Despite the saturation of the market with many varieties of high-tech polymer pipes, metal for the installation of heating systems, hot and cold water supply are widely used today. metal pipes for these purposes, they are mainly made from steel and copper, less often from aluminum. Each type of such pipes, depending on the material of manufacture, has a set of individual characteristics that provide the consumer with enough room for maneuver when choosing.
One of the most common types of pipes are zinc-coated steel products - a material that has many positive characteristics, but is specific in application. Consider what kind of material it is, and how to properly use galvanized pipes for heating.

The main enemy of steel pipes is corrosion. One of the ways to protect against it is to apply a protective layer of zinc to the surface of the steel pipe, after which the material is classified as a separate subgroup - a galvanized pipe for water supply and heating systems.
The method is moderately expensive, so the cost of a steel pipe after galvanizing remains affordable - an approximate price ratio can be found according to the table:
Zinc coating can be applied to a steel pipe made by any technology - straight-seam, with a spiral seam, seamless, therefore, galvanized pipes are classified in the same way as ordinary pipes by the factor of the presence of a seam.
There is no independent standard for galvanized products. Steel pipes with zinc protection are produced in accordance with normative documents for electric welded products with a straight seam (GOST 10704) and material for gas pipelines (GOST 3262-75).
Zinc Coating Methods
Zinc coating, depending on the operating conditions of the pipe, can be carried out both on its outer surface and on its inner one.
There are 4 methods of galvanizing pipes, each of which is used depending on the size of the products and the requirements for the thickness and strength of the zinc coating:


Parameters of zinc coated steel pipes
Main technical parameters steel pipes zinc coated are:
- outside diameter(10.2 - 165 mm);
- weight of 1 m of pipe (0.4 - 22 kg);
- conditional passage (6 - 150 mm);
- wall thickness (1.8 - 5.5 m);
- length (4 - 12 m).
As with ordinary pipes, the walls of galvanized products can be light, reinforced or standard, the accuracy of execution is assigned to ordinary or increased.
Important! A protective zinc coating should be applied to the entire surface of the product and have a thickness of 30 microns. Peeling of the protective layer, peeling and swelling on it are not allowed (“Steel water and gas pipes”, Specifications, GOST 3262-75, amend. No. 4,6).
Advantages and disadvantages
Most of the characteristics of galvanized VGP pipes, both positive and negative, coincide with the parameters of black steel products, but there are also individual qualities.
Advantages
- Strength (especially tensile strength).
- Fire resistance.
- Low coefficient of thermal elongation.
- Absolute tightness.
- Durability.
- Possibility of use as a heat exchanger.
- Possibility of installation, including current repair, with your own hands.
- Two assembly methods (welding, threaded connection).
- Ease of disposal.
The fact that the external laying of the gas pipeline from the main to consumers is only allowed from steel material speaks in favor of steel GWP pipes.
Flaws
- Significant share.
- Electrical conductivity.
- High thermal conductivity (the need to insulate pipes in heating and hot water systems).
- Susceptibility to corrosion if the zinc protection is damaged.
Mounting and assembly methods
Galvanized pipes that form a heating or hot water system are mounted in three ways:
- welding;
- flange connection;
- threaded connection;
- soldering.
Each of the above methods has its pros and cons. Consider these installation methods and the nuances associated with them.
Welding of galvanized pipes
Zinc-coated water and gas pipes can be connected by electric or gas welding - both types of installation are convenient because they take little time. But there is one negative factor, the effect of which must be minimized, since it cannot be completely eliminated.
The fact is that the temperature of the weld reaches 1200 degrees, and zinc boils at 906 degrees and begins to evaporate from heating during the welding process. In doing so, the following happens:
- the harmful effects of zinc vapor on the welder, up to the onset of suffocation, as they are poisonous;
- evaporating zinc exposes steel and makes it vulnerable to corrosion;
- zinc vapor contributes to the formation of pores and cracks in the weld, reducing the strength of the joint.
For maximum localization of these processes, before starting welding, apart from the mandatory device for effective ventilation of the room, it is necessary to perform the following actions.
- weld the joint with subsequent cleaning of the weld from slag and coating the bare section of the pipe with zinc-containing paint (zinc dust content - 94%, binder - 6%) - cold galvanizing.
To prevent boiling of the zinc layer, you can process the junction hydrochloric acid 5 cm on both sides, but in this case, acid fumes will form during welding.
Important! According to paragraph 4.6 of the joint venture ( Building Regulations) 73.13330.2012, the device of welded joints on pipelines made of galvanized steel is not allowed, since with inner surface pipes, zinc is not removed before welding, and zinc fumes, the formation of which cannot be avoided in this case, cause the formation of pores and shells in the seam. But this document is of voluntary use, and if the project does not contain a reference to the mandatory use of this paragraph, then the installation of galvanized pipes by welding is permissible.
In order to minimize the impact of zinc on the quality of electric welding, installation should be carried out in accordance with the following recommendations:
- perform welding at low speed, but avoiding burning the pipe, and with an increased current strength;
- use electrodes with rutile coating (electrode composition contains titanium oxide).

Electric welding of zinc-coated pipes requires certain skills from the welder. In addition to the composition of the outer coating of the electrode, the quality of the weld is affected by the thickness of its rod, which determines the power of the arc - an excessively thick electrode will burn through the wall, and a thin one will not provide the necessary strength of the welded joint. For welding galvanized pipes with a wall thickness of 1.5 - 5 mm, electrodes with a diameter of 2-3 mm are used.
Flange connection of galvanized pipes
This method is based on bolting together fragments of pipes, at the ends of which flanges are welded - steel rings with an inner diameter equal to the outer diameter of the pipe, and holes around the perimeter for mounting bolts. Two flanges of different fragments are applied to each other using an intermediate sealing gasket and tightened with bolt nuts or studs.

In this method of installation, there is the same negative factor as in the welded joint - in the process of welding the flanges to the pipes, zinc boils and the protective layer in the area of the weld is destroyed. Therefore, it is also necessary to take measures to localize the temperature effect on the zinc layer, and after welding, clean the seam and apply an anti-corrosion zinc-containing coating (cold galvanizing) on it.
The flange connection is not compact, therefore it is used in most cases when laying pipelines in utility rooms or outside. On the mating side of the flange there is an annular area called a mirror. Between the two mirrors of the joined flanges, before tightening them, a paronite gasket with a hole is installed, the diameter of which must match the inner diameter of the pipe. The outer diameter of the gasket is equal to the distance between the opposite fixing bolts.
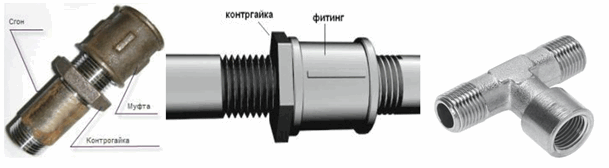
Threaded connection
This mounting method eliminates the need for thermal methods connections and is carried out using fittings various kinds, designed to connect individual fragments of the pipeline after cutting threads on them.

Threaded assembly also has its drawbacks:
- the process of threading is laborious and time consuming;
- a cutting tool (die) when cutting a thread removes a layer of steel of a certain thickness along with a protective zinc coating.
- tightness threaded connection is provided by thread wrapping with FUM tape, sealing paste or tow with paint applied, which eventually lose their properties and require replacement.
Soldering galvanized pipes
To mount a heating or hot water system from galvanized pipes without damaging the zinc layer, soldering is used, which is performed in the following sequence:
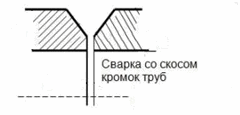
- the connected ends of the pipe are facing and, if the wall thickness is more than 3 mm, a chamfer is made on the outer edges;
- the joints are degreased by heating, after which the flux (HLS-B composition) also heated to plasticity is applied in a thick layer to the surface adjacent to the planned joint;
- the ends are arranged with a gap of 2-3 m;
- the burner flame is set to excess oxygen.
The size of the burner is selected depending on the diameter and wall thickness of the galvanized pipe:
For high-quality soldering of a galvanized pipe, it is necessary to follow the rule: the size of the burner must be one unit smaller than when welding pipes of the same dimensions without zinc coating. During the soldering process, the flame must be concentrated on the edges to be joined and the joint gap in order to exclude heating and evaporation of zinc from under the flux layer.

The connecting seams of well-made soldering of galvanized pipes do not need additional anti-corrosion protection, but applying zinc-containing paint as an insuring operation will not be superfluous.
The specifics of the use of galvanized pipes in heating and hot water systems
Zinc Coated Pipes heating systems ah and water pipes are applied taking into account operating conditions.
If the coolant temperature does not exceed 65 degrees, then the zinc coating successfully performs its functions. In the northern regions, where this parameter is much higher, the inner zinc layer reacts with water under the influence of high temperature:
Zn + H2O = ZnO + H2.
Both substances resulting from such an interaction are negative factors:
- ZnO is flakes that precipitate and clog the lumen of small diameter pipelines;
- H2 is hydrogen, which, when mixed with air in a certain proportion, is explosive or at least forms plugs in the system.
Therefore, in hot water and heating systems with a coolant temperature above 60 degrees, it is allowed to use pipes that have only an external protective zinc coating, which will protect the pipeline from corrosion during periods of downtime. However, when water gets on the surface of a hot pipe, the zinc shell begins to peel off from the base, therefore, in order to avoid this, it is necessary to paint such pipelines over zinc, which will lead to an even greater increase in the cost of the system.
Conclusion: the use of pipes galvanized on the outside in hot water and heating systems with a coolant temperature above 60 degrees is unreasonably expensive, and galvanized on the inside is harmful and dangerous.
Conclusion
A galvanized water and gas steel pipe is a material in demand today, but it must be used and installed taking into account the characteristics of the protective coating, so that the advantages of zinc are used rationally, and do not become a factor that only increases the cost of work.
Without round pipes, it is still difficult to build cities: lay heat and gas pipelines, communications for residential buildings, build popular frame objects, as well as manufacture transport, various units, assemblies, and furniture.
It is clear that "creative" enterprises need high-quality products. The popularity of round pipes is easy to explain: products that are in constant demand are produced, focusing on GOSTs, and sold at affordable prices.
The requirements for the manufacture of these products, the range of round pipes are described in detail in the following documents:
GOST 10704-91 (On longitudinal electric welded steel pipes),
10705-80 (On steel electric-welded pipes),
10705-91 (About electric-welded steel pipes with a diameter from a minimum of 10 to a maximum of 530 mm),
10706-76 (On longitudinal electric welded steel pipes),
20295-85 (On steel welded pipes for main gas and oil pipelines),
GOST 3262-75 (On steel water and gas pipes).
Assortment, round steel pipe (GOST 8732-78) - the requirements for steel pipes, seamless, obtained by hot deformation, while seamless, cold-formed, are presented in detail in GOST 8734-75.
Types of round pipes and their manufacture
In the conditions of a difficult situation that has developed in the global and domestic rolled metal markets, consumers are extremely interested in the range of round pipes: welded straight-seam, spiral-seam, seamless products obtained different ways, including, water and gas pipes(VGP). The reliability of the constructed communications, buildings, transport, household items - in a word, the comfort of the human environment depends on the quality of these products.
Welded seam pipes
 Production of welded pipes accounts for more than half of the total. By the way, it was from welded pipes in 1852 that this industry began its development. The advantages of a welded pipe are still appreciated today: thanks to the latest developments of scientists, modern products have acquired excellent characteristics and are not inferior in terms of activity to seamless varieties. The range of steel round pipes has expanded significantly since the end of the 19th century.
Production of welded pipes accounts for more than half of the total. By the way, it was from welded pipes in 1852 that this industry began its development. The advantages of a welded pipe are still appreciated today: thanks to the latest developments of scientists, modern products have acquired excellent characteristics and are not inferior in terms of activity to seamless varieties. The range of steel round pipes has expanded significantly since the end of the 19th century.
The production of welded pipes is much cheaper than seamless ones. The production technology allows you to save metal: the products are much cheaper in price, while they are lightweight, which is extremely convenient and in demand during transportation and installation. In addition, the raw material (sheet steel) makes it possible to obtain products of the highest quality with minimal deviations in thickness.
make round pipes in several ways. The most famous of them:
- furnace welding;
- electric welding;
- gas welding;
With the help of furnace welding, hot-formed pipes are obtained. At the core this method lies the processing of a steel billet using special equipment: a furnace and a forming and welding mill. For example, a round steel pipe (GOST 3262-75), made of steel type 2 kp with reduction (compression in diameter), can "boast" of high ductility of the metal and a high-quality weld.
The steel strip GOST (3262-75), which can be found on the website, warms up to about 1300 ° C and is blown, while the edges are cleaned of scale, which is designed to ensure high quality of the weld. In a word, the workpiece is brought to the desired state in order to carry out the main welding procedure on the forming and welding mill and give it the desired shape with a given diameter.
Straight-line, perhaps, - the most popular. Their output is approximately half of the total pipe rolled products. The most demanded are thin-walled steel products of impressive diameter, which are distinguished by a hermetic smooth seam and high surface performance.
The manufacturing process of electric-welded round pipes is simple: a steel tape with the required performance characteristics is rolled up to the desired diameter, and then the edges are butt-welded, often arc welding. Further procedures of molding, calibration, testing make it possible to bring the products up to the requirements specified in GOSTs.
Welded spiral pipes
 To obtain spiral-seam pipes, rolled sheet steel is also used. This type of product has a number of advantages: the very location of the seams "slows down" the formation of longitudinal cracks leading to the failure of pipelines, facilitates repair work.
To obtain spiral-seam pipes, rolled sheet steel is also used. This type of product has a number of advantages: the very location of the seams "slows down" the formation of longitudinal cracks leading to the failure of pipelines, facilitates repair work.
There is also the possibility of producing products with a small diameter and thin walls. True, these products also have a significant drawback - their manufacture requires a larger amount of metal.
Seamless pipes and pipes VGP
Pipes without a seam, water and gas pipeline (VGP) products are an extremely popular product, since they can withstand powerful mechanical loads. Seamless pipes are produced by hot and cold forming on special equipment.
For the manufacture of, for example, a very wide range of round pipes steel GOST R 52079-2003 “Welded steel pipes for main gas pipelines, oil pipelines and oil product pipelines. Specifications” uses another technology - welding in a protective environment. Here all the advantages of gas and electric welding are linked. Protective gases, by displacing air from the working chamber, contribute to the creation of a special environment where the welding process using tungsten electrodes is as efficient as possible. Pipes made in this way are distinguished by a high degree of tightness, strength and wear resistance. By their own performance characteristics do not concede to seamless analogues.
Scope of application - enterprises of the oil and gas industry, the production of various units. Made in accordance with GOSTs, the VGP steel round pipe is a product that is indispensable in the construction of life support systems. Her "duties" are the supply of water, gas, the installation of adjustable, spacer fittings. As well as seamless pipes VGP, especially their galvanized variety, is necessary in the construction of boiler houses to provide city residents with heat during the cold season.
Engineering networks are an integral part of any residential, commercial or industrial facility. Particular attention in the design of communications is given to water supply, sewerage and gas distribution networks. For device of all engineering networks used VGP pipe. Depending on the manufacturing technology, this type of product can be divided into several groups. Today, the most demanded pipe products for laying communications are VGP pipes and electric-welded straight-seam products. They are supplied without thread and are available in a wide range.
Scope of application of VGP pipe
As mentioned earlier, this type of metal products is universal. The VGP pipe is equally successfully used for laying gas and water pipelines. There are no restrictions on the nature of the objects either. It has been successfully used for a long time to provide gas and water to residential buildings, commercial buildings, and industrial complexes.
VGP pipe production technologies
The raw material for the manufacture of pipe products in this category is high-quality steel. To date, domestic enterprises have launched the production of two versions of the VGP pipe: galvanized and non-galvanized. In the first case, a high degree of metal corrosion resistance is achieved due to the zinc coating. However, galvanized products have a higher cost. The second version of pipe products is recommended for use as plumbing systems. They meet all sanitary and hygienic requirements, and also have a more affordable cost.
All products are manufactured in accordance with GOST 3262-75, GOST 380, GOST 1050 and GOST 1050. Each of the standards regulates technical specifications products and their scope. Depending on GOST, a VGP pipe can be selected for water supply, gas distribution networks, sewerage or heating systems.
Electric-welded longitudinal pipe and VGP: main differences
- Electrowelded longitudinal pipe products are manufactured by continuous reduction.
- The VGP pipe has a threaded or knurled cylindrical thread, and also differ in nominal bore.
In fact, electric-welded longitudinal pipe products are the main ones for the production of high-quality water and gas pipeline elements of engineering communications. With reduction technology VGP pipe gets a smaller diameter, it becomes resistant to corrosion and is durable.
Electric pipes andwater pipes - welded pipes having a similar production method, appearance, but differ in some respects. AND steel water and gas pipes gost(steel pipe VGP) , electric-welded (ES pipes) pipes are made from strip, sheet metal, the blank is molded on special mills, and then welded, forming a seam that gives rolled products high strength and wear resistance. GOST electric welded steel pipes are straight seam, a straight seam is formed by welding along the longitudinal axis. This seam is performed first from the outside, then from inside. At GOST of water and gas pipelines pipe seam is even more reinforced. Also, VGP pipes can undergo reduction - billet drawing on mills to reduce their cross section, while the wall thickness may change, or may remain the same. Straight-seam pipes are the most demanded in the market.
Longitudinal pipes electric welded ones can be additionally thermally processed along the entire seam or throughout the entire pipe and be hot-reduced. ES pipes, which contain few alloying elements, can be subjected to recrystallization annealing. Rolled steel from grade St1 is not subjected to thermal action. Heat treatment in a protective environment is previously agreed with the buyer at the plant. Combines have the right to choose a certain type of heat treatment of electric-welded pipes themselves.
It is believed that because of the seam, welded pipes are not very reliable in use, however, the production of pipes on high-precision equipment and high-quality welding of the seam, strength tests, seam control (radiography) and the issuance of quality certificates for these products guarantee a durable, reliable material, which will last more than one year. Only a rough external influence can violate the integrity of this rolled product, in particular, pipe bending leads to damage to the seam. For pipelines, steel round pipes are used, since plastic and metal-plastic pipes cannot withstand the required pressure of gas or water.
Those and other pipes can be additionally galvanized, which makes them suitable for domestic water supply. Such pipes serve for a long time, rust does not appear inside the pipe, various wastes do not stick to them, but the weight of the pipe increases. Pipe galvanized may be a quarter heavier than non-galvanized. The steel grade from which the pipe is made also affects the anti-corrosion properties of rolled pipes. In addition, galvanized pipes are resistant to high temperatures, so they are used for heating networks in which water temperatures are over 140 degrees C. To prevent the pipelines from rusting underground, a bituminous coating is used, it increases the life of the pipes. Professionals connect galvanized pipes with care, since the coating can be damaged; threads or welding are used to connect pipes. Galvanizing of pipes occurs by immersion in a zinc melt or using toxic zinc salts.
The difference between the VGP pipe and the ES:
1. According to GOSTs:
Water-gas and electric-welded pipes have their own quality standard. Steel pipes VGP are produced according to GOST 3262-75 (this State Standard regulates the assortment and technical conditions of pipes), and ES pipes - in accordance with GOST 10704-91 (implies the assortment electric-welded straight-seam pipes ) and
GOST 10705-80 (standardizes technologies for the manufacture of electric-welded pipes).
2. The difference between black pipes in size:
GWP and ES pipes differ in wall thickness, outer section, inner diameter, nominal bore. Conditional passage is called the average value of the internal section of the pipe in mm. Water and gas pipes are measured and designated according to the conditional passage; steel pipeselectrowelded straight seam - standardized by outer diameter.
|
Type of pipe |
Outer diameter(overall diameter) |
Conv. pass |
Wall thickness |
|
Pipes VGP GOST 3262 |
10.2 - 165.0 mm |
6 - 150 mm |
2.0 mm to 5.5 mm. |
|
Electric-welded pipes GOST 10705 80 |
10 - 530 mm |
1- 32 mm |
|
|
Electric-welded pipe GOST 10704 91 |
10 - 1420 mm |
Limit deviations for the mass of pipes, wall thickness are prescribed in GOSTs.
Water and gas pipelines pipes gost 3262 in the days of the USSR it was measured in inches, many people still use this designation.
For example, a pipe with a nominal bore of 25 mm is considered an inch ( pipe vgp d 25), half inch - 15mm ( pipe vgp d 15),
three quarters of an inch Vgp pipe DN 20,
an inch and a quarter - a water and gas pipe with a nominal bore of 32 mm;
1.5 inches - DN 40,
two-inch pipe - with a nominal bore of 50mm ( pipe vgp d 50).
table Vgp pipe diameters, range of electric-welded straight-seam pipes is on our website in the section "Metal rolling". There is also a division of VGP pipes according to wall thickness into: light, ordinary and reinforced.
In this way, water pipe with nominal bore 50 mm ( pipe vgp 50) has an outer diameter of 60 mm, it corresponds to an analogue - electric-welded steel pipe GOST 10704 91 60thaya - with an outer diameter of 60 mm.
For VGP pipes Du 15 analog- diameter outer pipes electric welded = 21,3
3. By application:
Electrofusion pipes gost 10704 used for external water and gas pipelines with different pressures, oil pipelines, heating networks; in the production of furniture, in the construction of buildings and for the construction of structures: fences, poles, supports, for laying cables. GOST 10705 applies to pipes that are intended for pipelines and various designs. ES pipes are used in food, chemical, automotive, mechanical engineering, nuclear engineering, as well as for the manufacture of shafts, bearings, etc.
Pipes VGP 3262 75 they are mainly used for internal (drinking) water supply, they are intended for small gas pipelines, supplying communications to rooms, pipe 3262 used for heating systems, fabrication of metal structures, in mechanical engineering and aircraft building, in industrial construction, in agriculture; thick pipes are needed for main pipelines; some pipes are threaded. The water and gas pipe is widely used by housing and communal services.
The required section, the diameter of the pipe is selected for the water supply, taking into account the throughput of the water supply system, the number of pipe joints and the total length of the water supply, as well as the number of pipe turns. For risers, a Vgp pipe Du 25 and 20 is usually used; for supplying water to the equipment, a 15th pipe and 10 mm are taken.
4. According to steel grades and GOSTs for steels used.
Steel water and gas pipes GOST 3262 are made from St1 - St3 (ps / sp / kp), steel 10, steel 20, 08ps / kp according to GOST 380 and GOST 1050. These carbon steels chemical composition and mechanical properties are not indicated.
For the production of ES pipes, grades are used: St1-4, 08, 20, 10 according to the same GOST 380 and GOST 1050. ES pipes are made from low-alloy and carbon steels. Electrowelded pipes are divided into quality groups: A, B, C, D, mechanical properties, chemical composition, pressure tests are determined.
5. By pressure test. All pipes are tested for tightness and strength using hydraulic pressure. This is one of the types of non-destructive testing.
Pipes VGP GOST 3262 must withstand hydraulic pressure:
- light and ordinary pipes
- 2.4 MPa,
- reinforced - 3.1 MPa.
For ES pipes, these indicators are equal to:
- for pipes with a diameter of up to 102 mm, the pressure gauge shows 6 MPa,
- more diameter of steel pipes - 3Mpa.
Also, various electric welded pipes are subjected to impact bending, flattening, expanding test, bending, stretching and other strength tests.
Buy electrowelded pipe, buy Vgp pipe
Electric welded pipe price per ton water and gas pipe price, water and gas pipe diameters the client can independently find on the company's website. Vgp pipe price, es pipe price depend on the manufacturer, steel grade and wall thickness, pipe weight, zinc coating. The smaller the wall of the pipe, the lighter it is, respectively, the lighter the manufactured structure, the lower the cost of metal and its delivery by transport.
Our managers can always get the following information: GOST 10704 longitudinally welded steel pipes price per meter pipe steel electrowelded price for the quantity you need, 102*3.5 electric welded pipe price per meter, steel water and gas pipe price per meter . We are always happy to help the buyer with the delivery of pipes to the site and ordering a small batch from other regions, which will be significantly more profitable for the client than on his own. We also carry out wagon deliveries of rolled metal pipes.
 |
 |
The range of pipes produced at present is very extensive. They are made from special pipe blanks or ingots by rolling and pressing, from strip and sheet steel, but there are also those that are poured by special machines.
There are round pipes, among which electric-welded pipes and VGP pipes, that is, water and gas pipelines, stand out. How they differ from each other, we will try to figure it out now.
Electric pipes
These products come in different sizes. They are straight-line, and their assortment is observed by certain state standards.
They are made from steel of increased hardness, which are poorly drawn and rolled out, by electric welding. The edges of the blanks are connected parallel to the axis.
These products have found application in construction:
- pipelines;
- heating networks;
- low pressure gas pipelines;
- other types of communications.
The welded pipe is distinguished by a reinforced longitudinal seam, which is performed first from the outside, and then from the inside. Thanks to this technique, the products are very reliable and able to serve for a long time.

In principle, such products are a type of electric welding, but their seam is even more reinforced. Therefore, the VGP pipe boasts even greater strength, and reduction gives it anti-corrosion resistance.
These pipes have gained popularity among consumers due to the following characteristics:
- a variety of processing options - welding or bending;
- low price.
They are standardized according to inner diameter conditional passage and wall thickness. These parameters determine the choice of VGP pipes for different types works. They produce such pipes in the usual form and galvanized. The first option is good because the zinc layer applied to the surface of the product perfectly prevents the corrosion process. However, it also makes the pipe heavier by almost a quarter.
Pipes are also classified by length: there are measured ones, multiples of the measured ones, but with deviations and different allowances, non-dimensional ones. Usually such products do not have a thread, but they can be made: cylindrical, knurled, short and long.
In addition, pipes are also distinguished by wall thickness: they can be ordinary, reinforced and light. As for accuracy, there are also differences in this parameter: there are VGL pipes of ordinary accuracy and increased, according to existing GOSTs. This type of pipes is used for heating systems, gas and water pipes.
Electric pipes:











How to understand: will the kitten be fluffy?
What kind of light alcohol can be drunk for pregnant women: the consequences of drinking
Why do the legs swell in the ankles and ankles of the feet in pregnant women: causes and methods of treatment
The wedding of Prince Harry and Meghan Markle: scandalous and secret details of the marriage (photo) The future marriage of Prince Harry year NTV
How to close white plums for the winter