NATURAL ADHESIVES, compositions based on natural high-molecular compounds used for joining (gluing) various materials; are divided into adhesives of animal and plant origin. Adhesives of animal origin include compositions based on proteins: collagen, albumin and casein. Adhesives of plant origin include compositions based on natural rubber, gutta-percha, natural resins, polysaccharides (starch, dextrins, gums) and proteins (zein, soy casein). Natural adhesives may contain water, antiseptics (for example, phenol), stabilizers (alkalies, etc.), resins that increase stickiness (for example, rosin). The main advantage of natural glue over synthetic glues is the absence of special safety requirements.
Natural adhesives based on collagen are liquid adhesive solutions, gel-like or solid products. From solid collagen adhesives, produced in the form of flakes, cubes, granules, powders, tablets, tiles, aqueous solutions are prepared by heating. Collagen adhesives cure in approximately 2 days (at 20 °C) due to water evaporation and gelatinization. Natural adhesives based on albumins are powdered products that are mixed with water and slaked lime before use. Albumin adhesives cure within a few minutes (at 80 °C) as a result of chemical reactions and evaporation of water. Natural casein-based adhesives are powders that are mixed with water. The curing time of casein adhesives ranges from several minutes to 24 hours (at 20 °C); the process occurs due to chemical reactions or due to the evaporation of water. Natural adhesives of animal origin have low water, atmospheric and biostability, so they cannot be used for gluing products used outdoors. The most durable adhesive joints are formed by casein glue, the most water-resistant - by albumin. Natural adhesives of animal origin are used for carpentry (making furniture and other products from wood and plywood), for gluing leather, paper, and textiles.
Among natural adhesives of plant origin, the most important for practical use are adhesives based on natural rubber (see the article Rubber adhesives). Adhesives based on natural resins (Canadian and fir balsam - products of processing fir resin) are used for gluing optical glasses. Natural starch-based adhesives are used mainly in everyday life for gluing wallpaper and gluing paper. Natural adhesives based on dextrins are used for gluing paper, photographic paper, and cardboard. Natural adhesives based on plant proteins are used in the production of plywood.
Bone glue in most variations is an appropriate base based on organic components. They allow you to effectively connect elements made of wood, cardboard, hardboard and other similar materials. The connection itself is characterized by maximum strength; even if the structure is destroyed, you can notice that it is not the adhesive layer that is deformed, but the adjacent layers of wood or analogues. The mixture in question includes safe organic components that are approved for use in educational institutions and children's rooms.
Types of bone glue
To prepare the base composition, several main types are used, differing in the main components:
- Flesh option.
- Fish composition.
- Pure bone glue.
The latest version is the most common, the composition is obtained from animal bone waste. The most valuable specimens are considered to be pellets obtained from horns. The set includes collagen, gelatin and cysteine, which have excellent viscosity and are capable of firmly gluing products made of wood and similar materials.
The leather analogue is made from waste from the leather industry. In fact, the main part of the material consists of subcutaneous tissue, cut off during the tanning of hides. Oligopeptides and natural leather trimmings are often added to the composition of this glue. Output - scales, tiles, powder.
Fish bone glue is prepared from bones, heads, scales, entrails, and fins. This substance is the most expensive, but it was often used for icon painting and other works that required maximum care and accuracy. A composition is produced for fastening dissimilar parts, produced in the form of granules or flakes. Let's consider the features of all variations, as well as the features of their operation.

Furniture made of wood with PVA
Separately, PVA glue can be noted. It is completely synthetic, but safe, like its protein variations. Its use is legally permitted in preschool institutions.
Advantages:
- Excellent parameters for joining wood, cardboard, paper.
- High elasticity.
- Resistant to moisture.
- Excellent adhesion of treated surfaces.
- Transparent after drying.
Preparation
Bone is mainly sold in dry form. The mass is small brown or yellow granules, sometimes this material is presented in the form of small slabs. Can the quality of the composition be determined visually? The purer and lighter the material, the better the product. The cooking process is also extremely important. For example, a tile needs to be crushed into crumbs, and then used for its intended purpose. The preparation of bone glue is divided into the following stages:
- Soak. Powder or granules are poured with cold, pre-boiled water. Tap liquid can negatively affect the quality of the finished mass. Fill the container so that all elements of the adhesive composition are covered. Soaking is considered correct if the substance becomes soft and gelatinous. The soaking process takes from 4 to 12 hours, depending on the amount of product being processed.
- Cooking. The swollen glue should be boiled for about 15 minutes in a steam bath. Maintain the temperature at about 60-80 degrees. The result should be a homogeneous liquid mixture without lumps. It is important not to heat the mass over an open fire and not to bring it to a boil. Otherwise, the protein from which the granules are made will begin to deform, and the adhesive ability will decrease. After a thin film has formed on the surface, the adhesive mixture is ready.

Peculiarities
The readiness of bone glue for wood can be checked in another way. The stick used to stir the substance is raised above the composition. If the product drips down in drops, the process is not completed; complete readiness is indicated by the flow of the mass in a monotonous stream.
To cook natural glue, a special device is used - a glue bottle. It consists of two vessels of different sizes, one of which is inserted into the other. A large container is filled with water, and the second reservoir contains the resulting glue. At the next stage, a small vessel is placed in a large tank and placed on fire. The optimal manufacturing material for the glue is copper.
You can prepare glutinous glue yourself. To do this, you will need to take two containers of different sizes. The outer shell could well be a tin can. Insert a tin can attached to a wire inside it.
The quality of the adhesive composition can be improved by adding various fixing substances. This will allow you to use glue for fastening not only wooden surfaces, but also other analogues.

Among the components used, the most popular, along with efficiency, are the following materials:
- Drying oil. About 10 grams of linseed oil or 40 granules of natural drying oil are added to the composition. This component allows you to increase the resistance of the working seam to moisture.
- Glycerol. An equally effective component makes it possible to use glue when processing leather surfaces. Added at the rate of two teaspoons per liter of finished substance.
- Chalk powder combined with wood ash. After sifting this mixture, add it in small quantities. The paste improves putty properties,
- Phenol, ammonia, borax. These components are an excellent antiseptic that prevents the formation of fungus and mold.

Storage
Natural protein-based adhesives have their own characteristics. Users who use such formulations for the first time should take into account some features.
Among them:
- Adding boiled water. This is necessary if you want to make the mass thinner or extend the cooking time of the composition.
- The optimal operating temperature varies from 30 to 70 degrees Celsius. After this, the finished adhesive mass retains its properties for two hours (provided the ambient temperature is 20-25 degrees). Then the composition begins to cool, and its properties are lost.
- Ready-made wood glue cannot be stored for long periods of time. Within a day it loses its properties. In this regard, to use it, it is necessary to use as many granules as required for a specific operation. On the third day, the composition begins to decompose and smell unpleasant, which is due to its protein base. The glue is applied in layers no thicker than 0.2 millimeters. A thicker layer simply will not set properly.

Exploitation
Casein glue can serve as an analogue for gluing wooden furniture. It consists of sodium fluoride, kerosene, copper sulfate and slaked lime. This composition is not used very often because it has a short shelf life and is prone to drying out, changing color and decreasing in volume.
Working with wood glue is somewhat different from using synthetic analogues (for example, PVA (polyvinyl chloride analogue), which is also used for gluing cardboard and wood).
Preparation
The operating algorithm can be derived as follows:
- The glue is prepared according to the above method, with precise control of the cooking temperature.
- All bonding surfaces must be dry and clean. The maximum moisture content for wood is no more than 10 percent (veneer - half that).
- The adhesive mass is applied with a bast or bristle brush to both surfaces, the thickness of the seam is 0.1-0.2 mm.
- You need to wait three minutes. This will allow the adhesives to grip securely and not be squeezed out when connecting the parts.
- After fixing the elements, you will need to grind them together.
- It is advisable to tie the parts to be processed with twine or compress them with a clamp.
- Full use of the product is allowed no earlier than after six hours of exposure.
conclusions
All of these types of wood glue are environmentally safe. It is better to carry out construction operations with the hide version or PVA. These substances have excellent setting parameters and are affordable. For restoration and gluing of delicate and thin surfaces, glue made from fish raw materials is suitable.

Basic criteria for choosing wood glue:
- The lighter and more transparent the granules or tiles, the better the quality of the raw materials used.
- The most expensive and best glue is made from fish waste. It meets the highest standards. Used for restoration work and joining delicate surfaces.
- Bone and flesh composition is used for routine repair work.
.
Animal glues. Glutin (protein) adhesives are obtained from materials rich in collagen, - bones, tendons, skin trimmings and raw animal skins, as well as their lower parts. layer (mesh), scales and swim bladders of fish, etc. They produce: dry adhesives - briquettes, decomposed. shapes, tiles with an area of up to 400 cm 2 and a thickness of up to 1.5 cm, lentil-like granules measuring 3-5 mm, scales,; galertu - jelly with 40-50% dry residue; liquid adhesives solutions in water. Before use, dry adhesives and gallerette are filled with water to swell, and then heated to 65-70 ° C (usually in a water bath). The heated solution is applied to the surfaces to be joined and the joints are maintained under pressure of 0.3-1.0 MPa at 20 °C for at least two days. In the homeland Common industrial adhesives are flesh, bone and fish technical adhesives. Used for joining wood, leather, paper, for preparing adhesive paints, fish glue (due to its unpleasant odor) - for gluing these same materials in technology. The strength of adhesive joints when chipping is at least 6 MPa, 50 °C. Adhesives are characterized by low water resistance and rot under the influence of microorganisms. Casein glues are obtained from casein or products of its processing (for example, halalite). Produced in the form of powders and solutions in alkaline or neutral media. Powders are diluted with water before use. Approximate recipe for liquid glue (in weight parts): 100, rosin 36, liquid glass 40, phenol 2.5, water 600. Solutions are stored for at least 6 months, powders - up to 5 months, after which they are retested for adhesive ability. Duration of gluing at 20 °C from several. min (for paper) up to 24 hours (for wood). max. casein stationery is common, used for joining wood, plywood, paper, cardboard, paper with glass, wood with fabric, etc. The strength when chipping adhesive joints of wood is 10 MPa (after 24 hours in water 7 MPa). Liquid adhesives are non-toxic and non-flammable. Albumin adhesives. Approximate composition (parts by weight): albumen 100, water 900, lime milk 7.5. Retains adhesive properties for 6-9 hours. Adhesives cure at 100-120 ° C, and when ammonia and paraformaldehyde are introduced into their composition, at room temperature. They are used for gluing the same materials as casein adhesives, but form more water-resistant adhesive joints.
Vegetable glues. Most considered common K. Starch-based adhesives - powders containing technical. with the addition of flour and antiseptic. Before use, they are filled with cold water, and then, when hot water is added, they are brewed and cooled. Use ch. arr. for gluing wallpaper and gluing paper. Dextrin adhesives - aqueous solutions of products of partial breakdown of homopolysaccharides; use ch. arr. dextrin obtained from starch. Stored for at least 6 months. They glue paper, photographic paper, cardboard at room temperature for 3-6 minutes, and glue the paper onto glass and wood. NK-based adhesives - solutions natural rubber in gasoline or its aqueous suspensions; dry residue 35% (see Rubber adhesives).
Balsam - a product of fir cleaning resin.
They are glued using hot melt adhesive processing technology, heating the parts to 55-60 °C and cooling to room temperature. Used for gluing lenses, prisms and other optical devices. silicate glass parts. Does not deform optical fiber. details; disadvantage - low (with a separation of 4-6 MPa). Lit.: Collection of technical specifications for adhesive materials, ed. D. A. Kardashova, L.. 1975, p. 383 408, 420-424. G V.
Komarov.
Chemical encyclopedia. - M.: Soviet Encyclopedia. Ed. I. L. Knunyants. 1988 .
See what “NATURAL ADHESIVES” are in other dictionaries:
Synthetic based adhesives monomers, oligomers, polymers or mixtures thereof. K. s. received max. widespread compared to other adhesives (see Natural adhesives. Inorganic adhesives) due to the possibility of easy and targeted change... ... Chemical encyclopedia
Natural or synthetic substances used to join various materials due to the formation of an adhesive bond between the adhesive film and the surfaces of the materials being bonded. The strength of the adhesive connection depends on the adhesion of the cement to... ... Great Soviet Encyclopedia
adhesives- adhesives compositions based on organic and inorganic substances capable of joining (gluing) various materials: wood, leather, paper, fabrics, glass, porcelain, ceramics, metals, plastics, rubber; the action is due to the formation... ... Encyclopedia "Housing"
Based on their origin, carbons are classified into natural (animal, plant, fossil) and synthetic, which, in turn, are divided into thermoplastic and thermosetting. In the aircraft industry, only synthetic compounds are used. Thermoplastic... Encyclopedia of technology
ADHESIVES- natural or synthetic substances used to join various materials. The action is based on the formation of an adhesive bond (see Adhesion) between the adhesive film and the surfaces of the materials being bonded. As adhesives in foundries... ... Metallurgical dictionary
Natural calcined pozzolans- - are materials of volcanic origin, clays, shales or sedimentary rocks activated by heat treatment. Term heading: Minerals Encyclopedia headings: Abrasive equipment, Abrasives, Roads...
Natural porous aggregates- - inorganic granular bulk building materials obtained from porous rocks of volcanic origin (pumice, slag, tuff, large-porous basalts, andesite-basalts and andesites) or sedimentary origin... ... Encyclopedia of terms, definitions and explanations of building materials
adhesives Encyclopedia "Aviation"
adhesives- in the aircraft industry. Based on their origin, carbons are classified into natural (animal, plant, fossil) and synthetic, which, in turn, are divided into thermoplastic and thermosetting. In the aircraft industry, only synthetic... ... Encyclopedia "Aviation"
Natural bitumens- Natural bitumens are amorphous hydrophobic materials extracted from asphalt rocks with organic solvents or boiled down. [Belyaev L.N., Dmitrieva G.K., Ivanov Yu.A., Tkachenko D.B., Yakovlev O.I. Waterproofing of enclosing... ... Encyclopedia of terms, definitions and explanations of building materials
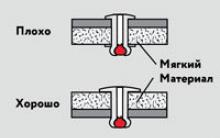
- The strength of the adhesive joint depends on the strength of the adhesive sticking to the surfaces being bonded (adhesion), the strength of the adhesive film and the properties of the materials being bonded.
- The glue is applied to the surface of the parts in a thin layer. The glue fills the roughness, penetrates the pores of the material and, when dried, forms a hard and durable layer that holds these parts together. The strength of the gluing will increase significantly if you compress the parts to be joined with a clamp, a vice, or use a press.
- To obtain a reliable connection, it is necessary to carefully prepare the surface of the parts, for which dust, dirt, grease, and rust are removed from them. Wood, metals, stone
The materials are cleaned with fine-grained sandpaper. Porcelain, glass and rubber are washed with warm water, then (after drying) they are degreased with gasoline. To make the seam less noticeable, mineral pigments of the appropriate color are added to the glue,
Usually 8-10% pigment (by volume) is enough, since a large amount of dye does not make the color of the adhesive film more intense.
- If objects are porous and easily absorb liquids, then the surfaces to be glued are pre-impregnated with a very liquid adhesive solution. Adhesives are applied using a brush, swab, or spatula. Glue is injected into the cracks, for example, with a grease gun (used, in particular, for lubricating a car).
Natural adhesives
- Natural adhesives include adhesives prepared on the basis of substances of plant and animal origin.- Vegetable glues
Note that in pastes to increase their “operational” properties
add some substances:
- gelatin- surface-active substance; reduces the surface tension of water, which improves the wettability of paper (by the way, gelatin itself is an adhesive);
- glycerin and honey- plasticizers, softeners and, to a small extent,
degrees of antiseptics;
- alcohol (rectified)- reduces surface tension, improves wettability, permeability of the glue and accelerates its drying;
- formalin- antiseptic that prevents mold formation;
- potassium alum tanning agent for paper and glue, protecting them from moisture.
Attention! Here and below, adhesive compositions are given in parts (by weight).
Starch paper glue
Compound
Starch 10
Alcohol 4
Water 8
Potassium alum 1
Water 3
- The starch is first poured with a small amount of cold water and stirred until the lumps disappear, then carefully
while stirring, pour in boiling water, heat the paste to a boil, obtaining
homogeneous mass, and add alum dissolved in water.
Glue for paper made from flour (wheat)
Compound
Flour 6
Water 6
Potassium alum 1
Glycerin 1
Water 250
- Flour is diluted in water. Alum previously dissolved in water is added. Then pour boiling water over the mixture, add glycerin and heat to a boil. To obtain high-quality glue without lumps, do not forget to stir it!
Glue for thick paper made from flour and gelatin
Compound
Wheat flour 40
Technical gelatin 5
Glycerin 8
Aluminum-potassium alum 3
Formalin 4
Alcohol (rectified) 2
Water 600
- The glue is boiled in an enamel or aluminum container. To avoid clumping, the flour is diluted in a small amount of cold water, then poured with hot water and placed in a water bath, gradually heating the water to a boil. After this, alum dissolved in hot water is introduced into the paste, everything is filtered through double gauze and gelatin, previously soaked in water, is added. After the resulting paste has cooled, alcohol and glycerin are poured into it, thoroughly mixing the glue.
- As an antiseptic, you can add camphor to the glue (0.5% by weight of the solution or camphor alcohol (1-2%).
Glue for restoration of graphic works
Compound
Wheat flour 20
Glycerin 1
Potassium alum 0.5
Alcohol (rectified) 2.25
Gelatin (1% solution) 150
- Glue is prepared in the same way for thick paper
Paste for gluing engravings
Compound
Wheat flour 50
Aluminum-potassium alum 7
Formalin 7
Water 2250
- Flour is diluted in a small amount of cold water in an enamel or aluminum bowl, the lumps are rubbed by hand. Then potassium alum is added. In another bowl, boil water, add it to the paste and heat it in a water bath,
stirring thoroughly as it thickens quickly. Then the paste is cooled for 10 minutes and poured into a glass container, adding formalin.
- To avoid the formation of a crust when the paste cools, place a sheet of paper on the surface and pour in a little water. The prepared paste is suitable for use for 4-5 days, then it becomes thick (it can be softened with water).
- When working, the paste is applied in a thin, even layer, which speeds up its drying and does not cause stretching of the paper.
Pastes for gluing wallpaper (for gluing walls)
Compound
Rye flour 1.5
Wood glue
(10% solution) 1
Water up to 10
- Sift the flour and dilute it in 2 liters of warm water, and then brew it with boiling water with continuous stirring. Separately, prepare a solution of wood glue and, after heating it to a boil, pour it into the prepared flour paste. If the paste has not brewed well, it must be boiled before use. The paste must be passed through a sieve with a fine mesh (600 holes/cm2).
- To cover walls with waste paper (newspapers), use less flour - 1.2 kg.
Paste for pasting simple wallpaper
Compound
Rye flour (or starch) 1.2-1.5
Potassium alum 0.05
Water up to 10
- The paste is prepared in the same way as in the previous recipe. Alum or carbolic acid (25 g per 10 l) is administered as an antiseptic.
- To cover walls with high-quality wallpaper, instead of 1.2-1.5 kg of rye flour, take 2 kg of wheat flour and be sure to filter the paste through a sieve (600 holes/cm).
Paste for gluing linkcrust
Compound
Wheat starch or baked flour 3
Wood glue (10% solution) 2
Alum or carbolic acid 0.03-0.05
Water up to 10
- This glue is prepared in the same way as paste for gluing walls. Alum is dissolved in water before being added to the paste. After cooling, the paste is passed through a sieve (600 holes/cm2).
- Adhesives based on substances of animal origin
- When collagen, which is the adhesive base of bone, flesh and fish glue, is heated in water, it turns into gluten, which is why these glues are usually called glutinous (in everyday life they are known as wood glue). Chemical composition
and the structure of collagen have not yet been sufficiently studied.
- Glutin has the following properties: it swells in cold water, dissolves when heated, forming colloidal solutions, which, after cooling, turn into an elastic gelatinous mass. Under the influence of high temperatures, as well as when treated with acids and alkalis, glutin decomposes and loses its adhesive ability.
- Under the influence of various substances (potassium dichromate, formaldehyde, soluble compounds of aluminum and iron), glutin loses its ability to swell in water and becomes insoluble.
Collagen-based adhesives
- Bone glue is made from degreased animal bones. Hide glue is obtained by boiling flesh in water.
- Bone glue is produced in the form of solid tiles, small pieces
and in the form of glue jelly, the so-called gallerta. Hide glue is produced in the form of solid tiles, pieces, and flakes.
- To work, hard bone and flesh glues are dissolved in water at a temperature of 60-65 ° C. Heating the glue above 70 °C leads to a decrease in its viscosity and a decrease in adhesive ability.
Composition of liquid glue
Bone or flesh glue (hard) 100
Water 200
Phenol (5% solution) 2
- The tile adhesive is loaded into the glue cooker, filled with water and left to swell for 8-10 hours. Then the adhesive is boiled in a water bath at a temperature not exceeding 60-65 °C. The glue is considered ready if, when grasped with a brush (brush), it flows off without noticeable clots. A phenol solution is added to the finished glue solution to prevent it from rotting.
Technical gelatin
is pure glutin. Unlike bone and flesh glues, it is obtained from selected raw materials: the horny core, that is, the button bone, the frontal bone.
- The following types of gelatin are produced: food, photographic and technical.
- Technical and photographic gelatins are widely used in painting for priming canvases, as well as for gluing paper, etc.
- To prepare gelatin glue, dry technical gelatin is poured with a small amount of water and allowed to swell (swelling of gelatin glue occurs in about 1 hour). The swollen gelatin glue is heated in a water bath at a temperature of 65-70 °C.
- For sizing canvas, a 6-8% glue solution is usually used; for gluing paper and preparing emulsion primer, a 12-15% solution is used. A small amount of glycerin (0.2-0.3% by weight) is introduced into the glue as a plasticizer.
Fish glue also belongs to collagen. The raw materials for its production are sturgeon swim bladders (lower grades of glue are made from fish heads, scales, and bones). The swim bladder consists almost entirely of pure collagen.
Isinglass
- To obtain fish glue, the swim bladder is kept for several hours in a 15-20% salt solution, then soaked in clean water and dried in air. Then the outer shell is peeled off from the bubble, leaving the inner one, which is used for glue (it is finally dried and plates are pressed from it).
- To prepare liquid glue for work, the glue plates are soaked entirely for 24 hours in cold water. The swollen glue is softened and kneaded, then boiled in a water bath, like bone and flesh glue, filtered through gauze or a sieve and an antiseptic is injected into it.
- To prepare emulsion primer, take a 12-15% glue solution.
- During restoration work, for example, to strengthen fragile paintings peeling off from the canvas, a 5-6% solution is used. Honey is added to the glue being prepared as a plasticizer in a ratio of 1:2.5.
- In conclusion, we present recipes for simple adhesive compositions based on collagen adhesives. They are used for gluing wood, glass, porcelain, earthenware, ceramics and for joining wood with fabric or other material. Such adhesives provide a strong seam, they are easy to use, and the components for their preparation are not in short supply.
Universal non-gelling (non-thickening) adhesive
- Tile wood glue is crushed and soaked (12 hours) in vinegar essence diluted in half with cold water. After the glue has completely swollen, the excess liquid is drained (it can be reused), and the swollen glue is carefully dissolved over low heat. The resulting syrupy mass has adhesive properties and does not thicken in the cold; When stored, this glue does not mold or rot. If the glue turns out to be somewhat runny, thicken it by heating it for some time in a water bath. The duration of heating depends on the required thickening of the glue. This glue should be stored in a jar with a tight-fitting lid.
Glue "Syndeticon"
- This glue also does not gel and produces a strong adhesive joint.
- First, sugar-lime syrup is prepared; To do this, dissolve half a glass of granulated sugar in 1 liter of hot water and add 100 g of freshly slaked lime (fluff). The mixture is heated with stirring for 3 hours (the mixture should be well heated, but it should not be brought to a boil). The sugar-lime solution is allowed to settle and the liquid is drained. 500 g of pre-crushed tile adhesive are soaked in the drained solution (12 hours). The swollen glue (excess liquid is drained) is dissolved over low heat. The finished adhesive mass does not gelatinize and is used cold.
- Syndeticon glue produces a strong seam; it is used to glue paper, cardboard, wood, porcelain, earthenware, ceramics, and is also used for gluing fabric to wood, glass, and metal; Skin can be glued onto the same materials. Metal to metal or glass to glass can be glued together if a fabric spacer is placed between them.
- Syndeticon glue is well preserved in a closed jar; it does not mold or rot.
Glue for gluing leather to cardboard
Compound
Wood glue 10
Turpentine 1
Water 20
Starch 20
Water 30
- Mix glue, turpentine and water, boil the swollen glue in a water bath, add starch and water and cook again until the starch dissolves.
Glue for gluing leather to metal
Compound
Wood glue 1
Acetic acid 1
(8% solution)
Turpentine 1
- The wood glue is soaked until it swells completely, then the water is drained and acid and turpentine are added to the glue. After this, the glue is heated in a water bath, stirring thoroughly until dissolved.
- Apply hot glue to a dry, clean metal surface and press the skin.
Fish glue for earthenware
Compound
Fish glue 1
Acetic acid 4
(20% solution)
Water 4
- The glue filled with water is allowed to swell, then acetic acid is added and boiled in a water bath for 45-60 minutes.
Fish glue for gluing engravings
Compound
Fish glue 12
Glycerin 0.5
Water 87.5
- The glue is poured with a small amount of water, and when it swells, pour in the specified amount of water and cook in a water bath. Glycerin is added to the finished cooled glue.
Fish glue for edging
Compound
Fish glue 15
Wood glue or gelatin 15
Honey 5
Water 65
- The glue is poured with a small amount of water; when it swells, it is cut into small pieces with scissors, mixed with wood glue, filled with water and boiled in a water bath until a homogeneous mixture is obtained. Then honey is added to the slightly cooled mixture.
- Casein based glue
- Pure casein is a yellowish-white powder. Casein is characterized by both acidic and alkaline properties (with a predominance of acidic ones). It does not dissolve in water and organic solvents, but only swells, but it dissolves well in aqueous solutions of ammonia, borax, phosphate salts, soda ash and caustic soda, forming colloidal solutions.
- To work, casein glue powder is dissolved in an alkaline solution, obtaining a colloidal-viscous mixture. The amount of alkali used to dissolve casein depends on the type of alkali and the concentration of the casein solution.
Liquid casein glue (“classic”)
Compound
Casein (powder) 100
Caustic soda 4
Soda ash 16
Ammonia (28% solution) 13
Bura 15
Trisodium phosphate (crystalline) 12.5
Sodium fluoride 6.4
Water 600
- Casein dissolves in alkalis both when heated and at room temperature. Two methods are used to dissolve casein. The glue sold in stores is a mixture of casein and slaked lime.
- 1st method. Casein is poured into a vessel, filled with 3-4 times the amount of water and left for 8-10 hours, after which the swollen casein is thoroughly stirred and an alkali solution is gradually added.
- 2nd method. Casein pre-swells in water heated to 35-40°C, after which, with stirring, an alkali solution is added to it and the temperature is raised (in a water bath) to 60°C; in this case casein dissolves. With this method, the dissolution rate is much higher.
Casein cement glue
- Casein-cement glue is used for high-strength gluing of boards, frames and other wood products. The tensile strength of such adhesive joints is 80 kgf/cm2.
Casein (powder) 100
Portland cement
(grade 400) 75
Water (at temperature
10-20°C) 220-250
- To prepare casein-cement glue, pour water into a glass bottle, and then gradually add casein powder while stirring. If the glue thickens too much, stop stirring and allow the adhesive solution to liquefy (then you can continue stirring). After 30-40 minutes, add cement, previously sifted through a sieve (64 holes/cm2). Mixing is carried out until a homogeneous mass is obtained (approximately 50-60 minutes). After 10-15 minutes of settling, the glue is ready for use. Working condition of glue 3 h.
- When gluing materials with a thickness of more than 5 mm, the parts are compressed with a force of 3-5 kgf/cm2, when gluing materials with a thickness of 0.5 to 4 mm - 1-2 kgf/cm2.
- The gluing time depends on the room temperature and lasts approximately 12 hours.
- Casein-cement glue is used not only for gluing wood, but also for joining stone materials.
- To prepare casein yourself, use cottage cheese with minimal fat content: 100 g of cottage cheese is mixed with 200 ml of hot water, stirred, drained (and so on 3 times). After this, separate the cottage cheese (draining the water through cheesecloth), squeeze it out and place it in an enamel pan, into which 0.5 liters of a 3% borax solution is poured.
- The contents are heated to a temperature of 40-50 °C, stirred and left for 3-4 hours. After this, stir again until the curd is completely dissolved.
Lime-casein adhesive for wood
Compound
Casein (powder) 50
Slaked lime 8
Water 150
- Casein is soaked in water for 30-40 minutes and lime is added. The shelf life of the glue is only 40-45 minutes.
Lime-silicate casein adhesive for plywood and oak wood
Compound
Casein (powder) 100
Slaked lime 10-15
Liquid glass (specific weight 1.34 g/cm3) 15
Water 300-400
- Casein is soaked in water for 30-40 minutes and the remaining components are added.
Silicate-casein adhesive for glass
Compound
Casein (powder) 1
Liquid glass 6
- When gluing, objects are pressed and left until the glue hardens completely (3-4 hours).
- Albumin-based glue
Egg white based adhesive for stone and ceramic materials
Compound
Egg white 3
Quicklime 1
Plaster 5
Water 1
- Separately mix the protein with lime, and the gypsum with water. The resulting compositions are thoroughly mixed.
Synthetic adhesives
- Despite a number of advantages (availability, low cost, ease of handling), natural adhesives are not universal and have low resistance to microorganisms and water. Therefore, these adhesives are increasingly being replaced by numerous synthetic adhesives, characterized by high bonding strength of various materials and sufficient resistance to external factors.- The most famous and widespread synthetic adhesives, which have proven themselves in practice, should be considered adhesives BF-2, BF-4 and BF-6, Moment, epoxy adhesives of various brands, etc.
- Phenol based adhesives
Adhesives BF-2 and BF-4 They are a thick transparent liquid of light brown color. They are used for gluing aluminum and its alloys, copper and its alloys, steel of various grades, plastics of thermosetting and thermoplastic types, for example, bakelite, aminoplast, textolite, organic glass, as well as materials such as wood, plywood, ceramics, porcelain, glass , fiber, leather.
- When gluing, proceed as follows: the edges of the objects to be joined at the joint are smeared with a thin layer of glue using a wooden stick or brush and dried in air until the glue stops sticking to the finger. Then a second, thicker layer of glue is applied, which is again slightly dried. The parts to be glued are tightly connected - clamped with a clamp or tied with twine - and heated to accelerate polymerization.
- To heat small-sized products or parts to be glued, place them in a saucepan or metal can and fill them with water. The water is brought to a boil, which should continue for at least 3 hours, after which the pan is removed from the heat, cooled in air and the products are removed. It is more convenient to heat the products or parts to be glued in a thermostat, where it is easier to create favorable conditions for polymerization of the glue. Heat treatment of parts at 120-150 °C requires 1 hour.
- The resulting adhesive joint after hardening is not afraid of moisture, is resistant to low (-50 ° C) and high (+100 ° C) temperatures, and can withstand the effects of boiling water, gasoline, alcohol, oils, kerosene.
Glue BF-6 is a thick transparent liquid of light brown or yellow color, used for gluing fabric products.
- The areas of the products to be glued are first cleaned of dust with a brush, moistened with warm water and wrung out well. Having straightened the edges of the wetted areas of the fabric, apply two layers of glue to them and air dry (after applying each layer) until the glue stops sticking to the finger. Then the parts of the fabrics to be glued are connected and carefully smoothed with a hot iron through a moistened fabric for 2-3 seconds at intervals of 10-15 seconds until the surface to be glued becomes dry.
- Cold-curing urea adhesives
.
Glue KM-3-liquid (low-viscosity) The adhesive components are stored separately until use. The tensile strength of the adhesive joint (on ash and oak samples) is not less than 130 kgf/cm2. KM-3 adhesive is limitedly water-resistant and petrol and oil resistant.
Compound
Powdered urea-formaldehyde resin grade SMK-2 100
Ethyl alcohol 10
Lactic acid 400
Water (temperature
16-20°C) 50
- When preparing the adhesive mixture, the temperature of the constituent components should be 15-20 C. Water, lactic acid and alcohol are poured into the vessel. With continuous stirring, SMK-2 resin powder is gradually poured into the mixture. After this, the mixture is stirred for 20-40 minutes until lumps of undissolved resin disappear, then filtered through a brass sieve No. 60 (576 holes/cm2). To maintain the temperature of the glue at 20 ° C, it is cooled with water.
- At ambient temperatures up to 20 °C, the glue remains in working condition for 2-4 hours, but its viscosity increases. Gluing temperature is room temperature.
- The glued parts are kept for 1.5-2 hours in a press, vice, under a load, etc. When joining materials with a thickness of more than 5 mm, the specific pressure should be 3-5 kgf/cm2, when gluing thin ones (0.5-4 mm ) materials - 0.5 - 1 kgf/cm2. When gluing without pressure, no holding time is required.
.
Glue K-17-liquid (low-viscosity) The glue components are stored separately, in a ventilated place at a temperature of 0-20 ° C, in tightly sealed containers, but not more than six months. The strength of the adhesive joint of wood (oak or ash) is at least 130 kgf/cm2. K-17 adhesive is limitedly waterproof and petroleum oil resistant, and temperature stable.
Compound
Urea-formaldehyde resin
MF-17 with the addition of 8% wood
flour (based on the mass of pure resin) 100
Oxalic acid Selected
(10% aqueous experimentally
solution)
- The temperature of the glue components during its manufacture should be 16-20 °C. The components are mixed for 5-10 minutes. If there is no wood flour in the resin, the hardener is introduced into the resin one day before preparing the glue.
- At a temperature of 20 °C, the adhesive hardens within 3-5 hours from the moment the hardener is introduced.
- Gluing temperature is room temperature. When gluing materials with a thickness of more than 5 mm under pressure, the latter should be in the range of 3-5 kgf/cm2, for thin materials (0.5-4 mm thick) - 1 kgf/cm2. The gluing time depends on the room temperature. When gluing without pressure, the holding time is 12-15 minutes under pressure - slightly less.
.
Glue KM-12 - liquid (low-viscosity) The adhesive components are stored separately until use. Depending on the temperature conditions, the shelf life of the resin is from 1 to 5 months, the storage temperature is 15-20 ° C. The tensile strength of the adhesive joint on laminated wood samples (ash or oak) is no less than 130 kgf/cm. KM-12 adhesive is limitedly water-resistant, petrol- and oil-resistant.
Compound
Urea-formaldehyde resin grade M 100
Ammonium sulfate
(40% aqueous solution) 3.5
- When preparing the adhesive mixture, the temperature of the components should be 20 °C. The glue components are mixed for 15-20 minutes.
- At ambient temperatures up to 20 ° C, the glue remains in working condition for 3-6 hours, at temperatures above 20 ° C - from 2 to 4 hours. When gluing materials with a thickness of more than 5 mm, parts are maintained under a pressure of 3-5 kgf/cm, at gluing thin materials (0.5 mm thick) - at 1 kgf/cm2.
- The holding time when gluing under pressure depends on the room temperature and is usually 1.5-2 hours. When gluing without pressure, holding time is not required.
- Polymethacrylic adhesives
Polymethacrylic adhesives used for gluing organic glass and similar materials.
Compound
Organic solvents 100
Organic glass
(shavings or sawdust) 3-4
- The shelf life of polymethacrylic adhesive solutions is determined by their viscosity. The approximate storage period should be no more than a month at a temperature not exceeding 25 ° C in a closed glass container, protected from light.
- The tensile strength of the adhesive joint is equal to the strength of organic glass (on average 120 kgf/cm2).
- To prepare the glue, pour the required amount of sawdust or organic glass shavings into the glue bottle and then, stirring, pour in the solvent. Stirring is continued for 25-30 minutes at a temperature of 15-25 ° C, after which the mass is left
in a closed vessel for 2-3 days at the same temperature for swelling and dissolution of organic glass. To speed up dissolution, the mixture is stirred periodically. The adhesive solution is considered suitable after 2-3 days from the start of its preparation. The temperature during gluing and curing of glued materials should not be lower than
18 °C. It is necessary to glue plexiglass blanks up to 4 mm thick under a pressure of 0.5-1.5 kgf/cm2, with a thickness of more than 4 mm - under 2-5 kgf/cm2.
Glypthal glue AMK
- Glypthal glue AMK, produced with the MHP marking, is a solution of glypthal resins in organic solvents with the addition of a drier.
- AMK glue is used for gluing wool, glass and cotton fabrics to metal surfaces, for gluing glass and gluing ceramics to metals.
- When gluing, a layer of glue is applied to a plate of degreased metal (consumption 100 g/m2). After drying it for 2 hours at 15-25 ° C, apply a second layer of glue (the same consumption) and immediately apply the fabric. The fabric is carefully smoothed to the surface and a third layer of glue is immediately applied on top of the fabric (consumption 200 g/m2). The materials to be glued are dried at 70-80 °C for 4 hours.
Glue-71
- Glue-71 is universal, intended for gluing washable wallpaper, facing tiles, linoleum and other materials on lime-whitened, oil-based, concrete, and wooden substrates. It has high adhesive properties, thanks to which the adhesive strength is not lost when washing surfaces lined with wallpaper, tiles, and linoleum.
- The glue is harmless to use, non-toxic, non-flammable, and is packaged in tightly closed metal cans, which allows it to be stored for a long time.
Polyvinyl acetate glue (PVA)
- PVA glue is made on the basis of polyvinyl acetate emulsion.
- Glue is used for gluing wood, paper, cardboard, cotton fabrics together, as well as for gluing fabrics with wood and glass and metal with wood.
- An aqueous, unplasticized emulsion is used as the basis for PVA glue.
- The glue is applied in a thin layer onto a previously cleaned surface. Duration of open exposure (before joining parts) - 3 minutes.
- The surfaces to be glued are connected under pressure. Bonding temperature is 15-30 °C. Duration of gluing is 1-3 hours. The strength of adhesive joints, for example fabrics when delaminating, is 1.2-1.4 kgf/cm2.
- The glue must be stored at a temperature not lower than -0 °C. Guaranteed shelf life is 6 months from the date of manufacture.
The process of joining wooden elements using an adhesive takes into account the properties of the material and the glue itself. Additionally, it is necessary to take into account the features of further operation of the finished product. This condition will be affected by the ability of the synthetic or natural glue to withstand moisture, temperature changes, or direct exposure to the sun.
When choosing how to glue wood to wood, you need to familiarize yourself with the properties of the selected glue and the material itself. The furniture industry offers ready-made furniture sets and raw materials for self-production of the necessary structures. In the latter case, natural wood is produced (which is an expensive pleasure) and various options for plywood, solid wood, and veneer. The material is different:
- operational characteristics;
- quality of the wood composite used;
- properties of interaction with substances of natural or chemical origin.
Therefore, gluing wood requires careful preparation of all elements and the correct choice of glue used.
The quality of the process of gluing wooden parts allows you to create a solid structure with high strength characteristics from several elements. This technique is often used in the construction and furniture industries. In everyday life, craftsmen use wood glue for the purpose of restoration or full production of corresponding products.
The process of gluing wooden blocks
Advice! Additional screwed-in screws, dowels, and the use of dowels will help strengthen the strength of the glued element.
Experts recommend pre-treating the composite. This technique helps clean surfaces from unnecessary excess, level the surface, and remove waste dust. During the cleaning process, the pores of the material are additionally “opened” and the fibers are able to absorb the applied layer of glue much more efficiently. The penetrated molecules of the substance are connected to each other in the body of the wood, forming thin thread-like plexuses. This “web” additionally glues the wood fibers together, promoting a stronger connection of the elements.
It is important to choose high-quality materials for work. This will affect the final strength of the product.
- A composite of ꟾ or ꟾꟾ grades is selected. This means that the material is selected from dense wood, on which there are no or little visible knots. Chips and cut cracks are not allowed. This assortment is distinguished by a beautiful natural pattern and uniform texture.
- The components of the glued structure must have the same shade.
- Defective raw materials are completely eliminated.
Important! In the furniture industry, the use of ꟾꟾꟾ grade wood (cracked material with dried knots or chips) is not allowed. This composite is difficult to glue and is characterized by low strength.

Wood range
As a result of properly performed work, the glued parts form a more durable product than a monolithic structure made of solid wood.
Connection types
In carpentry practice, there are several ways to firmly and aesthetically connect wood parts. A strong seam is formed between the parts using glue, which increases the permissible force impact on the finished product and extends the service life of the entire structure.

Recommendations! For gluing, it is necessary to select workpieces with the same type of cut (radial or tangential). With the latter technology, the board has a pronounced pattern, which requires a textured selection of elements.
When gluing the boards into a solid blank, the craftsmen monitor the correct direction of the growth rings. The lines should form an angle at the junction of about 15° or generally be directed in opposite directions.

Direction of growth rings of glued blanks
Having folded the boards or beams, you need to check the joints in width and length. In these directions, the heartwood and sapwood should be aligned respectively.
Important! The thickness of the adhesive seam must correspond to the limits of 0.08 - 0.15 mm. This indicator is directly proportional to the decrease in the strength of the finished joint.
Craftsmen receive the parts or workpieces they need in terms of shape, size and strength. During the work, processing technology and gluing rules are observed.
The connection of composite parts by means of gear milling is used for the wood joining process:
- along the long side of the workpiece;
- in width;
- end planes.
The finished material can withstand large mechanical loads of a static and dynamic nature. The spliced parts are ground and leveled. With additional cladding, such connections correspond to the characteristics of solid structures.
Shield selection
In the furniture industry, it is recommended to select composites with an end width of about 2 cm. If you plan to precisely fit finished parts, then it is better to choose a material “with a reserve”. During the process of chipping, sanding and finishing, the excess part will be removed with carpentry tools.
To make a standard furniture panel, a board with an end of about 5 cm is cut. As a result, the two formed blanks produce the same pattern and shade. Such elements look more natural and aesthetically pleasing as part of one wooden product.
The technology for selecting raw materials involves the use of homogeneous wood. The cut should have a width of 1.2 m. This will allow for high-quality processing of the ends.
The length of the blanks should have a margin of 4-5 cm. This technology will allow you to correctly glue the wood and accurately process the finished product.
Types of adhesive composition
In carpentry, glue with different physical and chemical properties is used. This allows you to create workpieces for the appropriate purpose and with certain performance characteristics. The mixtures on the market are divided into groups.

Wood glue
- Synthetic origin. The composition includes a mixture of polyvinyl acetate and synthetic resins. The main characteristics of such connections are:
a) resistance to wet environments;
b) no fungus or mold forms in taped seams;
c) high strength of the workpiece.
The percentage of formaldehyde contained in the glue is important. Excess of the substance is characterized by volatility, a pungent odor, and harmful effects on the human body.
Modern production of PVA-based glue is harmless and suitable for household use. This composition is excellent for gluing wood.

PVA for carpentry
The carbinol-based mixture is available in two substances:
a) liquid – mixed with a hardener and is excellent for joining different materials;
b) paste - characterized by the addition of a special filler and is suitable for working with stone, porcelain, and wood.
On sale you can find glue marked BF-2 or BF-4. The basis of these compounds is a resinous substance, which is diluted with an alcohol composition. The standard packaging is a metal tube with different capacities. Before gluing wood, it is recommended to read the instructions on the tubes of such glue.
2. Natural origin. Such mixtures include compositions based on animal, plant or mineral components. Typically, the release form is a semi-finished product, which is combined with a hardener and prepared before direct use.
Many compositions are similar in preparation technique:

Attention! The general provision in such instructions is to prohibit direct contact of the container with fire.
Casein glue is produced from low-fat cottage cheese mixed with an alkaline composition. The powder packaged in bags has a yellowish tint. The bulk mixture is diluted in water at room temperature with constant stirring in a ratio of 1:2 powder/water, respectively. The finished substance has no restrictions on the temperature of use, copes well with a humid environment and guarantees a strong connection.

Casein glue
Vegetable adhesives include compositions with protein, starch, and castor bean compounds. Such substances are characterized by:
a) low degree of adhesion;
b) long setting period;
c) high water absorption.
Therefore, craftsmen do not recommend using such glue for working with wood.
In vegetable glue, the addition of cellulose esters is allowed. The latter composition has found application in carpentry, and is represented by the AGO and AK-20 brands. This nitro mixture has a liquid-like structure, already prepared for use.
Advice! If the nitro glue has thickened, you can add a few drops of solvent to it.

Important! Pressed tiles strongly absorb moisture, which negatively affects the adhesive characteristics of the prepared mixture. Therefore, an important storage condition is a completely dry place.
High-quality tile adhesive has special characteristics:
- transparency;
- fragility (a piece can break off);
- broken with sharp fragments.
Attention! If the purchased tile adhesive is flexible and has a darkish tint, it means the substance is of low quality.
Wood joining process
Before applying the adhesive, the material is prepared for work:
- boards, boards, beams are cleaned;
- the material must be thoroughly sanded;
- check the smoothness and evenness of surfaces for connections;
- the workpieces are wiped free of dust.
The diluted mixture or ready-made glue must be applied with a flat and wide brush to both planes. The thickness of the applied layer is “regulated” according to the recommendations on the packaging and the type of wood used. Craftsmen are guided by the rule: the thinner the ends being connected, the less glue is applied to the surface.
When applying a layer, it is desirable to achieve slight wetting of the material. With the correct dosage, an even strip between the planes of the wood will act as excess.

Extruded adhesive with correct seam thickness
If drips have formed during work, they must be removed. The glue can be easily removed with a spatula in a slightly set state.
The applied substance must be absorbed into the wood. Therefore, the working parts are left separately for a short time for aging. While waiting, there should be no open windows, no air conditioners, or drafts in the room.
Attention! If natural glue is applied while hot, then you need to instantly connect both halves of the wood. Otherwise, the substance will lose its effectiveness.
After connecting the parts, it is necessary to ensure additional pressing of the glued material. To do this, the entire workpiece is crimped with clamps, a vice, and special frames. The compression force can reach 1.2 MPa.

Holdfast
Elements glued in accordance with all rules and regulations are distinguished by strength and durability. Such pieces of furniture or details do not have visible seams and look quite aesthetically pleasing.










Home care for hippeastrum
Create a photo book online with your own hands
How to make a New Year's wreath on the door with your own hands New Year's wreath from a foam blank
Drip irrigation for a summer residence
How to sharpen kitchen knives correctly - instructions for use How to sharpen a knife on a whetstone