To determine the required hole diameter for threading, the table is the most convenient tool. It is possible to make mathematical calculations for this purpose, but if the table is compiled in accordance with GOST, there is no need for unnecessary manipulations.
- The threaded hole is used to create detachable connections. But if there are no problems with external threading, since any necessary fasteners made according to GOST can be purchased in stores, then internal thread requires a more careful approach;
- For cutting internal metric threads of sizes M4, M5, M6, M8, M10, M12, hand tools or specialized machines are used;
- To obtain a metric internal thread, it is required to make an appropriate hole for the future thread in the workpiece;
- The holes made for metric cutting must correspond to the diameter of the tool that is used for cutting;
- Each hole made requires the use of a tool of a certain size;
- For these purposes, the master must correctly select the diameter of the drill for threading;
- Cutting large holes large diameter specialized machines are used. In them, drills are distinguished by a conical shank type;
- Conventional drills are equipped with a cylindrical shank;
- The size of the cone is directly related to the size of the drill. The larger the diameter of the drill, the larger its cone;
- If necessary, perform internal threading of the M4, M5, M6, M8, M10, M12 type, the diameter of the required hole is selected based on the thread diameter and thread pitch;
- To determine what size the diameter should have, you need to determine the size of the holes. To simplify this task, a special table compiled in accordance with GOST is used. This means that the table provides for standardized operations. Due to this, it is possible to obtain the same type of product, which is suitable for various types of threaded connections.
Focusing on the table and following strictly its parameters, you can do it yourself internal thread the desired diameter, and hardware, bolts, purchase at a specialized store. In this case, the connection will be perfectly matched.
Types of cutting

The thread looks like helical grooves with a constant cross section. In this case, the thread is divided into two types:
- internal;
- outdoor.
Threaded connection has a wide scope. It is problematic to find places where it is not used. Due to the thread, rotation, translational movement, and fastening are imparted to the parts. Almost all mechanisms, machines and assemblies necessarily include a threaded connection.
In this case, the cutting is divided into two large groups:
- Single cutting;
- Multi-threaded threaded connection.
Depending on the direction of movement of the screws along the thread, it is divided into:
- Left-sided;
- Right-sided.
If we take into account the size systems standardized according to GOST, cutting can be divided into three more types.
- Trubnaya. Its distinguishing feature is the initial diameter, which focuses on the size of the pipe hole. In this situation, only external cutting is carried out.
- Metric. It is characterized by a profile made in the form of a triangle. The profile angle can be 60 degrees. Dimensions are specified in millimeters. If the step is large, the marking includes numbers and alphabetic values. The number is the outside diameter. If the metric thread has a non-standard small pitch, then a number is added to the letter designation of the type M4, M5, M6, M8, M12, which indicates the pitch. In this situation, the marking is presented as M6x0.6.
- Inch. For inch threads distinctive feature the value of the angle of the profile appears. For inch types, it is usually up to 55 degrees. The size of the hole is indicated in inches, and the pitch depends on the number of threads.
Taps
- The tap is the main tool for cutting threads. In this case, taps can be manual or machine. According to this characteristic, it is determined whether the tap is used on hand tool or used as a working tool of a specialized machine;
- Hand taps are produced in sets;
- Typically, the kit includes three taps;
- The first two taps from the set perform preliminary measures, and the last one brings the thread to the required finishing state;
- With the help of a tap-closer, it is possible to obtain cutting that is optimal in size and shape;
- Each tap has its own number indicated on the shank;
- In some cases, there are only two taps in the kit, where the first is preliminary, and the second is finishing;
- Taps are made on the basis of high-alloy steel, which allows them to work with hard grades of metal;
- To fulfill external thread, a special die is used;
- The die is round or prismatic.
Internal thread
- To equip a workpiece with a threaded hole internal type, the first step is to correctly select the size of the drill for M4 or another thread size according to GOST.
- Having selected a drill, the master proceeds to make holes for the thread.
- To switch to the use of a special tap for cutting M4, the hole made is first processed with a tool - a countersink. This allows you to achieve the desired cleanliness of the hole.
- In the process of cutting grooves in a metal workpiece, the material is slightly extruded. Because of this, it is important to choose the right drill size. The drill is used slightly larger than the internal thread diameter of the tool being used.
- When working with a metal of increased hardness, it will not be possible to significantly change the size of the hole when forming grooves due to the characteristics of the material.
- If metal of medium or low hardness is being processed, the dimensions of the hole made vary greatly. If the size of the hole coincides with the internal threaded diameter, active extrusion will begin during processing. Excess will adversely affect the tap. The tool will start to overheat, chips will stick to internal surfaces. As a result, you will get threads with incorrect grooves, plus you are at great risk of breaking your tap.
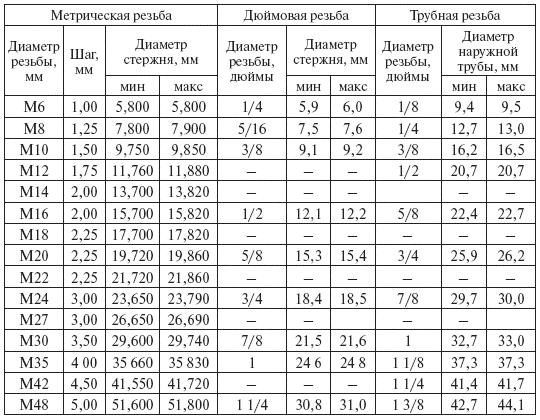
- To determine the diameter of a suitable drill, a specialized table is used. It clearly indicates all the main parameters, which allows a beginner to quickly understand all the nuances.
table
The table consists of several main columns.
- The first indicates the dimensions of the metric thread. It happens from M2 to the maximum value of M48;
- The second column is where the major step is indicated. It is used for each metric thread size. Moreover, depending on the diameter, the pitch is different, gradually increasing as the diameter of the thread grows. When you cut grooves, focus on these parameters;
- The third column indicates the diameter of the drill (hole) for metric cutting with coarse pitch.
Sometimes it may be necessary to use a fine step, which happens quite rarely. But even in this case, the table provides a separate column, the indicators of which should be guided in such situations.
Table 1.
| Diameters | Tolerances for rod diameter | Diameters | Tolerances for rod diameter |
||
| carving | rod | carving | rod | ||
| Coarse thread | |||||
| 3 | 2,94 | -0,06 | 12 | 11,88 | -0,12 |
| 3,5 | 3,42 | -0,08 | 16 | 15,88 | -0,12 |
| 4 | 3,92 | -0,08 | 18 | 17,88 | -0,12 |
| 4,5 | 4,42 | -0,08 | 20 | 19,86 | -0,14 |
| 5 | 4,92 | -0,08 | 22 | 21,86 | -0,14 |
| 6 | 5,92 | -0,08 | 24 | 23,86 | -0,14 |
| 7 | 6,90 | -0,10 | 27 | 26,86 | -0,14 |
| 8 | 7,90 | -0,10 | 30 | 29,86 | -0,14 |
| 9 | 8,90 | -0,10 | 33 | 32,83 | -0,17 |
| 10 | 9,90 | -0,10 | 36 | 35,83 | -0,17 |
| 11 | 10,88 | -0,12 | 39 | 38,83 | -0,17 |
| Thread with fine pitch | |||||
| 4 | 3,96 | -0,08 | 24 | 23,93 | -0,14 |
| 4,5 | 4,46 | -0,08 | 25 | 24,93 | -0,14 |
| 5 | 4,96 | -0,08 | 26 | 25,93 | -0,14 |
| 6 | 5,96 | -0,08 | 27 | 26,93 | -0,14 |
| 7 | 6,95 | -0,10 | 28 | 27,93 | -0,14 |
| 8 | 7,95 | -0,10 | 30 | 29,93 | -0,14 |
| 9 | 8,95 | -0,10 | 32 | 31,92 | -0,17 |
| 10 | 9,95 | -0,10 | 33 | 32,92 | -0,17 |
| 11 | 10,94 | -0,12 | 35 | 34,92 | -0,17 |
| 12 | 11,94 | -0,12 | 36 | 35,92 | -0,17 |
| 14 | 13,94 | -0,12 | 38 | 37,92 | -0,17 |
| 15 | 14,94 | -0,12 | 39 | 38,92 | -0,17 |
| 16 | 15,94 | -0,12 | 40 | 39,92 | -0,17 |
| 17 | 16,94 | -0,12 | 42 | 41,92 | -0,17 |
| 18 | 17,94 | -0,12 | 45 | 44,92 | -0,17 |
| 20 | 19,93 | -0,14 | 48 | 47,92 | -0,17 |
| 22 | 21,93 | -0,14 | 50 | 49,92 | -0,17 |
- Internal thread: cut with cutters. Tap - a metal-cutting tool for cutting internal threads in pre- drilled holes. There are manual (rotated with a knob) and machine, nut and tool (uterine and ram). When cutting deep threads, a set of three taps is usually used: the first tap (designation - one risk) is preliminary, the second (two risks) cuts the thread and the third (three risks or no bottom) calibrates it. Nut taps are suitable for cutting short threads (as in a nut) and have successive cutting edges; after passing the entire length, a full thread is obtained.
- Of great importance right choice hole diameters. If the diameter is larger than it should be, then the internal thread will not have a full profile and a weak connection will result. With a smaller hole diameter, the entry of the tap into it is difficult, which leads to the breakdown of the first turns of the thread or to jamming and breakage of the tap. The diameter of a hole for a metric thread can be approximately determined by multiplying the thread size by 0.8 (for example, for an M2 thread, the drill should have a diameter of 1.6 mm, for M3 - 2.4-2.5 mm, etc. (see. . table).
- It is necessary to lubricate the cutting part of the tap with thick oil (e.g. grease), animal fat (lard) or vegetable oil- it is better not to use liquid engine oil, as it often spoils the thread - and insert it into the hole.
- Then you need to carefully monitor that the tap goes exactly along the axis of the hole in order to avoid breakage. After cutting 4-5 turns, the tap is removed from the hole and cleaned of chips. After that, it is lubricated again and screwed into the hole again, another 4-5 turns are cut, continuing the operation until it stops (with a blind hole or until the tap exits (with through hole).
- Then they clean the first tap, put it in place and take a tap with two risks, lubricate it, manually screw it into the hole and, as soon as it starts to cut into the metal, put a collar on it. After cutting every 5-6 turns, the tap is cleaned of chips and lubricated until the hole is completely passed.
- Then they clean the second tap, put it in place, take the last tap with three risks, also grease it, screw it into the hole by hand until it engages, put on the knob and carefully calibrate the thread. Chip cleaning and lubrication are repeated as before.
- Inch taps thread is cut in the same way as metric. Clamps are used for threading pipes, usually with adjustable cutting elements in the range of threads for pipes with inside diameter 1/4 to 4 inches. Threads on pipes and stubbles of large diameter are best cut into screw-cutting lathes.
- The diameter of the drill bits for drilling holes for metric threads should be selected according to Table 2.
| Outside diameter threads, mm | Drill diameter (mm) for | |
| Cast iron, bronze | Steel, brass | |
| 1 | 0,75 | 0,75 |
| 1,2 | 0,95 | 0,95 |
| 1,6 | 1,3 | 1,3 |
| 2 | 1,6 | 1,6 |
| 2,5 | 2,2 | 2,2 |
| 3 | 2,5 | 2,5 |
| 3,5 | 2,9 | 2,9 |
| 4 | 3,3 | 3,3 |
| 5 | 4,1 | 4,2 |
| 6 | 4,9 | 5 |
| 7 | 5,9 | 6 |
| 8 | 6,6 | 6,7 |
| 9 | 7,7 | 7,7 |
| 10 | 8,3 | 8,4 |











Chicken in kefir - recipes for marinated, stewed and baked poultry for every taste!
Simple Chicken Recipe in English (Fried) Recipes in English with translation
Chicken hearts with potatoes: cooking recipes How to cook delicious chicken hearts with potatoes
Recipes for dough and fillings for jellied pies with mushrooms
Stuffed eggplant with chicken and mushrooms baked in the oven with cheese crust Cooking eggplant stuffed with chicken