Mechanical restoration is a process during which the dimensions and configuration of workpieces and parts are changed. If we talk about metal products, then special cutting tools are used for their processing, such as cutters, broaches, drills, taps, cutters, etc. All operations are performed on metal-cutting machines according to the technological map. In this article we will learn what are the methods and types of mechanical processing of metals.
The forges of Bologna, belonging to the estate industry group, are used for cleaning operations for the manufacture of stainless steel used for the production of aircraft parts operating in aggressive atmospheres. Since this steel was provided by the customer, bolognese blacksmith products found differences in mechanical characteristics between parts. - The topic of the dissertation was to conduct a material admission act, including: - Comparative micrographic examination between healthy areas and affected areas. - First of all, it was necessary to check the purity of the inclusion, and then the students had to measure the grain size in the raw state and in the hardened and tempered state.
Processing methods
Machining is divided into two large groups. The first includes operations that occur without removing the metal. These include forging, stamping, pressing, rolling. This is the so-called using pressure or impact. It is used to give the desired shape to the workpiece. For non-ferrous metals, forging is most often used, and for ferrous metals, stamping is most often used.
Start chapter navigation. End of navigation box section. Surface treatment allows you to change the properties of the surface layer of steel. The first surface treatment was gilding, for aesthetic purposes, and then corrosion protection was requested.
The surface finish is now variable and allows for lower part cost when core properties are not required: less efficient but machined steel is used. It also allows surface and core properties to be coupled, such as a hard surface and a ductile core.
The second group includes operations during which part of the metal is removed from the workpiece. This is necessary to give her required dimensions. Such mechanical processing of metal is called cutting and is performed using the most common processing methods are turning, drilling, countersinking, grinding, milling, reaming, chiselling, planing and broaching.
On the other hand, one of them is limited by the size of the processed part. In addition, surface treatment also leads to additional costs and environmental problems: handling of toxic products, energy consumption. Surface treatment is usually last operation pre-delivery: any subsequent operation may impair local treatment. However, this is not systematic and even processing can change the dimensions of the object slightly and needs to be corrected when the tolerances are very precise.
Surface treatment mainly consists of four types. Machining: this is the deformation of the material on the surface, it is possible to remove it; diffusion treatment: this is due to the fact that atoms penetrate the steel, thereby changing the content of alloying elements on the surface; conversion treatments: this consists in forming a layer chemical reaction between iron and the environment, coatings: this consists in applying another layer of material to the steel. Processing by conversion or coating can be carried out by electrolysis: the part to be treated is quenched in a bath and an electric current is passed between the electrode and the part.
What is the type of processing
Manufacturing metal part from a blank is a laborious and rather complicated process. It includes many different operations. One of them is mechanical processing of metal. Before starting it, make up technological map and make a drawing of the finished part indicating all the required dimensions and accuracy classes. In some cases, a separate drawing is also prepared for intermediate operations.
Ions in solution migrate to the part and react to form a conversion layer or precipitation. Powder paint. The main treatment is polishing, which is the removal of material in order to eliminate scratches and have a perfectly smooth surface. In fact, scratches have the dimensions of an abrasive invisible to the naked eye. In addition to aesthetics, this gives optical properties.
Removal of material can also be accomplished by acid dissolution, optionally using electric current. On the contrary, the metal can be grounded by abrasive scratches of a given direction, a certain shape, or by a blow: sand or a ball.
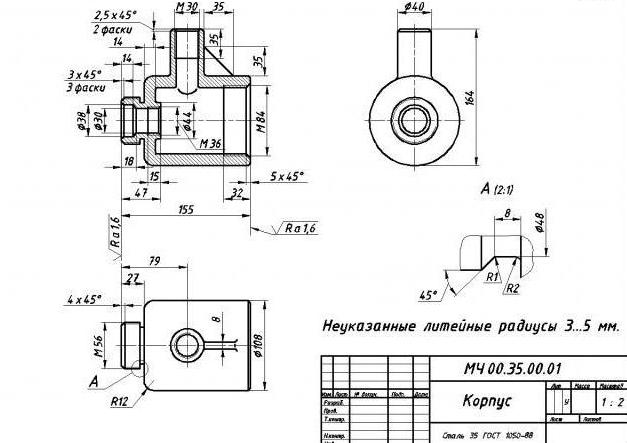
In addition, there is roughing, semi-finishing and finishing machining of metal. For each of them, the calculation and allowances are performed. The type of metal processing as a whole depends on the surface to be treated, the accuracy class, the roughness parameters and the dimensions of the part. For example, to obtain a hole according to the H11 grade, rough drilling is used with a drill, and for a semi-clean reaming to the 3rd accuracy class, you can use a reamer or countersink. Next, we will study the methods of mechanical processing of metals in more detail.
Finally, the steel can be coated. Note that the paint is low stability to temperature and against abrasion. It may be desirable to promote the attachment of another material, such as paint, or, conversely, to reduce it in order to reduce sticking and friction phenomena.
To improve adhesion, the workpiece is first removed for degreasing or, depending on the subsequent processing, to remove the oxidized layer. The workpiece can then be blown or fired to create a roughness. The surface condition is characterized by the phenomena of adhesion and friction, but not in an impressive way. On the other hand, two extremely smooth surfaces can create a suction effect: since there is no air between the contacts that are in contact, the atmospheric pressure that gives the parts to each other is not balanced.
Turning and drilling
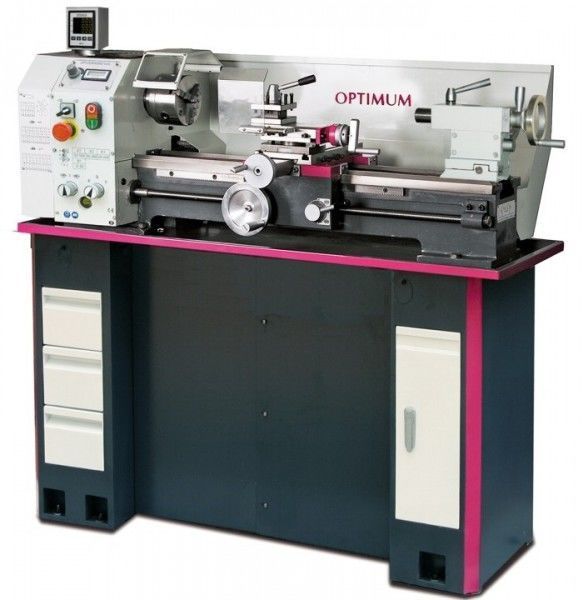
Turning is performed on machines of the turning group with the help of cutters. The workpiece is attached to the spindle, which rotates at a given speed. And the cutter, fixed in the caliper, makes longitudinal-transverse movements. In new CNC machines, all these parameters are entered into the computer, and the device itself performs necessary operation. In older models, for example, 16K20, longitudinal and transverse movements are performed manually. On lathes it is possible to turn shaped, conical and cylindrical surfaces.
To get the best surface condition, grinding or even polishing is performed. Phosphating is a transformation method that consists in creating a layer of iron phosphates. It is obtained by soaking zinc or magnesium phosphate into a solution, which promotes paint adhesion, and in a thick layer protects against corrosion.
Surface sealing is useful to prevent breakage from impact, matting, and wear. The first way to harden a surface is to harden, so machining is applied. In addition to sandblasting and blasting, rolling can also be practiced: metal repelling rollers. expensive, also allows for very high quality surface finishes with very tight dimensional tolerances.

Drilling is an operation that is performed to obtain holes. The main working tool is a drill. As a rule, drilling does not provide a high accuracy class and is either rough or semi-finishing. To obtain a hole with a quality below H8, reaming, reaming, boring and countersinking are used. In addition, after drilling, cutting can also be performed internal thread. Such machining of metal is performed using taps and some types of cutters.
Solidification creates compressive stresses, the surface is prestressed, which also contributes to its hardening. Note that the diffusion treatment introduces atoms within the iron mesh and also compresses the surface. Surface quenching is also possible. The principle is to heat the surface without overheating the heart. A torch or induction heating is used: an electromagnetic wave creates a surface current that causes Joule heating. The equipment includes a heating element and immediately after the pressure shower.
Milling and grinding
Milling is one of the most interesting ways of metal processing. This operation is performed using a wide variety of cutters on milling machines. There are end, shaped, end and peripheral processing. Milling can be both rough and semi-finishing, and finishing. The smallest quality of accuracy obtained during finishing is 6. With the help of cutters, various dowels, grooves, wells, undercuts are machined, profiles are milled.
Recent methods offer other ways of heating: laser, plasma cutter, high frequencies. During welding work carburetion gas can be used to enrich the weld with carbon. Preheating and welding acceleration control the cooling conditions and thus quench in air.
Nitriding involves introducing nitrogen into steel. Nitrogen forms nitrides with iron and alloying elements; nitrides are very hard ceramics. A combination zone is formed on the surface, formed from iron nitrides, and then a diffusion zone, in which nitrogen is in the solid solution of the insert. In this diffusion zone, nitride hardening precipitates can be obtained at the grain boundaries.

Grinding is a mechanical operation used to improve the quality of roughness, as well as to remove an excess layer of metal down to a micron. Usually, this processing is the final stage in the manufacture of parts, which means it is finishing. For cutting, abrasive wheels are used, on the surface of which there is a huge number of grains that have different shape cutting edge. During this processing, the part is very hot. In order for the metal not to be deformed and not chipped, cutting fluids (LLC) are used. Machining of non-ferrous metals is carried out with the help of diamond tools. This makes it possible to provide best quality manufactured part.
Nitriding can be done in three ways. Processing temperature imposes molybdenum steel. Carbonitriding is a combination of nitriding and carburizing and is carried out at a temperature of about 800 ° C, after which surface quenching occurs, which forms martensite with nitrogen. mixture of carburizing gas and ammonia.
The surface conversion layer contains nitrides and iron sulfides which improve slip and prevent trapping. The underlying layer is a very hard nitride layer. Galvanized sheet, easily recognizable due to the iris, which brings out the zinc crystallites.
In the machine-building, metalworking industries, in construction they use various ways metal processing, cutting - one of their varieties.

Since there are a huge variety of metal parts, they differ in shape, size, weight, alloy composition, therefore metal cutting is also carried out in several ways. The main ones can be distinguished:
The paint already mentioned above protects against corrosion by creating a barrier to environment when the temperature is moderate and there is no risk of abrasion. were abandoned due to the presence of miniium, a toxic lead oxide, but some paints contain a zinc filler that provides improved protection. Some antifouling paints prevent the entrapment of marine animals and algae, which, through their metabolism, degrade the paint or can accelerate corrosion. On the other hand, the phosphating undercoat facilitates both paint adhesion and improves corrosion protection.
- turning;
- drilling;
- milling;
- planing;
- grinding.
Each type involves the use of specialized equipment - often these are stationary machines.
Turning metal parts
This method is used when the original workpiece needs to be slightly brought to the right sizes and configuration. To do this, experts use lathe, a set of drills or cutters. The part to be processed is placed in a special rotary device, around which the cutting mechanism moves.
Soft chromatization consists in the formation of a diffusion layer of small thickness. This is done in the same way as hard chromatization. Chromatization can be applied after phosphating. This process should not be confused with chromium plating or chromating. Galvanization consists of coating zinc steel by immersion in a liquid zinc bath, which is very effective against atmospheric corrosion, but poorly resistant to temperature and resists poor abrasion.
The galvanized steel can then be chromated: a portion of it is dipped in a bath of potassium or sodium dichromate, which creates a conversion layer, sometimes referred to as the "bichromatized" portion. but prevents the formation of white zinc oxide, so it is essentially an aesthetic effect. On the other hand, it promotes the adhesion of paint. Bare steel cannot be chrome plated.
Due to the force exerted, the edge of the drill tip cuts into the part and removes the excess layer, which turns into different kind shavings. Depending on what type of cutting is performed, chips can be:
It is also possible to electrolytically tinn and then designate as "tin". In galvanization, as in tinning, the metal oxide is oxidized and the reaction prevents rusting. hard chrome plating and nickel plating are no longer used for corrosion protection: they cause accelerated corrosion in case of scratches. For very aggressive conditions such as high temperatures or highly corrosive products, ceramic metal can be coated. way plasma spraying: the ceramic powder is melted in the plasma torch and then projected onto the metal or solidified; by reacting with a gas. The deposit is brittle and presents a risk of cracking on cooling.

- elemental - obtained by processing a superhard metal such as titanium, processes are performed at low speeds;
- merged - formed during high-speed turning of parts made of non-hard steel, copper, tin, plastic;
- fracture - occurs as a result of cutting metal-plastic parts;
- stepped chips are obtained as a result of processing metals of medium hardness.
For different types of metal, a suitable speed is selected, so refractory and superhard metals must be sharpened at a minimum speed. It is calculated before starting work and set in the parameters grinder, then the speed is maintained automatically.
Again, this is more of a chapter common culture. The main elements of the main methods of treatment must be known. The surface treatment is designed in such a way as to provide a special appearance and characteristics of metal parts. Their use is as follows: anti-corrosion, anti-wear, appearance, conductivity, coefficient of friction, etc. For this purpose metal coating applied electrolytically or chemically. This process consists of three main phases: - degreasing or degreasing metal supports, - processing in the proper oral form, - washing the part.

It must be understood that more accurate and clean works are provided at a lower speed, and roughing can be carried out at the maximum allowable.
An important point is the metal alloys from which the cutters are made. The sharpener should be made of a stronger alloy than the part to be cut. Most often, titanium, tungsten, tantalum are used for cutters.
There are thirty methods grouped into 5 families: mechanical processing, thermochemical processing, water and dry processing, paints, conversion treatment. Surface treatment is mainly used in the automotive, telecommunications, electronics, aerospace, jewelry and hardware industries. Among the various contaminants that can be found in baths and sludges are: organic, phosphorous or nitrogenous materials, suspended solids, organohalides, cyanides, fluorides, metals and salts.
Depending on what kind of turning is necessary, the cutters have various forms and dimensions, a variety of cutting elements will allow you to work with high accuracy and less chips, that is, without significant waste.
The cutter can be classified according to the main types of processing:
- boring;
- threaded;
- groove;
- checkpoint;
- cutting;
- undercut;
- shaped.
The lathe itself can be mechanical and automated with a software control panel. The latter gives the greatest accuracy and speed of work, this type of machine tool has replaced the mechanical one and is gradually replacing them from production.
All calculations - speed, required angles, thread directions are calculated in software complex, this opens up wide opportunities for the production of non-standard parts. If a mechanical one were used for them, it would take considerable time to set up and a large percentage of rejects is not ruled out.
Drilling metal workpieces
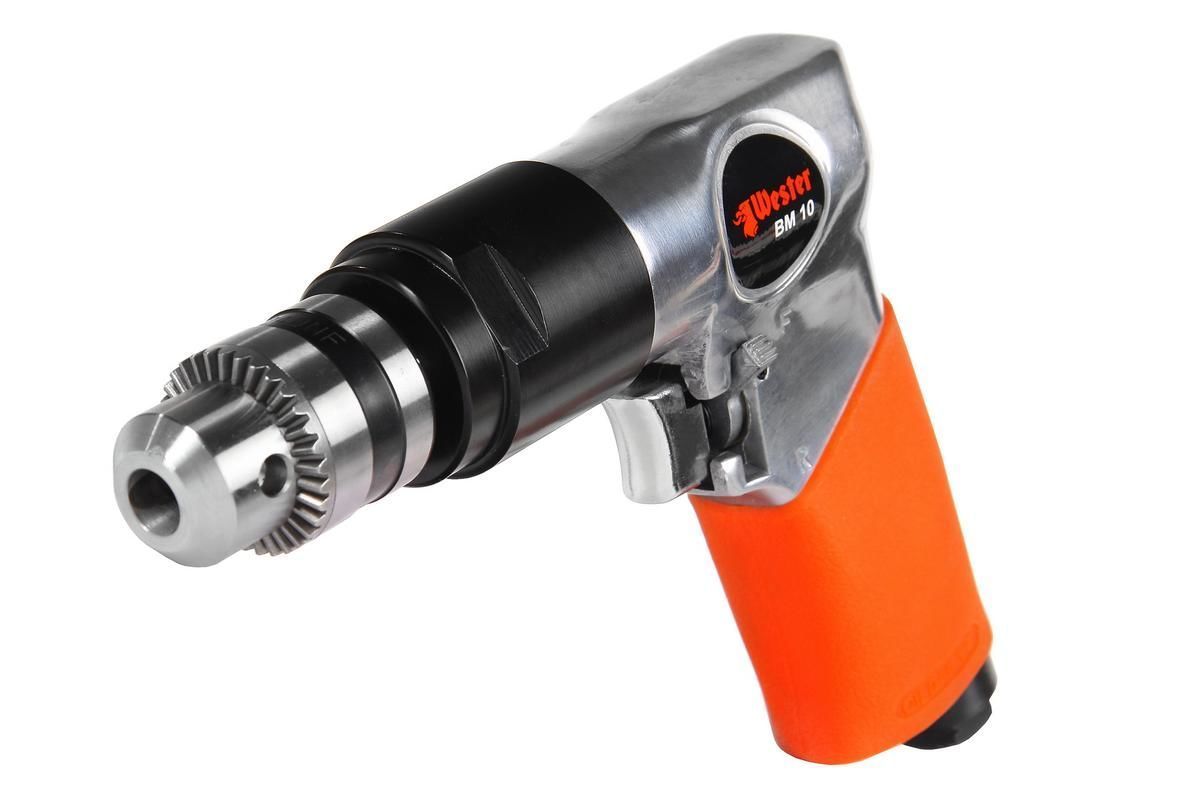
Another type of cutting of metal parts is drilling, it is performed on the appropriate equipment, and the cutter itself is called a drill. The essence of the method is that the drill or countersink is driven mechanically and rotates around its own axis.
Drilling machine. Customization and other tricks
Due to such movements, the tool crashes into a metal part, making a hole in it. The drill is driven by a manual fixture, mechanical and automated machines. Using a drill, you can make holes in a metal workpiece different kind, size and depth:
- feather;
- spiral;
- centering.
The most common spiral type of drill, it consists of three parts: the working part, the neck and the shank. The cutting piece has two edges located at a certain angle with respect to each other, for example, to cut a cast iron part, an angle of 118 o is required.
Steering rack drilling machine
The shank is needed to fix the drill in the chuck of the machine or drill. It can have two shapes: cylindrical or conical. A foot is installed at the end of the shank, which is needed to push the drill out of the socket after use.
The neck of the drill is a transitional link that is necessary to ensure the exit during the grinding process of the abrasive wheel. The drill is marked on the neck.
Before starting drilling, you need to mark the part, it is better to make the center in-depth with a center punch so that at the beginning of work the drill does not fly off the intended point.
Various tools can be used to drill metal parts:

Milling of metal parts
Metal cutting with a milling cutter is one of the most common methods. The main cutting element in the design of the machine is a cutter - a round wheel with jagged edges. The electric motor drives the cutting mechanism, at high speed the cutter cuts into the metal workpiece and removes layers in the right places.
Turning and milling machine DMG CTX gamma 2000
The result is a cut into parts and chips of waste material. Previously milling machines driven only by a specialist, due to the high speeds and wheel diameter, a lot of waste and defective parts were obtained. Modern machines are controlled software, thanks to which high level cutting precision.
Milling machine for metal Corvette 416 Enkor
Cutters can be different sizes and shapes and are used depending on the required size of the cut, the type of metal being processed.
The latest generation machines are equipped with a laser, which allows not only to achieve maximum precision, but also to perform work on complex figured cutting. The thermal laser burns the edge in the right places, and the grinding laser passes several times along the edge, cutting the metal, this approach ensures that the minimum layer of workpiece material is removed. The output is a clean cut, without burrs and chips, such a part will not require further cleaning.
Planer cutting of metal
Processing of metal by cutting in a planing way involves the removal upper layers the surface of the part being machined. This type of processing involves the use of specialized machines:
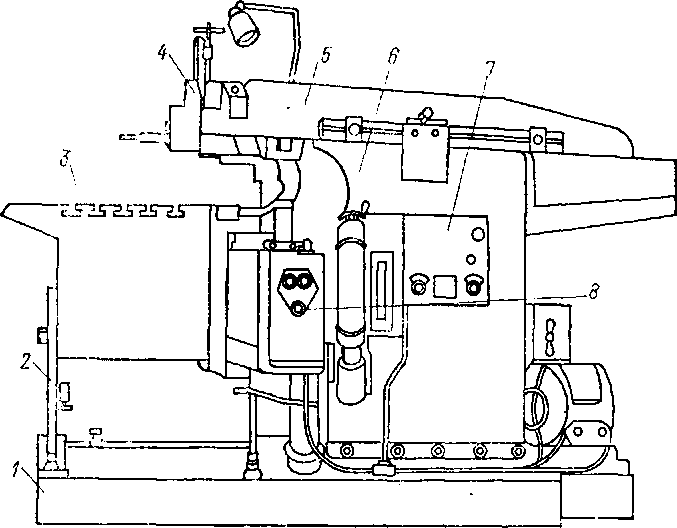
- planing and slotting;
- cross and longitudinal section;
- edge-cutting.
The machines differ in the way of movement of the cutting mechanism, productivity, quality of metal processing.
A feature of planing machines is the use of only straight planing cutters, they are installed at short overhangs, since they do not differ in vibration resistance, but are quite simple to operate.
The disadvantage of such cutters is the impossibility of obtaining the most accurate cutting results. To eliminate this drawback, some machines have the ability to mount several cutters.
Working with planers it is important to consider that the cutting parts are quite powerful and are capable of plunging into the metal to a great depth from the first press, which can ruin the product.
Grinding as a way to cut metal
The grinding method for cutting metal parts involves the use of various abrasive wheels. They consist of small grains of mineral origin, which are connected to each other by a bunch.

The cutting technique is reduced to the following process: when the abrasive nozzles move, the sharp edges cut off the upper layers of the metal and leave a smooth recess behind them. All movements are carried out at a very high speed, sometimes it reaches 3000 meters in one minute, for comparison, when turning, the maximum speed is 30 meters.
Due to the high speed and the chaotic arrangement of the grains, very small chips are obtained, which scatter in all directions and for several meters. This feature should be taken into account when organizing safe conditions worker.
Grinding allows you to achieve precise cutting results, however, the machine consumes a lot of electricity, 10 times more than, for example, a lathe. Another feature of grinding is the high degree of heating of the metal part itself, in some cases up to 1000 o. This must be taken into account when processing soft metals, such as copper, tin, cast iron and others, they can simply melt from the action of the grinding wheel.
Video: The amazing possibilities of CNC machines










The influence of the middle name on the name Yuri
Name Ilya - meaning and contraindications
Baby keeps crying
What does the name Aidar mean, the mystery of the name
Name Ilya - meaning and contraindications