New time humanity, in terms of relations with natural environment, beginning almost under the same sign, and throughout its history - the existence of human civilization is still the largest environmental problem of our time. But since ecology is the science of the relationship of species with the environment, and in this case we are more interested in one particular species - the person himself - we will leave this problem without a solution and move on to others, albeit less global, but still much more amenable to solution. .
Over the past millennia, civilization and technology have made a significant leap in their development. The appearance of human settlements has changed, the languages of antiquity have sunk into oblivion, appearance"reasonable man" has changed beyond recognition. But one thing in a person's life has remained unchanged: everything that civilization is able to collect in its barns, store behind high fences of special bases, shove home cabinets and refrigerators on the shelves - all this is taken from the environment. And the whole rhythm of human life, both in past eras and today, was determined by one thing - the possibility of access to certain natural resources.
How do pollutants from the lithosphere get into the soil? Various soil pollution, most of which are anthropogenic in nature, can be divided according to the source of these pollution entering the soil.
With precipitation. Many chemical compounds (gases - oxides of sulfur and nitrogen) released into the atmosphere as a result of enterprises, then dissolve in droplets of atmospheric moisture and fall into the soil with precipitation.
Settling in the form of dust and aerosols. Solid and liquid compounds in dry weather usually settle directly in the form of dust and aerosols.
With direct absorption of gaseous compounds by the soil. In dry weather, gases can be directly absorbed by the soil, especially wet soil.
With plant debris. Various harmful compounds, in any state of aggregation, are absorbed by leaves through stomata or settle on the surface. Then when leaves fall, all these compounds enter the soil.
Soil pollution is difficult to classify; in different sources, their division is given in different ways. To summarize and highlight the main thing, the following picture of soil pollution is observed:
Garbage, emissions, dumps, sludge;
heavy metals;
pesticides;
Mycotoxins;
radioactive substances.
There are natural resources that humanity needs, like air. But, perhaps, there is no such resource, except for the air itself, the absence of which would become an insoluble problem for a person in less than a minute.
It is known that atmospheric pollution occurs mainly as a result of the work of industry, transport, etc., which together emit more than a billion solid and gaseous particles “to the wind” every year.
The main air pollutants today are carbon monoxide and sulfur dioxide. But, of course, we must not forget about freons, or chlorofluorocarbons. It is them that most scientists consider the reason for the formation of the so-called ozone holes in the atmosphere. Freons are widely used in production and in everyday life as refrigerants, foaming agents, solvents, as well as in aerosol packages. Namely, with a decrease in the ozone content in the upper atmosphere, doctors attribute an increase in the number of skin cancers.
It is known that atmospheric ozone is formed as a result of complex photochemical reactions under the influence of ultraviolet radiation from the Sun. Although its content is small, its importance for the biosphere is enormous. Ozone, absorbing ultraviolet radiation, protects all life on earth from death. Freons, getting into the atmosphere, under the influence of solar radiation, decompose into a number of compounds, of which chlorine oxide most intensively destroys ozone.
Blessed raindrops - another gift from heaven - have always made people happy. But in some areas the globe the rains have become a serious hazard. A complex and difficult problem of acid rain has arisen, which was first raised at the international level by Sweden at the UN conference on the environment. Since then, it has become one of the main environmental problems of mankind.
Acid rains have a detrimental effect on the nature of water bodies, damage forest vegetation and agricultural crops, and finally, all these substances pose a certain danger to human life.
The third, no less important than the sky above your head and the earth under your feet, factor in the existence of civilization is water resources planets.
Mankind uses mainly fresh water for its needs. Their volume is slightly more than 2% of the hydrosphere, and the distribution of water resources across the globe is extremely uneven. In Europe and Asia, where 70% of the world's population lives, only 39% of river waters are concentrated. The total consumption of river waters is increasing from year to year in all regions of the world. It is known, for example, that since the beginning of this century, fresh water consumption has increased 6 times, and in the next few decades it will increase by at least 1.5 times.
The lack of water is exacerbated by the deterioration of its quality. The waters used in industry, agriculture and everyday life are returned to water bodies in the form of poorly treated or generally untreated effluents.
Thus, pollution of the hydrosphere occurs primarily as a result of the discharge of industrial, agricultural and domestic wastewater into rivers, lakes and seas. According to the calculations of scientists, at the end of the 20th century, 25,000 cubic kilometers may be required to dilute these same wastewaters. Fresh water or almost all the really available resources of such flow! It is not difficult to guess that it is precisely in this, and not in the growth of direct water intake - main reason aggravation of the problem of fresh water.
At present, many rivers are heavily polluted - the Rhine, Danube, Seine, Ohio, Volga, Dnieper, Dniester, etc. Pollution of the world's oceans is growing. And here a significant role is played not only by sewage pollution, but also by the ingress of a large amount of oil products into the waters of the seas and oceans (Fig. 6.). In general, the most polluted inland seas are the Mediterranean, North, Baltic, Inland Japan, Java, as well as the Biscay, Persian and Mexican Gulfs.
In addition, man carries out the transformation of the waters of the hydrosphere through the construction of hydraulic structures, in particular reservoirs. Large reservoirs and canals have a serious negative impact on environment: change mode ground water in the coastal strip, affect soils and plant communities, in the end, their water areas occupy large areas of fertile land.
By changing his world, a person, whether he wants it or not, significantly interferes in the life of his neighbors on the planet. According to the International Union for Conservation of Nature, since 1600, 94 species of birds and 63 species of mammals have become extinct on Earth. In addition, rare insects are decreasing in number and disappearing, which is associated both with the reaction to the use of various kinds of pesticides and with the destruction of their indigenous habitats.
The mechanism of death of a species is much simpler than it can be imagined. Zoologists realized this when they were able to analyze a large number of unsuccessful cases of animal acclimatization in lands that are certainly suitable for imported species. It turned out that the importation of small groups of animals ended in failure. It turned out that 2-3 pairs of animals in the absence of constant, even relatively rare contacts with their own kind, cannot inhabit the territory. In most cases, their ability to reproduce is suppressed or they die from the so-called "stress", or tension disease. A similar situation arises with a large rarefaction of the natural population. It is absolutely not necessary to destroy every one of the animals in order to doom a species to extinction, it is enough to significantly reduce its numbers, reduce or separate habitat areas, in which humanity, especially in recent centuries, has noticeably succeeded.
the greenhouse effect
When a few decades ago scientists started talking seriously about the manifestation on our planet greenhouse effect- their statements were taken seriously only by a narrow circle of the same scientists. The events recent years: the unheard-of heat in North America and the European continent, which caused a sharp deterioration in health even in healthy people, numerous heart attacks and heat strokes, crop burnouts from droughts and numerous floods, hurricanes and storms - not in words, but in deeds convinced us of the opposite. This sad reality is no longer forecasts, but news reports ... The average temperature on our planet is + 15 degrees, this is maintained due to the greenhouse effect. It was thanks to him that the conditions were created for the emergence of life on Earth (without this phenomenon, the temperature would have been -15). As you know, the absorption of infrared rays in the atmosphere occurs due to carbon dioxide, as a result of which heat is released and a comfortable habitat is created for the animal and plant world. So, the more carbon dioxide, the more heat. With each new step in the technogenic development of civilization, humanity is rapidly destroying the harmony created by nature, using two reliable methods for this: increasing production capacity and massive destruction of forests. According to the UN, in thirty years this will lead to an increase in the general temperature background of the planet - by 3 degrees. It would seem - a little. It would seem that this will not affect us yet ... More - or already? 30 years is only a third of a person's life... For the time being - a third... Is it worth being optimistic, or are we more like an ostrich hiding its head in the sand here? If the current trend continues, then in 2050 the amount of carbon dioxide in the planet's atmosphere will increase by 2 times. For peak temperatures, the increase will be from 4.5 to 5.5 degrees. This will cause the melting of glaciers in the mountains, which, in turn, will raise the level of the world's oceans by one and a half meters! As a result, there will be an increase in susceptibility coastal zones catastrophes and storms, the circulation of precipitation will change (according to scientists, they can be reduced by up to 40%!), which will cause catastrophic yield losses and population migration inland ... All this is no longer forecasts, but the reality of the near future . It is no longer possible to completely stop the process of global warming - humanity has gone too far! Now even those who did not want to hear about it are forced to make concessions to their native home - the planet Earth. The governments of industrial countries annually review their options and sign agreements to reduce emissions into the atmosphere. A good example is Japan, which in 2010 implemented a government program for citizens to buy environmentally friendly electric vehicles.
However, not everything inspires joy. Fact to Consider: There are so many chlorofluorocarbons accumulated in the refrigerators and air conditioners that we already have in our homes that even if we could suddenly stop all production, we would have enough harmful emissions for a long time, and we would hardly feel the effect. !
Ozone depletion
The ozone layer is located in the stratosphere at an altitude of 12 to 50 km (the highest density is at an altitude of about 23 km). And, despite the fact that the concentration of ozone in the atmosphere is less than 0.0001%, the ozone layer completely absorbs short-wave ultraviolet radiation that is harmful to all living things. For a long time, the ozone layer has been rapidly depleted due to human activities. Here are the main reasons for its thinning: 1) During the launch of space rockets, holes are literally “burned out” in the ozone layer. And contrary to the old belief that they close immediately, these holes have been around for quite some time. 2) Aircraft flying at altitudes of 12-16 km. 3) Emission of freons into the atmosphere Destruction of the ozone layer by freons The main cause of the destruction of the ozone layer is chlorine and its hydrogen compounds. A huge amount of chlorine enters the atmosphere, primarily from the decomposition of freons. Freons are gases that do not enter into any chem. reactions. Freons boil and quickly increase their volume at room temperature, and therefore are good atomizers. Because of this feature, freons have long been used in the manufacture of aerosols. And since, expanding, freons are cooled, they are now very widely used in the refrigeration industry. When freons rise to the upper atmosphere, from them under the action ultraviolet radiation a chlorine atom is split off, which begins to convert ozone molecules into oxygen one by one. Chlorine can stay in the atmosphere for up to 120 years, during which time it can destroy up to 100,000 ozone molecules. In the 80s, the world community began to take measures to reduce the production of freons. In September 1987, 23 leading countries of the world signed a convention, according to which, by 1999, the countries had to reduce freon consumption by half. In September 1987, 23 leading countries of the world signed a convention, according to which, by 1999, the countries had to reduce freon consumption by half. An almost equal substitute for freons in aerosols has already been found - a propane-butane mixture. Such aerosols are already widely used. For refrigeration plants, things are somewhat worse. The best substitute for freons now is ammonia, but it is very toxic and still much worse than them in physical terms. parameters. Good results have now been achieved in the search for new substitutes, but so far the problem has not been finally resolved. Thanks to the joint efforts of the world community, over the past decades, the production of freons has more than halved, but their use is still ongoing and, according to scientists, at least another 50 years must pass before the stabilization of the ozone layer.
Matt painting plays an important role in today's films. The first matte paint was made in 1907 by Norman Don and you can now see how the traditional matte paint of the time evolved from The Wizard of Oz to the world famous film Avatar.
Matt painting(Matte Painting) are large-scale hand-drawn images used in film, television and production. computer games to create an illusion of the environment in the frame, which for some reason cannot be photographed in nature or reproduced with the help of material scenery.
The main task of Matte Painting specialists is to make the resulting images photorealistic so that they blend seamlessly with outdoor shooting.
Step 1. Like any project, large-scale hand-drawn images need a pre-drawn sketch. I made this sketch. For the convenience of working with the lesson, I numbered the buildings.
Step 2. Here is a photo that matches our sketch perfectly. Open it in Photoshop and delete the clouds using the Magic Wand Tool.
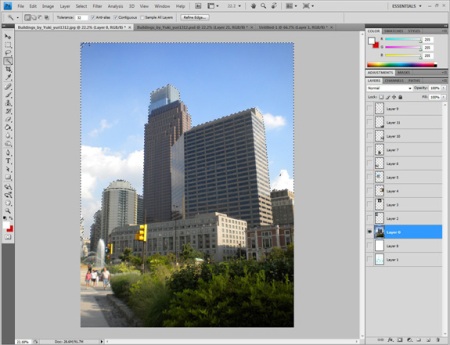
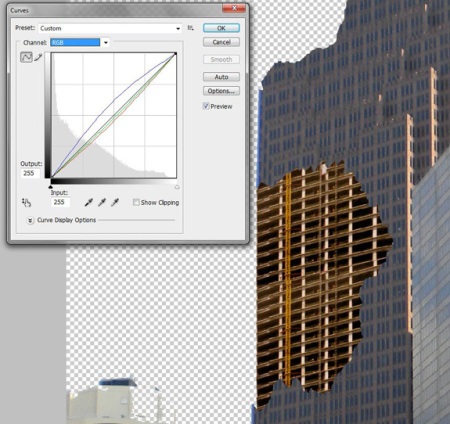
Step 3. We need to achieve the effect of devastation, complete chaos, and this will not work with green foliage on the trees. Therefore, select the Lasso Tool and select all the green areas at the bottom of the photo (trees, grass, leaves, etc.). Set the Feather Radius to 60. Then change the curves to something like this:
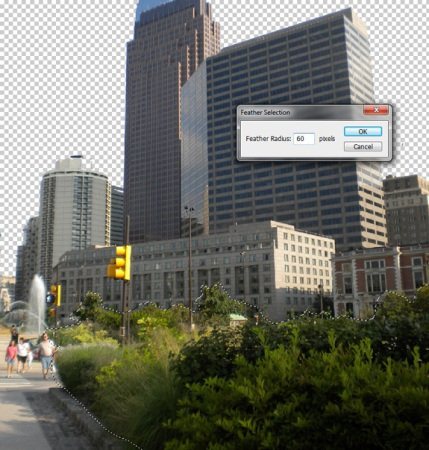
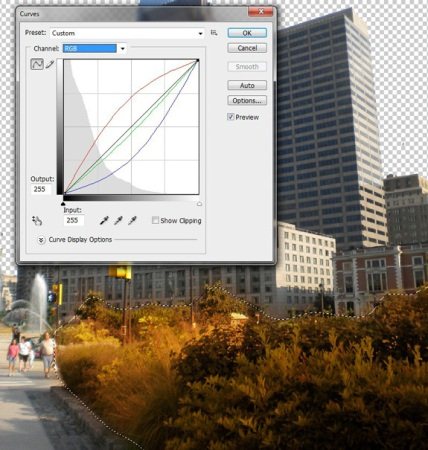
(click to enlarge)
Step 4. In this step, you must decide for yourself which part of the building you would like to destroy. To do this, using the Lasso Tool, select a fragment of the building. Then erase the edges using the tool Eraser (Erase Tool).

Step 5. Then, darken the building with the help of the tool Dimmer (Burn Tool) with a brush of rust, the link to which is at the beginning of the lesson.
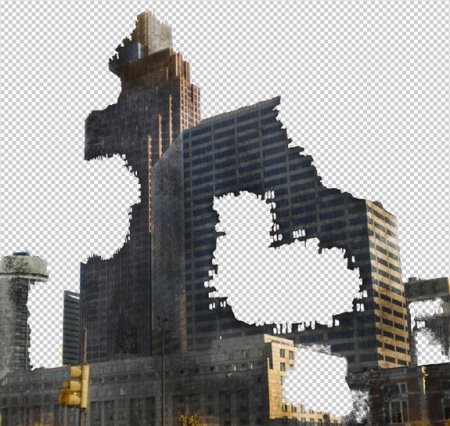

Step 6. Now we need to “gut” the buildings a bit. Let's follow the sequence, and stick to the numbering of buildings according to our sketch. I found the second image from the list of resources to be suitable for building B1 in the sketch. Cut out part of the building.

Step 7. Now paste this piece into the matte paint and fit it to fit our building as well. Select Free Transform from the Edit menu, hold down the Ctrl key and drag the corners of the transformed area so that part of the pasted building fits in perspective with our image:

Step 8. After you have fitted the fragment to our building, duplicate the layer and substitute it in the missing areas. It is necessary to achieve a neat connection of the fragments and fill in all the gaps. Then merge these layers with the keyboard shortcut (Ctrl + E).
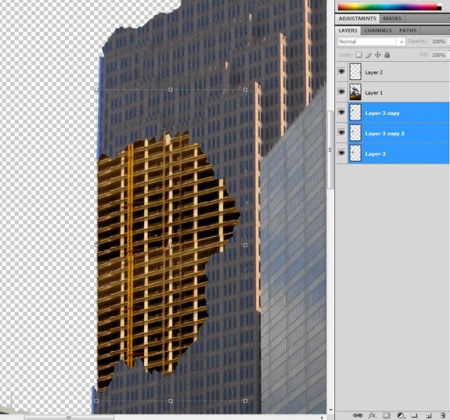
Step 9. Now adjust Curves (Curves): Red 150, Green 122, Blue 95.
Step 10. Then, we'll simulate destruction using the method we used in steps 4 and 5. We'll come back to this layer a bit later.
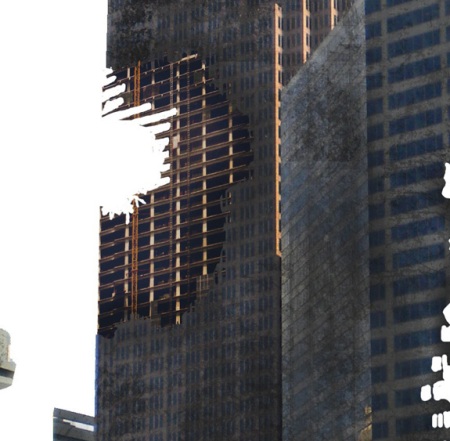

Step 11. Let's move on to the second building B2. Please select suitable photo, I took for example Destroyed Building 2. Now, repeat the steps from the 7th step. Pay attention to the perspective, try not to confuse anything.


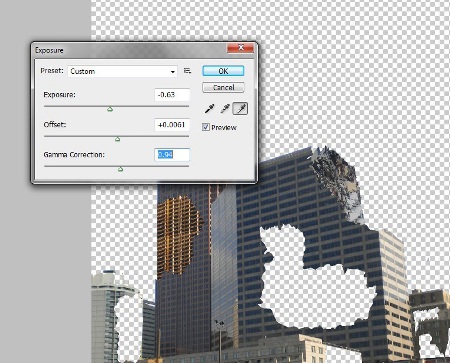
Step 12. Go to the exposure settings through the menu Image – Correction – Exposure (Image – Adjustments – Exposure).
Set these values:
Exposure: -0.63
Offset: +0.0061
Gamma Correction: 0.94.


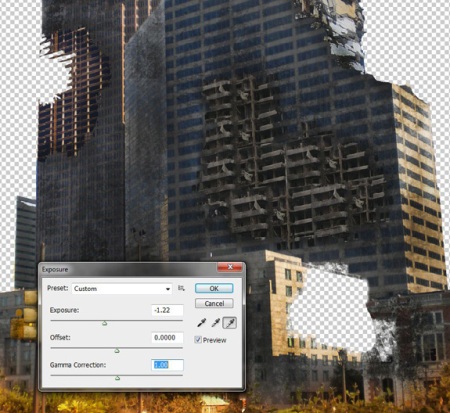
Step 14. Change the exposure settings again:
Exposure: -1.22
Offset: 0
Gamma Correction (Gamma-Correction): 1.00.
Then select the tool Dimmer (Burn Tool) and applying fantasy try to make the building look old and ruined.
Step 15. Do the same for the rest of the buildings. The main rule is to observe perspective and light / shadow, and then you will not spoil anything. Here short stroke my actions.
Greenhouse effect - ozone depletion
In the beginning, chlorofluorocarbon (CFC) refrigerants, which appeared in the 1930s, were considered as substances with only advantages. However, in the 1980s, when scientists began to look at their environmental impact, these refrigerants became a source of concern due to two things: greenhouse effect and possible depletion of the ozone layer. The greenhouse effect is a consequence of the fact that some gases earth's atmosphere block infrared radiation emitted by the earth's surface. Phenomenon greenhouse effect It allows maintaining the temperature on the Earth's surface at which the emergence and development of life is possible. If not, the average surface temperature of the globe would be about 20 K lower than it is. In other words, in the absence of the greenhouse effect, our planet would be uninhabited.
The retention of infrared in nature is due to water vapor contained in the air and clouds. However, other gases that are products of human activity, in particular carbon dioxide and refrigerants of the chlorofluorocarbon (CFC) category, also delay this radiation. Due to the fact that the presence of CO2 and CFC in the atmosphere (including) increases the efficiency of confining terrestrial infrared radiation compared to natural natural efficiency, the average temperature of the Earth's surface rises more than necessary, causing an artificial greenhouse effect, which is added to the natural greenhouse effect. effect. Although the concentration of all CFCs in the atmosphere is much lower than CO2 concentration, their effectiveness in retaining infrared radiation is many thousand times higher than that of CO2, in particular due to their very long lifetime (58 years for R11, 100 years for R12 and 250 years for R115, which is part of R502).
Stratospheric ozone depletion is a very different phenomenon because it is associated with energetic ultraviolet radiation from the Sun. The outermost layer of the atmosphere from the Earth is the stratosphere, which is a spherical layer with a thickness of about 35 km, starting at an altitude of 15 and ending at an altitude of about 50 km from the Earth's surface.
This layer contains ozone, which absorbs 99% of the ultraviolet radiation from the Sun that hits the Earth, acting as a protective screen for life on Earth.
The released chlorofluorocarbons (CFCs) slowly rise up and reach the stratosphere, where their molecules undergo photolytic dissociation under the action of ultraviolet radiation, as a result of which the chlorine atoms contained in these molecules are released (for example, a fluorochlorocarbon such as R11 has the chemical formula CC13F). Free chlorine atoms interact with ozone molecules ( chemical formula 03), constituting the ozone layer, forming chlorine oxide G10 and molecular oxygen. It is believed that one chlorine molecule can cause the destruction of many thousands of ozone molecules, according to various estimates, this number reaches from 10 to 100 thousand molecules.
While the greenhouse effect of CFCs is clear, their effect on the stratospheric ozone layer is a matter of debate. Therefore, in November 1992, at the Copenhagen Conference, 92 scientists from all over the world, at the initiative of the volcanologist Haroun Tazieff, adopted the “Appeal of the 92”, calling on the authorities of all countries that signed the Montreal Protocol to return to its decisions.
Be that as it may, scientists have tried to compare different refrigerants with each other in terms of:
- the greenhouse effect, assigning to refrigerants such an indicator as the possibility of global warming of the atmosphere over a 100-year period, i.e. the possibility of global warming, which is usually denoted by the abbreviation GWP (Global Warning Potential)
- ozone depletion by giving refrigerants an ozone depletion capability factor, commonly abbreviated as ODP (Ozone Depletion Potential).
The following conclusions can be drawn:
- from the point of view of the greenhouse effect, the impact of R22 is no more than 37% of the impact of R11, Rl34a ~ no more than 29%, and the effect of ammonia on the increase in the greenhouse effect is generally zero;
- from the point of view of ozone layer depletion, the effect of R22 is at the level of about 5% of the effect of Rll, while R134a and ammonia have practically no effect on the ozone layer.
According to Pohlmann 1998
Since here we consider the near zone of the explosion, which, in turn, is divided into zones of characteristic effects, and which are identified as sequentially developing sources of seismic vibrations, we will analyze the main features of these zones. In addition to the zone of elastic seismic vibrations, all the others are characterized by the formation of cracks, i.e. discontinuity of rocks.
The volume and degree of destruction and, consequently, the intensity of cracking, both towards the free surface and deep into the massif, is determined by the volumetric energy density attracted by the elastic-plastic stress wave in different parts of the seismic emitter (explosion source).
It is known that seismic radiation is determined by the rate of development of cracks in the destroyed part of the massif, the rate of development of which is not more than 0.38 Cp with a relatively large oscillation period. The paper notes that the meaning of engineering measures to control the action of the explosion and increase efficiency The use of BB energy is reduced to a decrease in the radius of the source of the seismic emitter and to a more uniform distribution of the energy concentrated within its limits, an increase in the rate of development of cracks and a decrease in the time for cracks to reach the surface of the outcrop.
With an increase in the growth rate of cracks, an increase in their number, the initial seismic impulse also decreases. The most intensive development of cracks as a result of the advancement of the seismic front is observed at a distance of (0.5-0.6) ro. Along with the advance of the front, the parameters of seismic vibrations in the zone of their primary formation decrease, the share of energy attracted due to unloading in the area of the source of the seismic emitter decreases, and, as a result, the seismic effect decreases.
The development of cracks is determined by the type of destruction of rocks: brittle, ductile and brittle-plastic. In brittle fracture, cracks are oriented perpendicular to the action of normal tensile stresses. Ductile fracture is characterized by the displacement of particles along slip areas oriented along the directions of shear stresses, but the rate of cracking is much higher than the rate of development of plastic deformations.
There are two points of view on the process of crack formation. According to S.D. Volkov, the process of crack development goes through three stages (Fig. 3.4):
- initiation and slow development of crack formation foci;
- accelerated cracking;
- cracking at a constant rate.
Acad. S.G. Ultimately, the process of destruction of brittle media is presented as a chain reaction, i.e. the rate of cracking catastrophically increases. Such a representation is quite consistent with the concept of the fractal nature of destruction with the formation of an attractor in the form of a bifurcation branch, i.e. similar to the Cayley tree, where the applied load on the medium with defects is reoriented (shifted) from the defect where the cracks have grown together to the defects where it has not yet happened, while branching takes the form of a chain reaction. The stresses do not have time to relax and the phenomenon is similar to the creep phenomenon.
The distribution of stresses and strains in this case, according to the theory of catastrophes, is probabilistic in nature, and in magnitude they can be even lower than the ultimate strength of the rock for destruction. In this case, the crack formation rate will apparently depend on the number of possible crack nucleation sites.
If we assume that there are no centers of crack formation in the closed volume V, then during the time dt they will “wake up” nodt under the action of the load Fo. For various reasons, they will not all grow; among the total mass of defects no there are active and passive ones, the first cracks with a speed vtr, and the second stop growth. The probability of encountering active cracks will be:
Pa = nt/no, and passive Pp = 1-Pa.
According to V.A. Padukov, we have:
where f and q are coefficients characterizing the branching and formation of crack formation chains; no - concentration of initial crack centers; nt is the concentration of active foci.
Integrating (3.3) and performing transformations, we obtain:
It is clear that the rate of crack formation will be proportional to the concentration of crack nucleation sites:
where k is the coefficient of proportionality.
Let us perform a qualitative analysis (3.4 and 3.5), highlighting three cases.
1. f Pa, or nt tends to the limit no / (q-f), then the cracking rate will be equal to:
![]()
2. With f=q and Pa=Pp, dnt/dt=no, i.e. nt=not and, therefore, Vtp=knot.
This fully corresponds to the energy theory of destruction, when the efficiency of destruction depends not only on the magnitude of stresses, but also on the amount of energy transferred to the array in a certain time, i.e. It is about the load exposure time. This also does not contradict the theory of catastrophes and the kinetic theory of S.N. Zhurkov.
3. For f>q, we have:
Here, the rate of crack formation increases according to the exponential law, i.e. in the form of a chain reaction like a rock burst.
The change in the rates of development of cracks and the rate of cracking in ores and apatite-nepheline rocks showed that the speeds across the layering were 200-300 m/s, and along - 300-800 m/s, and the time of the process of cracking the area was:
T = (0.6/3)W ms,
where W is the resistance along the sole, and the speed is:
vtr = 300-1600 m/s.
Measurement of Cp in the massif showed that it is 1000-4200 m/s, which means that the crack growth rate is about 0.38 Cp.
The recognized seismic hazard criteria are particle displacement velocity V and seismic wave stress σ. Ho according to Ya.I. Zeitlin, they are effective only for a limited range of explosion power, because. it is obvious that at the same given distances at the same speed, the danger from a more powerful explosion will be the same as a less powerful one. But this is not confirmed by practice.
The disadvantage of the criteria V and σ is that they do not take into account the time of the blast wave or take into account the time in the wrong proportion.
Specific energy can be defined as:
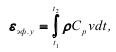
where ρСр is the acoustic rigidity of the medium; V is the displacement speed.
On the seismogram, a phase with a maximum amplitude is distinguished, on both sides of which the displacement intensity rapidly decreases, but more than 50% of the entire wave energy is contained in the region of the maximum.
When considering plastic deformations, it should be taken into account that residual deformations add up, which can be the physical basis for softening, since the emergence of new centers of weakening, defects, microcracks is a manifestation of residual deformations. This means that they accumulate under successive multiple loading, which means that the energy of pulses must be taken into account not only in the region of the peak value, but everywhere where they are capable of causing plastic deformations.
It is known that the critical speed with a static action is less than with a dynamic one. Taking into account the fact that longitudinal waves predominate in the nearest zone, the action of which can be considered quasi-static, then the energy will be:
![]()
where A is the power of the explosion; τ is the characteristic time of energy arrival, after which further arrival at the same level will not lead to an increase in danger.
In rocks, τ is approximately estimated at 1 ms, in which case most seismic waves in such rocks will be quasi-static and then the Vmax and σ criteria are effective criteria, meaning that the damage energy of rocks is very small. For seismic waves, it is sufficient when the stresses in the wave reach critical values. Ho peak voltages are not always a criterion of danger and depend on the moment of explosion. ME AND. Zeitlin believes that the critical value of a destructive seismic wave for rocks of medium strength is εcr (J/m2) of about 20,000.
In this tutorial, you'll learn how to create a powerful emotive decay effect using some brushes, layer styles, and adjustment layers.
Preview of the final result:
Step 1.
Start by creating a new document in Photoshop (Ctrl+N or File-New). You can choose your document size, but the main thing is that it should be vertical and have a transparent background (transparent). I used a size of 1600x2322 px with a resolution of 72 px/inch.
![]()
Step 2
We select one high-quality image of a cloudy sky from the presented images and open it in Photoshop (Ctrl+O). You can also combine several images of the sky and make one background from them for the composition, as I did.
Make sure your sky is dark and dramatic enough as this is the atmosphere that will work well with the other elements of the scene.
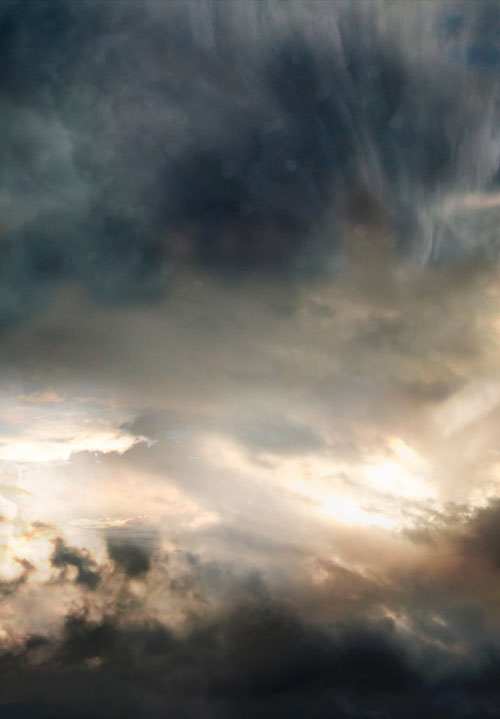

Step 3.
The next step is very important, as we must choose the main character of the composition, which is in the center of attention. I used a model from Fotolia, you can choose a similar image on other stocks (SXC, IStock). The main thing is that strong emotions are present in the image of your hero. Open the image of a young man in Photoshop and extract it from the background with the Pen tool. (PenTool (P)) . Select the contour around the hero (Ctrl+Enter), then copy (Ctrl+C) and paste (Ctrl+V) it into the main document above the background layer.
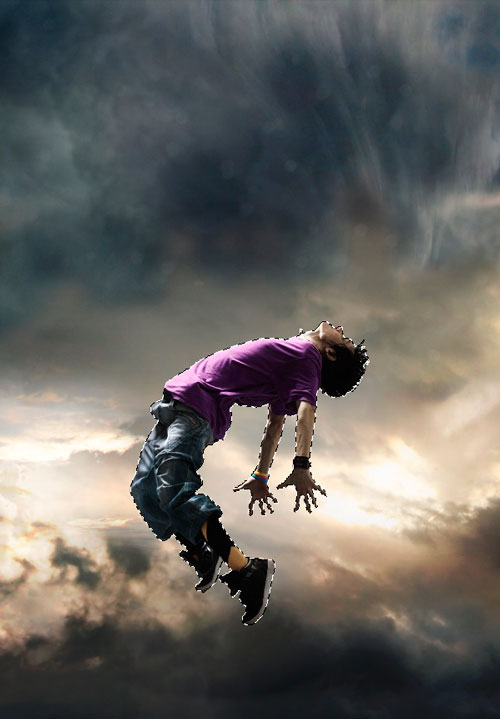

Step 4
Download the splatter brushes from the resources of the lesson and load them into the program through the menu Edit - Manage presets - Brushes - Load ... (Edit-Preset Manager-Brushes-Load...). Choosing an Eraser (Eraser tool) and set up the brush we need from the splatter set in the settings panel (F5 or Window-Brushes). In the "Brushprint Shape" section (Brush Tip Shape) set interval (Spacing) at 25%, then run the eraser over the hero's legs, erasing some of them.
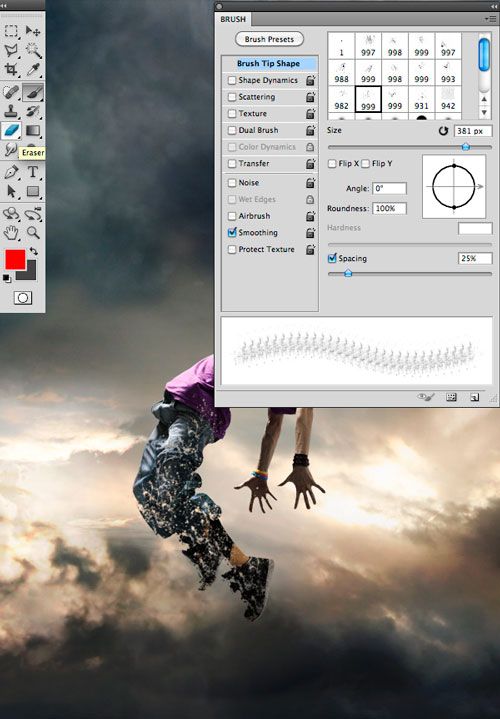
Step 5
Now, I would like to change the color of the hero's clothes. Selecting the Lasso Tool (lasso tool (L)) and highlight the t-shirt and open areas legs. Then create a Gradient Map Adjustment Layer. (click on the black and white circle icon at the bottom of the layers panel and choose Gradient Map from the menu). You can also change the color of clothes using the Selective Color adjustment layer. (selective color), it's optional. Use for the color gradient map from rich yellow to light yellow.
Change the blending mode of this layer to Color. (Color). Try to avoid fluorescent (poisonous) colors, choose shades that are present in the background of the composition.
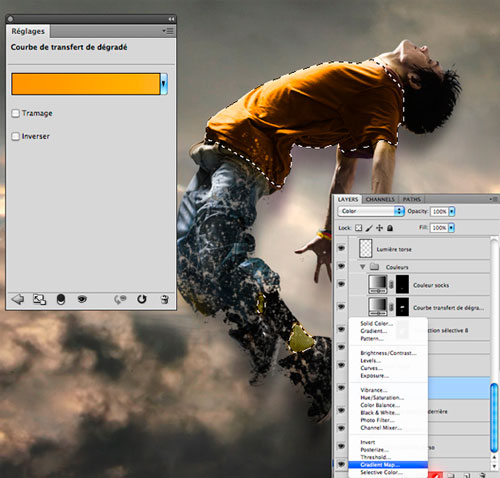
Step 6
Next, select the Brush (BrushTool (B)) from the splash kit. Create a new layer (Ctrl+Shift+N) and draw on it splashes of the color of the young man's T-shirt (orange) rising up from it. Also, using these brushes, let's draw splashes falling from the hero's head down on a separate layer. Here we use the color of the guy's hair (when using the brush, hold Alt to sample the color (activation of the Eyedropper tool (Eydropper Tool)) ) .
For the splashes falling from the trousers, we use the gray-blue color of the jeans. We draw splashes from trousers in different directions. There was a kind of destruction effect.
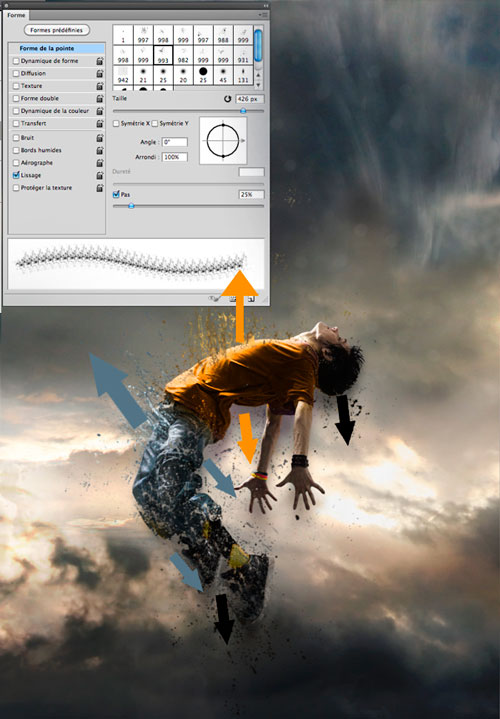
Step 7
There are many ways to give the character the impression of madness and obsession. Personally, I prefer adding red veins on the arms, neck and face, as well as darkening the eyes and mouth, using a brush. (brush) small size black color with blending mode (Blend Mode) Soft light (soft light).
Draw veins with a brush on a separate layer (Ctrl+Shift+N).

Step 8
In this step, I created a thin pendant around the young man's neck. Its position at the top is determined by the moment of the hero's jump. Draw a pendant with a brush (brush) small size. I used a tablet for this purpose.
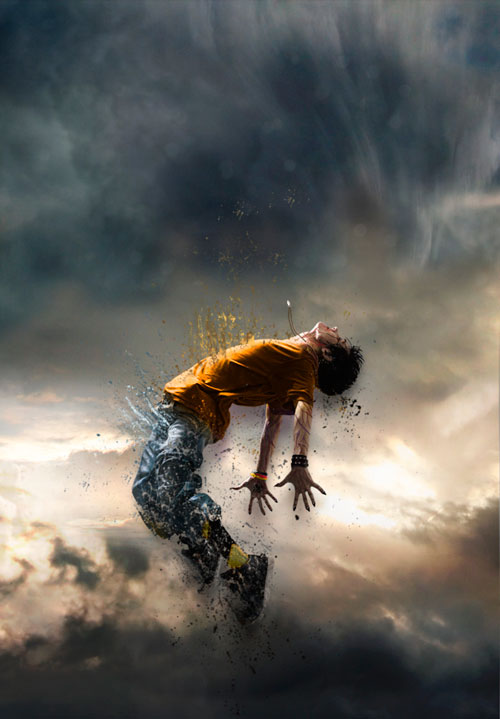

Step 9
Now let's give the pendant a supernatural look. To do this, add a semblance of wave radiation around the pendant. On a new layer (Ctrl+Shift+N) use soft round brush (brush) white color over the suspension. Then, with an eraser (Eraser) with a soft brush of a smaller size, the middle of the previous spot, leaving only the edges of the white circle. Opening Layer Styles (click on the "Add Layer Style" icon at the bottom of the layers panel) and make settings for the "Embossing" parameter (Bevel and Emboss) for the ring layer. After completing the settings, duplicate (Ctrl+J) double this layer. Increasing the size of duplicates using Transform (Edit-Transform or Ctrl+T) to get a gradual increase in the rings on top of each other. You can lower the opacity (opacity) duplicates, because the farther the ring waves are from the suspension, the more transparent and wider they are.
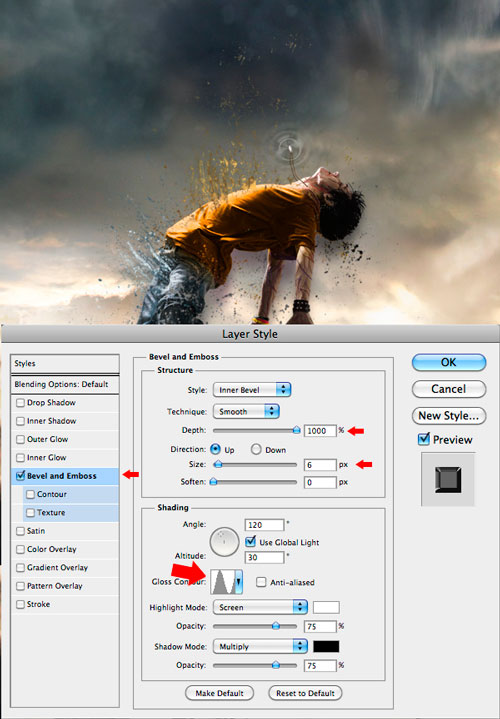
Step 10
To complete the work on the suspension, add rays of light on top of it. Download brushes (brush) rays from the lesson materials and load them into the program. On a new layer (Ctrl+Shift+N) use white rays coming out of the center of the pendant.

Step 11
Also, using the ray brushes, draw the light coming out of the hero's body. Thus, we create the impression of the release of some supernatural force during the process of destruction of the character.
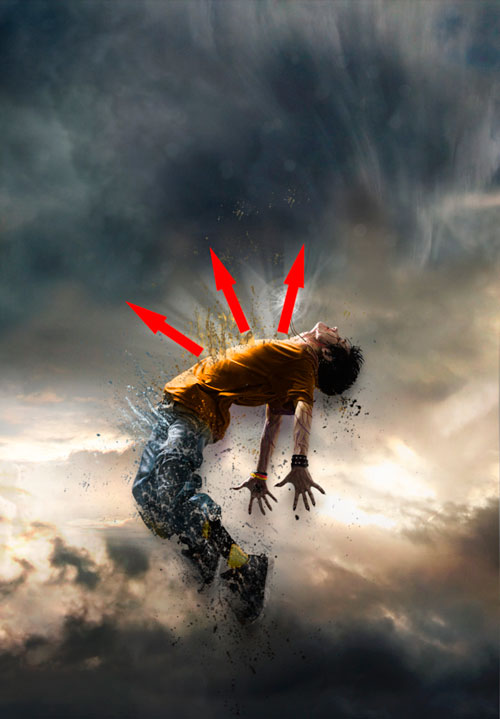

Step 12
Now that the main part of the work with the hero is done, we will work on the atmosphere of the composition. Create a Gradient Map Adjustment Layer (Layer-New Adjustment Layer-Gradient Map) to make the background darker, closer in character to our character. Make adjustments from the screenshot below, then change the blending mode of this layer to Color. (Color) and lower the opacity (Opacity) up to 27%.
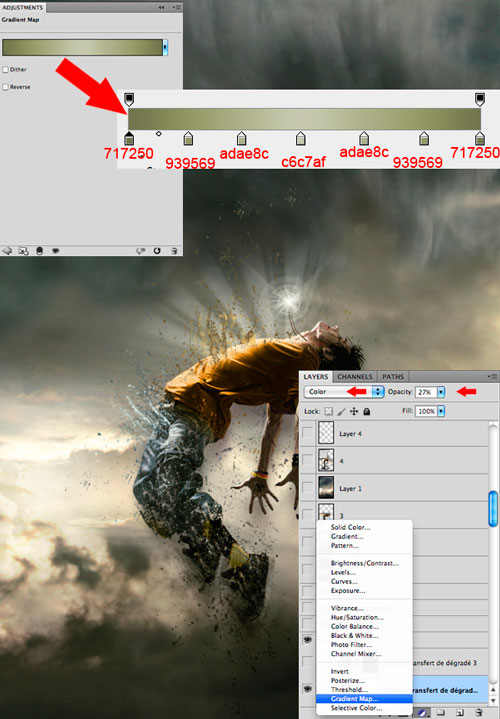
Step 13
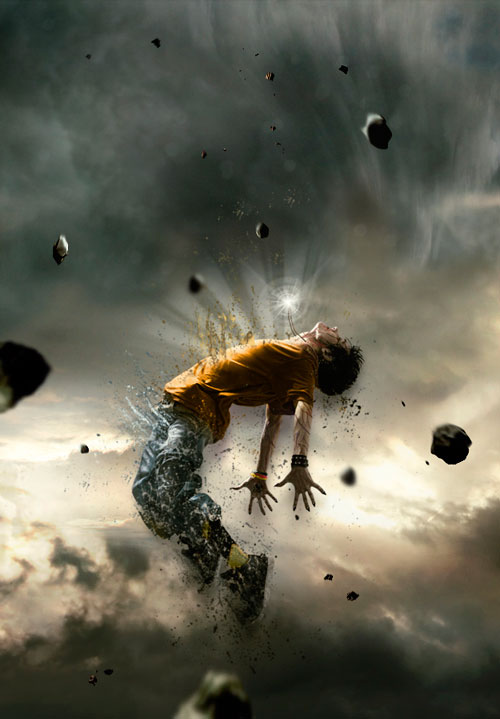

Step 14
Now apply some blur to the meteorites to give some of them the effect of their approach. Selecting the Blur tool (blur) and use it only on meteorites that are closer to us. We do not wash away the stones near the young man.
The farther the meteorites are from the model, the more they should be blurred.

Step 15
To make the meteorites look like they are in motion, apply the Finger tool to them. (Smudge Tool) with an intensity of 5-10%. Strokes are performed in the direction from the bottom up from the stones, simulating speed.

Step 16
To create the light falling from above, use white ray brushes. It is important that the rays look more intense at the top, and closer to the hero's body they dissipate. To add magic to the picture, you can paint on a separate layer (Ctrl+Shift+N) several small figures moving along with streams of light.
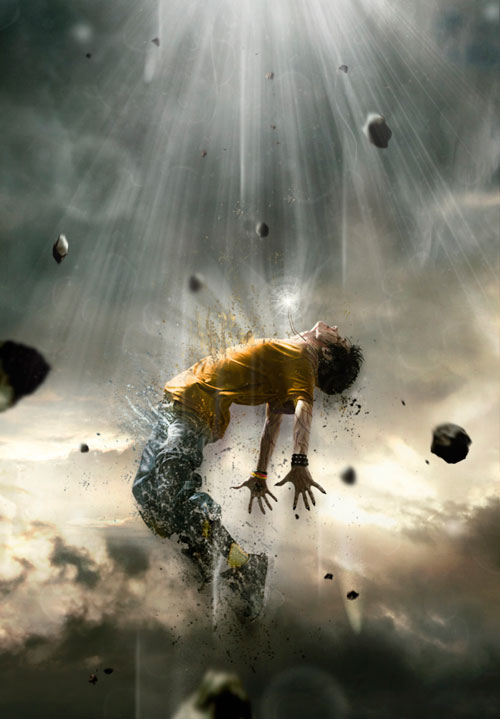

Step 17
Let's return to our hero. After we have created streams of light falling on the body of a young man, we must create a reflection from the rays of light on his body and face. Selecting a Soft Round Brush (brush) white color and draw along the upper part of the guy's figure. Then change the blend mode (Blend Mode) this layer on the overlap (Overlay).
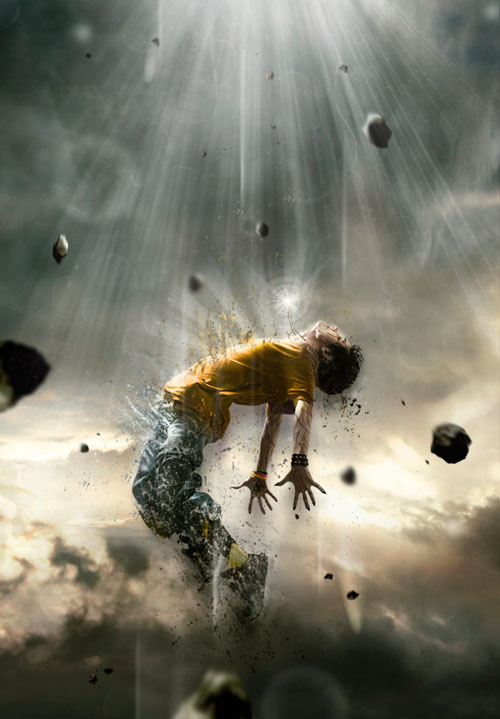

Step 18
Add a few more rays of light around the hero with brushes (brush) so that the image harmoniously fits into the overall plot of the composition and looks emotionally powerful.
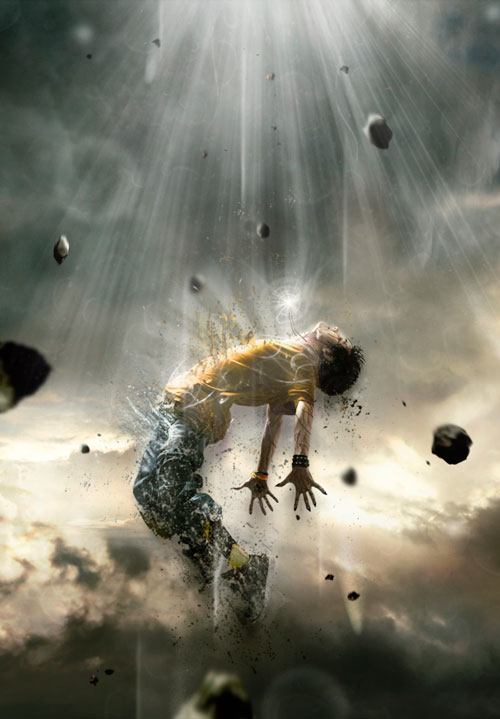

Step 19
If you think that the destruction effect is missing, add some more particles to the hero's body using the splash brushes (Splatter Brush).
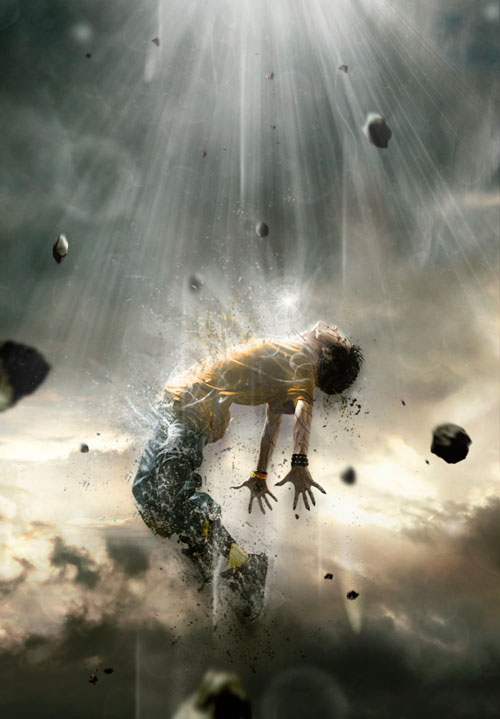

Step 20
To finish off, you can enhance the contrast, colors and bright areas of the composition using the techniques listed earlier. Finally, sharpen by duplicating all layers of the image onto a new layer. (Ctrl+Shift+Alt+E)











How to understand: will the kitten be fluffy?
What kind of light alcohol can be drunk for pregnant women: the consequences of drinking
Why do the legs swell in the ankles and ankles of the feet in pregnant women: causes and methods of treatment
The wedding of Prince Harry and Meghan Markle: scandalous and secret details of the marriage (photo) The future marriage of Prince Harry year NTV
How to close white plums for the winter