There are different forms of the past tense in English. Their difference lies in the quality of the action that took place or how long it was. Feature grammatical design of English speech lies in its logic.
Therefore, the British consider it incorrect in a monologue to jump from one grammatical construction to another when narrating past events. They call the Past Perfect tense the most intense and giving expressiveness to speech.
Features of the grammatical structure Past Perfect
If you need to talk about events that occurred in the past, when one of them happened before the other, then the past perfect tense is used. It is also called "pre-past" and past completed.
Native speakers admit that they rarely use this construction, but it sounds very good if it is grammatically correct.
Another feature of the Past Perfect grammatical structure is that it is almost never used in dialogic speech. It is used mainly in narration, most often in complex sentences when describing several actions.
Formation of the Past Perfect construction
The rule for forming the Past Perfect is quite simple and not cluttered with many verbs. Verb to have acts as an auxiliary in the form of the past tense - had. The main verb is in the third form.
It is necessary to distinguish between the formation of the third form of irregular and regular verbs. Regular verbs are called so because when forming past tense forms, there is one rule for them: the ending -ed (-d) is attached to the verb.
The Past Perfect education formula looks like this:
For example: Everyone had paid for purchases by credit cards.
Formation rule different forms At first, sentences will be given in a general form to understand its construction, and then we will consider the formation of the Past Perfect construction in complex sentences.
Past Perfect in affirmative sentences
A characteristic feature of the structure of sentences in English is a strictly fixed sequence of all members of the sentence:
- Subject.
- Predicate.
- Secondary Members.
If the predicate consists of two verbs, as in the case under consideration, then the auxiliary verb should come first, followed by the semantic one.
The famous American scientist had got the Nobel Price.
foreigner had spelled some words correctly.
Taxi had stopped far from my house.
Past Perfect in negative sentences
The fixed word order rule holds true for negative sentences as well. Particle not has its static place after the auxiliary verb.
When forming a negative form of the Past Perfect, it must be borne in mind that there are two alternatives:
- Full: had not.
- Brief: hadn't.
Word order in a negative sentence:
- Subject.
- Auxiliary.
- Negation.
- semantic verb.
- Secondary Members.
Some students had not studied subjects carefully.
My relatives had not returned in time.
The rival company had not given us a chance.
Past Perfect in interrogative sentences
There are two types of interrogative sentences in English:
- Are common.
- Special.
A general question is also called a “question-doubt”, that is, the person asking the question, as it were, asks the interlocutor about the information already heard.
The word order in this case is different from the affirmative sentence:
- Auxiliary.
- Subject.
- semantic verb.
- Secondary Members.
Had you heard the last news about the price of tickets?
Had she chosen the pair of new shoes?
Had he changed the headline of his article?
A special question implies the presence of an interrogative word, that is, it is a more specific type of interrogative sentence.
The sequence of words has changed and looks like:
- Question word.
- Auxiliary.
- Subject.
- semantic verb.
- Secondary Members.
whom had they elected as a President?
What had you done to make friends with us?
Using the Past Perfect Construction in Speech
Past Perfect is used in different speech situations, it depends on the context:
- The action ended up to some point in the past. The border of the moment is indicated by the so-called verbal time barriers: by Sunday, by 17 o'clock.
They had begun to work by 19 o'clock in the evening.
My sister had read the book by Wednesday. - One of the actions ended before the other. A later action is described in the Past Simple. Parts of sentences with different actions can be combined with conjunctions as soon as, after, before, when and others.
Pupils carefully made the task after the teacher had given it.
After the tourist had known the local currency of Spain, he paid for everything in cash.
When she returned home her parents had slept already.
If the speaker delimits the sequence of actions in the process of his narration, then it is necessary to grammatically arrange the tenses.
It is very difficult for people who begin to study such subtleties of English speech at first. But with regular practice, the process is gradually brought to automatism.
Only when the dinner for my family was ready I understood that I had forgotten to salt it. After my friends had gone away I began to clean the room.
When the performance was over, we had called a taxi. - The action began in the past and continued for a certain period of time until the next action in the past or during this action.
The peculiarity of this Past Perfect position is that:- The Past Perfect time performs the functions of the Past Perfect Continuous construction here. This is due to the fact that Continuous is not used with state verbs.
As for me, I had understood the things become worse.
He had hated they impolite with people. - When the negative in the Past Perfect is directed to action:
Everybody got to know that parents had not seen him since the beginning of the war. - When using verbs of motion:
tourists had traveled for several days until there was a happy event.
- The Past Perfect time performs the functions of the Past Perfect Continuous construction here. This is due to the fact that Continuous is not used with state verbs.
Translation of sentences from Past Perfect into Russian
When translating a narration using the Past Perfect into Russian, one must be guided, first of all, by the basic rules for using constructions in speech and control their presence: 
- The completion of the action at the mentioned moment, indicating the date or time in the past.
- The precedence of one action to another in the past.
Of course, there are many exceptions to the general rules when using the Past Perfect in speech, and all the nuances are mastered by directly entering the language environment.
But, despite the apparent complexity of the formation of this construction, especially in sentences with several actions, it will turn out to be much easier with regular practical use of it in speech.
The main thing is to know the rules of formation (Had + Verb 3) and the general rules for using the Past Perfect in speech, described above. In this case, the speaker will automatically begin to feel this construction and use it appropriately.
past perfect formed with the help to had in past tense form ( had- for all persons) and the past participle of the semantic verb: I / he had written. Past Participle (participle) of regular verbs is formed by adding the ending to the infinitive –ed: to invite- invite ed. When added to a verb –ed sometimes there are changes in its spelling: to stop - stopp ed. Past Participle irregular verbs you need to remember: to tell-told-told. Additionally about.
Abbreviated forms:
‘d= had
hadn't= had not
Using the Past Perfect
1. An action that took place before another action in the past. Indicated by the notation of time ( by Monday - by Monday, by evening - by evening, by 3 o'clock - by 3 o'clock, by that time - by that time) or other (later) actions expressed by time .
Examples: I had came to them by 5 o'clock. I came to them at 5 o'clock.
I had translated the text by Wednesday. – I translated the text by Wednesday.
my parents were glad to hear that I had passed all exams. My parents were happy to hear that I passed all the exams. (first I passed the exams - Past Perfect is used, and then my parents heard about it - Past Simple is used, i.e. one action happened before another)
my sister said that I had given her wrong address. My sister said I gave her the wrong address. (at first I gave my sister the wrong address - Past Perfect is used, and then the sister said that the address was wrong - Past Simple is used, that is, one action happened before the other)
2. An action that began up to a certain moment in the past and lasted until that moment. Past Perfect is used most often with verbs that are not used in the Continuous form. Additionally about.
Examples: When Sally arrived to the party, her friends had been there for half an hour. When Sally came to the party, her friends had already been there for half an hour.
3. Verbs in the Past Perfect can express two or more previous actions, and one of them can precede the other.
Examples: She said that she had drawn the money from her account and (had) sent them to her sister. She said she had withdrawn money from her account and sent it to her sister. (action expressed by the verb had drawn precedes the action expressed by the verb had sent)
4. If two or more past actions are transmitted in the sequence in which they occurred (i.e., actions are listed), the Past Simple form is used.
Examples: He entered room, took something from the desk and went out. He entered the room, took something from desk and left. (here the verbs entered, took, went out denote a chain of actions that followed one after another, so they are expressed using Past Simple)
5. If the sequence of actions is interrupted by a mention of previously completed actions, then such previously completed actions are used in the Past Perfect.
Examples: He entered the room which he had reserved the day before, took something from the desk and went out. He entered the room he had booked the day before, took something from the desk and left. (here the verbs entered, took, went out denote a chain of actions that followed the bottom after another, so they are expressed using the Past Simple. These actions are interrupted by the verb had reserved- an action that happened earlier, therefore Past Perfect is used here)
The past perfect tense often seems complicated and incomprehensible, because there is no analogue in Russian. In this article, we will talk about how and when to use the Past Perfect, as well as compare it with other tenses that express the past.
Most often, the Past Perfect is used to refer to an action that preceded another or several other events in the past. But that's not all there is to know about this time. In the article we will talk about the rules for using the Past Perfect, and also, using examples, we will analyze which tense form should be chosen when talking about the past - Past Simple vs. Past Perfect, Present Perfect vs. past perfect.
Past Perfect Education
To get started, we suggest that you familiarize yourself with the table below and figure out how Past Perfect Tense is formed.

Examples of affirmative sentences in Past Perfect:
I had lost my old phone. - I AM lost your old phone.
We had talked it over before. - We are discussed before.
He 'd called his mom. - He called mom.
Examples of negative sentences in Past Perfect:
They didn't talk much. - They did not say lot.
I hadn't finished my make-up by that time. - I still didn't finish paint by then.
Examples of interrogative sentences in Past Perfect:
Had you washed your hands? - You washed up arms?
Had she come home? - She came home?
Using the Past Perfect
Let's find out when the Past Perfect is used:
- The Past Perfect is used when we have two actions in the past and it is important for us to show that one of them happened before the other. The event that happened earlier is described using the Past Perfect, and the second action is described using the Past Simple.
She came to the office to meet him, but he had already left. - She came to the office to meet him, but he's already gone.
I was not hungry because I had lunch with my colleague. - I AM was not hungry as i am had lunch with a colleague.When describing the point at which an action was completed in the past, we often use constructions with by. For example, by Friday (by Friday), by the end of the year (by the end of the year), by July 11th (by July 11th), by 5 o'clock (by 5 o'clock), by then (to that time).
They had to run out of money by the end of the month. - By the end of the month they have run out money.
my sister had finished all her wedding preparations by the end of the spring. - My sister finished all preparations for the wedding towards the end of spring.Let's look at the features of this Past Perfect function:
- Past Perfect is used in sentences with verbs that are associated with thought processes: think (think), know (know), decide (decide), believe (believe, believe), hope (hope), remember (remember), forget (forget) etc. We use these verbs in Past Simple, and the second part of the sentence - in Past Perfect. For instance:
I thought you had called Eric to invite him to the party. - I AM thought, What are you called Erica to invite him to the party.
We hoped that he had caught the train. - We hoped, what he managed On the train.
He remembered that he had left his passport at home. - He remembered, what left home passport. - Past Perfect is used when you need to explain the reason for what happened. In the part of the sentence where the reason is indicated, we use the Past Perfect, and where the result of the action is the Past Simple. The words because (because) and as (because) will help connect the two parts of the sentence.
I was very upset as my son had forgotten about my birthday. - I AM was very upset because my son forgot about my birthday.
I got this job because I had prepared for the interview really well. - I AM got this job, because very good got ready to the interview. - The Past Perfect is used with state verbs (for example, be, have, know) when we talk about how long the action lasted until a specific moment in the past. Such sentences often accompany the words since (since some time) and for (during some period).
He told me that his best friend had been ill since last week. - He told me that his best friend sick with last week.
When they got married, they had known each other for 10 years old - By the time they got married, they were familiar 10 years.
- Past Perfect is used in sentences with verbs that are associated with thought processes: think (think), know (know), decide (decide), believe (believe, believe), hope (hope), remember (remember), forget (forget) etc. We use these verbs in Past Simple, and the second part of the sentence - in Past Perfect. For instance:
- Past Perfect is used in conditional sentences of the third type - in the part of the sentence where there is a condition. In such sentences, regrets are expressed about what happened in the past and cannot be changed in any way in the present. For instance:
If you had left earlier, you would not have missed the train. - If you released earlier, you wouldn't have missed the train.
He would have passed the exam if he had not skipped so many classes. - He would have passed the exam, if not walking so many lessons. - Another way to express regret about the past is the I wish + Past Perfect construction. Please note that English affirmative sentence in this case it will be translated into Russian as negative.
I wish I had studied better at school. - It's a pity that i'm at school did not study it is better.
I wish they had invited us to the birthday party. - It's a pity, what they not invited us for a birthday. - The Past Perfect is used in indirect speech.
Direct speech Indirect speech past simple “I read about it,” he said. - "I AM was reading about it,” he said. He said that he had read about it. - He said that was reading about it. “They were two hours late,” mom complained. - "They late for two hours, ”mother complained. Mom complained that they had been two hours late. - Mom complained that they late for two hours. “I have found the keys!” Rob cried. - "I AM found keys! Rob shouted. Rob cried that he had found the keys. - Rob shouted that found keys. “We have done our homework,” the children said. - "We made homework,” said the children. The children said that they had done their homework. - The children said that made homework. Please note that in modern spoken English in indirect speech, the use of Past Simple and Present Perfect is allowed.
My wife told me that she was here in childhood. My wife told me that she was here as a child.
Past Simple vs. past perfect
Let's look at the difference between Past Simple and Past Perfect. Past Simple is used when actions occur in chronological order, and Past Perfect is used when you need to show which action happened first, before the rest of the actions.
He started the car, turned the radio on and fastened the seatbelt. - He started car, turned on radio and fastened safety belt.
The actions are described in chronological order: first he started the car, then turned on the radio and fastened his seat belt.
He started the car, turned the radio on, but before he had fastened the seatbelt. - He started car, turned on radio, but before that fastened safety belt.
The actions are not described in chronological order: first he fastened his seat belt, and then he started the car and turned on the radio.
Please note that the word when (when) is often used in such sentences.
When I got home, my son took my car. - When I am came home my son took I have a car.
When I got home, I found that my son had taken my car. - When I am came home, I found that my son took my car.
If it is clear from the context that one action happened before another, you can use both Past Perfect and Past Simple. The following marker words often help to understand the context and sequence of events: before (before, before), after (after), as soon as (immediately after, as soon as), first (first, first), earlier (earlier), etc.
I didn't worry about speaking in front of so many people. I gave / had given public speeches earlier. - I AM didn't worry about speaking in front of a lot of people. Me and previously spoke in public.
Before he proposed to her, he spent / had spent many hours looking for a perfect ring. - Before you do her sentence, he spent many hours in search of the perfect ring.
We were late because Eric spilled / had spilled the coffee and had to change. - We late because Eric shed coffee and he needed to change.
I agreed to go to the cinema with her even though I saw / had seen that film before. - I AM agreed go to the cinema with her, even though I saw This movie before.
Present Perfect vs. past perfect
English learners often wonder what is the difference between Present Perfect and Past Perfect. The Present Perfect is used for an action that has ended so far, while the Past Perfect is used for an action that has started and ended at a certain point in the past. The difference between these times is shown schematically below.
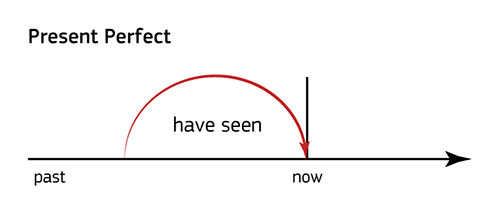

The main marker words Past Perfect and Present Perfect: already (already), just (just now), yet (already; not yet), ever (ever), since (s), for (during).
Let's look at the difference between Present Perfect and Past Perfect with examples:
| Present Perfect (action completed by a certain moment in the present) | Past Perfect (action completed at a certain point in the past) |
|---|---|
| He has already left, but you can call him and ask to wait for you. - He already gone but you can call him and ask him to wait for you. | When I called the police, the thief had already gone. - When I called the police, the thief already ran away. |
| I haven't finished cooking yet. Can you, please, wait a bit? - I AM not finished yet to cook dinner. Can you please wait a little? | He came home very early yesterday. I hadn't finished cooking dinner yet so he ate a sandwich. He came home very early yesterday. I AM not finished yet cook dinner, so he ate a sandwich. |
| We have been married to 20 years, and now he wants to get divorced. - We married 20 years old and now he wants a divorce. | We had been married to 20 years and got divorced in 2018. - We were married 20 years old and divorced in 2018. |
And now we offer to pass a small test on Past Perfect.
Past Perfect Tense is translated as "past perfect tense".
We use this tense to say that an action in the past has ended. to or before some time in the past.
For instance:
When I watched the series, I went to bed.
What was the first action? First I watched the series, and then went to bed. That is by that time, When I went to bed, I already watched the series.
To show that the first action ended before the second happened, the Past Perfect must be used in the first part of the sentence.
In other words, we use the Past Perfect to show the sequence of actions, that is, what one past action happened before another.
Look at the picture:

That is, by the time I watched the movie (second act), I had already read the book (first act).
Bonus: Want to learn easily English Times? Sign up and find out how easy it is to learn tenses and start speaking English in 1 month using the ESL method!
As you can see, it is not difficult to understand and remember this time. Now let's figure out how to form such sentences correctly.
Formation of the Past Perfect tense in English
The Past Perfect is formed using had(this is the past tense form of the verb have) and the past tense of the verb.
Verbs in the past tense
There are regular and irregular verbs in English. Depending on the verb, this form is formed as follows:
- if the verb is correct, then we add the ending -ed to it: cook - cooked, finish - finished.
- if the verb is irregular, then we put it in the 3rd form: do - done, eat - eaten
There is no rule by which one can determine the correct or irregular verb in front of us. The only way to find out is by looking it up in a dictionary or memorizing it.
The same is true for the forms of irregular verbs. They must be memorized or looked up in a dictionary.
Past Perfect Time Formation Scheme:
Actor + had + regular -ed verb or 3rd form of an irregular verb
| I | ||
| You | ||
| We | done | |
| They | had | worked |
| She | played | |
| He | ||
| It |
Important: Usually The past perfect is used in complex two-part sentences. Moreover, we use the Past Perfect in the part of the sentence that refers to the action that happened first (before the other).
In another part, the time is most often used Past simple - past simple.
The two parts of the sentence are connected by the words:
after- after
before- front
when- when
by the time- by that time
She had done her homework before he called.
She had done her homework before he called.
After they had eaten breakfast they went to work.
After breakfast, they went to work.
Abbreviations
We can abbreviate had in a sentence. It will look like this:
had = 'd
I 'd cooked dinner when they arrived.
I cooked dinner when they arrived.
Negative sentences in Past Perfect in English
.jpg)
To make the sentence negative, you need to add the negative particle not to the auxiliary verb had.
The outline of such a proposal would be:
Actor + had + not + regular -ed verb or 3rd form of an irregular verb
| I | |||
| You | |||
| We | done | ||
| They | had | not | worked |
| She | played | ||
| He | |||
| It |
He had not worked before he graduated from an university.
He didn't work until he graduated from university.
We had not read the book before we went to bed.
We didn't read this book before we went to bed.
Reduction
We can abbreviate had and not as follows:
had + not = hadn't
For instance:
I hadn't called him before he wrote me.
I didn't call him before he texted.
Interrogative sentences with Past Perfect in English
To form interrogative sentence, you need to put the auxiliary verb had in the first place. The outline of such a proposal would be:
Had + character + regular -ed verb or 3rd form of an irregular verb?
| I | ||
| you | ||
| we | done? | |
| Had | they | worked? |
| she | played? | |
| he | ||
| it |
Had they finished work before they left?
Did they finish work before leaving?
Had he drunk coffee before he went to work?
Did he drink coffee before he went to work?
So, we have analyzed the theory, and now let's move on to practice.
Reinforcement task
Translate the following sentences into English:
1. I watched TV after reading a book.
2. She had breakfast before going to school.
3. They got married before they bought a house.
4. When the rain stopped, we went for a walk.
5. We went to the cinema after we had dinner.
6. He went home after finishing work.
The palette of the English system of times is simply replete with diversity. Some of the shades shine brighter, some dimmer. One of the most saturated can be called Past Perfect. How, with the help of grammatical constructions and the lexical diversity of this tense, to make speech expressive?
The past completed tense, as Russian-speaking “students” often call it, carries a certain sense of completeness. In other words, for example, when describing an event, we often make comments about what happened before the main action. “When my mother came, I already fell asleep” - in this sentence there are two past tenses - “came”, “fell asleep”. Which one happened first? The second means that we will express it Past Perfect.
Education
This form is one of the simplest. Yes, you will need an auxiliary verb. "had" + V 3 or Ved. Remember that all verbs in English can be grouped into regular and irregular. The latter have 3 forms, which, well, what to do, you have to learn by heart. All of them are placed in the table of irregular verbs. At this time, we need the 3rd column - V 3. If the verb is correct (it is not in the table), then we add the ending -ed.
I had worked. - work - the correct verb
I had taught. - teach is an irregular verb.
Let's take a closer look at the formation of all types of sentences in paste perfect using the example of to ask.
In writing, and in colloquial speech, abbreviated forms are often used, which facilitate the process of perception.
I had = I'd, you had = you'd, he had = he'd
had not = hadn't
I had written a composition by six o'clock. = I'd written a composition by six o'clock. I had written the composition by 6 o'clock.
I had not written a composition by six o'clock. = I hadn't written a composition by six o'clock. I had not written an essay by 6 o'clock.
As you can see, there is nothing terrible and difficult in education. It is worth remembering once that in the question had is placed before the subject, and in negation not is added to this auxiliary verb. It is important to remember that had is not translated.
Using The Past Perfect Tense
This time is not difficult in terms of use, if you only clearly understand the situations of its use. Some sentences often use signal words such as just, already, never, yet.
1. The action ended before another event in the past. The sentence can be complex (consist of two), one of which (dependent) is introduced by the unions when, before, after, or simple, in which the preposition by is used as an indicator of the end of the action.
- With the help of prepositions by the end of the year, by 3 o'clock, by Monday, by the time, before, after.
They had finally got their long-awaited pay rise by the end of the year. By the end of the year, they finally got the long-awaited pay raise.
Before he opened the door, he had called his sister. — Before he opened the door, he called his sister.
By that time they had finished their work. By that time they had already finished the work.
- Structures often used no sooner ... than (as soon as), hardly ... when (hardly, as), scarcely ... when (as soon as, so immediately), barely ... when (barely, like), which, by their meaning, can transform the sentence (inversion). As a rule, they are emotional in nature.
I had scarcely opened the window when the wind came blowing in. - As soon as I opened the window, the wind immediately began to blow.
Jack had no sooner arrived than he was told to come back. - Jack did not have time to arrive, as he was told to return.
- If there is no signal word in the sentence, then you will have to carefully read the context .
I tried to pnone Ann this morning. But there was no answer. She had gone out. I tried to call Anna this morning. But, there was no answer. She's already gone.
The rules for Past Perfect distinguish the following context patterns, remembering which it will be easier for you to use the desired form.
a. After designs: this/that/it was, the first/second/only/ best/ worst time smth happend:
It was the second serious mistake he had made in that job. — It was his second serious mistake he made in his work.
Those were the first things she had bought since Chrismas. It was the first thing she bought since Christmas.
B. With verbs that convey hope, plan, expectation, intention (but not fulfilled).
I had intended to visit a museum, but I ran out of time. I was going to visit the museum, but I didn't have enough time.
C. In indirect speech, with verbs such as say, tell, ask, inform, wonder. Moreover, Past Perfect is used in the subordinate clause.
I wondered if Jim had a chance to discuss the problem with them. I asked if Jim had the opportunity to discuss this problem with them.
2. An action that started before another action but is still ongoing. Here, stative verbs or, as they are also called, non continuous verbs are often used. All the little secrets of these verbs are revealed in the article "".
I knew he had been married for nearly 50 years ago. I knew that he got married about 50 years ago.
George made no answer and we found that he had fallen asleep for some time. George didn't answer and we found that he had been asleep for some time.
How to distinguish Past Perfect from other tenses?
| past perfect | past simple | Present Perfect |
| When the sequence of actions is violated (action precedes). Before I ate, I played and slept. The verb in the main clause in the Past Simple | Everything goes in order (actions are performed chronologically) Played, slept, ate. | When the action in the main clause is in the present |
| Was Ann at home when he came? No, she had already gone to work. Was Anya at home when he came? No, she already left for work (first she left, then he came) | Was Ann at home when he came? Yes, but she went to work soon. Was Anya at home when he came? Yes, but soon she left for work. (He came, then left - actions one after another) | |
| I wasn't thirsty. I had drunk a cup of tea. - I didn't want to drink. I just had a cup of tea. | I' m not thirsty. I' ve just drunk a cup of tea. - I don't want to drink. I just had a cup of tea. | |
| His car was dirty. He hadn't washed it for weeks. Yesterday he cleaned it. — His car was so dirty. He hasn't washed her in weeks. He washed it yesterday. | His car is dirty. He hasn't washed it for weeks. — His car is so dirty. He hasn't washed her in weeks. |
According to the rules for the Past Perfect, this tense can be used in the passive voice. All uses Past Perfect Passive the same, but the shape of the structure is slightly different. The negation and the question are built according to the same principle as in the active voice (after had - not, and auxiliary ch. had before lying down)
I + had + been + V3 (Ved)
He (she, it) + had + been + V3 (Ved)
You + had + been + V3 (Ved)
They + had + been + V3 (Ved)
We + had + been + V3 (Ved)
I had been introduced to his friends before. “I was introduced to his friends earlier.
By three o'clock the dinner had been cooked. By 3 o'clock dinner was ready.
This article had been translated when they phoned. The article was translated when they called.
Well, as you can see, Past Perfect grammar is not too difficult. You look at the sentence, determine which of the actions happened first, and put in the correct form. If you learn how to use this time correctly, then believe me, you can tell any story or just retell the story in English without any problems.











How to cook ham in the oven at home
Pain in the lower abdomen during pregnancy, reasons for what to do Can the lower abdomen hurt if pregnant
Protein for muscle gain
The best vitamins for men according to customer reviews
How to lose weight on a vegan diet?