The company World of a Machine Tool offers to buy modern machines for deep drilling holes at competitive prices. The company provides qualified advice on commercial and technical issues, as well as free delivery throughout the Russian Federation.
These machines are designed for drilling and boring deep holes, the length of which is 100-150 times the diameter. In the process of such metal processing, three technological issues are solved:
The shotgun is also an ideal weapon for close range shooting. When firing rounds loaded with multiple projectiles, rifles can compensate for their inaccuracy with a large shot distribution, making them especially useful in closed areas with one or more enemies. A skilled agent can use them in interior locations, but beware of their strong retreat.
Far from being a shotgun, the precision rifle is the perfect weapon for taking out long-range targets. Its telescopic sight gives greater accuracy to the agent. Its surgical precision, combined with its deep drilling bullets, makes this precision rifle a deadly tool to have in your arsenal. These rifles are useful for dressing up watchtowers and eliminating patrols before invading an enemy outpost. Due to the limited head refills, shots are usually perfect.
- centering and alignment of a long drill;
- its lubrication and cooling;
- forced chip removal.
The last two points are solved through the use of a special cutting fluid (abbreviated as coolant) supplied to the hole under high pressure.
Basic technologies for metal deep drilling on CNC machines
When using a special drilling equipment in the first place is the requirement for high geometric accuracy of workpiece processing. This is due to the fact that the parts obtained are used in nuclear power, steel mills and the aerospace industry.
There are two options in this category: Compact Machine Gun and Pistol. This type of pistol has the problem of barrel control and its accuracy at long ranges. The pistol is a great secondary weapon due to its portability and portability, and is generally more accurate than compact submachine guns. There are several types of handguns, but in general they are especially useful when invading a setup or reloading a primary weapon. Fast-acting guns may be needed in situations where fighting is paramount.
They are formidable in short to medium range, but the biggest problem with many pistols is their low ammo capacity. The drilling of an artesian or semi-artesian well is a construction and geology work built below ground level using processes, technologies and equipment similar to those used for drilling. oil wells. An artesian or semi-artesian well, from a technical point of view, is a deep tubular well.
For deep drilling, the following metal processing technologies are used on the machine:
- Rifle. The oldest easel technique used in enterprises for more than 150 years. It is used in the production of holes of small diameter (from 1 mm) and a depth of up to 100 d.
- DTS ejector technology. Coolant circulates between the inner and outer drill rods. This makes it possible to apply this technique on traditional drilling and turning machines without retooling them. This method of deep drilling allows you to make holes with a diameter of up to 200 mm.
- STS/BTA Technology (Single Bar STS System). A special drill rod is used, through which coolant is supplied under high pressure directly to the cutting edge. Chip removal occurs along with the liquid. This technique allows you to drill holes with a diameter of more than 200 mm.
When ordering a CNC metal drilling machine from us, one personal manager works with the client. He provides any advice of a technical and commercial nature. There is a special showroom for buyers.
Deep artesian or semi-artesian tubular well drilling uses large tools and equipment, such as rotary air drilling rigs, which are more efficient than the old percussion or rotary drilling rigs and which drill 3 types of wells with greater accuracy: in sediments, in rocks, or mixed.
Artesian and semi-artesian well
An artesian well is a deep tubular well drilled in places where the pressure line of the aquifer is above ground level, causing water to flow spontaneously without the need to push the pump. The search for an artesian well depends solely on the region and geological condition, and not on the technique or equipment used in drilling. A semi-artesian well is known to be a deep tubular well that is not plugged, which is drilled in places where the pressure line of the aquifer is at or below ground level. Since there is no pressure, the water does not flow out spontaneously and therefore needs a pump to extract it. The vast majority of tubular wells in Brazil are of this type, although they are also referred to as "artesian" wells.
Good in precipitation, rocks or mixed
A well in sediment is a tubular well constructed in areas whose subsoil is composed of sedimentary rocks with permeable areas that contribute to the formation of an aquifer. In this well, filters are installed at the height of the producing sands to collect water flowing in the formation. The area close to the surface is sealed to prevent abstraction of water from the level ground water which reduces the risk of contamination. To reach the rock, the drill passes through a portion of the sediment, which is sealed to prevent penetration and possible contamination. A mixed well is a deep tubular well designed to collect water in two formations: sediment and rock. In this well drilling, sediment penetrates until it encounters water fractures in the rock. The sedimentary part is not sealed, it is lined with pipes and filters to use water from favorable sandstones. It is also known as a gushing or growing well. . Kasimba well, also known as kaipira well or cistern, is not a deep tubular well.In addition, clients are provided with:
- prompt preparation of a commercial offer;
- product quality assurance;
- free shipping across the Russian Federation.
Do you need original CNC metal deep drilling machines? Contact the World of the Machine Operator!
Showing only one result
DESIGNS.
Manually dug to capture and store water from the water table, which is the most superficial permeable layer of soil where rainwater enters. For this reason, the water level in this type of well varies with the amount of rain. It meets important supply needs when there is no alternative, but has sanitary restrictions that limit its use.
Consulting Artes Artesianos does not make this type good. Stabilizers are used as wear parts to maintain drilling accuracy. These products are heat resistant, offer excellent solderability and come in a variety of stabilizer geometries. Protection is available to enhance protection against aggressive bonding materials and processes.
Specialized drilling and boring machines include machines designed to perform a certain type of processing or to obtain any specific types of surfaces in a given range of their sizes on parts of one or different technological classes. The most widely used machines are for deep drilling and boring, thread-cutting and nut-cutting, central, for finishing boring.
Our carbide stabilizers offer excellent wear resistance and are available in many shapes and sizes. Click here to learn more about carbide for use as stabilizers. This product combines the strength and toughness required for fishing and milling. Its wear resistance and thermal wear are exceptionally suitable for this application.
You determine the conditions of use and the desired result, we determine for you the cutting tool for the corresponding suitable processing. We will gladly take this information into account and implement the tool in accordance with your drawing. Do you have a new project and need the tools to get the best solution for this part? We assist you in designing, defining the geometry and determining the optimal parameters.
- Do you already know the tool you want?
- We will provide you with a tool with the correct geometry.
7.4.1. Machines for deep drilling and boring.
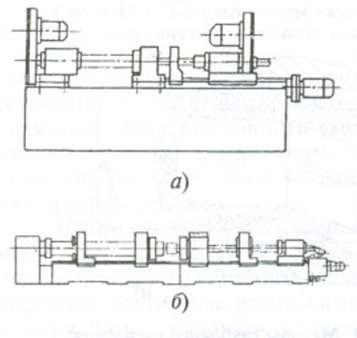
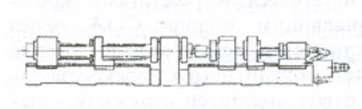
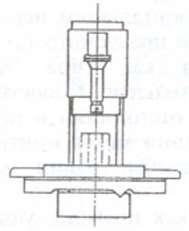
Designed for drilling (including annular), reaming and boring holes with a large ratio of length to diameter, reaching in some cases 100 or more. Modern machines use three drilling methods (Fig. 7.17). When drilling with a single-edged tool, cutting fluid (coolant) is supplied through the hollow part of the tool shank, and is removed along with the chips through the outer chip groove of the shank.
Tools are manufactured with maximum precision and repeatability. This allows the user to produce their products with a reliable process and with the required precision. High feed rates are possible thanks to the use of high quality carbide blanks, cutting geometries and innovative cooling systems and high performance coatings, always adapted to the specific application. Thus, the processing time for drilling is very short.
The ideal combination of carbide type and coating, number of cutting edges and their geometry, combined with the machining parameters we recommend, provides optimal time tool service. A unique identification code on each tool tail allows traceability and quality assurance. Thanks to short times machining, long tool life and maximum precision machining are kept at a low level. Our re-sharpening services and interchangeable drill heads provide significant savings while delivering better performance to increase profitability.
This method is usually used for processing holes with a diameter of not more than 30 mm.
Ejector drilling is performed by a tool with several cutting edges, which provides coolant supply through the annular space between the drill stem and the chip removal pipe located inside it, and the removal along with the chips through this pipe. To enhance the flow of chip and coolant removal, the pipe has channels through which part of the liquid from the annular space enters directly into it, creating an ejector effect.
Features Specific and optimal solution for a wide range of applications. High operating parameters, maximum feed rate and long and stable service life. Good balance between wear resistance and toughness. Curved cutting edge - ideal for chip removal.
Reliability and high performance. Micro drills with oil hole for deep drilling with small diameter. This new generation completes and enhances our very high performance range for small diameter drilling. Benefits High durability Regular chip removal Quiet cutting and regular cutting forces.
The VTA method is based on the use of tool heads screwed onto a hollow stem, equipped with cutting edges and guide plates. The coolant through the sealing sleeve is fed through the annular gap around the tool stem to the hollow central part of the head and is removed with chips crushed due to the shape of the cutting edge through the inner channel of the stem. The BTA method is used for processing large diameter holes and for ring drilling of holes with a diameter of 120 - 150 mm. Boring deep holes with a diameter of up to 2500 mm is carried out with heads with two-sided, as a rule, arrangement of cutting blocks.
Finish - standard - secure for fast chip removal. The service life is twice as long. Benefits High productivity Excellent accuracy High quality deep hole drilling. Ideally for the automotive, aviation and medical industries, the new platelet drills combine chemical vapor deposition for the outer plates and the former physical vapor deposition process for the inner plates, thus optimizing their efficiency and speed.
Another exceptional innovation is that chip breezes optimize chip evacuation, making the core of the drill more rigid. Reducing weight and improving the functionality of components is at the heart of the philosophy of the automotive, aerospace and medical industries. This trend is increasing the demand for ever faster and more efficient drilling products that can be used on various types materials and various conditions drilling.
Fig.7.17. Deep drilling methods:
a - single-edged tool; 6 - ejector; in- VTA method
With deep drilling and boring, depending on the diameter of processing and material, the accuracy of size H7 - H9 is achieved, deviations from the alignment of the sections of the machined hole are within 0.03 - 0.05 per 100 mm (with non-rotation of the product 0.08 - 0.12 per 100 mm), surface roughness Ra = 0.32 - 2.5 µm.
High speed and high efficiency for use on various materials. Bridge breezes are designed in such a way that their four edges can be used, thus reducing the production costs of customers. Exclusive cutting angles allow excellent chip evacuation even in case of deep drilling.
Thanks to the combination of high rigidity and low strength, the new model is thus able to drill more deep holes primarily for drilling this category. Piercing is the most banal operation in the mind of the general public, without the need for any specific explanation, as if it were significant. This is due to the success of power equipment, which the drill pioneered and which still holds the sales record.
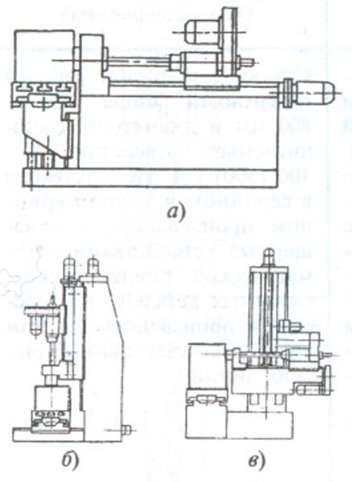
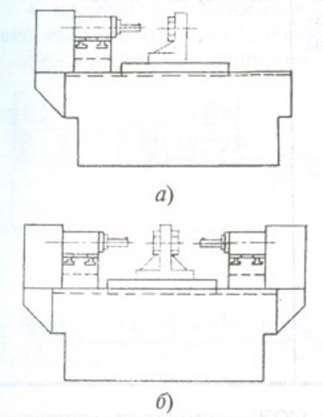
The classification of machine tools according to the main layout and design features is given in Table 7.12. As the main parameter of the machines, the largest nominal diameter drilling (in solid material) in parts made of medium hard steel.
Most horizontal machines have long, compound beds. Machine tools for processing especially large and heavy parts can have separate beds for workpieces and for the tool part, including those located on foundations of various heights.
These machines, once used by professionals only because of their cost, are now available to everyone with Taiwanese concoctions, and their design combined with their weight asynchronous motor and belt drive make the machines quiet, if only a few body vibrations can be easily controlled with foam pads. The torque is high relative to the selected speed Accuracy and guidance are much better than with power tools.
The range is extensive and the choice will depend on your premises, which must have sufficient available height and space to be compatible with the passage of long or bulky pieces. Second important point regarding rotational speeds. At this last point in FIG. 1 shows two machines that differ only in height and stroke. There's nothing to stop a little maintenance on a column that can only be cleared on the day it needs to be processed big room. With drilling machines it makes sense to say "who can do the most".
The design features of the spindle assemblies of tool stocks are determined by significant axial forces and the need to supply significant amounts of coolant through the spindle. The rotation drives for both the workpiece headstock and the tool headstock are made stepwise from an asynchronous motor or steplessly adjustable - when using a DC motor. Electromechanical or electrical torque sensors are built into the tool rotation drive to protect against overloads. In feed drives, with relatively small strokes, screw gears and hydraulic cylinders are used, and with large strokes, rack and pinion gears are used.
The machines are equipped with control devices that provide automatic or semi-automatic operation. In machines with coordinate movements of the table and the headstock, CNC devices and automatic change of tool settings (tools with guide bushings) can be used.
Mineral oils with the addition of soluble organic compounds of sulfur and chlorine are used as coolants. Coolant in significant volumes (200 - 1800 l / min) is supplied to the cutting zone under a pressure of 2.5 - 8 MPa (with an increase in the diameter of processing and an increase in coolant consumption, the pressure decreases) by high-pressure gear, screw or vane pumps. Waste fluid is thoroughly cleaned of chips using multi-stage cleaning systems using magnetic separators and rods, centrifuges, filters and sludge in baffled tanks.
Table 7.12. The main types of machines for deep drilling and boring
|
Type and schemes of machines |
Application area |
|
|
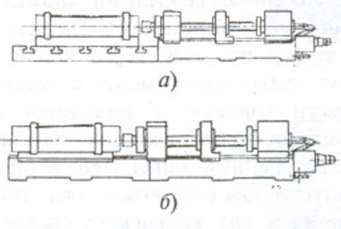
With a longitudinally MOVING power table for processing parts such as bodies of revolution 1) |
Single and multi-spindle horizontal machines with spindle heads mounted on a power table, moving along the frame guides along the drilling axis; with a fixed headstock of the workpiece, pressed from the side of the beginning of drilling by the guide bushing of the tool; with rotation of the tool and possible additional rotation of the workpiece (a); with the possibility of maintaining the tool and workpiece in steady rests (b) |
Machine tools with a nominal drilling diameter of 3 - 80 mm. They are used for processing small and medium-sized long parts such as bodies of revolution in serial production, and when equipped with automatic loading devices - in large-scale production |
|
With a headstock of a turning or swivel (hollow) type for processing parts such as bodies of revolution
|
One- and two-spindle horizontal machines with a spindle head movable along the drilling axis, moving along the bed guides; with workpiece clamping in the headstock chuck and its support in annular or open roller rests; with rotation of the workpiece and possible additional rotation of the tool |
Machine tools with a nominal diameter of drilling in solid material 80 - 320 mm (nominal processing diameter 250 - 2500 mm). Used for processing long and large parts such as bodies of revolution in various production conditions |
|
With table-plate for processing free-form parts 3) |
Single-spindle horizontal machines with a spindle head movable along the drilling axis, moving along the bed guides; with clamping of the part on the table-plate, fixed (a) or having an adjusting axial movement along the frame guides (o), with rotation and feed of the tool; with the possibility of supporting the tool stem in steady rests and guide sleeve |
Machines with drilling diameter 80 - 320 mm (machining diameter 250 - 2500 mm). Used for processing large free-form parts in various production conditions |
Continuation of Table 7.12
|
Type and schemes of machines |
Main layout and design features |
Application area |
|
With coordinate movement of the table (spindle head) for processing free-form parts 4) |
Single-spindle horizontal (a) and vertical (b) machines with a cross movement of the table or horizontal with a cross movement of the headstock (c) with the possibility of equipping with interchangeable (including automatic) tool adjustments for holes of different diameters and a CNC device |
Machines with a drilling diameter of 4 - 40 mm (up to 20 mm for vertical machines). Used to machine one or more holes in free-form parts in various production conditions |
7.4.2 Finishing and boring machines (OPC) are designed for fine finishing boring of cylindrical and free-form generatrix of precise holes with high accuracy and surface quality and relative positioning. The machines can also perform additional trimming of outer and inner ends, turning grooves, turning outer cylindrical, conical and curved surfaces. The machines are intended for processing parts in large-scale and mass production, however, the creation of relatively easily reconfigured OPCs has led to the possibility of their use in the stable production of parts with a lower seriality.
The OCR classification given in Table 7.13 is not exhaustive. Machine tools are also made in which the workpieces are mounted in a chuck mounted on a spindle, and the tool in a caliper mounted on a movable table; machines with movable heads and a two-coordinate table; combined machines with horizontal and vertical movable spindle heads, etc.
The quality of processing on ORS is determined by the roundness of the cross section and the profile of the longitudinal section (cylindricality) of the bored hole. In horizontal machines with a movable table, the deviation of holes from roundness in the entire range of boring holes is within 0.5 - 1.2 microns, and the roughness is not coarser than Ra = 0.32 + 0.63 microns (depending on the material of the workpiece).
Rigidity, vibration resistance and thermal stability of the OPC are subject to high requirements, which leads to corresponding requirements for the basic parts, which are made of high-quality gray cast iron and have a box shape with good ribs. As a rule, the rigidity of the bed of horizontal machines with a sliding table allows the machine to be installed on a foundation on three supporting elements. The expediency of manufacturing frames and bridges from granites or artificial materials (for example, syntegran) with high damping capacity and thermal stability has been recognized. For horizontally moving assemblies, one flat and one V-shaped sliding guides, traditional for precision machine tools, are mostly used, and for vertically moving assemblies, closed rectangular guides are used.
Table 7.13. The main types of finishing and boring machines
|
Type and schemes of machines |
Main layout and design features |
Application area |
|
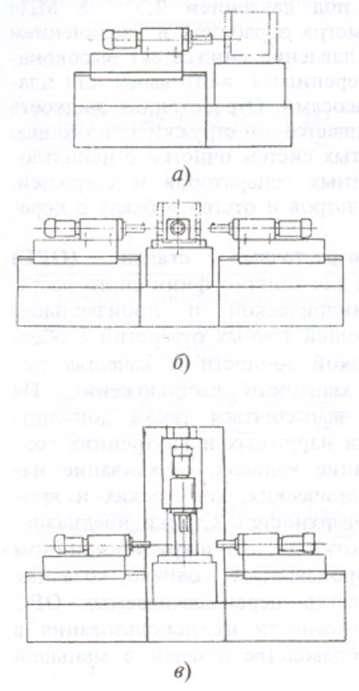
Horizontal with sliding table 1) |
Single or multi-spindle machines with stationary parallel spindle heads located on U-shaped beams ("bridges") rigidly fixed to the frame with one (a) or two opposite (b) sides of the workpiece; a table movable along the guides of the bed parallel to the axes of the spindles, on which the workpieces are fixed in the fixture |
Machines with a width of the working surface of the table 320 800 mm and a diameter of boring holes 8 - 400 (500) mm. They are used in serial and large-scale production, and equipped with devices for automatic change of workpieces - in mass production, including as part of automatic lines |
|
With fixed table and movable spindle heads 2) |
Single or multi-spindle machines with spindle heads located on power tables movable parallel to the spindle axis relative to the workpiece on one (a), several sides in the horizontal (b) and several sides in the horizontal and vertical planes (in). Fixed table with a horizontal working surface for setting the workpiece (usually in a special fixture) |
Machines with a width of the working surface of the power table 500 - 1250 mm and a boring diameter of 8 - 400 (500) mm. They are used in large-scale production, including as part of automatic lines, for processing body parts with limited requirements for shape accuracy and relative position of machined surfaces. |
Spindle heads are the most critical components of the OPC, mainly determining the accuracy and quality of processing. Single-spindle heads, as a rule, are unified units, the connecting dimensions of which are standardized (GOST 19590-85). Devices can be built into the spindle heads for radial feed of the cutter when boring holes of raal diameters and trimming the ends, for adjusting the cutters during wear, retracting the cutter from the surface being bored during the reverse stroke, clamping the workpiece, processing control, etc.
Continuation of Table 7.13
|
Type and schemes of machines |
Main layout and design features |
Application area |
|
Vertical with movable heads on the power table (platform)
|
Single and multi-spindle machines with spindle heads located on sleds or force tables movable parallel to the spindle axis; fixed (roll-out for changing workpieces) table with a horizontal working surface for installing a workpiece or fixture |
Machines with a width of the power shed 630 - 1250 mm and the largest diameter of boring holes 8 - 400 (500) mm. Used in serial and large-scale production for machining holes (including those with an increased length-to-diameter ratio) in medium and large body parts |
|
Vertical with movable headstock
|
Single-spindle machines with a vertically movable rack along the rails headstock, which provides the ability to work with interchangeable spindles for various ranges of boring holes. Fixed, roll-out or cross horizontal table |
Machines with tables 400 - 630 mm wide. Used in the repair production of various types of engines |
In machine tools for processing a certain part, an unregulated drive of the main movement with an asynchronous electric motor is used, and in reconfigurable machines, an adjustable DC drive is used. In all cases, a belt drive is used as the last link to reduce spindle vibration. If it is necessary to isolate the spindle units from the influence of the disturbing effects of the drive, it is possible to use a belt drive with two arcs of belt contact with a driven pulley mounted on the spindle head due to the location of the tension roller on the other side of the drive pulley (relative to the driven pulley).
The supply of working bodies is carried out using hydraulic cylinders or gears.
A rolling screw-nut, and in the latter case, when widely adjustable electric motors are made, it is relatively simple and reliable to ensure the smoothness of small working feeds required for finishing.
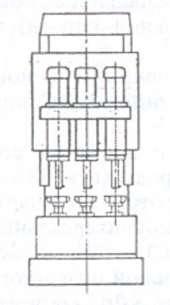
7.4.3. Multi-spindle drilling machines for processing flat parts. The machines are designed for drilling a large number of holes in parts such as gratings, dies, printed circuit boards etc. in serial and large-scale production. The most widely used machines for processing printed circuit boards from non-metallic materials for the electronics industry. Most of these machines provide the ability to perform contour milling of the outer end faces of workpieces, windows and grooves of various configurations. The machines are equipped with CNC devices, automatic change of tools and parts.
High productivity is achieved due to the number of simultaneously operating spindles and the speed of the mechanisms. In this regard, aerostatic supports and guides of the executive bodies are widely used, which damp vibrations well and increase thermal stability during intensive work, materials, for example, granite or its artificial substitutes (such as granite).
Spindle speed when drilling non-metallic materials reaches 100 - 120 thousand min "1, travel speed - 12 000 - 15 000 mm / min with an acceleration and deceleration time of 0.1 - 0.15 s. This ensures the accuracy of center-to-center distances of the order of 20 µm and the error of deviation from the milled contour is about 30 µm.











How to atone for your sins. How to atone for sin
The Crime of the Soviet Power and the Treasure of the Russian Orthodox Church - New Martyrs and Confessors of Russia Who are the New Martyrs of the 20th century
Prayer Easter Week
Can a husband and wife be godparents of the same child, for different children from the same family?
What prayers should be read in the morning and evening