The cutter is the main working element of any lathe, by means of which a part of the metal is removed from the workpiece, which is necessary to obtain the part of the required size and shape. In the industrial sector, turning tools are the most common, which we will discuss in this article.
The publication discusses the device and dimensions of turning tools, studied their classification and varieties, and also provides recommendations for sharpening cutting tools at home.
The first machines were invented. Worker-oriented machine tools are beginning to mass-produce parts. The machine transforms iron: it measures the size, file, hole to produce precisely all kinds of parts: screws, gears, rods or cylinders. At the same time, the American Whitney invented a tool capable of producing identical rifle parts.
These new production methods improve the performance of workers. Working in factories, they perform tasks that are no longer required. Invention electrical power allows you to replace the steam engine with an electric motor. Each car is then given its own engine. This reduces the number of accidents, reduces energy consumption and improves working conditions.
1 Design features
Any turning tool consists of two elements - a head and a rod that holds it. The rod is used to fix the cutting head in the seat of the lathe, it can have a square or rectangular section.
Consider the most common rod sizes:
Locomotive assembly plant
The work on the chains ruined the lives of the workers. Thus, the time of production decreases very quickly, and the product costs less, because the worker produces more for the same wage. This is mechanization, which will allow the production of more objects in much less time. Thus, employers are not required to hire a skilled worker; it is enough to use the services of an unskilled worker, whose work will consist of nothing more and nothing less than operating a machine that will perform tasks in its place.
- square: 40, 32, 25, 20, 16, 10, 8, 6, 4 mm;
- rectangular: 63*50, 50*32, 40*25, 32*20, 25*20, 25*16, 20*16, 20*12, 15*10.
Basic working part the incisor is its head. This design consists of several planes, which are reduced to each other at a strictly specified angle, which allows the same cutter to perform many metalworking operations.
Description computer program in the form of coded instructions that can be used by a machine with numerical control, is recorded on magnetic tape, the machine must then have a tape recorder or be stored in a microcomputer that the machine directly controls. The technician only intervenes to program the machine and make sure it works correctly.
Similarly, the loading and unloading of parts is provided either by devices built into the centers themselves, or by robots, which are articulated arms equipped with a control program. The centers are controlled by microcomputers connected to a central computer responsible for managing the entire chain. This computer must be capable of recognizing parts as the circuit is designed to process various parts, storing the corresponding programs in memory and, depending on the recognized part, send the corresponding program to the appropriate center.
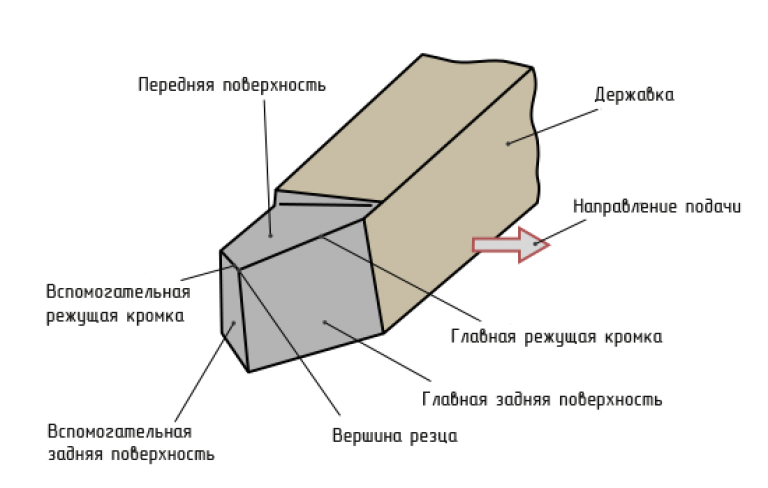
You can see the standard turning tool device in the diagram, its typical design consists of the following main components:
- back corner (a);
- front corner (Y);
- taper angle (B);
- cutting angle (Q);
- entering angle (F)
The major clearance angle, designated by the nomenclature Alpha, is the angle between the cutting plane and the back of the cutter. This element performs an important functional task - they reduce the friction force of the back side of the cutter on the workpiece, which ensures minimal surface roughness of the part. The smaller the clearance angle, the more the cutter wears out and the worse the machining accuracy. In practice, the relief angle is reduced when working with hard steel and increased when working with soft metals.
Lead curved cutter
The term "workshop without a man" corresponds to the final stage in the evolution of machine tools with numerical control and the implementation of robotic chains. So the next step is to make this monitoring unnecessary, at least for a certain period of time, in order to, for example, ensure that the chain runs alone during the night, having prepared a sufficient supply of blanks in advance. Among the issues that need to be addressed is the need to regulate changes in tools. A simple solution is to determine the service life of each tool, so that when this time is reached, the computer will send a replacement order to a center that already has the means to automatically remove the used tool and reassemble the new tool.
Rake angle (Y - gamma) is the angle between the front side of the cutter and the main cutting edge. Properly selected rake angle provides a thin removal of the layer of metal being removed, without crushing the underlying steel layer. If this angle is exceeded by 5 or more degrees from the norm, the strength of the cutting edge is significantly reduced, which leads to a decrease in its operational life by 3-4 times.
Cut off turning tool
However, without human supervision, a minor and localized incident can lead to a more serious accident or a general immobilization of the installation. Today, a computerized tool called numerical control is increasingly replacing hand-held equipment and allowing pre-programmed operations to be performed. Parts are sometimes made up to a thousand millimeters and can cost thousands of euros!
But if the machine replaces a person for certain tasks, it will always be indispensable for programming and maintenance. It is the machining technician who will produce the parts to be found in the automotive, steel, aviation, medical or space industries. It is he who conceives elements that can be several millimeters or several meters.

The main angle in the plan (F - phi) is the edge, the parameters of which affect the nature of cutting the metal the most. When this angle is changed, the thickness of the cut metal layer changes, which makes it possible to achieve different type cut at the same force and feed rate of the cutter. The smaller the angle F, the stronger this edge is, but at the same time it becomes necessary to significantly increase the feed force, which can lead to vibration during processing.
A mechanical technician is precise, observant, able to mentally represent parts in three dimensions from a plane. Indeed, the imagination of a three-dimensional element based on sketches or plans, seeing how it evolves in space and creates a prototype of production, for him is his main activity.
Today, a technician is indispensable for the smooth operation of all machines. But in the future there may be "seminars without men" and one can ask a question. Will the machine eventually replace the human? Portable electric machines. Pneumatic machines. In this photo we see the workers in full force.
1.1 Classification and types of incisors
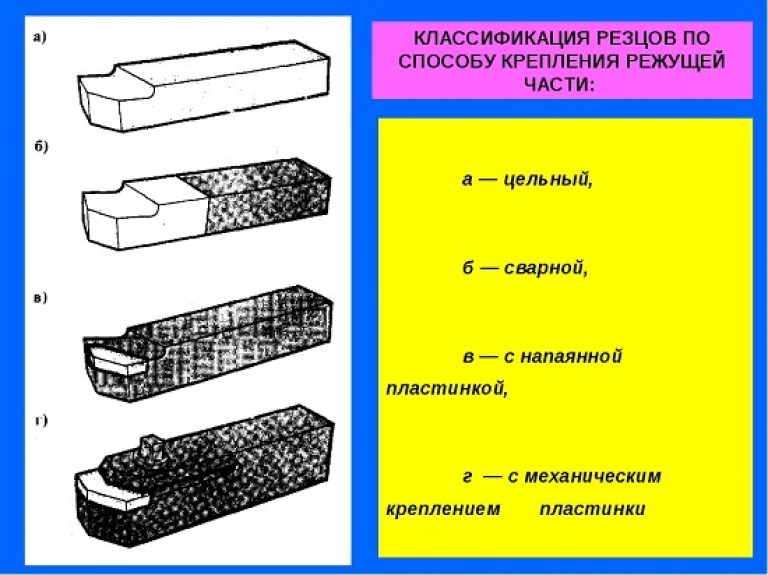
According to the provisions of the current GOST, turning tools are classified into varieties according to such parameters as the type of construction, build quality, mounting method, feed direction and processing method. Consider the types of cutters depending on their design:
- Solid - incisors in which the shaft and head are monolithic, this is the most expensive type of cutting tools. For their production, carbon types of steel are used, which ensures maximum wear resistance of the structure.
- Welded - the head is fixed on the rod by welding. The quality of the tool directly depends on the correctness of welding, non-compliance with the technology of which causes microcracks to appear in the connecting seam, leading to rapid deformation of the cutter.
- With mechanical connection. This method fixations are mainly used in the production of incisors from ceramic materials, however, there are also mechanical cutters made of steels of an adjustable type, the design of which allows you to change the position of the head in relation to the rod.
The number of cars produced is twice the number of workers
The chassis is rigidly aligned. Apparently there is one worker for each car. Chain work does not yet exist. 
Negative aspects: Chain work was immortalized by Charlie Chaplin in Charlot, this is a worker in a giant factory. He tightens the bolts daily. But the machines and work in the chain make him sick, he leaves his post, collects the orphan and the lives of the purposeful. This film talks about the negative aspects of working for the chain, in particular the slavery of a worker in his car.
Depending on the quality of metalworking, there are 3 types of cutters - roughing, semi-finishing and finishing. Roughing tools allow you to perform processing at high speed, they are also able to remove the thickest possible layer of metal. Such cutters are distinguished by high mechanical strength, they are resistant to heat and wear, but the processing quality is rather low. Semi-finishing and finishing cutters are used to finish the workpiece after roughing. They are designed to feed at low speed and remove the minimum thickness of the chip layer.
Working in chains involves always performing the same gestures on the workstation occupied by the worker. History of the Iron Working Library No. 918. EncyclopediaLarouse Multimedia. Calibration Calibration: Arming Inner diameter meme mouth of fire. Technique: a tool used for comparison to control mechanical production.
Cam: A non-circular piece with a lip or notch used to convert rotational motion into movement motion: a camshaft. Sensor: A device that supplies another variable in physical quantity, often an electrical one, which is a function of the former and can be used directly for measurement or control.
The cutting tool is also classified according to the method of installation in a lathe, depending on which cutters are radial and tangential:
- radial mounted at an angle of 90 degrees to the plane of the workpiece, which makes it possible to use more convenient types of cutting edges in sharpening;
- tangential cutters are mounted at an inclination different from right angle, they are characterized by a complicated installation scheme, but at the same time they make it possible to obtain the highest quality chip removal.
Depending on which side the cutting edge of the head is located in relation to the surface to be machined, the incisors are classified into right and left. Also, tools are divided into types according to the placement of the cutting edge relative to the holder (rod) into straight, drawn, curved and bent.
Tungsten carbide: A grey-black metal used to make filaments for incandescent lamps, heating resistors, and alloyed with steel. Fillers: planer in which the cutting motion is obtained by the direct movement of the tool. Milling: The work is done with a rotating cutting tool with several cutting edges that are regularly spaced around an axis.
Slotted machine: Slotted machine. Operator: The person who operates the device. Tool: The machine component that receives the tool. Lathe: A machine used to machine the outer part. Threading: screw on a screw, nut, etc. Milling Machine: A machine used to cut a rectangular cavity in a piece of wood or metal to accommodate a tenon of another piece.
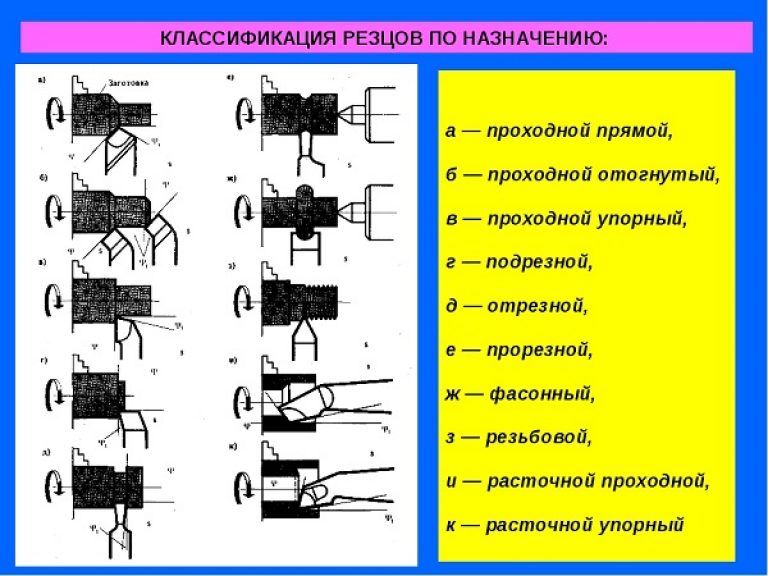
However, the main parameter for classifying cutting tools for lathes is the processing method, according to which the cutter can be:
- through passage - designed to perform such technological operations as turning and trimming, mounted on machines with longitudinal and transverse feed;
- scoring - is installed exclusively on machines with a transverse feed;
- cutting - for machines with a transverse feed, used for processing the ends and turning the annular grooves;
- boring - used for processing holes of a deaf and through type;
- shaped - designed for chamfering and processing shaped surfaces;
- threaded - can be round, straight or curved, used for cutting external and internal threads.
Also, the classification of incisors is carried out based on the material of their manufacture. There are three groups - from hard alloys (tungsten, titanium-tungsten and tantalum-tungsten), from high-speed and carbon steel. Universal are titanium-tungsten cutters, which are suitable for processing any type of metal.
Machine tower: support for a cutting tool consisting of several various tools, regularly located around the axis of rotation of this support. Turning: processing on a lathe. The grinding process is a type of cold machining by removing material. It allows you to re-clean and transform raw parts into finished parts thanks to a suitable tool that, rotating on its axis, takes care of the removal metal parts.
It usually consists of two separate roughing steps and subsequent finishing to completion as defined by the technical drawing. Tool rotation speed and fast feed enable fine adjustment of the engraving, which mainly depends on the hardness of the material to be machined.
1.2 Device for sharpening turning tools (video)
The key parameters that characterize the operational capabilities of any set of turning tools for metal are:
- cutting edge geometry;
- resistance to deformation and vibration of the edges and rod;
- material of manufacture;
- method of installing the structure in the tool holder;
- chip removal method;
- geometric dimensions of the tool;
- processing quality.
It is the ratio of these factors that forms the suitability of the cutter for a specific processing mode. When choosing a set of turning tools for metal, first decide which grade of steel you will most often process.
They are structurally very strong machines, they must absorb the significant vibrations generated by the motorized head oscillating. On tough materials or at very high speeds, lubricating fluids are also used for fast handpiece sawing as well as friction. This lubricant also retains chips, thus avoiding the risk of rubbing on cutting tools or pinching the cutting wire.
Boring tool for through holes
Our staff is highly qualified and follows each project with the utmost professionalism at every stage of the project with the client. Turning is one of the critical processes processing and metal processing. This is an industrial process carried out by removing chips through a rotating motor at high speeds along with a stationary and linear tool approach.

Then you need to determine the priority requirements for processing - this can be the accuracy of removal (thickness of the chip layer and compliance with the geometric dimensions of the workpieces) or its quality (lack of roughness, surface smoothness). Understanding these parameters allows you to correctly determine the required type of cutters in accordance with their characteristics specified by the manufacturer in the product passport.
Boring for blind holes
The parallel lathe is the most used in machining. The working motion consists of turning the workpiece while the tool slides parallel to the axis of rotation. Turning tools are high-strength materials because they are subjected to extreme stress and consist of different forms depending on the type of removal to be achieved.
Our skilled and specialized technicians carry out mechanical turning operations using high-precision CNC machines. program management. This always ensures the tolerance and shape required by the technical drawing. Welding is a process that allows two metal parts to be brought together by fusing, realizing the continuity of the material.
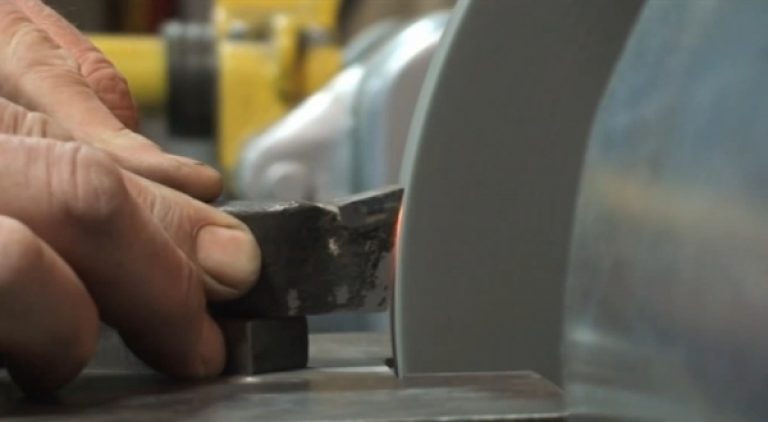
Sharpening of cutters during their operation is required regularly, since even products made from the most durable steel grades wear out over time. For sharpening, it is necessary to use special equipment - a grinding and grinding machine, while the unit must be equipped with a constant cooling system.
Such machines are equipped with two working circles: the first is made of silicon carbide (used for sharpening high-speed steel products), the second is made of electrocorundum (for working with carbide tools). When sharpening a cutter with your own hands, you first need to process the main surface, after which the back and auxiliary plane are sharpened, the front surface is removed last until a perfectly even cutting edge is obtained. Sharpening angles are checked using standard templates, which can be purchased from specialized stores.
Depending on the finished product, the company's certified technicians may adopt the most advantageous type. In particular, welds are performed in:. stainless steel cobalt alloy. A metal lapping operation is performed on a metal surface with the ultimate goal of minimizing its roughness to a more or less high degree until clear and transparent surfaces are obtained. The well-known mirror effect, achieved with appropriate special abrasives, is the most high level lapping, which makes them smooth and uniform.
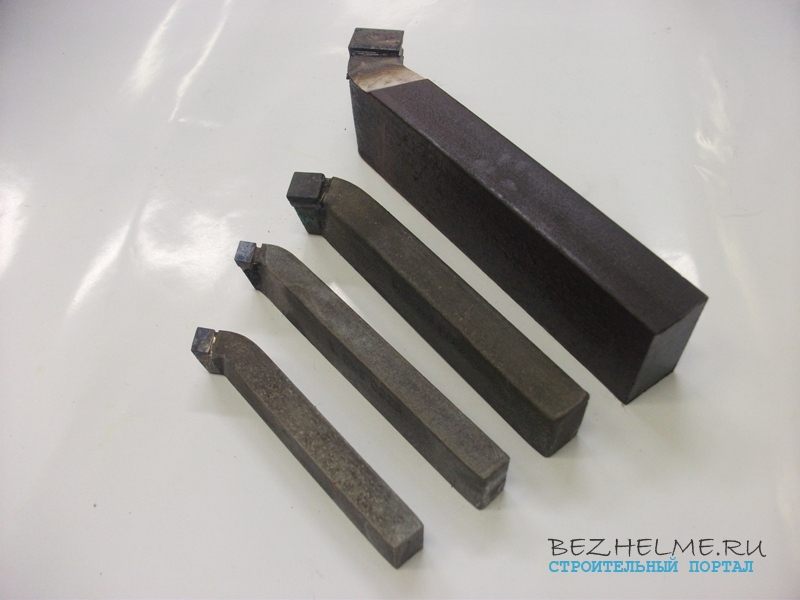
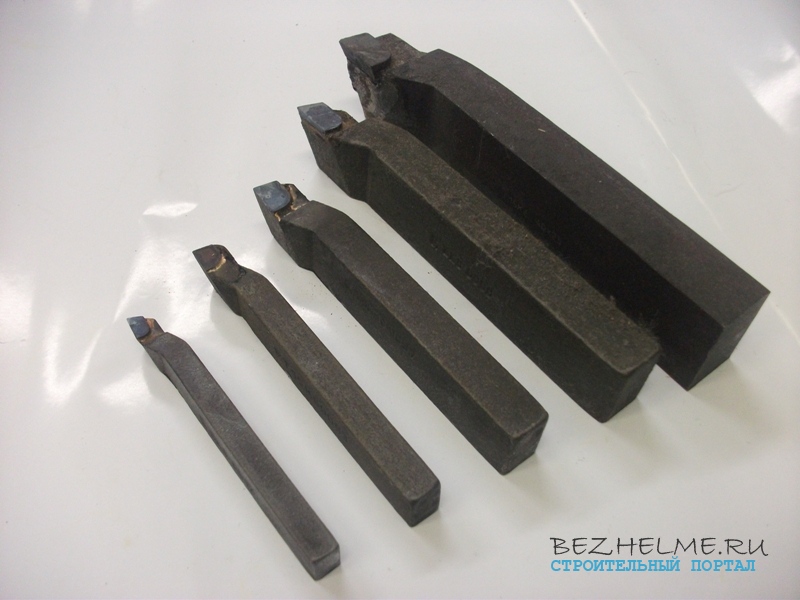
Very often, turning tools for metal are bought in our store, and if the suppliers who understand them correctly name each type of tool, then ordinary citizens often confuse the tools. In this article, I suggest that you familiarize yourself with the main types of turning tools - look at the photo, find out the size range and scope of each type.
This precision finishing process is done on metals with a tool called a lapping machine using abrasives that are bonded to the surface with the same tool made of hard material in hardness. It is a mechanical machining process that involves the removal of surface material. One of the main features of lapping is the use of these chemical, liquid, or pasta abrasives that are inserted between the piece and the hold-down support to retain free abrasive particles.
All models are from the Kanash factory, their products are one of the highest quality on the market.
Important! All models of cutters are made with plates of different brands - most often these are VK8, T5K10 and T15K6. Other hard alloys are used quite rarely (for example, T30K4 and the like).
detachable
One of the most sought after incisors. Used for cutting workpieces. It cannot be confused with anything else - a thin leg with a soldered carbide plate. The scope is cutting at a right angle, they also cut thin grooves.
There are right and left handed. In the photo, you can clearly distinguish the right from the left - on the left, just the same left-sided. All others are standard right, in 90 percent of cases they are required for work. It is very easy to distinguish - take the cutter with the plate down (like a knife) and if the leg is on the right, then the cutter is right. Left means left (less common). Look at the photo, you can see everything there.
Dimensional range of holders:
- 16 * 10 mm - for small "school" machines
— 20*12 mm
- 25 * 16 mm - the most popular
- 40 * 25 mm - large incisors, rarely found on sale, only on order.
Straight bent
The name itself speaks of its scope - they process the ends of the workpieces, and also chamfer. The bent part, as it were, bends around the workpiece from the side. A photo:

The size range is also very decent:
- 16 * 10 mm - small for school machines
— 20*12 — custom size
- 25 * 16 mm - the most popular
— 32*20 mm
- 40 * 25 mm - rarely found on sale, only on order as a rule
Through-thrust bent
The prefix "bent" is usually not used in everyday life, the incisors are simply called thrust through. But the bend can be seen, there are without it.
Scope - one of the most needed incisors. Used for processing cylindrical workpieces. The bend just allows you to grind round parts, removing as much metal as possible in one cut of the cutter. The processing of the part goes along its rotation!

The size range is also wide:
— 16*10 mm
— 20*12
— 25*16
— 32*20
— 40*25
There are also left and right. In the vast majority of cases, the right models are used.
straight through
The scope is the same as that of the bent through passage, however, it is more convenient to chamfer. And direct most often process metal surfaces. Rarely used in production.
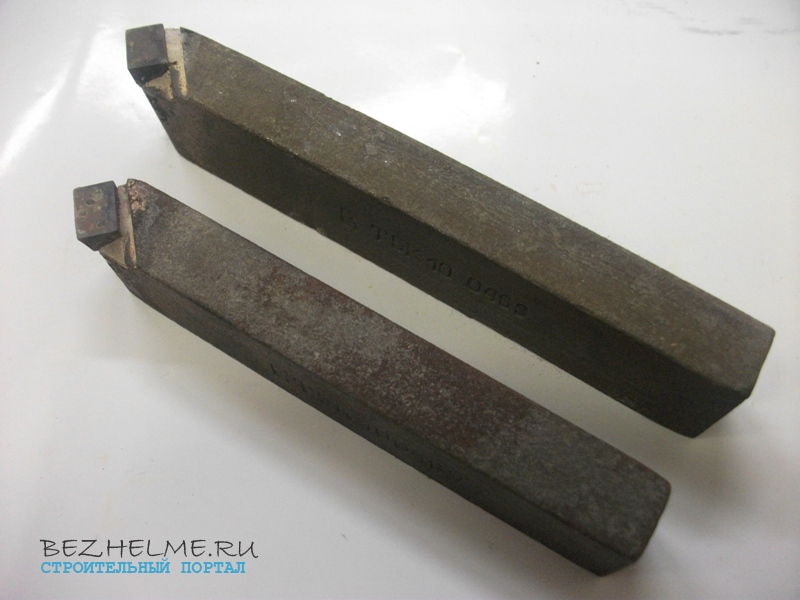

Size range:
- 25 by 16 mm - standard with square holder
- 25 by 25 mm - non-standard holder, for some special work
Scoring bent
Most often it is confused with a persistent through passage. The undercut has a triangular plate, pay attention! A photo:
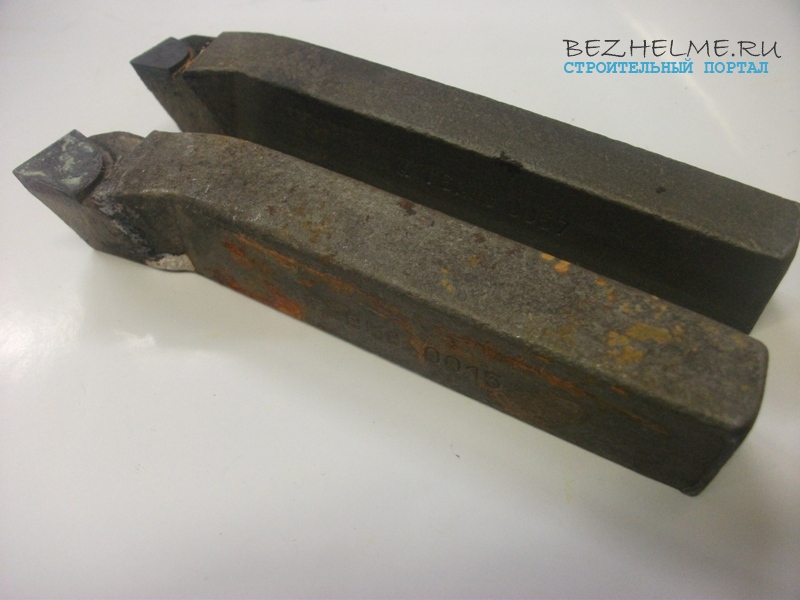

Scope: workpieces are processed across the axis of rotation (perpendicular). In addition to bent models, there may also be persistent ones (but they are not in demand as a rule).
— 16*10 mm
- 25 by 16 mm
- 32 by 20 mm
For external thread cutting
Scope: the name speaks for itself - they cut threads with such cutters. What? If you take a cutter from the factory, then, as a rule, it is “sharpened” under metric thread. For other types of threads, it will need to be reground.
The plate is installed “spear-shaped” (its correct name is cut-off, sold separately), it can be of a different alloy (brands are indicated at the beginning of the article). The resulting thread on the workpiece is external (the so-called "dad") - a bolt, stud, etc.
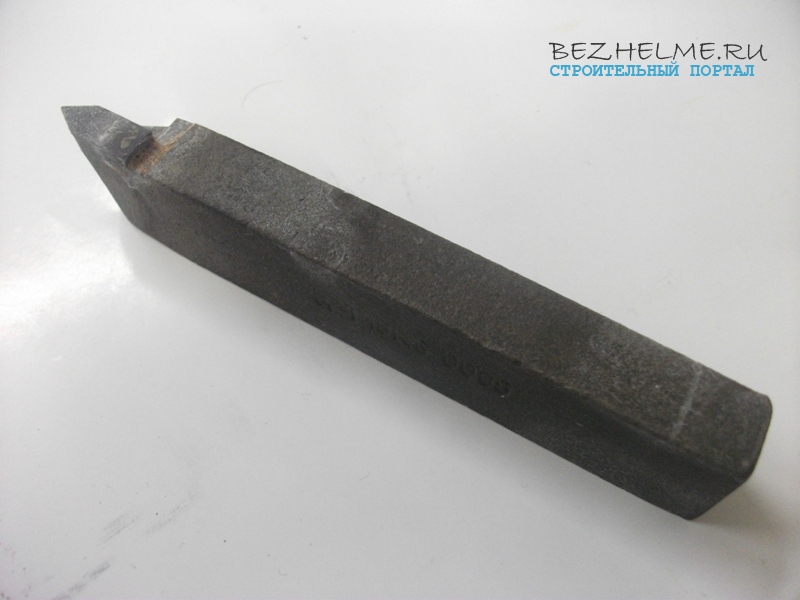

Most requested sizes:
16*10mm
25*16mm
32 * 20 mm - not used so often
For internal threading
If the outer thread can also be cut, then only the thread is cut with the inner one. large diameter. This can be understood by the size of the incisors themselves. A photo:

Important! Do not confuse this tool with boring tools for blind holes, they are similar in appearance, but fundamentally different! Boring below in the article, compare.
— 16*16*150
— 20*20*200
— 25*25*300 mm
The first and second digits are the size of the holder (it is square in cross section), and the third digit is the length of the holder. The longer - the deeper you can cut the thread inside the workpiece.
Please note that in order to use such a cutter, it is necessary that your machine be equipped with a fixture called "guitar".
Boring for blind holes
Scope - for boring blind holes. They work as if from the end, for which a sort of “bend” of the head is needed. Whereas the “internal” (see below) completely enters the workpiece with the holder.
- The plate of this cutter is triangular, the same as that of the scoring cutter (see above).
A photo: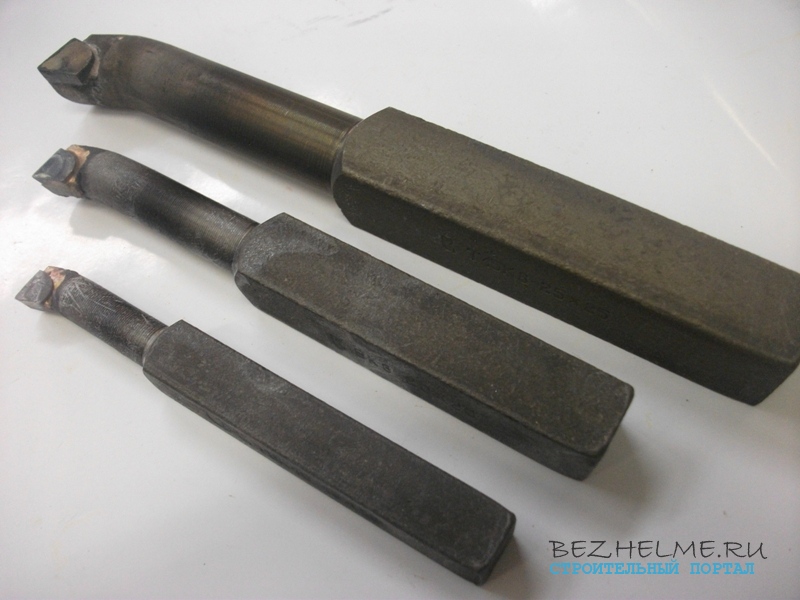 
— 16*16*170 mm
— 20*20*200 mm
— 25*25*300 mm
The larger the cutter, the larger diameter holes can be bored!
Boring for through holes
Scope - they bore parts "inside" along the entire length. The longer the holder, the more inside you can bore. Most often, the part is bored after drilling it with a large drill, it is also possible to work according to existing dimensions.
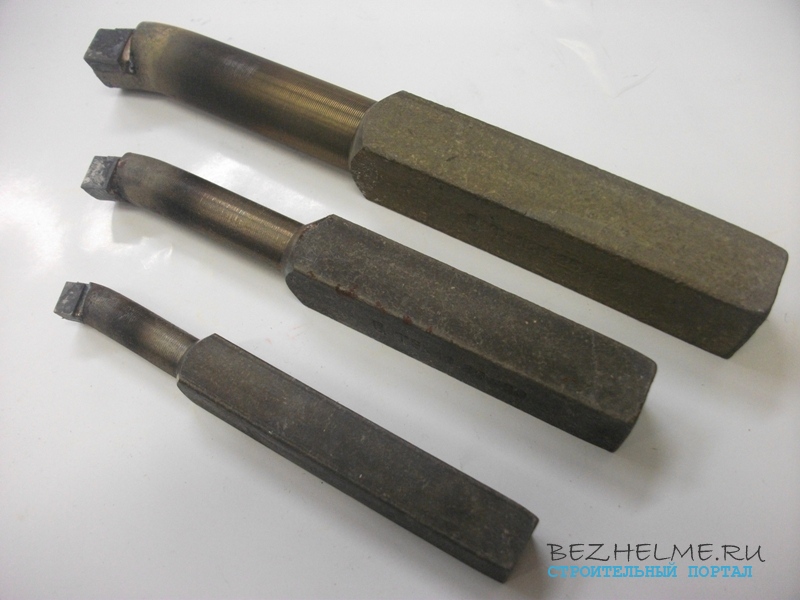

The plate is straight, there is no protrusion, which means that the cutter easily enters the “tube” resulting from drilling and bores it from the inside, passing through. The layer of chip being removed is approximately equal to the curvature of the cutter head
— 16*16*170 mm
— 20*20*200 mm
— 25*25*300 mm
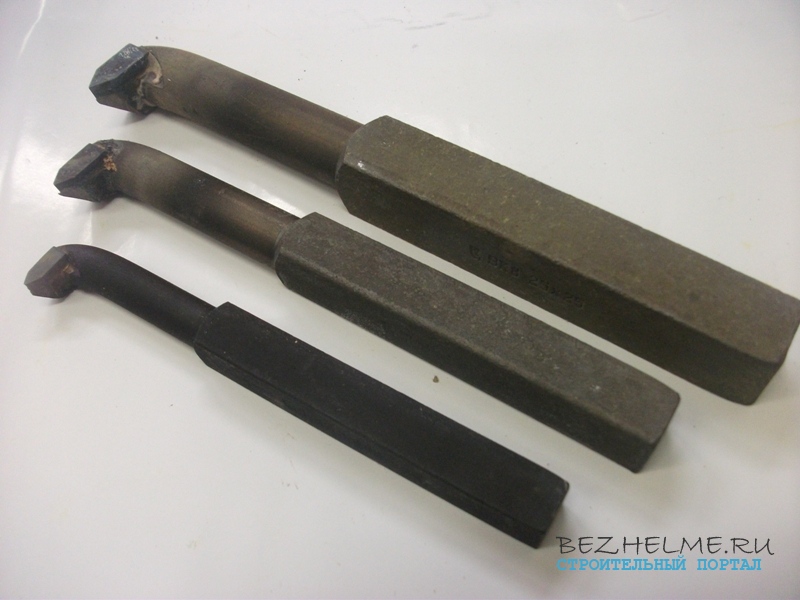
prefabricated
One of the rarest incisors. They are also called universal, because they are equipped with different plates, so that workpieces can be processed. various shapes at different angles. They differ from each other both in the size of the holder and in the shape of the insert that can be clamped.
The photo below shows 3 different models:
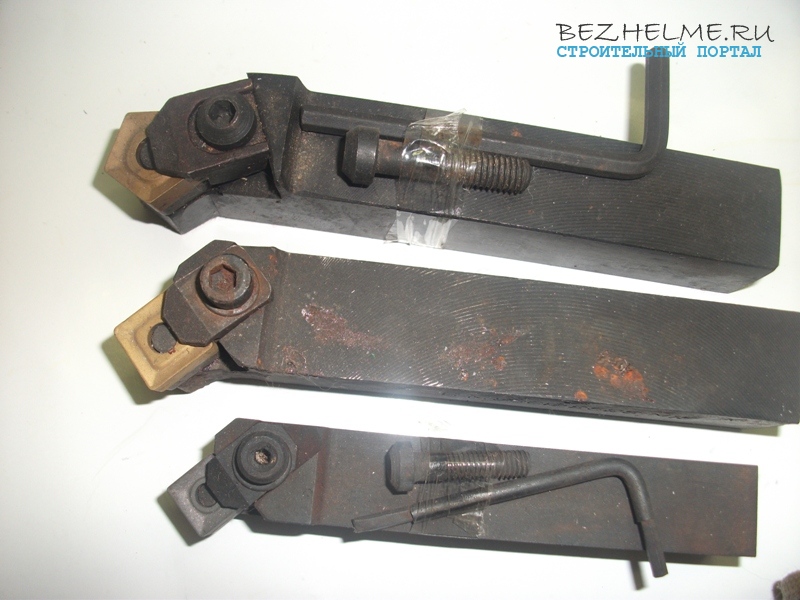

The smallest cutter has a 20 x 20 mm holder and is equipped with a 4-sided square insert.
A little more has a holder already 25 mm and the insert is also square, but larger in size.
Well, the third cutter is similar in parameters to the second one, it has a 5-sided plate by default, but you can get it and put it the same as on the second one - a large square one.
In terms of money, these cost around 300 rubles apiece, but it’s difficult to find them on sale, it’s sometimes problematic to even bring them to order.










Sun skirt: types and how to wear it Black sun skirt with a T-shirt how to wear
Ground bird cherry Ground bird cherry cook
Own business: production of chips
How to care for your skin in spring Face masks in spring
Seizures in the corners of the mouth: causes and treatment in adults and children