If you were attentive in anatomy lessons, then you probably remember that in the human body there are as many as 12 pairs of cranial nerves, one of which includes the facial, or, as it is also called, the trigeminal.
From its name, it is easy to guess that this nerve consists of three branches that provide sensitivity to certain areas on the face:
- the first branch is the eye, upper eyelid and forehead;
- the second - the lower eyelid, cheek, nostril, upper lip and upper gum;
- the third - the lower jaw, lower lip and gums, several chewing muscles.
When inflammation of the trigeminal nerve occurs, the patient experiences real torment from severe pain. At the same time, such an attack can be caused by a minimal impact on an unhealthy area - from applying makeup to brushing your teeth.
This pain is often compared to a shock of electricity penetrating the entire half of the face and spreading along each of the branches of the nerve.
Unfortunately, neuritis of the facial nerve cannot be completely cured. But it is possible to significantly reduce the manifestations of pain with the help of drug treatment. In particularly difficult situations, they resort to surgical intervention.
Symptoms of inflammation of the facial nerve
- "Shots" in the face
- Pain can occur from a light touch to the face with hands, during a smile or when talking.
- The attack lasts no more than 2 minutes, usually recurs no more than a few days or weeks
- Most often, inflammation appears only on one side of the face.
- Attacks of pain can be single, sometimes repeated up to hundreds of times a day
- Painful sensations are noticeable in the lower jaw, gums, cheek, lips
- During an exacerbation of the disease (as a rule, this happens in the cold season), the number of attacks increases dramatically
- Facial neuralgia tends to increase the number and intensity of pain attacks.
How and why the trigeminal nerve becomes inflamed
This disease has long been known throughout the world, but there is no unanimous opinion about why and how it occurs. But there are some assumptions.
- Viral infection. Neuralgia can be caused by any virus, but the most common culprits are herpes or shingles.
- Reduced immunity or immune dysfunction is the most favorable background for the development of any virus.
- Hypothermia. Being in a draft or exposing the ear and face to cold often causes inflammation of the facial nerve.
- Stress, physical or emotional overstrain, psychological shocks that reduce the protective functions of the body.
- Inflammation in periodontitis, gingivitis, pulpitis, periodontitis, other complications of caries.
- Unbalanced nutrition.
- Severe infectious diseases.
Neuralgia can also be associated with the aging of the body and the destruction of the myelin sheath of the trigeminal nerve. Sometimes one of the causes of the disease can be a tumor, as well as multiple sclerosis.
Diagnosis of inflammation of the trigeminal nerve
In order to diagnose neuralgia of the facial nerve, the doctor first of all evaluates the pain syndrome - its type, location and stimuli that provoke seizures.
Usually, pain occurs in the face suddenly and lasts no more than a minute. Mandatory palpation of the trigeminal nerve to detect a painful branch and the degree of its damage.
Computed tomography or magnetic resonance imaging are often prescribed, which help to identify the causes of the onset of the disease.
Treatment of trigeminal neuralgia
Today, many options are offered for the treatment of inflammation of the facial nerve, from the most conservative to radical ones.
- Taking anticonvulsants is the most common way to stop pain and neuralgia. Over time, an increase in dose or a change in the drug is required to avoid addiction. It has side effects: nausea, drowsiness, double vision, dizziness.
- Antispasmodics relieve spasm of the trigeminal nerve, and muscle relaxants reduce the tone of the facial muscles and help reduce their motor activity.
- Alcohol blockade of the nerve, or in other words, freezing. Unfortunately, it does not give a long-term result and requires constant repeated injections. This method is associated with a certain risk to the health of the patient, because it can cause bleeding and hematomas on the vessels.
- Surgical intervention and laser method of treatment.
- Microvascular decompression, which allows you to displace or eliminate the vessel that puts pressure on the facial nerve.
There are also folk ways to treat inflammation of the facial nerve. To do this, use the infusion of yarrow or highlander amphibian. Soothing decoctions with chamomile, mint, and motherwort help well. A compress of fresh geranium leaves or rubbing the cheek with any menthol ointment will help relieve pain.
Consequences of the disease and prognosis
Trigeminal neuralgia is not a fatal disease, but repeated bouts of severe pain can seriously harm your health. Often, patients with neuralgia develop depression, mental disorders appear. Pain provokes loss of appetite, weight loss and immunity.
In 75% of cases of inflammation of the facial nerve, it is possible to completely get rid of pain. It is important to diagnose the disease as soon as possible and begin its treatment. Remember that the best prevention of facial neuralgia is to protect against hypothermia and prevent head injuries.
The defeat of the branches of the trigeminal nerve causes severe physical and moral discomfort in a person. In some cases, the patient cannot lead a normal life due to the appearance of cramps in the muscles of the face.
A trigeminal nerve lesion causes severe pain that radiates to one side of the face. To reduce sensitivity and thereby reduce the manifestation of pain, you need to know how to treat trigeminal neuralgia.
Medical treatment
Pharmaceutical preparations form the basis of therapy for. According to the doctor's prescription, they can be supplemented with folk recipes. One of the most effective and popular means is Carbamazepine. It ensures the development of inhibitory processes in nerve fibers, due to which their painful excitation disappears.
You need to take the pills for about 8 weeks. The action of Carbamazepine is noticeable already on the 1-2 day of treatment, after taking the remedy, the pain of the facial nerve disappears for several hours. Since these tablets are very toxic, specialist assistance is needed in a thorough analysis and individual selection of a treatment regimen.
Carbamazepine is contraindicated during pregnancy and breastfeeding. It has a toxic effect on the developing embryo. In addition, pills are prohibited when a person has glaucoma, blood diseases, or heart block.
In addition to carbamazepine, for the relief of pain in the face are used:
- intravenous drugs (sodium oxybutyrate) - administered by ambulance doctors;
- anticonvulsants (Pantogam, Phenibut, Baclofen) - relieve pain for 2-3 hours;
- neuroleptics (pimozide) - additional treatment of the facial nerve;
- Glycine - prescribed for a long course to eliminate nervous excitement;
- antihistamines - used to enhance the therapeutic effect;
- anti-inflammatory drugs - non-steroidal drugs that eliminate facial pain;
- vasotonics - prescribed for concomitant pathologies of cerebral vessels;
- vitamins - during exacerbations, vitamins of groups B and C are used in the form of injections.
Drug treatment in combination with folk remedies only relieves pain in the area of the facial nerve, without helping to eliminate the root cause of the pathology. Trigeminal neuralgia is a complex disease that cannot be treated with oral medications. Pain-relieving tablets help by alleviating the patient's condition, reducing the excitability and conduction of nerve fibers.
Physiotherapy procedures
Physiotherapeutic treatment complements the medication, enhancing its effectiveness. The attending physician selects the necessary procedures depending on the degree of development of the disease, the strength of the pain syndrome and the presence of concomitant chronic pathologies in a particular person.
An effective method, the effectiveness of which is ensured by the impact of thin needles on certain points of the face, the collar zone and areas of the face located directly near the facial nerve. It is necessary to carry out such procedures only in a trusted clinic with a real professional, since the impact on acupuncture points has a strong effect on the functioning of all body systems.
electrophoresis
The impact of current on certain areas ensures the establishment of the work of the necessary parts of the body. Treatment of trigeminal neuralgia with herbal electrophoresis provides a lasting effect (in the case when the auxiliary agents and the treatment regimen are chosen correctly). Therapy with conservative means helps only in the first stages of the development of the disease.
Ultrasound
The procedure is the impact of ultrasound on the exit area of the branches of the trigeminal nerve with a small head (about 1 cm2). Treatment is carried out in a course of 10 procedures, affecting each zone for no more than 1-3 minutes.
Laser exposure
It is considered one of the most effective procedures. The impact of laser radiation on the skin contributes to the penetration of radiation directly to the inflamed area of the facial nerve. Thanks to this, the pain subsides, the general condition of the patient improves, and pain attacks bother him much less often.
Magnetotherapy
This method of physiotherapy improves the metabolic processes inside the cells of the body. Exposure to magnetic means ensures the removal of toxic substances, a decrease in swelling, a decrease in inflammation, the normalization of the work and condition of nerve fibers and small vessels.
Surgical intervention
If physiotherapy and pills do not provide the necessary help, the patient is offered to perform an operation to eliminate the cause of the disease. Only the attending physician can choose by what means to carry out surgical intervention, based on the data presented on the course of neuralgia.
rhizotomy
It is an operation to rupture the trigeminal nerve. An incision is made in the skin behind the ear and a branch of the trigeminal nerve is dissected, which provides sensitivity to certain areas of the face. Due to such a radical method, the effect is achieved.
 RF ablation
RF ablation
During surgery, the nerve node is exposed to high temperature, as a result, the nerve fiber is destructured, and the pain gradually subsides. Surgery is performed under local anesthesia, the patient does not need long-term hospitalization, therefore, if desired, he can leave the medical facility in a few hours and continue treatment with medications or folk remedies that the doctor will advise.
The lasting effect of the operation appears only after a month. That is why after the operation the patient will feel pain for a long time.
Microvascular decompression
It consists in removing or moving the choroid plexuses in contact with the trigeminal nerve. The operation is performed under general anesthesia, the main assistance is provided by neurosurgeons. The efficiency of this method is only 80%.
Glycerin injections
They are effective means against pain in case of inflammation of the facial nerve. Using a thin needle, the drug is injected into the branching of the trigeminal nerve. Such injections provide a long-term analgesic effect, but relapses are common in the later stages.
Folk ways to eliminate pain
Folk remedies can slightly alleviate your condition until the doctor prescribes an effective treatment.
Geranium
Fresh scented geranium leaves are used as compresses. The raw material is applied to a thin linen fabric and bandaged to a sore spot. The analgesic properties of fragrant geranium are determined by the presence of essential oils and other trace elements in the composition of the plant.
Help is due to the rich composition of the plant, which provides an anti-inflammatory and analgesic effect in the face.
Black radish
Freshly squeezed black radish juice must be rubbed several times a day into the affected area of the facial nerve. This method has a good and lasting effect, providing a decrease in the sensitivity of nerve endings and a decrease in pain.
With an exacerbation of the pain syndrome, it is necessary to boil an egg hard-boiled, cut it in half and attach it to the area that hurts the most. By the time the egg cools, the pain will subside or disappear altogether.
marshmallow root
Used for compresses for inflammation of the facial nerve. In the evening, it is necessary to prepare an infusion from the marshmallow root, pouring 1 teaspoon of dry raw materials with a glass of boiling water and insisting overnight.
In the morning, a decoction of chamomile is collected and kept in the mouth, and at this time gauze is applied outside, soaked in an infusion of marshmallow root. To enhance the effect, it is necessary to cover the gauze with compression paper and a woolen cloth. Help from such a remedy consists in a double effect on the affected nerve with folk remedies.
It is better to do compresses several times a day. In this case, the pain will recede faster, and relapses will occur less frequently.
The abuse of folk methods of treatment negatively affects health and causes complications. All analgesic properties of plants are due to their special composition.
Among the modern methods of treatment of neuralgia, radiosurgical intervention can be distinguished. During the operation, a cyber knife is used, so doctors manage to control the dosage of radiation, the place and strength of the photon flux on the inflamed area of the nerve ending.
The procedure is carried out quickly, local anesthesia is used to anesthetize the patient, so the rehabilitation period proceeds smoothly. As a prevention of relapse, you can use folk recipes, but only after consulting a doctor.
is a topical issue for many people. The disease is not fatal, but rather painful due to severe bouts of pain, the quality of life deteriorates. With timely diagnosis, therapy is carried out by conservative methods, in advanced cases, surgery may be required.
An inflamed trigeminal nerve causes a lot of discomfort
Where is the trigeminal nerve
Trigeminal nerve- a paired organ, part of the cranial part of the nervous system, has 3 branches that are directed to the frontal zone, lower and upper jaw, they carry impulses to various parts of the face.
The structure of the trigeminal nerve:
- nerve endings depart from the pons, which is located in the cerebellum;
- the main trunk passes to the temporal zone, consists of sensory and motor roots;
- branches - orbital, maxillary, mandibular;
- node - the point of divergence of the main branches;
- small branches connect the mucous membranes of the nose and mouth, ears, eyes, temples, jaws with the brain.
The trigeminal nerve is the largest of all nerve nodes that are located in the human skull, is responsible for facial expressions, chewing, provides skin sensitivity, control is carried out in the spinal cord. A more detailed structure can be seen in the photo.
The structure of the trigeminal nerve
Causes of inflammation of the trigeminal nerve
Inflammation of the trigeminal nerve (facial neuralgia) - the disease develops as a complication of various viral and bacterial diseases, but medicine continues to find out the exact causes of the pathology.
Primary neuralgia develops when the nerve roots are compressed, there are no other pathologies, the secondary form is a consequence of various diseases.
Why does the trigeminal nerve become inflamed:
- herpes, chicken pox;
- polio;
- HIV, syphilis, tuberculosis;
- sinusitis, other pathologies of ENT organs, chronic dental infections;
- craniocerebral damage;
- tumors that cause pinching of the nerve;
- congenital anomalies of the skull bones;
- multiple sclerosis;
- osteochondrosis, increased;
- hypertension, stroke;
- hormonal imbalance in women during pregnancy, menopause;
- hypothermia, severe intoxication.
Stroke can cause inflammation of the trigeminal nerve
Neuralgia can occur after tooth extraction, if the facial nerve was affected during the manipulation, if the filling was not installed correctly.
From the point of view of psychosomatics, neuralgia occurs in people who are trying to get rid of the pain of the past, old fears, resentments. Inflammation of the trigeminal nerve is a sign of anxiety and buckwheat. Metaphysicians associate any problems with the face with a person’s increased shyness, constant guilt, the desire to be the way others want to see him - such problems often occur in a child after a divorce of his parents.
First signs and symptoms
Neuralgia is always accompanied by a strong pain syndrome, more often burning, shooting discomfort affects the right side of the face - against the background of inflammation, muscle sensitivity increases, discomfort occurs even with a light touch, minor movements.
Symptoms of damage to the trigeminal nerve:
- an attack of pain occurs suddenly, lasts about 30 seconds, may appear several times a day or every quarter of an hour;
- discomfort occurs when brushing your teeth, during chewing, when touched;
- increased salivation and lacrimation, discharge of mucus from the nose, a taste of metal in the mouth;
- dilated pupils;
- spasms of facial muscles;
- Strong headache;
- a decrease or increase in the amount of saliva, a change in taste perception;
- sometimes before the onset of an attack, there is a feeling of numbness and tingling at the exit points of the inflamed nerve, skin itching;
- the affected part becomes hot, there is a general increase in body temperature;
- as the disease progresses, the intensity of pain increases, the duration of the attacks increases.
Inflammation of the trigeminal nerve causes severe headache
Some features of the clinical picture of the disease
Manifestations of inflammation of the trigeminal nerve largely depend on which branches are affected.
Signs of neuralgia, depending on the location of the focus of inflammation:
- branch 1 - the sensitivity of the upper eyelid, eyeball, back of the nose in the frontal zone worsens or completely disappears;
- branch 2 - violations occur in the lower eyelid, upper cheekbones and jaw, maxillary sinuses, lower nose;
- branch 3 - the entire lower part of the face and the oral cavity hurts, the chewing process is disturbed.
With neuritis of the facial nerve, sensitivity disorder is not observed, with the exception of a small area near the ear, but against the background of the disease, unilateral paralysis is almost always observed.
If the lower part of the face hurts, then the 3rd branch of the nerve is inflamed
Which doctor should I contact?
If signs of inflammation of the trigeminal nerve appear, it is necessary, additionally it may be required,.
Diagnostics
The doctor can determine the inflammation of the trigeminal nerve already during an external examination, after collecting an anamnesis, but sometimes a more thorough, comprehensive examination is required to check the condition of the vessels and tissues.
Methods for diagnosing facial neuralgia:
- clinical blood test;
- lumbar puncture;
- serological, biochemical blood tests;
- MRI, CT of the head;
- electroneurography;
- electromyography;
- x-ray.
Exacerbation of facial neuralgia most often occurs in winter, most of the attacks occur in the daytime.
An MRI of the head can help determine the degree of inflammation.
Treatment of inflammation of the trigeminal nerve
To eliminate the manifestations of neuralgia, an integrated approach is used, therapy includes taking medications, physiotherapy and manual methods, and traditional medicine can be used to enhance them.
Medical treatment
Therapy of facial neuralgia is aimed at eliminating pain, and the causes that caused the inflammatory process.
How to treat inflammation of the trigeminal nerve:
- novocaine intramuscular blockade to reduce the intensity of pain;
- antiviral drugs - Laferon, Gerpevir;
- injections of antibiotics - Amoxiclav, Klaforan;
- non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs - Movalis, Nimesil;
- tablets to prevent the formation of cholesterol plaques - Atoris;
- glucocorticoids - Hydrocortisone, Dexamethasone;
- muscle relaxants - Mydocalm, Mefedol;
- anticonvulsants - Rotaleptin, Finlepsin, Clonazepam;
- sedatives, antidepressants - Novo-passit, Amitriptyline.
Means Mydocalm is used in the treatment of trigeminal nerve
Lidocaine ointment relieves pain well - it is necessary to dry the oral mucosa with cotton pads, apply the agent in a thin layer on the gums from the inflamed side. Unpleasant sensations disappear almost immediately, the remedy can be used 4-6 times a day.
Additionally, drugs are prescribed to strengthen the immune system, vitamins of group B will help restore the functioning of the central nervous system.
Homeopathy to eliminate neuralgia
Homeopathic medicines activate the immune system - the body begins to fight inflammation more intensively, which leads to a rapid improvement in well-being.
Effective homeopathic remedies:
- Aconitum - quickly eliminates even severe attacks of pain;
- Agaricus - helps to get rid of all the main manifestations of neuralgia;
- Argentum nitricum;
- Gepar sulfur;
- Silicea.
Glonoin is a homeopathic remedy
The best safe remedy for the treatment of neuralgia and neuritis is Traumeel. It contains 14 plant components, minerals, the medicine is produced in the form of drops, granules, injection solution, ointment.
How to relieve inflammation folk remedies
Herbal medicines help reduce the manifestation of the inflammatory process in facial neuralgia, prolong the period of remission. But it is not advisable to use them as the main method of therapy, only in combination with medicines they will help get rid of the pathology.
Alternative medicine recipes:
- Mix 200 ml of black radish juice with 10 ml of lavender oil, rub the inflamed area, cover your face with a warm cloth, lie down for half an hour.
- Brew 250 ml of boiling water 1 tbsp. l. fresh red rose petals, leave for 30 minutes. Drink the entire portion of the medicine at once, repeat the procedure three times a day for 20–25 days.
- Pour 200 ml of vodka 4 tbsp. l fresh acacia inflorescences, insist in a dark place for a month, rub the affected area with tincture in the morning and evening for 30 days.
- Brew 220 ml of boiling water 1 tsp. chamomile inflorescences, strain after a quarter of an hour. A warm drink should be kept in the mouth for at least 20 minutes, the procedure should be carried out every 2-3 hours.
- Mix clay of any color with vinegar until a plastic homogeneous mass is obtained, make thin plates, apply them to the inflamed area for half an hour before going to bed.
Acacia flower tincture helps in the treatment of trigeminal nerve
A simple way to deal with pain is to lubricate the inflamed areas 5-6 times a day with fir oil. Within 3 days the skin will redden, swell, but then all unpleasant symptoms will disappear.Massage
Massage is an obligatory component of therapy in the treatment of inflammation of the trigeminal nerve, the procedure can be performed during an exacerbation of the pathology, and in remission. It is better to consult with a specialist beforehand so as not to increase the manifestation of unpleasant symptoms of the disease.
How to do massage at home:
- Rubbing the neck and shoulder.
- Stroking the back of the head closer to the base of the neck.
- Vibrating movements on the cheekbones.
- Light tapping with fingertips on the superciliary arches, frontal zone, nasolabial fold area.
Each movement should be performed easily, without much pressure, do 5-7 repetitions, the total duration of the procedure is 7-8 minutes. The massage course consists of 20-25 procedures, sessions should be carried out daily.
With advanced forms of neuralgia, massage is not only useless, but also dangerous.
Physiotherapy
Physiotherapy is prescribed after the elimination of the manifestation of an acute inflammatory process, they help to prolong the period of remission.
What physiotherapy methods are used in the treatment:
- electrophoresis with calcium chloride, anti-inflammatory, analgesic drugs;
- phonophoresis with hydrocortisone - the procedure is carried out even in the acute phase of neuralgia to reduce the frequency of attacks;
- magnetotherapy;
- heating with ultraviolet;
- laser irradiation;
- acupuncture.
Phonophoresis with hydrocortisone helps to reduce the number of seizures
Operation
Surgical intervention is necessary if traditional methods of treatment do not bring a noticeable therapeutic effect, relapses of neuralgia become more frequent, various complications develop.
To eliminate the pathology, 2 main methods are used. Radiofrequency destruction - the affected area is treated with current, the roots of the trigeminal nerve are destroyed, improvement occurs after 1 procedure. Microvascular decompression - open the posterior cranial fossa, divide the trigeminal nerve, insert a special gasket between the roots.
What to do during pregnancy
Inflammation of the trigeminal nerve and neuritis are often diagnosed during pregnancy, most drugs, especially analgesics, are contraindicated for expectant mothers, so they try to use safe methods of treatment in therapy.
How to treat neuralgia during pregnancy:
- gymnastics for facial expressions, massage will help to eliminate the asymmetry of the face;
- apply a special bandage to support the lowered half of the face;
- acupressure;
- acupuncture;
- physiotherapy.
Facial acupuncture can be used during pregnancy
To calm the pain, you can take Ibuprofen, muscle relaxants, but only as directed by a doctor, gels and ointments that are intended for children during teething bring relief. Often, pathology occurs against the background of vitamin B deficiency, so pregnant women must be prescribed vitamin complexes that contain this element in sufficient quantities.
Possible consequences of the disease
It is difficult to ignore the manifestations of facial neuralgia, but if you do not start therapy in a timely manner, self-medicate, against the background of the inflammatory process, severe concomitant diseases will begin to develop.
What is dangerous facial neuralgia:
- partial or complete atrophy of the masticatory muscles;
- facial asymmetry;
- wrinkles, severe peeling of the skin;
- loss of eyebrows, eyelashes;
- keratitis, conjunctivitis;
- loosening of wisdom teeth.
Inflammation of the trigeminal nerve causes the eyebrows and eyelashes to fall out
Is it possible to warm the trigeminal nerve
If neuralgia is in the acute stage, any warming procedures are contraindicated, all external medicines should be at room temperature. Under the influence of heat, pathogenic microorganisms begin to multiply actively, with the blood flow the infection will penetrate into other organs. Warming up with salt, buckwheat is indicated only during the remission of the disease, if the nerve is simply frozen.
You can warm the trigeminal nerve only when you have a cold or in the process of remission
Prevention
To avoid inflammation of the trigeminal nerve, recurrence of the disease will help simple preventive measures, constant monitoring of health.
How to prevent the development of pain in the defeat of the trigeminal nerve:
- timely treat dental pathologies, diseases of the nasopharynx;
- avoid hypothermia, stress;
- eat right and balanced;
- take a contrast shower, play sports, walk more often in the fresh air.
B vitamins will help prolong the remission stage, you need to take it twice a year.
Inflammation of the trigeminal nerve is disease of one of the largest nerves, which is located in the area of \u200b\u200bthe teeth and face.
This disease has been known to physicians for quite a long time, but so far they cannot come to a single decision: how best to treat this ailment and whether it can be cured at all.
It is worth understanding why this disease appears. It is believed that it is hypothermia that causes inflammation of the trigeminal nerve, but do not forget about other factors that contribute to the development of this disease, namely:
- virus or infection;
- inflammation of the brain, ear;
- anesthesia of the nerve when visiting the dentist.
There is also 2 types of inflammation trigeminal nerve, it is primary and secondary:
- primary inflammation- a disease that occurs when hypothermia, while there are no changes in the head area.
- BUT secondary inflammation takes place to be with a disease of the brain or ENT - organs.
To the main symptoms of inflammation of the trigeminal nerve relate:
- taste disorder;
- sharp bouts of pain;
- violation of the normal functioning of the eyes, ears;
- violation of facial movements;
- increased or decreased lacrimation;
- paralysis of the facial muscles.
Diagnosing this disease is quite easy, since it has pronounced symptoms that are very difficult to confuse with symptoms characteristic of other types of the disease.
In order to make sure and confirm your diagnosis, doctors may prescribe examinations such as or CT.
Healing procedures
For many years, treatment was almost impossible, due to the fact that it was not clear how to treat inflammation of the trigeminal nerve.
Now already developed many different options treatment of trigeminal neuralgia. 
However, they often contradict each other.
The type of treatment for inflammation of the trigeminal facial nerve is selected by the doctor, depending on the intensity of inflammation, the duration of your illness and other reasons, but basic treatment in all cases will be directed to the treatment of pain attacks.
The main drug used in the treatment of inflammation of the trigeminal nerve is this.
The drug is prescribed only by a doctor and the dosage is individually selected for each patient.
Usually the drug begins to act after 2-3 days, an analgesic effect is noticed. The duration of anesthesia is on average 3-4 hours.
The dosage of carbamazepine, at which the patient can talk and eat calmly, should be left unchanged for a month. After a month, the doctor may prescribe an extension of the course or a gradual decrease in the dosage of the drug.
Treatment with carbamazepine for inflammation of the trigeminal facial nerve lasts until then until the patient has noted a complete absence of seizures for six months.
In turn, the treatment consists of both etiotropic therapy, which involves the fight against the very cause of the disease, and complex measures necessary to eliminate pain symptoms. If appointed drug treatment inflammation of the trigeminal nerve, other tablets are also used.
In turn, etiotropic therapy directed:
- If the viral nature of the disease is detected, the following drugs are prescribed: laferon, herpevir, acyclovir and others.
- If an aneurysm or mass is found in the vessels, surgery may be performed to remove the affected parts.
- In multiple sclerosis, drugs are used that regenerate the myelin sheath of the nerve.
- Cholesterol-lowering drugs are used to improve metabolism in nerve tissues and to avoid cholesterol plaques. It can be Atoris or Rosuvolostatin.
To reduce the intensity of pain attacks, various medications are prescribed. pharmacological groups:
- Painkillers and non-steroidal anti-inflammatory agents, for example: nimesil, analgin, ketanov. But they help only at the beginning of the attack.
- Can be used in combination with pain relievers sedatives which will increase their efficiency. For example, the combination of Diphenhydramine and Analgin perfectly reduces the intensity of pain. Side effect: drowsiness.
- Anticonvulsants, like carbamazepime, is used to reduce the pulsation of nerve tissues. In turn, they can cause drowsiness.
- Opiate painkillers(i.e. morphine derivatives) can also be used due to their high analgesic effect. But because of their narcotic effects, they are used only when other drugs do not help.
There are also a huge number of ways to treat inflammation with folk remedies, for example:
- onion juice;
- a compress of garlic and lemon juice;
- propolis tincture.
But folk remedies cannot guarantee a complete cure for the disease, so you should not rely on them completely, but use them as prophylactic agents.
Possible Complications
In the treatment of inflammation of the trigeminal nerve, some problems may arise in the form of complications.
This may be caused by improper treatment, self-medication, or other factors.
The main complications include such:
- weakening of the motor functions of the facial muscles;
- violation of the normal functioning of the organ of hearing;
- cerebellar hematoma;
- ataxia, that is, impaired coordination of movement.
 These complications concern, first of all, certain groups of the population. This is first of all elderly people, because their immunity and health is weaker than that of other people, so they are more susceptible to diseases.
These complications concern, first of all, certain groups of the population. This is first of all elderly people, because their immunity and health is weaker than that of other people, so they are more susceptible to diseases.
These complications also apply to people who have there is a metabolic disorder or suffering from cardiovascular disease.
Forecast
The prognosis given by the doctor may depend on many factors.
Basically, it depends on the age of the patient, the nature of the disease or possible past diseases associated with the vessels and nerves of the face. Of course, if the patient is young, then the treatment will proceed quickly and without subsequent relapses.
In contrast to elderly patients, for whom neuralgia associated with a violation of the body's metabolic processes, unfortunately, can not always be cured.
Preventive measures
Everyone knows that it is much easier to prevent a disease than to treat it. In turn, this applies to inflammation of the trigeminal nerve.
From the very beginning from take care of the basic things like a daily routine and a healthy lifestyle. No matter how trite it may sound, but an adequate daily routine and good nutrition prevent many diseases. 
Elderly people who do not adhere to a diet are most susceptible to atherosclerosis, which is the cause of neuralgia.
Necessarily hypothermia must be avoided, as this is the main cause of inflammation.
Therefore, it is better to dress well in damp and cool weather, so as not to encounter this disease in the future.
Be sure to listen to various symptoms and treat various respiratory diseases in a timely manner.
If you have any symptoms of inflammation of the trigeminal nerve, you should immediately consult a doctor and follow all his recommendations regarding diet and lifestyle.
And, of course, by no means don't self-medicate Or wait until the neuralgia goes away on its own. The longer you delay treatment, the worse the consequences can be.
Video: Trigeminal neuralgia
Details of inflammation of the trigeminal nerve. Where is the focus of inflammation located, what symptoms and pain syndromes indicate trigeminal neuralgia.
trigeminal neuralgia- This is a chronic inflammatory disease of the trigeminal nerve (the largest sensory nerve of the face), characterized by paroxysmal pain syndrome.
This disease is also called facial or trigeminal(from Latin trigeminus or trigeminal) neuralgia.
Some statistics!
Trigeminal neuralgia occurs in 40-50 cases per 100 thousand of the population, about 5 people per 100 thousand of the population fall ill annually.According to statistics, women over 50 years of age are more likely to get sick. Young people get sick less often, a few cases of the disease in preschool children are described.
Some interesting facts!
- The first descriptions of trigeminal neuralgia are found in ancient sources. So the Chinese healer Hua Tuo was the first to use acupuncture for this ailment, but this procedure did not cure, but only temporarily eliminated the pain syndrome. Hua Tuo was executed by the ruler of the Chinese Empire, who suffered from this ailment because the doctor was not with him, during the onset of an attack of facial pain. So this pain was unbearable for the commander.
- Trigeminal neuralgia refers to idiopathic diseases, that is, diseases with an unexplained cause. There is a lot of controversy over what leads to this disease among scientists, but a consensus has not yet been found.
- Symptoms of trigeminal neuralgia can resemble a toothache, which is why dentists are often the first to deal with this condition. In this case, patients indicate pain in an absolutely healthy tooth, such a tooth can be mistakenly removed.
- Stressful situations and surgical interventions on the face and in the oral cavity contribute to a temporary (up to several months) subsidence of the pain syndrome in trigeminal neuralgia.
- Habitual non-narcotic analgesics are not effective in the treatment of neuralgia, they can only temporarily reduce pain, with each dose they help less and less.
- Frequent bouts of unbearable pain in trigeminal neuralgia can disrupt the mental state of the patient, leading him to depression, fear, aggressive states, psychosis.
- An attack of pain in trigeminal neuralgia can cause even a light touch, for example, applying a cream to the face.
How do nerves work?
Nervous system- one of the most important and complex systems of the body, which regulates, controls and implements all the processes that occur in the human body. We cannot do anything: neither move, nor think, nor show emotions, nor breathe, nor resist foreign agents, and are not even able to reproduce without the participation of the nervous system.The human nervous system, especially the brain, has not yet been fully studied and is a storehouse for new discoveries and Nobel Prizes. After all, it is practically impossible to predict a person's reaction to various stimuli at one time or another, even to fully imagine the capabilities of a person, to understand the compensatory and restorative capabilities of the brain after injuries, infections and other pathological conditions of the nervous system.
And the most important function of a person, carried out by the nervous system - the intellect, distinguishes and exalts us above other creatures of the planet Earth. A huge number of scientists are working on the creation of artificial intelligence, but at the moment this is not possible, the human nervous system is thought out by nature to the smallest detail and is unique.
The structure of the nervous system
central nervous system
The human central nervous system is brain and spinal cord.The main functions of the central nervous system:
- regulates the functioning of all organs and systems, coordinates their joint synchronous work,
- provides an adequate response of the body to various factors of the world around us,
- the implementation of mental functions, mind, thinking, emotions, and so on, which distinguishes us, humans, from other creatures.
- bark brain,
- large hemispheres brain (end brain),
- diencephalon: thalamus, hypothalamus, epithalamus, pituitary gland,
- midbrain: roof of the midbrain, peduncles of the brain, aqueduct of the midbrain,
- back brain: pons, cerebellum, medulla oblongata.
Rice. Schematic representation of the main structures of the brain.
Peripheral nervous system
The peripheral nerves include the cranial and spinal nerves.The main functions of the peripheral nervous system:
- collection of information from the environment, as well as the internal state of human systems and organs,
- transmission of impulses with information to the central nervous system,
- coordination of the work of internal organs,
- movement implementation,
- regulation of the functions of the circulatory system and others.
- somatic nervous system- carries out movements and collects information from the outside and from the inside.
- Autonomic nervous system:
- sympathetic nervous system activated at the time of stress, danger, reaction to environmental and internal factors;
- parasympathetic nervous system - activated during rest, rest and sleep;
- enteric nervous system responsible for the work of all parts of the gastrointestinal tract.
According to their functions, the cranial nerves can be divided into:
- sensory nerves- responsible for the perception and transmission of a nerve impulse to the brain by the sense organs (hearing, vision, smell, taste, sensitivity of the skin and mucous membranes);
- motor nerves- responsible for the work of muscles;
- mixed nerves- nerves that have sensory and motor functions.
*Nuclei of cranial nerves- these are the formations of the nervous system that receive and transmit nerve impulses to the peripheral nervous system, namely the cranial nerves.
Nerves under the microscope
Neuron (nerve cell or neurocyte)- is a structural unit of the nervous system, these cells are highly specialized, capable of reproducing and transmitting nerve impulses, which are very similar in their characteristics to electrical ones.Neurons vary in size depending on function and type, on average from 10 to 30 µm (minimum 3, maximum 120 µm).
"Nerve cells don't regenerate!" - true or myth?
How many times have each of us heard this expression from doctors, teachers, parents. But American scientists in 1999 partially debunked this myth. Elizabeth Gould and Charles Gross proved that the central nervous system produces thousands of new neurons every day throughout life, they suggest that due to these new cells a person improves memory, new skills and knowledge appear. That is, these are such sheets of white paper, on which each person writes something new for himself. Research is still being carried out in this direction, no one knows what they will lead the scientific world to, but most likely, these studies will turn our ideas about the work of the nervous system upside down. And, perhaps, new discoveries will help find effective treatments for diseases that are currently considered irreversible, such as multiple sclerosis, Parkinson's disease, Alzheimer's syndrome and others.The structure of neurons
 What is a neuron made of?
What is a neuron made of?- Processes dendrites- receive impulses from other cells, usually have a branched shape (like a tree, each branch is further divided into branches). A neuron usually contains a large number of dendrites, but in some cells this process may be single (for example, retinal neurons that transmit impulses from photoreceptors in the eye).
- Neuron body (soma) with the nucleus and other organelles. The body of a neuron is covered with two layers of fat (lipid membrane), a protein layer and accumulations of polysaccharides (carbohydrates). Due to this structure of the cell membrane, the body of the neuron is able to process nerve impulses, and the impulse accumulates in it.
Soma also provides nutrition to the cell and the removal of waste products from it. - axon hillock- a section of the neuron body from which the process of the neuron axon departs, the function of this structure is the regulation of the transmission of a nerve impulse to the axon, that is, excitation of the axon.
- axon process- a long process through which information is transmitted to other neurons. Each neuron has one axon, the longer it is, the faster the nerve impulse is transmitted. The terminal sections of the axons are divided into terminal branches, it is they that are connected to other nerve cells. The axon may or may not be myelinated.
- myelin sheath is such an insulator of electricity, it is a membrane consisting of lipids and proteins. It consists of glial cells (Schwann cells in the peripheral nervous system and oligodendrocytes in the central nervous system), spirally envelops the axon. Between the glial cells there are gaps - Rvanier's interceptions, which are not covered with myelin. Thanks to myelin, electrical impulses are transmitted quickly through the nerves.
Types of neurons, depending on the functions performed:
- motor neurons - transmit impulses from the central nervous system to the peripheral nerves of the muscles,
- sensory neurons - convert impulses from the environment or internal environment and transmit them to the central nervous system,
- intercalary neurons - neurons that transmit impulses from one neuron to another, mainly intercalary neurons are represented by nerve cells of the central nervous system.
Nerve fibers- axons of neurons.
Nerves- accumulation (bundles) of nerve fibers.
Neuron connections
 Neurons connect with each other to form synapses. Through them, one nerve cell (transmitting) transmits a nerve impulse to another nerve cell (receiving).
Neurons connect with each other to form synapses. Through them, one nerve cell (transmitting) transmits a nerve impulse to another nerve cell (receiving). A synapse can also connect a nerve cell with cells of an innervated tissue (muscle, gland, organ).
The brain and spinal cord is a vast collection of interconnected neurons that have an extremely complex relationship.
Components of a synapse:
- Axon of the transmitting neuron(its presynaptic ending), is able to stimulate the production of special chemical, impulse-transmitting neurotransmitters. Mediators of the nervous system (neurotransmitters, neurotransmitters) are produced in the synaptic vesicles of the presynaptic ending.
- synaptic cleft through which momentum is transmitted.
- The receptive part of the cell– or receptors on any receptive cell. Receptors can be located in the dendrite, axon or body of a neuron, on the membrane of sensitive cells in muscles, internal organs, sensory organs, glands, and so on.
 Groups of neurotransmitters (neurotransmitters):
Groups of neurotransmitters (neurotransmitters):- Monoamines: histamine, serotonin;
- Amino acids: Gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA), glycine, glutamic and aspartic acids;
- Catecholamines: adrenaline, norepinephrine, dopamine;
- Other neurotransmitters: acetylcholine, taurine, ATP, etc.
How is a nerve impulse transmitted?
nerve impulse- this is natural electricity that passes through electrical wires (nerves) in different directions and along certain trajectories. This electricity (impulse) is of chemical origin, carried out with the help of mediators of the nervous system and ions (primarily sodium and potassium).Stages of formation and transmission of a nerve impulse:
- excitation of a neuron.
- The inclusion of the sodium-potassium pump, that is, sodium moves inside the excited cell through special sodium channels, and potassium moves out of the cell through potassium channels.
- The formation of a potential difference between the membranes of the synapse (depolarization).
- Formation of a nerve impulse - action potential.
- Transmission of a nerve impulse along nerve fibers through synapses:
- secretion of neurotransmitters in the synaptic vesicles of the transmitting ending,
- the release of mediators (or substances that destroy them - in the process of inhibition) into the synaptic cleft,
- stimulation of depolarization of the perceiving cell (opening of sodium and potassium channels) - when the nerve fiber is excited, or hyperpolarization (closing of sodium-potassium channels) during inhibition ** ,
- impulse transmission further along the nerve fibers to the central nervous system or innervated organ.
The speed of transmission of a nerve impulse along nerve fibers covered with myelin is 2-120 m/s.
In addition to the transmission of nerve current through synapses, it is possible to directly propagate the impulse by contact, without the participation of mediators, with a dense arrangement of nerve cells.
Interesting! You can watch the video: “The incredible is around us. Nervous system".
Reflex- this is the reaction of the body to any stimulus from inside or outside the body. The central nervous system is necessarily involved in this process.
Reflex is the basis of the functioning of the nervous system, almost all nervous processes take place with the help of reflexes.
During the reflex, the nerve impulse passes through the reflex arc:
- receptors of certain cells, organs and tissues,
- sensory nerve fibers form and transmit nerve impulses from the innervated organs,
- analysis of impulses in the central nervous system,
- motor nerve fibers transmit impulses to the innervated organs - a response to an irritant.
- conditional,
- unconditional.
These reflexes develop as an automatic response to external and internal factors. Unconditional reactions exercise a person's ability to self-preservation, adaptation to environmental conditions, reproduction, preservation of homeostasis - the constancy of the internal state of the body. They are genetically determined and passed down from generation to generation.
Examples of unconditioned reflexes: sucking breast milk by a newborn baby, sexual, maternal and other instincts, blinking at the threat of eye injury, coughing and sneezing when foreign particles enter the respiratory tract, and so on.
Trigeminal nerve
 The trigeminal nerve is the 5th cranial nerve. It got its name because it contains three branches:
The trigeminal nerve is the 5th cranial nerve. It got its name because it contains three branches:- ophthalmic (upper) branch,
- maxillary (middle) branch,
- mandibular (lower) branch.
Characteristics of the trigeminal nerve
| Parameters | Characteristic | ||
| ophthalmic nerve | maxillary nerve | Mandibular nerve | |
| Type of nerves | Sensitive | sensitive | mixed nerve, contains sensory and motor fibers |
| What is innervated? |
| Skin of the eyelid (lower), upper lip and side of the face, upper teeth |
|
| Main functions | Skin sensitivity, tear regulation, meningeal sensitivity | Skin sensitivity |
|
| Place of exit from the skull | The outer wall of the orbit. | rounded hole - located under the orbit. | Foramen ovale - located under the eye socket. |
| Main branches of the nerve |
|
|
|
| Nerve nodes (ganglia)** formed by the trigeminal nerve | Eyelash knot:
| Pterygoid node:
| Ear node:
|
| nuclei in the brain | motor fibers the trigeminal nerve is located in the pons (hindbrain) - trigeminal motor nuclei. Sensitive fibers The trigeminal nerve passes through the legs of the brain, is represented by sensory nuclei in the brain:
|
||
***Nerve nodes or ganglia- an accumulation of nervous tissue, containing nerve fibers and nerve centers, connects two or more nerve fibers to each other, receives impulses both from the endings and from the central nervous system (ascending and descending flows).

Rice. No. 1: The ophthalmic and maxillary nerve and their branches.

Rice. No. 2: Mandibular nerve and its branches.
Causes of trigeminal neuralgia
According to the mechanism of occurrence of trigeminal neuralgia, this pathology can be primary or true (isolated lesion of only the trigeminal nerve) or secondary (manifestation of neuralgia as a symptom of systemic diseases of the nervous system).The exact cause of the development of trigeminal neuralgia has not been clarified, as mentioned above, it refers to idiopathic diseases. But there are factors that most often lead to the development of this disease.
Factors that contribute to the development of trigeminal neuralgia:
- Compression of the trigeminal nerve in the skull or its branches after leaving the skull:
- vasodilatation of the brain: aneurysms (pathological expansion of blood vessels), atherosclerosis, hemorrhagic and ischemic strokes, increased intracranial pressure as a result of osteochondrosis of the cervical spine, congenital anomalies in the development of blood vessels, and so on - the most common cause of the development of trigeminal neuralgia,
- tumor formations brain or facial area along the branches of the trigeminal nerve,
- injury and post-traumatic scars
- injuries in the jaw-temporal joint,
- proliferation of connective tissue(adhesions) as a result of an infectious inflammatory process, sclerosis with damage to the myelin sheath of nerve fibers.
- congenital anomalies development of the bone structures of the skull.
- Viral nerve damage: herpetic infection, poliomyelitis, neuro-AIDS.
- Diseases of the nervous system:
- multiple sclerosis,
- children's central paralysis (CP),
- meningitis, meningoencephalitis (viral, tuberculosis),
- encephalopathy due to head injuries, infectious processes, hypoxia (lack of oxygen in the brain), lack of nutrients,
- brain tumors and circulatory disorders in the nuclei and fibers of the trigeminal nerve, and so on.
- Odontogenic causes(related to teeth):
- "failed" filling or extraction of teeth or other surgical interventions in the face and oral cavity.
- reaction to anesthesia of the canals of the teeth,
- jaw trauma with damage to the teeth,
- dental flux.
Factors that increase the risk of developing trigeminal neuralgia:
- age over 50 years,
- mental disorders,
- chronic fatigue ,
- stress,
- hypothermia of the face (for example, in a draft),
- avitaminosis (lack of B vitamins),
- metabolic disorders: gout, diabetes mellitus, thyroid disease and other endocrine pathologies,
- helminthiases (worms),
- fasting, malabsorption of nutrients in the intestines, bulimia, anorexia,
- inflammation with swelling of the mucous membrane of the maxillary and other paranasal sinuses (chronic sinusitis),
- inflammatory processes and ulcers (abscesses, phlegmon) in the oral cavity - gingivitis, pulpitis,
- suppuration of the bones of the skull, especially the jaws (osteomyelitis),
- acute and chronic infectious diseases with severe intoxication: malaria, syphilis, tuberculosis, brucellosis, botulism, tetanus, and so on.
- autoimmune diseases,
- severe allergic diseases.
Mechanism of development (pathogenesis) of trigeminal neuralgia
Many scientists around the world have been discussing the pathogenesis of the development of trigeminal neuralgia for many years. Depending on the causes that contributed to the occurrence of trigeminal neuralgia, two theory of the mechanism of its development:
And although there are “dark spots” in each theory, it is assumed that both mechanisms for the development of pain syndrome take place, that is, they sequentially follow each other. That is why the treatment of trigeminal neuralgia should be comprehensively aimed at restoring the myelin sheath of nerve fibers and inhibiting nervous processes in the brain.
Symptoms of trigeminal neuralgia
The main symptom of trigeminal neuralgia is pain in the face, but there are other manifestations and complications of this disease that do not cause such discomfort as unbearable pain, but may additionally point to trigeminal neuralgia.| Symptom | How is it manifested? | When does the symptom occur? |
| Pain in the face | Pain syndrome usually manifests itself in only one half of the face. The pain is paroxysmal or it is also called paroxysmal, attacks are replaced by periods of calm. The pain is unbearable, shooting in nature, it is often compared with electric shock. The patient at these moments freezes in the position in which the attack began, tries not to move, clamps his hands at the site of pain localization. Attacks of pain usually last from a couple of seconds to several minutes. Quiet periods can range from a few hours to several months. Sometimes, with an atypical course or a long-term course of the disease, pain in the face and head is almost permanent. With the duration of the disease, the duration of the attacks increases, and the period of remission is shortened. |  Pain usually appears after exposure to irritating factors. There are zones on the face, the so-called trigger zones (in the literature you can find the term algogenic areas), with a slight irritation of which a pain attack can begin. At the same time, a rough impact on these points during an attack often leads to its relief (cessation). Localization of trigger points is individual:
 Rice. Possible trigger zones in trigeminal neuralgia. |
Pain localization****
| With damage to the ophthalmic branch of the trigeminal nerve. | |
| With damage to the maxillary branch of the trigeminal nerve. | |
| With damage to the mandibular branch of the trigeminal nerve. | |
| With the defeat of all branches of the trigeminal nerve and with the central cause of neuralgia (brain tumors and so on).  |
|
| Redness of the face and sclera, increased salivation, lacrimation, the appearance of mucous discharge from the nose | These symptoms are localized on the affected side, appear during a painful attack. | Hyperemia of the face and increased production of the salivary, lacrimal glands and mucous glands of the nose are associated with disorders of the autonomic nervous system, the branches of which are part of the sensory fibers of the branches of the trigeminal nerve. |
| Twitching of facial muscles | Muscle tremor is similar to mild local convulsions or nervous tics, occurs against the background of pain. In this case, chewing and facial muscles are involved. There may be a narrowing of the palpebral fissure on the affected side, associated with spasm of the eyelids. | Muscle twitching is associated with a reflex spread of increased excitability to the motor fibers of the trigeminal nerve and other cranial nerves innervated by the muscles of the face.  Photo of a patient during an attack of trigeminal neuralgia. |
| Mental disorders | The patient becomes irritable, there is a feeling of fear, anxiety. When laughter, conversation, eating leads to the development of pain, the patient closes, is silent, refuses to eat. In severe cases, suicidal tendencies (the desire to commit suicide) can be observed. | Mental disorders in a patient occur against the background of frequent debilitating bouts of unbearable pain, the duration of the disease (years), the appearance of seizures against the background of minor irritation factors of trigger zones. Patients develop apathy, psychosis, phobias, depression, and so on. |
| Loss of sensation in the face (paresthesia) | Feeling of tingling, crawling on the affected side. There may be a dull aching pain, reminiscent of toothache from caries and pulpitis (which leads patients to the dentist). Sometimes there is a lack of sensitivity of the skin along the branches of the trigeminal nerve. | This symptom occurs in a third of patients and is usually a harbinger of an approaching pain attack (a few days or a few months before the paroxysm). Paresthesias are associated with widespread damage to the myelin sheath of nerve fibers, which leads to a violation of their sensitivity in the direction of increased excitation and impaired conduction of the nerve impulse along the sensory fibers of the nerve. |
| Violation of blood circulation and lymphatic outflow (trophic changes) |
| Trophic disorders along the course of the trigeminal nerve may occur after several years of the disease. Due to a violation of the innervation of the muscles and skin of the face by the trigeminal nerve, prolonged and frequent pain attacks, there is a violation of blood circulation and lymph flow in the affected half of the face. This leads to tissue malnutrition (lack of oxygen and nutrients). In order not to irritate the trigger zones, the patient spares the diseased side of the face: chews on the healthy side, does not smile, does not open his mouth wide, and so on. Over time, this leads to atrophy of the masticatory and facial muscles (reduction of muscle tissue, decrease in their functions), which in turn also leads to a violation of the trophism of the muscles and skin of the face.  Photo of a patient with atrophy of facial muscles on the right side. |
****Trigeminal neuralgia usually develops on one side and is most often right-sided. With the course of the disease, the localization of pain does not change. Only with severe pathologies of the brain is it possible over time to spread the process to the second half of the face.

Diagnosis of trigeminal neuralgia
Examination by a neurologist

- Anamnesis (history) of life: the presence of factors and diseases that could cause trigeminal neuralgia (tumors, vascular pathology of the brain, previous diseases, surgical interventions in the oral cavity or on the face, and so on).
- Disease history:
- the onset of the disease is acute, sudden, patients clearly remember when, where and under what circumstances the first attack of paroxysmal pain began,
- attacks of pain alternate with periods of remission,
- pain syndrome provokes even a slight irritation of one of the trigger zones of the trigeminal nerve,
- one way process
- pain is not stopped by anti-inflammatory and analgesic drugs.
- Complaints to attacks of acute unbearable pain that appears suddenly after irritation of trigger zones, and the appearance of other symptoms of trigeminal neuralgia (given above in the table).
- Objective examination during the interictal period:
- General state usually satisfactory, consciousness is preserved, neurotic reactions are possible, a violation of the mental state of the patient.
- When examining the patient won't let you touch your face in the area of trigger zones, he himself points to them, without bringing his finger to the skin or mucous membrane.
- The skin is often unchanged, with a severe long-term course of the disease, dry skin, the presence of peeling, folds and wrinkles, facial asymmetry, drooping of the upper eyelid and other symptoms of facial muscle atrophy are possible. Visible mucous membranes are not changed.
- Sometimes there is a violation of the sensitivity of the skin of the face (paresthesia).
From the internal organs(cardiovascular, respiratory, digestive and other body systems), usually no pathological changes are detected during the examination. - Neurological status in patients with trigeminal neuralgia without pathology of the central nervous system is not changed. There are no pathological reflexes, signs of inflammation of the meningeal membranes (meningeal signs).
- Objective examination of the patient during an attack of paroxysmal pain:
- Pain occurs after exposure to the trigger zones of the trigeminal nerve, and the pain syndrome itself spreads only along the branches of the trigeminal nerve.
- Patient posture: freezes or tries to stretch the muscles of the face with his hands, does not answer questions or answers in short phrases. At the same time, the patient has a very frightened and suffering look.
- On the skin perspiration (sweat) appears on the face, the skin of the diseased side of the face and the mucous membrane of the sclera turn red, lacrimation is possible, the patient often swallows due to increased salivation, mucous discharge “stream” may appear from the nose.
- Possible appearance convulsive twitches mimic muscles of the face on one side.
- Breath the patient is getting smaller or more frequent.
- Pulse increases (more than 90 per minute), blood pressure does not change, or slightly increases. When pressing on the trigger points of the trigeminal nerve, an attack of pain can be temporarily stopped.
- When conducting novocaine blockade trigeminal nerve (the introduction of novocaine along the branches of the trigeminal nerve, basically, these are those trigger points), the attack temporarily stops.
The diagnosis is made on the basis of specific complaints, the presence of trigger zones, the localization of pain along the branches of the trigeminal nerve, the appearance of the above symptoms during an attack, an objective examination, and instrumental diagnostic data.
Instrumental research methods
 Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) of the brain and spinal cord
Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) of the brain and spinal cord MRI– most informative a method for studying the structures of the brain, its vessels, nuclei and branches of the cranial nerves.
This method is visual (that is, we get an accurate three-dimensional image on the screen and on paper), however, unlike x-ray methods, MRI is based on magnetic, and not on radiation. That is, it is safe for the patient.
If trigeminal neuralgia is suspected, MRI is necessary to detect or exclude brain tumors, vascular disease, the presence of diffuse or multiple sclerosis, and other possible causes of the development of the disease.
For a more accurate study of the pathologies of the cerebral vessels, MRI is used with the introduction of a contrast agent into the vessels (angiography).
Disadvantages of the method:
- high cost of research;
- contraindications: the presence of metal objects in the body (the remains of fragments, pacemakers, metal plates that are used for osteosynthesis in complex bone fractures, metal dentures, crowns), severe psychological illness, claustrophobia.
 Computed tomography (CT)
Computed tomography (CT) CT- X-ray diagnostic method that allows you to visualize the structures of the brain and spinal cord in layers. In terms of information content, it is slightly inferior to magnetic resonance imaging, since MRI allows you to form a three-dimensional image, and CT - a two-dimensional image. CT can detect diseases of the central nervous system that could lead to the development of trigeminal neuralgia.
The main disadvantage of computed tomography is a large beam (radiation) load and high cost (but the CT method is more accessible and cheaper than MRI). 
Electroneurography
Electroneurography - an instrumental method for studying the nervous system, which makes it possible to determine the speed of conducting an electric current (impulse) along the nerve fibers of peripheral nerves.
What does electroneurography reveal?
- presence of nerve damage
- the level of damage (that is, where exactly),
- pathogenesis of the lesion (damage to the myelin sheath or damage to the axon),
- prevalence of the process.
- demyelination(damage to the myelin sheath of axons), which is a key factor in the pathogenesis of trigeminal neuralgia,
- other nerve changes characteristic of other nerve lesions, allowing to differentiate diseases of the nervous system.
Electroneuromyography (ENMG)
ENMG- a kind of electroneurography, allows you to study the speed of passage of electric current through the peripheral nerve with a parallel study of the reaction of the muscles that are innervated by this nerve.
In addition to the parameters that electroneurography reveals, ENMG reveals pain tolerance and the sensitivity threshold of possible trigger zones of the trigeminal nerve, as well as the degree of contraction of muscle fibers in response to increased nerve excitation.
 Electroencephalography (EEG)
Electroencephalography (EEG)
EEG- a method of diagnosing the nervous system, in which a special device electroencephalograph registers the biological electrical activity of the brain, depicting them in the form of curves. This method allows you to identify structures through which the passage of impulses is impaired.
What is revealed by EEG during a paroxysmal attack of trigeminal neuralgia?
- changing curves by synchronized or non-synchronized type,
- signs of epileptic foci in the hindbrain and midbrain, at the locations of the nuclei of the trigeminal nerve.
Additional consultations of narrow specialists in trigeminal neuralgia
- ENT - it is necessary to identify and, if necessary, cure chronic diseases of the nasopharynx.
- Neurosurgeon - if a pathology of the central nervous system is detected, which could lead to the development of neuralgia, it is necessary to resolve the issue of the need for surgical treatment.
- Dentist - for differential diagnosis of trigeminal neuralgia with dental diseases and, if necessary, sanitation of the oral cavity.
Laboratory research methods
With trigeminal neuralgia, laboratory diagnostics is not very informative, usually the biochemical parameters of blood and other biological fluids are normal. At the moment, there are no specific laboratory indicators indicating neuralgia, in general, including trigeminal neuralgia.But against the background of taking medications for the treatment of neuralgia, it is necessary to control their tolerance. To do this, periodically conduct biochemical studies of the liver, a general analysis of urine and blood.
If there are symptoms of inflammation of the meningeal membranes (meningeal signs), it is necessary to perform a lumbar puncture, followed by a laboratory study of the cerebrospinal fluid (cerebrospinal fluid). This is necessary to rule out meningitis.
With herpetic lesions of the trigeminal nerve, it is necessary to control the level of immunoglobulins A, M, G to herpes types I, II, III.
Treatment of trigeminal neuralgia
Treatment of trigeminal neuralgia should be complex:- elimination of the causes that provoked the development of trigeminal neuralgia.
- decrease in excitability of the central nervous system;
- stimulation of the restoration of the myelin sheath of the damaged trigeminal nerve - at the moment there are no means to completely restore myelin, scientists from all over the world are working on the development of such an effective drug, but some measures are used to stimulate the restoration of the myelin sheath;
- physiotherapeutic effect on the branches of the trigeminal nerve and trigger zones.
Drug treatment of trigeminal neuralgia

| Drug group | A drug | Mechanism of action | How to apply? |
| Anticonvulsants(selection of the drug and its dose is carried out individually) | Carbamazepine (finlepsin) | Effects of taking anticonvulsants:
Other effects: release of glutamate (a neurotransmitter that contributes to the inhibition of a nerve impulse) and inhibition of the production of neurotransmitters that contribute to the excitation of nerve fibers (dopamine and norepinephrine). Attention! Anticonvulsants are psychotropic drugs and have many side effects, so they are available in pharmacies only by prescription. | The drug is administered gradually from small doses, then the dosage is increased. Treatment begins with 100-200 mg 2 times a day, then adjusted to 400 mg 2-3 times a day until the pain attacks stop. Later, you can reduce the dose to maintain the therapeutic effect to 100-200 mg 2 times a day. The treatment is long. |
| Phenytoin (difenin) | Start with a dose of 3-5 mg per kg per day, then increase the dose to 200-500 mg per day. The dose is taken once or divided into 2-3 doses, only after or during meals. The treatment is long. | ||
| Lamotrigine | The initial dose is 50 mg 1 time per day, then the dose is adjusted to 50 mg 2 times a day. The treatment is long. | ||
| Gabantin | The mechanism of action of this drug is not known, its high efficacy in trigeminal neuralgia has been experimentally proven. | The initial dose is 300 mg per day, the maximum is 1800 mg per day. The drug is taken in 3 doses. | |
| Stazepin | Start with 200 mg per day, increase the dose to 600 mg per day. Taken in 3 doses. | ||
| Muscle relaxants | Baclofen (Baclosan, Lioresal) | Baclofen is effective in the treatment of neuralgia by stimulating the production of the neurotransmitter GABA (gamma-aminobutyric acid). Effects of the use of muscle relaxants:
| The initial dose is 15 mg for 3 doses, then gradually it is increased to 30-75 mg per day for 3 doses. |
| Mydocalm |
| The initial dose is 150 mg per day for 3 doses, the maximum dose is 450 mg per day for 3 doses. | |
| Vitamin preparations | B vitamins (neuromultivit, neurovitan and other complexes) |
| 1 tablet 3 times a day with meals. |
| Omega-3 Unsaturated Fatty Acids (Bio Supplement) | Unsaturated fatty acids are the building blocks of myelin. | 1-2 capsules per day with meals. | |
| Antihistamines | Diphenhydramine, pipalfen | Enhance the effect of anticonvulsants. | Diphenhydramine 1% 1 ml at bedtime at night, Pipalfen 2.5% - 2 ml at bedtime as an injection. |
| Sedative and antidepressant drugs | Glycised (glycine) | Glycine is an amino acid that is a neurotransmitter that inhibits the processes of excitation of the nervous system. It has a calming, anti-stress effect, normalizes sleep. | Dissolve 2 tablets 3 times a day, under the tongue. |
| Aminazin | Aminazine blocks receptors that receive impulses from transmitting nerve fibers. Due to this, the drug has a sedative effect and reduces psychotic reactions in acute and chronic psychoses. | 20-100 mg every 4-6 hours inside. Injection administration of the drug is necessary for acute psychotic reactions. A single dose of 25-50 mg is administered, if necessary, the drug is administered repeatedly. Reception of this drug is continued until the mental state of the patient is normalized. | |
| Amitriptyline | It has an antidepressant effect by regulating the release of neurotransmitters. | Initial dose: 75 mg in 3 doses, then increase the dose to 200 mg in 3 doses. The drug is recommended to be taken with food. |
In severe trigeminal neuralgia, constant pain, even narcotic drugs (sodium oxybutyrate, cocaine, morphine, and so on) are recommended.
Previously, blockade of the branches of the trigeminal nerve with 80% ethyl alcohol (alcoholization), glycerin and novocaine was widely used. However, at the moment, it has been proven that, despite the rapid analgesic effect, these procedures contribute to additional traumatization and destruction of the myelin sheath of the trigeminal nerve, which later (after six months) leads to the progression of the disease with short remissions and prolonged pain attacks.
Be sure to spend correction of those conditions that may have led to the development of the disease:
- treatment of ENT pathology,
- therapy of vascular diseases of the brain,
- adequate sanitation of the oral cavity,
- antibacterial (or antiviral) and immunocorrective treatment of infectious diseases,
- prevention of proliferation of connective tissue (scars) after injuries, surgical treatment and infectious processes, for this it is effective to prescribe biostimulants (aloe extracts, placenta, FiBS), short courses with small doses of glucocorticosteroids (hormones) and physiotherapy procedures,
- normalization of metabolism, with its violations (diet, vitamin therapy, hormonal correction, and so on),
- other measures, depending on the causative diseases and conditions.
Surgical treatment for trigeminal neuralgia
Surgical treatment of trigeminal neuralgia is recommended if it can effectively solve problems with minimal risks of postoperative complications. They also offer facilitating surgical manipulations in the absence of a clinical effect from the drug therapy performed (after 3 months of no positive results).- Prompt solution of problems that caused neuralgia:
- removal of brain tumors(the volume of the operation is determined by the type, localization and prevalence of the tumor process),
- microvascular decompression- displacement or resection (removal) of dilated vessels that put pressure on the trigeminal nerve or its nuclei,
- expansion of the narrowed infraorbital canal(place of exit of the trigeminal nerve) - low-traumatic surgery on the bones of the skull.
With the effective elimination of the causes that caused compression of the trigeminal nerve, often attacks of trigeminal neuralgia disappear, the outcome is recovery.
- Surgical intervention aimed at reducing the conduction of the trigeminal nerve:
- Cyber Knife– modern effective treatment of trigeminal neuralgia. At the same time, unlike other traumatic operations, the risk of complications is minimal (5% on average). Cyber Knife is a type of radiosurgery that does not require punctures, incisions or other traumatic manipulations. It is possible to conduct outside the hospital hospital (outpatient).
This method is based on the effect of a thin beam of radiation on the site of increased excitability of the nerve fibers of the trigeminal nerve or its nucleus. - Gamma Knife like CyberKnife, a radiosurgery method in which beams of radiation destroy the trigeminal ganglion. It also has a low risk of complications. In terms of its effectiveness, Cyber Knife is inferior.
- Trigeminal ganglion balloon compression a catheter is inserted through the skin into the region of the trigeminal nerve node, through which a balloon is installed and filled with air. This balloon compresses the ganglion, eventually destroying the branches of the trigeminal nerve, which eliminates the conduction of nerve impulses to the central nervous system. This method has a temporary effect and can lead to the development of complications (numbness of the face, distortion of facial expressions, violation of the act of chewing).
- Resection of the trigeminal ganglion- a complex traumatic operation that requires craniotomy, removal of the ganglion by excision with a scalpel and a long postoperative recovery, and also has a high risk of complications.
- Other types of surgeries aimed at removing the trigeminal ganglion or branches of the trigeminal nerve are traumatic and often lead to complications.
- Cyber Knife– modern effective treatment of trigeminal neuralgia. At the same time, unlike other traumatic operations, the risk of complications is minimal (5% on average). Cyber Knife is a type of radiosurgery that does not require punctures, incisions or other traumatic manipulations. It is possible to conduct outside the hospital hospital (outpatient).
- capabilities of the medical institution and surgeons,
- financial capabilities of the patient (radiosurgery methods are quite expensive),
- the presence of comorbidities,
- the general condition of the patient,
- causes that led to the development of neuralgia,
- the presence of individual indications and contraindications for a certain type of operation,
- patient response to drug treatment
- the risk of postoperative complications and so on.
Physiotherapy for trigeminal neuralgia
 Physiotherapy- effective measures for the relief of pain in trigeminal neuralgia. Depending on the degree of damage, the frequency of relapses, the cause that caused neuralgia, one or another method of physical impact on the trigeminal nerve or its nuclei is prescribed.
Physiotherapy- effective measures for the relief of pain in trigeminal neuralgia. Depending on the degree of damage, the frequency of relapses, the cause that caused neuralgia, one or another method of physical impact on the trigeminal nerve or its nuclei is prescribed. Physiotherapy methods
| Method | the effect | Method principle | Duration of treatment |
| Ultraviolet irradiation (UVR) of the face and neck | Removal of pain syndrome. | Ultraviolet irradiation (namely medium wave) promotes the release of neurotransmitters that inhibit the excitation of nerve fibers and natural analgesics. | 10 sessions |
| laser therapy |
| The laser affects the localization of each branch of the trigeminal nerve, as well as the nodes formed by this nerve. Laser irradiation depresses the sensitivity of nerve fibers. | On average, 10 procedures of 4 minutes are recommended. |
| UHF |
| Exposure to ultra-high frequencies contributes to:
| 15-20 sessions of 15 minutes |
| electrophoresis |
| Electrophoresis - the introduction of drugs with the help of electric current directly into the desired area of the nerves. For pain relief, enter:
Also, using electrophoresis, you can introduce B vitamins, which will improve the nutrition of the nerve and damaged myelin sheath. | It is better to alternate these procedures with other methods of physiotherapy every other day, 10 procedures in total. |
| Diadynamic currents |
| For this method, Bernard currents are used, which are electric currents with an impulse of 50 thousand hertz. The electrodes are placed on the trigeminal nerve trigger zones, including the nasal mucosa. Bernard's current lowers the threshold of pain sensitivity, blocks the branches of the trigeminal nerve, thereby reducing the intensity of the pain syndrome, until it stops completely. The use of diadynamic currents in combination with electrophoresis and other methods of physiotherapy is effective. | Several courses for 5 days with a break of 5-7 days, the procedure lasts for 1 minute. |
| Massage | Prevention and treatment of atrophy of mimic and masticatory muscles. | Massaging the muscles of the face, head and neck improves blood circulation and lymph flow, thereby improving their nutrition. Massage is carried out carefully, it should not affect trigger zones and provoke the development of pain attacks. Stroking, rubbing, vibration movements are used. A course of massage is prescribed only against the background of a stable remission of the disease. | 10 sessions. |
| Acupuncture (acupuncture) | Removal of pain syndrome. | Acupuncture affects nerve receptors that transmit impulses to nerve fibers. In this case, several points are selected in the trigger zones and several points are remotely on the opposite side. Sometimes the needles are set for a long period - a day or more, periodically scrolling them. | The duration of treatment is selected individually, often only a few procedures are enough.  |
All physiotherapeutic methods of treatment should be used in combination with drug therapy and the elimination of factors that led to the development of the disease, since physical procedures are powerless as monotherapy (mono-one).
Prevention of trigeminal neuralgia
- Prompt medical attention for the treatment of acute and chronic diseases of the ENT organs, timely sanitation of the oral cavity, and so on.
- Annual preventive medical examinations in order to identify diseases of internal organs, endocrine glands, nervous and cardiovascular pathology.
- Avoid injury to the face and head.
- Avoid drafts and other types of hypothermia.
- Blood pressure control and treatment of hypertension, vegetative-vascular dystonia, atherosclerosis and other vascular diseases.
- Healthy lifestyle:
- complete physical activity
- proper sleep and rest,
- adequate response to stressful situations,
- proper healthy nutrition containing a sufficient amount of vitamins, trace elements, unsaturated fatty acids and amino acids.
- hardening,
- smoking cessation, drug and alcohol abuse, etc.
- Can't self-medicate pain in the face, remember that any manipulation can aggravate the course of trigeminal neuralgia.

Be healthy!


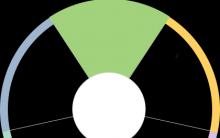








The meaning of the name diamond is sonan
Pirantel instructions for use for
What is a genetic passport What does a genetic passport include
Nebilet - a powerful tool in the fight against hypertension
Solution, aerosol Berodual: instructions for use for inhalation