Collect set of tools, materials, medicines for primary surgical treatment of wounds. Primary Wound Surgical Instrument Set
Primary surgical treatment wounds(PHO) is a surgical intervention aimed at removing nonviable tissues, preventing complications and creating favorable conditions for healing any wound.
A set of instruments, materials, medicines for the primary surgical treatment of wounds.
Primary Wound Surgical Instrument Set Indications. Accidental wound. Equipment: TECHNIQUE OF PERFORMANCE
SURGICAL WOUND TREATMENT
1.
2.
- sterile: forceps - 2 pcs, clamps for linen - 4 pcs, surgical tweezers - 2 pcs, anatomical tweezers - 2 pcs, syringe (10 ml) - 2 pcs, scalpel - 1 pc, scissors - 2 pcs, hemostatic clamps - 4-6 pcs , Farabef hooks - 2 pieces, sharp-toothed hooks - 2 pieces, cutting needles - 4 pieces, piercing needles - 4 pieces, grooved probe - 1 piece, button-shaped probe - 1 piece, suture material, bix with dressing material, gloves, drains;
- other: antiseptics for the skin (cutasept, iodonate), antiseptics for wounds (3% hydrogen peroxide solution, 0.06% sodium hypochlorite solution), 70% ethyl alcohol, a preparation for disinfecting instruments (deactin, neochlor), a preparation for local anesthesia (lidocaine, novocaine).
3. Take tweezers and a swab soaked in ether or ammonia, cleanse the skin around the wound from contamination.
4. With a dry swab or a swab moistened with hydrogen peroxide (furacilin), remove foreign bodies and blood clots that are loose in the wound.
5. Swab moistened with iodonate (alcoholic solution of chlorhexidine), process the operating field from the center to the periphery.
6. Delineate the operating area with sterile linen.
7. Swab moistened with iodonate (alcoholic solution of chlorhexidine), treat the operating field.
8. Using a scalpel, dissect the wound throughout.
9. Excise, if possible, the edges, walls and bottom of the wound, remove all damaged, contaminated, blood-soaked tissue.
10. Change gloves.
11. Separate the wound with a sterile sheet.
12. Replace instrumentation.
13. Thoroughly bandage the bleeding vessels, sew large ones.
14. To resolve the issue of suturing:
a) apply primary sutures (stitch the wound with threads, bring the edges of the wound together, tie the threads);
b) apply primary delayed sutures (stitch the wound with threads, do not pull the edges of the wound, do not tie the threads, bandage with an antiseptic).
15. Treat the operating field with a tampon moistened with iodonate (alcoholic solution of chlorhexidine).
16. Apply a dry aseptic dressing.
Bandage a clean wound.
1. Place the patient on a couch, operating table.
2.
3.
4.
5.
6.
7.
8. Secure the bandage with a bandage, glue or adhesive plaster.
Bandage the purulent wound.
TECHNIQUE FOR PERFORMANCE OF WOUND BANDING
1. Place the patient on a couch, operating table.
2. Remove with tweezers, holding the skin, the surface layers of the dressing with a dry ball, discard them in a kidney-shaped tray. Peel off the dried bandage with a ball soaked in 3% hydrogen peroxide solution.
3. After removing the surface layers of the dressing, abundantly moisten the inner layer with 3% hydrogen peroxide solution. Carefully remove wet wipes with tweezers.
4. Treat the skin around the wound with a ball soaked in an antiseptic solution (alcohol solution of chlorhexidine) from the edge of the wound to the periphery.
5. Take another sterile tweezers.
6. Make a toilet of the wound: remove pus with tweezers or a sterile ball, rinse the wound with an antiseptic solution (3% hydrogen peroxide, furacilin), dry with a sterile ball.
7. Use tweezers to put sterile napkins with a therapeutic agent on the wound (depending on the stage of the wound process).
Secure the bandage with a bandage, glue or adhesive plaster All surgical instruments can be assembled into sets that allow you to perform typical surgical procedures.The operating nurse's instrument table should contain the “connecting instruments” - ie. those that only the operating nurse works with - scissors, anatomical tweezers small and long, 2 forceps, 4 linen pins for processing and delimiting the operating field.
Basic set - it includes tools general group, which are used in any operations and are included in the elements of the operation.
For specific operations, special tools are added to them.
Basic set of surgical instruments
Figure 12. Basic set of surgical instruments.
1 - clamp of the "Kornzang" type (according to Gross-Mayer) straight; 2 - linen claws; 3 - bulbous probe (Voyacheka); 4 - grooved probe; 5 - a set of surgical needles; 6 - atraumatic needle with suture thread.
1. Kornzang is used to process the operating field. There may be two of them.
2. Linen pins - for holding the dressing material.
3. Scalpel - should be both pointed and abdominal, several pieces, because during the operation, they have to be changed, and after the dirty stage of the operation - thrown away.
4. Hemostatic clamps Billroth, Kocher, "mosquito" - are used in large quantities.
5. Scissors - straight and curved along the edge and plane - several pieces.
6. Tweezers - surgical, anatomical, gripping, they must be small and large.
7. Hooks (retractors) Farabef and toothed blunt - several pairs.
8. Probes - bulbous, grooved, Kocher.
9. Needle holder.
10. Needles are different - a set.
A set of surgical instruments for PCO wounds
(applies to work only on soft tissues)Removal of microorganisms trapped in the wound by excision of the edges and bottom of the wound or tissue dissection;
- removal of all damaged tissues, blood clots, which are a breeding ground for microorganisms;
- transfer of all types of wounds to cut to speed up the regeneration processes;
- thorough, complete and final hemostasis;
- restoration of the anatomical integrity of damaged tissues by suturing and, if necessary, wound drainage.
Indications: PHO are subject to:
Extensive wounds of soft tissues with loose, torn, uneven edges and heavily contaminated;
- all wounds with damage to large blood vessels, nerves, bones.
PHO is carried out within 24 - 48 hours and should be, as far as possible, one-step and comprehensive. Preparation for PHO consists in cleaning the skin around the wound, processing the operating field according to the method used in this medical institution, and premedication. PHO begins with general or local anesthesia.
Contraindications:
Shock, acute anemia,
- collapse, development of purulent inflammation.
A common set of tools is used for PHO.
Laparotomy Surgical Instrument Set
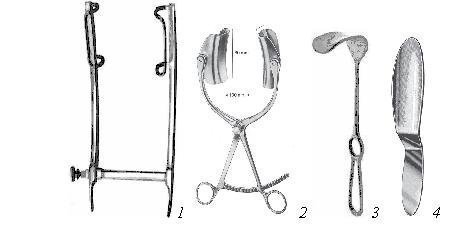
Figure 13. Set of instruments for laparotomy.
1 - rack retractor according to Gosse; 2 - Collin's retractor; 3 - surgical retractor (mirror) according to Kocher; 4 - Reverden spatula
To perform, operations on any organ abdominal cavity, perform gluttony or laparotomy.
Indications: it is used for acute and chronic diseases of the abdominal and retroperitoneal organs, injuries and injuries, sometimes for diagnostic purposes.
An extended general set is used - a general set, which is expanded with Gosse and Mikulich retractors, abdominal mirrors - Ru and saddle, hepatic and renal mirrors.
Expand the hemostatic clamps and add clamps Mikulich, Fedorov, fenestrated, hepatic - renal, ligature dissector and Deschamp's needle.
- Tweezers and scissors should be both small and large (cavity).
- Intestinal and gastric pulp,
- Reverden's spatula,
- Hepatic tube and spoon.
Set of surgical instruments for appendectomy and hernia repair
Surgery to remove the appendix and hernia repair.Indications: acute attack of appendicitis, infringement of hernial contents. The operation should be performed urgently, in the first hours after the onset of the disease. In case of not restrained hernia - in the "cold" period, after a complete examination of the patient.
A set of instruments: a general surgical set is used, cavity instruments are added - Mikulich's clamps; abdominal mirrors - saddle and Ru.
Set of surgical instruments for laparocentesis (abdominal puncture)
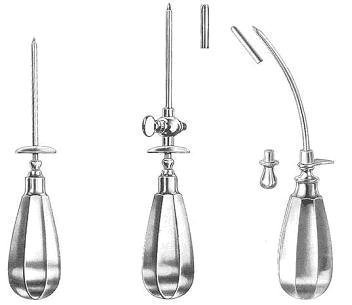
Figure 14. Trocar set.
It is carried out with ascites, a similar operation can be used to diagnose injuries and diseases of the abdomen.
A common set of tools is being assembled, since patients are obese and in order to insert the trocar, it is necessary to make an incision in the tissues, and then suture. In patients with a small amount of subcutaneous fat, only the trocar can be used.
Do not forget the PVC tubes for the diameter of the trocar!
Cholecystectomy Surgical Instrument Set
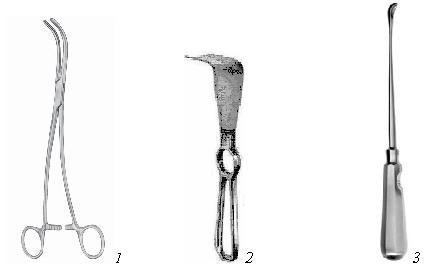
Figure 15. Cholecystectomy instrument set.
1 - ligature dissector; 2 - liver mirror; 3 - a spoon for removing gallstones
It is used for diseases of the gallbladder, liver, liver injuries.
Surgical instruments:
1. General set of instruments extended for laparotomy
2. Clamp Fedorov
3. Ligature dissector, Deschamp's needle
4. Liver mirrors,
5. Hepatic tube and hepatic spoon
6. Hepatic - renal clamp
7. A scoop used for liver injury to remove blood from the abdominal cavity.
Set of surgical instruments for gastric resection
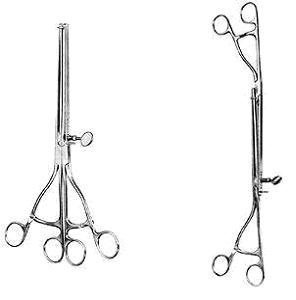
Figure 16. Lana's gastric-intestinal forceps, double.
Figure 17. Lever stomach suture.
It is used for perforated and common stomach ulcers and 12 duodenal ulcers, for injuries of the stomach, stomach tumors.
Tools:
1. Extended general set for laparotomy
2. Bagasse
3. Liver mirrors
4. Fyodorov's forceps, ligature dissector
5. End clamps
Instruments for operations on the chest wall and chest cavity organs
Instruments are used for trauma to the chest wall, for penetrating wounds, for injuries to the organs of the chest cavity, for purulent pathology and specific diseases of organs.Tools:
1. General set of tools,
2. Doyen's Rib Raspatory and Doyen's Rib Cutters,
3. Screw mechanical retractor,
4. End Luer Clamps,
5. Clamp Fedorov,
6. Ligature dissector and Deschamp's needle.
7. Special instruments used in cardiovascular surgery.
Set of surgical instruments for craniotomy
Toolbox - A common toolbox is used, but widening of the wound requires the use of pointed hooks.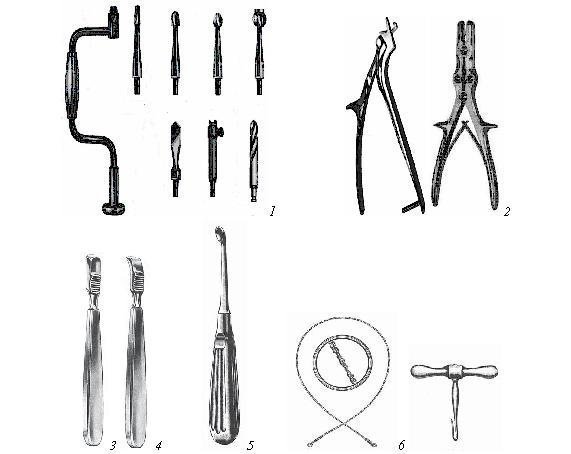
Figure 18. Special set of instruments for craniotomy.
1 - brace with a set of cutters
2 - Dahlgren Nippers, Luer Nippers
3, 4 - raspatory - straight and curved
5 - Volkman's bone spoon
6 - saw Jigli with handles and Palenov's guide
1. Rasp
2. Brain spatulas of various widths
3. Rubber balloon "pear"
4. Special neurosurgical hemostatic clamps
Tracheostomy kit
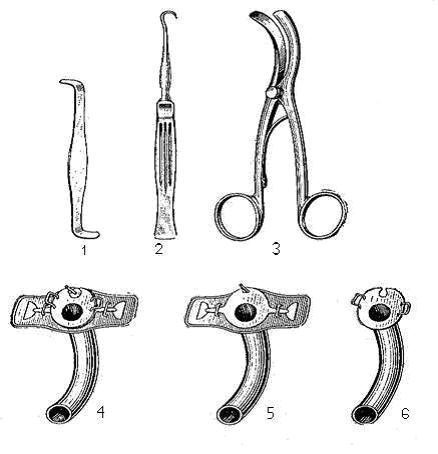
Fig. 20. Tracheostomy kit.
1 - blunt hook for the isthmus of the thyroid gland; 2 - a sharp hook for holding the larynx and trachea; 3 - tracheal dilator; 4,5,6 - tracheostomy cannula, assembled and disassembled.
Opening the windpipe. Emergency tracheostomy is performed with the aim of immediately providing air access to the lungs, in case of blockage of the airways, in patients with tumors of the larynx or vocal cords.
Indications:
Damage to the larynx and trachea;
- stenosis of the larynx and trachea due to inflammatory processes and neoplasms;
- foreign bodies of the trachea and larynx;
- the need for long-term mechanical ventilation.
Tools:
1. General purpose tools.
2. Special set of tools:
- Single-tooth hook - a small blunt hook
- Trousseau trachea dilator
- Double tracheostomy cannulas of various sizes, consisting of an outer and an inner tube. The outer tube has holes in the side for a strap that ties it around the neck.
Skeletal Traction Surgical Instrument Set
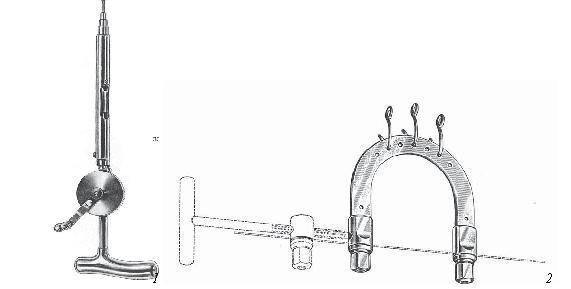
Figure 21. Skeletal traction tool kit.
1 - hand drill; 2 - Kirschner brace with a wire for skeletal traction.
This kit does not need a common set of tools. It is used to stretch the bone in case of fracture.
Tools:
Drill, hand or electric
- Kirchner bracket
- A set of knitting needles
- Wrench for tightening nuts
- Key for tensioning the spoke
This kit also requires rubber plugs to hold the gauze ball in place.
Limb Amputation Surgical Instrument Set
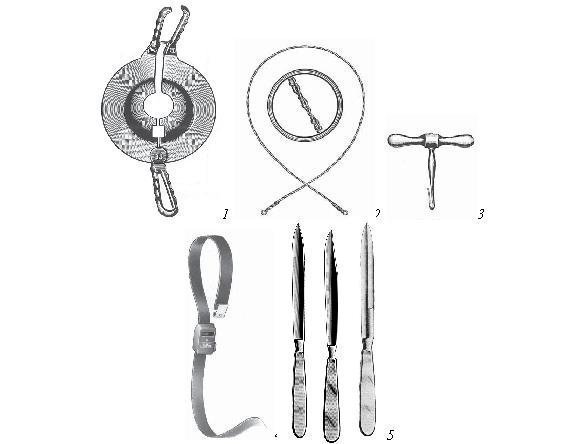
Figure 22. A set of instruments for limb amputation.
1 - retractor; 2 - wire saw Jigli; 3 - Palenov handles; 4 - hemostatic tourniquet; 5 - a set of amputation knives.
Removal of the distal part of the limb.
Indications:
Limb injuries;
- malignant tumors;
- tissue necrosis as a result of frostbite, burns, obliterating endarteritis.
Purpose of amputation: saving the patient's life from severe intoxication and infection emanating from the lesion and creating a workable stump suitable for prosthetics.
Set of tools:
General surgical kit
1. Hemostatic tourniquet
2. A set of amputation knives.
3. Raspatory for displacement of the periosteum
4. Arc or sheet saw and Jigli's wire saw
5. Bone clippers Liston or Luer
6. Rasp for smoothing sawdust bones
7. Blade of a safety razor in the Kocher clamp for truncation of nerve trunks
8. Bone holder Olier or Farabef
9. Retractor for protecting soft tissues when sawing bones and for shifting soft tissues before sawing
10. Volkmann spoon
Surgical Instrument Set for Suturing and Removing Sutures
For suturing1. Surgical forceps.
2. Needle holder.
3. A set of needles.
4. Scissors.
To remove stitches
1. Anatomical forceps.
2. Sharp-pointed scissors.
EAT. Turgunov, A.A. Nurbekov.
Surgical Instruments
Target:
Removal of microorganisms trapped in the wound by excision of its edges, bottom, tissue dissection
Removal of all damaged tissues, blood clots, which are a breeding ground for microbial flora
Transfer of all types of wounds to cut to speed up the regeneration processes
Thorough. Complete and final hemostasis
Restoration of the anatomical integrity of damaged tissues by suturing and, if necessary, drainage of wounds
Indications: extensive wounds of soft tissues with multiplied, torn, uneven edges and heavily contaminated soil, all wounds with damage to large blood vessels, nerves, bones.
Contraindications: shock, acute anemia, collapse, development of purulent inflammation.
Tools:
Claws for strengthening the operating linen - 8 pcs.
Abdominal and pointed scalpels - 4 pcs.
Surgical tweezers - 4 pcs.
Hemostatic clamps of Billroth and Kocher - 15 pcs.
Cooper's scissors - 3 pieces
Curved scissors Richter - 1 pc.
Sharp hooks, 3 teeth - 2 pcs.
Farabef hooks - 2 pcs.
Deschana ligature needle - 1 pc.
Grooved probe - 1 pc.
Button-shaped probe - 1 pc.
Folkman spoons - 1 pc.
Straight and curved forceps - 2 pcs.
Different cutting needles - 15 pcs.
Intestinal needles - 10 pcs.
Syringes and needles for them different sizes- 5 pieces.
* see the listed tools in the manual "General surgical instruments
A set of instruments for opening an abscess and a technique for opening abscesses.
Indications: subcutaneous panarats, abscessing boils, abscesses, etc.
Equipment: syringe 2-5 ml, injection needles, 0.5% novocaine solution, antiseptic solutions, scalpel. Scissors, hemostatic clamps, tweezers, button probe, sterile surgical linen, napkins, balls, turundas, drains, gloves, alcohol, iodonate.
Sequencing:
1. Treat the operating field with an antiseptic and remove it with sterile linen.
2. Provide local anesthesia.
3. By sticking a sharp-pointed scalpel into the thinnest place, open the abscess, dissecting the skin by 1.5 - 2 cm.
4. With the help of napkins, balls and turundas and by washing with antiseptics, pus is removed.
5. The cavity of the abscess is drained and drained (a rubber graduate, a turunda with a 10% sodium chloride solution or a rubber strip is inserted).
6. An aseptic bandage is applied and fixed with an adhesive plaster or bandage.
Pleural puncture instrument kit
Puncture of the pleura is performed to clarify the diagnosis, to remove liquid contents from the pleural cavity, to remove air from the cavity.
Indications: exudative and purulent pleurisy, hemopneumothorax.
Tools: 2 syringes with a capacity of 20 ml (one with 0.5% novocaine solution, the other empty), a thick needle 6-8 cm long for puncture with a rubber tube and cannula, a hemostatic clamp with a secure lock.
Technique: the patient is seated on a dressing table in the position of flexion of the trunk and with the hand of the corresponding side raised. In the area of the puncture with a thin needle, soft tissues are infiltrated in layers to the pleura with 0.5% novocaine solution. After preparation of the operating field, a puncture is performed at the lowest point of the cavity or below the fluid level established by physical and X-ray examinations.
With the left hand, they fix the skin, pulling it down along the edge, and right hand a needle is injected with a tube clamped with a clamp directly above the upper edge of the rib. The needle is passed to a depth of 3-4 cm strictly along the edge of the rib to exclude damage to the neurovascular intercostal bundle. The nurse opens the clamp when the fluid is aspirated and closes it as directed by the surgeon at the end of the suction. The fluid should be evacuated slowly in an amount of no more than 1 liter in 15 minutes, thereby avoiding displacement of the mediastinum. After removing the needle, the puncture site is treated with iodonate and sealed with a sterile gauze napkin.
Lumbar puncture instrument kit
Indications: taking cerebrospinal fluid for research and to reduce intracranial pressure in case of injuries and symptoms of brain drainage; the introduction of drugs and anesthetic solutions for spinal anesthesia; the introduction of air into the subarachnoid space for the purpose of pneumoencephalography.
Tools: alcohol, iodonate, 0.25% novocaine solution, 3 syringes with a capacity of 5 ml needles, Biri's needle with a mandrel, forceps. Surgical gloves. Glass tubes (for collecting cerebrospinal fluid), napkins, gauze balls.
Position of the patient with a lumbar puncture and the proposed puncture site.
Operation technique: after skin treatment, local anesthesia with 0.25% novocaine solution - 10 - 15 ml. Iodonate draw a straight line connecting highest points scallops of the ilium.
The index finger of the left hand determines the gap between the spinous processes located at the point of intersection of the above line with the midline of the spine. The skin is re-wiped with alcohol, the upper edge of the spinous process near the lumbar vertebra is felt with a finger, an injection is made directly above it with a needle with a mandrel strictly along the midline and it is carried out perpendicular to the surface of the lumbar, the needle is passed to a depth of 4-6 cm.When penetrating into the canal, the mandrel is removed, from the cannula, cerebrospinal fluid begins to flow out in drops.
Venesection instrument set
Indications: difficult venipuncture due to poor development of veins, the presence of a thick subcutaneous fat layer, poor filling of veins in coma and collapse, the need for long-term infusion therapy.
Equipment:
A glass for novocaine
Anesthesia syringe - 20 ml, injection needle
Kornzang, tweezers
Execution technique:
After processing the operating field, covering it with surgical linen, local anesthesia of the proposed incision site is performed
The skin and subcutaneous fat is dissected by 3-4 cm (scalpel)
Stopping bleeding (anatomical tweezers, haemostatic forceps)
Selection of vein X Billrolt forceps and anatomical forceps)
2 catgut ligatures (Deschamp's needle) or a clamp are placed under the vein
Above the imposed ligature, the lumen of the vein is opened in the transverse direction with the tip of sharp scissors.
The upper edge of the vein opening is grasped with a Golstead forceps (mosquito) and lifted
A pointed cut of a sterile vascular catheter is inserted into the lumen
Then it is fixed, the wound is sewn up tightly
The catheter is fixed to the skin with a silk ligature, aseptic bandage
Set of instruments for bone panaritium surgery
Panaritium - acute purulent disease of finger tissues. Bony felon is essentially secondary osteomyelitis of the phalanges of the fingers.
Depending on the prevalence of the process, the operation may consist in dissecting the tissues of the finger, sequestrectomy and further treatment as a purulent wound or amputation of the finger at the level of the lesion.
Tools:
Syringe with injection needle for local anesthesia according to Oberst-Lukashevi
Novocaine 0.5%, flagellum (gum)
Scalpel, Billroth or Holstead forceps
Pointed spoon Volkmann
Luer Nippers - for nibbling sharp protuberances during amputation
Raspatory straight and curved
When forming a stump - a needle holder with skin needles, suture material
Set of instruments for diagnostic puncture of the lymph node
Sterile packing contains:
Bank (50-100 ml) for novocaine - 1 piece
Syringe with a capacity of 20 ml - 1 pc
Injection needle for local anesthesia - 1 piece
Puncture needle (Duffaut) - 1 piece
Kornzang - 1 piece
Surgical gloves - 2 pairs
Glass tubes for collecting contents - 4 pcs
Slides for the preparation of smears - 4 pcs
Large kidney tray - 1 piece
Napkins, balls - 4-8 pcs
Antiseptic
All of the above is necessary and when taking a smear - prints from the tumor.
All surgical instruments, depending on their functional load, can be conditionally divided into the following categories:
1. For research and diagnostics by the method of bougie and sounding (probes, bougie).
2. Clamping (auxiliary, hemostatic, intestinal, fenestrated clamps).
3. Stitching (needles, surgical awl, transosseous knitting needles).
4. For expanding and pushing back the edges of wounds and cavities (shoulder blades, retractors, tweezers, hooks, mirrors).
5. Cutting (scalpels, saws, knives, scissors, raspatories, etc.).
They are arranged in sets, which include both basic and special surgical instruments:
1. For primary surgical treatment (PCO) of wounds on soft tissues - for extensive tissue damage, wound contamination, disorders of large blood vessels, nerve fibers, bone tissue.
2. For laparotomy - for the treatment and diagnosis of pathologies or injuries of the abdominal and retroperitoneal organs.
3. For removal of the appendix and hernia repair - in case of emergency interventions during acute attacks of appendicitis and hernia infringement.
4. For laparocentesis - for ascites and for the diagnosis and treatment of other diseases and injuries of the abdominal cavity.
5. For cholecystectomy - for the treatment of pathologies and injuries of the liver and gallbladder.
6. For gastric resection - for ulcers, tumors and stomach injuries.
7. For surgical intervention on the organs of the chest cavity and chest wall - for injuries, purulent pathologies and specific diseases of the corresponding organs.
8. For craniotomy. Replicates the general set of surgical instruments and includes additionally pointed hooks.
9. For tracheostomy - in case of damage, inflammatory processes, the appearance of neoplasms and the ingress of foreign bodies into the larynx and trachea.
10. For skeletal traction in traumatic injuries of the limbs.
11. For amputation of a limb in trauma, malignant neoplasms, tissue necrosis.
12. For removing and suturing.
In the company "M.P.A. medical partners ”you can buy surgical instruments from the world's leading brands:
- Erbe is one of the leading companies in the production of equipment for physiotherapy, aquatic, electro- and cryosurgery.
- KLS Martin Group is a German manufacturer and developer of innovative medical equipment: surgical instruments, coagulators, operating lamps, etc.
- Aesculap is another German brand with more than two centuries of history. Specializes in the production of instruments and implants for various areas of surgery.
- Ethicon is a division of Johnson & Johnson Corporation that specializes in the development of instruments for minimally invasive interventions.







Energy drinks: give vigor, but take away health What will happen if you drink 4 energy drinks
Mustard for weight loss: how to use the seasoning with maximum benefit Is it possible for children to have mustard
The benefits and harms of mustard for the human body Table mustard benefits and harms
How to treat the ear after piercing: types of antiseptics, their composition, rules and features of the treatment of a pierced ear
Sistine Chapel in the Vatican: description, history, architectural features