of raspberries.
Amurchanka
Amphora
Arbat
Indian summer
Balm
Barnaul
Berdskaya
brilliant
Brigantine
Bryansk
Vega
Vislukha
Volnitsa
high
Hussar
Gloria
Gift of Siberia
Amurchanka's daughter
Vislukha's daughter
For health
Zorenka Altai
Illusion
Spark
Kaliningrad (Prussian)
Bryansk Cascade (Cascade)
Kirzhach
Kokinskaya
Bell
coral
Wren
red rain
Credo
Canby
Lazarevskaya
weasel
Amateur Sverdlovsk
Maroseyka
Malakhovka
Marlborough
Meteor
Milton
Michurinskaya Dessert
Malling promise
Reward
Tenderness
Novokitaevskaya
Novosibirsk large
Kuzmin's news
Newburgh
Abundant
Siberian light
insight
Omsk steppe
Orbit
Pavlovskaya
Patricia
Peresvet
charm
Turn
glade
early sweet
Early Surprise
Ruby Bulgarian
Ruby
Samara dense
Seedling Ruby
Siberian girl (Rhythm)
shy girl
Slav
Soviet
Falcon
Sun
flash
Companion
steppe
Tarusa
Tenkovskaya early
Trojan
ember
Luck
Chelyabinsk large-fruited
Shosha
Anniversary
Youth Agawam
Materials used: strawberryfarm.info/raspberry-sort-4.html
sort-info.ru/malina
asprus.ru/blog/sovremennyj-sortiment-maliny/
There is no such person who would not love raspberries. The one who claims that ripe berry he did not like it, he simply never ate a ripe, personally picked fruit. – has not only original taste qualities, but also differs healing properties. It is actively used for colds as an antipyretic.
Raspberries need watering, fertilizing, pruning and loosening. If you periodically hold such events, then the shrub will not remain in debt and will delight you with delicious fruits:
- Watering should be frequent, especially in the spring, when the shoots begin to wake up from hibernation, and the young growth makes its way out of the ground. Do not forget about irrigation on hot summer days.
- In the spring, it is also necessary to take care of loosening the soil. The procedure is required so that more air and nutrients enter the roots. As the soil becomes overgrown with weeds, they are weeded out, which is also a favorable moment for the growth and development of the bush.
- During the period of active growth, it is necessary to make top dressing. During the period of growth and fruiting, 2-3 top dressings are usually done. The first one has already been submitted in early spring. It needs to be prepared chicken manure, mixed with a spoonful of saltpeter, diluted in a bucket of water. It is recommended to apply nitrogen fertilizers - once per period, either in spring or autumn. After the harvest period, potash fertilization is required. Before flowering, you need to feed it with complex fertilizer - nitroammophos or Zdravnem. This will form a large number of buds.

To get neat, juicy berries that you won’t be ashamed to put up for sale, canned whole or just enjoy juicy fruits, you need to monitor the health of the shrub.
Although the plant is immune to diseases and pests, if left untreated, it can become infected and die.
Be sure to pay attention to the condition of the shoots and leaves. The following pests and pathogenic bacteria are distinguished:
- Raspberry beetle - insects wintering in the ground. Their appearance was noticed in May. They are a small pest with gray oval shapes. The beetle initially eats flowers and leaves, and then moves into the buds, eating them from the inside. After such an invasion, the berries sharply decrease in number, and the remaining ones are saturated with larvae.
- Kidney moth - a small butterfly with spots on its wings lays larvae on stems. The latter feed on the buds, corrode the stem and penetrate inside, descending along it to the roots. Thus injuring the entire plant from roots to buds, eating its contents.
- Stem fly - its activity occurs in late May - early June. She lays her eggs in the axils of the leaves, the hatched larvae eat their way into the center of the trunk, feeding on its core.
- Spider mite - weaves a web with inside leaves, sucking out all the juices from the greens. The leaf eventually dries up and falls off.
- Weevil is a beetle that lays offspring on buds. The larvae, feeding on the tender core, grow up and increase the beetle population.
- Chlorosis - the leaves become yellow, significantly deformed. It is required to apply top dressing with complex fertilizers.
- Purple spot - appears on the leaves, accompanied by peeling upper layers stem. Shoots must be quickly cut and burned. Then spray with Bordeaux liquid.
When pests such as the stem fly or bud moth appear, the shoot expands in one place, forming a bump. The damaged sprout must be removed under the root, so that not even a hemp remains. Burn everything. At the beginning of the formation of buds, it is recommended to spray the bushes with a solution of tansy.
Thus, the main thing is to notice pests or diseases that have appeared in a timely manner and apply methods to combat them.
More information can be found in the video:
As you know, there is no bad raspberry, it is tasty and very tasty. Of course, it all depends on the variety of raspberries. There are the best varieties of raspberries, early varieties raspberries growing in the garden and late raspberries. To choose a fruitful one, good grade raspberries, you need to understand the varieties, know their advantages and disadvantages.
Raspberry species
In order to clearly represent the pros and cons of a particular genus of raspberries, one should consider its classification by species.
Traditionally, the following categories of raspberry culture are distinguished:

Varieties of raspberries are wild raspberries, bush raspberries, and domestic raspberries.
Video “Varieties of raspberries”
From the video you will learn a lot of interesting things about different types raspberries.
Universal varieties
Very often, gardeners in search of the best varieties of raspberries forget that when choosing, it is necessary to take into account the geographical location. For example, the best varieties of raspberry bushes for central Russia and productive, unpretentious care, raspberry varieties in Ukraine will not be suitable in Belarus.
However, there are universal species suitable for most regions.
Consider the most prominent representatives of this variety:

The best early varieties
If you want to enjoy fragrant berries as soon as possible, grow such varieties as Molling Juno, Moling Promise, Lachka, Glen Lyon, Lyashka, etc.
Raspberries of the genus Molling Juneau at an early ripening period bears fruit with small fruits. Shrub of medium spreading with straight shoots. The crop favorably tolerates transportation, the plant resists pests and diseases. The fruits are sweet, dark red, stored for a long time after picking. The yield is high. Excellent fruiting in the southern Russian regions. 
Moling Promise has the following characteristics: collection up to 16 t/ha for the south of the Russian Federation up to 12-14 t/ha when the shoots are covered with snow for the winter. The plant is medium-sized (2 m), giving a lot of offspring. Annual branches are thin, straight with numerous spines. The fruits are large, up to 3-5 g, of the same size, orange-red, bright, with drupes.
Lachka - summer look. Sweet berry of early ripening with long fruiting. It is considered a high-yielding variety, from one hectare to 20 tons. Popular and in high demand in the markets.
Varieties of medium ripening
On private household plots medium-ripening varieties are most often grown, as they give good yields. The main advantage is the minimum susceptibility to diseases and unpretentiousness in care. Today, about 100 species of mid-ripening raspberries are known.
Varieties with an average fruit ripening period begin to yield in the first decade of July. These varieties include Black Jewel, Sokolitsa raspberry, Glen Ample, Tarusa, etc. 
Black Jewel is a black type of raspberry. His plants have intense growth energy, upright branches. The fruits are black with a blue coating, round, medium in size. Pleasant and fragrant taste, juicy, sweet. They transport well.
Raspberry Sokolitsa comes from Poland, it is used both for traditional production - in open ground, and in closed - film tunnels, greenhouses. Suitable for desserts, processing. Ripening dates - the end of June. Medium sprawling culture, shoots with few thorns, reach up to 2 m. Leaves of medium size, wrinkled, rich green. The fruits are large, sometimes very voluminous. They weigh 5-7 g. The shade is red, glossy. The drupes are small, one-dimensional, well kept. Frost resistance is high. Does not need excess moisture in the soil and air.
Raspberry Glen Ample has the following description: a productive, fruit-bearing variety on two-year-old shoots. Fruits in round, saturated red color, dense, tasty berries. The shrub is winter-hardy and drought-resistant. 
Tarusa is a berry plant with powerful branches, which is why it received the second name "raspberry tree". The length reaches up to 1.80 m, with a yield of up to 6 kilograms. One of the main advantages is straight-growing shoots without thorns, which makes it easier to harvest. The weight of the fetus is about 5 grams.
late maturing varieties
The description of raspberry varieties with late fruit ripening should begin with the following advantages: resistance to low temperatures and the possibility of large yields. The harvest consists of large, juicy and tasty berries. Today, more than 200 species of this crop are known with a late ripening period of both remontant and common species. Famous among them are Malling Leo, Octavia, Tadmor and Mac Black and others.
Molling Leo is a well-known variety, with very tasty, large, sweet fruits that weigh 6-7 grams. Resistant to aphids. Transportability is good, due to the dense consistency.
Octavia - features of the species: large rounded fruits with sourness, of the same size, weigh up to 7 grams. High transportability.
Tadmor is a very late ripening, one of the newest raspberry varieties. Among its features are: powerful fruits that weigh up to 8 grams. The color is bright, burgundy. Uniform maturation of the crop and excellent storage performance. After collection, they are perfectly stored and transported.
Mac Black is characterized by late fruiting on vigorous and winter-hardy bushes. Round fruits ripen a week after all varieties of late fruiting. Not without drawbacks: the berries have a low density, therefore it is recommended for private plots.
Repair varieties
Remontant culture with an annual shoot development cycle, in one season it grows and produces a crop. The best are All Gold, raspberry Polissya, Penguin, Hercules, Atlant, etc.
All Gold is a yellow-fruited species characterized by tasty, sweet and large berries, the weight of which can reach up to 12 grams. The fruits of All Gold raspberries are very fragrant, with an aftertaste of forest raspberries, amber, glossy, shiny, beautifully shaped. Harvest from one plant up to 9 kg. Feature- high resistance to major fungal diseases, high frost resistance. Low transportability harvested crop, does not allow them to be grown commercially. When transporting fruits over long distances, it is sometimes possible that the juice of berries can run out of plastic containers. The main purpose of this species is fresh consumption. The ripening period is medium-early. 
Propagated by seedlings with a bare root, it is best to acquire them in the dormant stage (in the spring, before bud formation or in the fall, when the leaves fall). Such seedlings should be immediately planted in the ground. Seedlings, which are sold in containers with soil, are planted in open ground in any season.
Raspberry Polissya - ripening period - late July - early October. The berries are medium, dark red, sweet, fragrant, dense texture, suitable for transportation. The plant is resistant to gray rot. 
Atlant is a high-yielding and large-fruited species that ripens in mid-August. Its peculiarity is voluminous, dense berries, weighing up to 5 grams, with a sweet and sour taste, tender and juicy pulp. Great for freezing and processing. When fresh, they have a long shelf life.
Hercules is characterized by a straight-growing, stocky plant, with long-term fruiting, up to the first frost. The berries are large, reach 10 grams, which together can give big harvest. Sweet and sour in taste. Resistant to fungal diseases. Its popularity is due to the fact that the harvest is plentiful and of high quality. Also, the advantages are the stability of aging, resistance to most diseases and pests.
The penguin has a standard crown type with a low shrub (up to 1.3 meters), consisting of a small number of shoots (5 - 8). It ripens at the end of summer, the berries are medium in size (up to 5 grams), dense, round in shape, maroon in color. They can be on the shoots after ripening (up to 5 days), without losing their taste characteristics. Resistant to common diseases and pests. Productivity from one - at proper care- up to 15 kg. 
As you can see, the varieties of raspberries are numerous and radically different from each other, the color of the berries (black, burgundy, red, yellow, ruby, orange, light red, bright scarlet, black-blue, orange). The taste spectrum is also diverse - sweet, honey, with sourness, with a blackberry aftertaste, fragrant, etc. In terms of ripening yields - early, mid-season and late. And further whole line differences that unite the culture we are considering, the queen of all berries - raspberries!
Video “About repair raspberries”
From the video you will learn a lot of interesting things about remontant raspberries.
Received by V. V. Kichina at NIZISNP. The bush is tall (2 - 2.5 m), upright, slightly sprawling, forms a moderate amount of shoots. Annual shoots are thick and medium, hairless, with a wax coating, prickly. The berries are medium (2.5 - 3 g), bright red in color, conical in shape, shiny, with a pleasant sweet taste and aroma, ripen together, transportable. A variety of garden raspberries with an average ripening period. Productivity is high (up to 100 kg) per hundred square meters. Winter hardiness is at the level of standard varieties, resistance to diseases and pests is average. Recommended for the Moscow region and other areas of the Non-Chernozem zone.
Modern, basic requirements for raspberry varieties.
Modern raspberry varieties should be well adapted to the weather conditions of a wide range and, if possible, combine frost resistance, flower resistance to late spring frosts, thaw tolerance and drought tolerance. In the northern latitudes, a deterrent for many large-fruited and high-yielding raspberry varieties is low winter hardiness; in the southern regions, hardy, albeit not very frost-resistant varieties are needed, but able to safely endure snowless winters and frequent thaws - not all varieties of bark are resistant to damping.New raspberry varieties should not yield the best varieties in terms of yield (120 c/ha) and resistance to the most dangerous pests and diseases.
Suitability for mechanized cultivation technology is an important requirement for modern raspberry varieties, therefore, the bush must be compact, low (1.5 - 1.8 m), with an optimal number of stems (4 - 8 shoots per bush), equal strength of growth and development, with shortened internodes along the entire length (3 - 5 cm), with a restrained growth rate of new shoots.
Shoots without thorns, but pubescent or with an intense waxy coating that prevents excessive evaporation of moisture. Flowering and ripening of berries should take place in a short time and simultaneously on all branches.
Raspberries should be large (more than 3 - 4 g), even in size and shape, dense, strong, not crumbling, attractive, transportable, resistant to rot on the bush and during storage. In addition, the berries must have high taste qualities and a strongly pronounced aroma, homogeneous, well-linked drupes, small few seeds, the required content of sugars, organic acids, vitamins and biologically active substances.
Standards for Raspberry Planting Material
Quality planting material raspberries must meet certain technical requirements.- The stems of raspberry seedlings with an open root system should be without leaves and shortened to 40 cm.
- Implementation of seedlings with a closed root system is allowed with leaves and without shortening.
- Seedlings should not be dried out, without mechanical damage.
- Infection with viral, phytoplasmic diseases and leaf-eating insects is not allowed.
- Varietal purity 100%.
- The length of the roots is not less than 15 cm.
- Number of shoots 1pc.
- The diameter of the base of the shoot is 0.8 - 1 cm.
Raspberries are one of the most popular crops. Its berries are useful, tasty and beautiful. How to choose the right varieties? What to pay attention to first of all?
First, you need to buy varieties that are zoned for your area. There is the State Register of Breeding Research, which contains a list of varieties that have passed the test and are recommended for cultivation in this region. At the same time, their winter hardiness, productivity and other indicators are taken into account. The list of raspberry varieties recommended for the Central region of Russia now includes about 30 items.
What is raspberry?

For those who seek to grow something original, which you cannot buy on the market, large-fruited varieties (with an average fruit weight of 10-12 g) are suitable. You can surprise neighbors and guests with late-autumn (remontant) raspberry varieties that ripen in August-September, when most of the raspberries have already departed. Good ones remontant varieties - Aphrodite, Firebird, Golden autumn, Bright, Incomparable, Orange miracle, Autumn. It is enough to plant six varieties - three large-fruited and three remontant, 3-4 bushes of each variety.

Raspberry varieties: Aphrodite, Vera, Yellow Giant, Cossack, Lemon and Maroseyka
How many raspberry bushes need to be planted to get a harvest?
To get a crop of 15-20 kg with minimal care, you need to plant at least 15-17 raspberry bushes different term maturation. The same number of berries can be collected from 8-10 bushes, if you take care of them intensively: in May-June, once a week, feed with urea at the rate of 30-40 g per bucket of water, water in hot, dry weather, weed, mulch the soil with humus or peat, remove excess shoots.
In autumn or early spring, organic fertilizers (rotted manure, compost, peat) must be applied at the rate of 5 kg per 1 sq. m. Fertilizers are embedded in the soil, digging it to a depth of 20-25 cm.
Large-fruited varieties of raspberries
It is better to use high-tech large-fruited varieties of different ripening periods.
- Early - Malakhovka, Maroseyka, Vera.
- Medium maturity - Arbat, Balm, Fantasy Scheherazade, Sun of Kyiv.
- Middle late - Cleopatra, Shulamith.
- Late - Tarusa, Shosha.





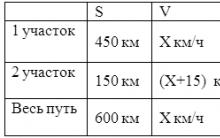

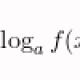



Living and dead water: myth or reality, what is the power of living and dead water?
Craniosynostosis, or premature fusion of the bones of the skull Frontal crest in a child
Beautiful hair How to achieve hair density at home: useful tips
Why mosquitoes bite some people, but not others
How to achieve beautiful hair