Capital is the main tool for a business owner, without which the entrepreneurial activity itself cannot even begin. Own capital consists of heterogeneous parts intended for specific purposes. One of the important and mandatory components of the capital of a legal entity is reserve capital. Unlike other shares of capital, there are some contradictory nuances in its formation, use and accounting.
Below we will consider the legal basis for its formation and application, main functions, connection with retained earnings, as well as the intricacies of accounting entries.
What is reserve capital
Any activity cannot be insured against losses. In entrepreneurship, where the financial issue is the main one, the constant presence of some financial “cushion” for unforeseen situations is especially relevant. It happens that it is impossible to obtain the necessary funds in any other way, while there are certain obligations to counterparties or an urgent need for immediate cash investments.
For these purposes, the enterprise must have a certain insurance fund - a reserve.
Thus, reserve capital is a certain part of the organization’s property (or its profit), which performs an insurance function that guarantees the operation of the enterprise without interruptions and compliance with responsibility to counterparties. It consists of retained earnings placed in it.
In a broader perspective organization reserve fund– financial source for:
- covering the lack of current assets when forming production reserves, unfinished projects, etc.;
- short-term financial investments.
Purpose of reserve capital:
- compensation for losses if this is not possible from other sources;
- redemption of bonds;
- repurchase of shares of LLC or JSC;
- payment of income to investors (if profits do not allow this);
- dividends on preferred shares;
- compliance with urgent obligations to creditors that cannot be repaid in any other way.
Laws of the Russian Federation on reserve capital
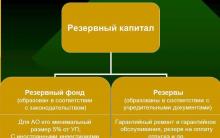
The creation of reserve capital is provided for legal entities - joint-stock companies and limited liability companies. But the legislative justification for the formation of this part of equity capital for enterprises of different forms of ownership has significant differences.
Reserve capital for JSC
The legislative framework for the functioning of joint stock companies is regulated by the Law on JSC - Federal Law No. 208-FZ of December 26, 1995. Clause 1 of Art. is devoted to reserve capital. 35 of this Law. In it, entrepreneurs-shareholders are legally required to create reserve capital in their enterprise. Its size must be determined by the charter documents of the joint-stock company, but in any case not be less than one twentieth of the total authorized capital.
To form it, you need to annually deduct a certain percentage of profit to this fund (the amount of deductions is also specified in the Charter). It can be anything, but not lower than 5% of net profit, until the fund reaches the value defined in the Charter of the joint-stock company.
The purposes of using the reserve fund of a joint-stock company are strictly fixed in the following closed list:
- covering possible losses of the joint-stock company;
- redemption of bonds;
- share repurchase.
IMPORTANT! All these goals can be achieved through the reserve fund if there are no other sources of financing. It is not permitted by law to use money from the reserve fund for purposes not specified in this list.
Reserve capital for LLC
The Law on LLC (Federal Law of 02/08/1998 No. 14-FZ) in Article 30 allows, but does not oblige the founders to create a reserve fund, as well as other funds for certain purposes. The dimensions are not strictly regulated, but it is necessary to streamline them in the statutory documents.
Since the LLC Law does not contain an indispensable obligation to create a reserve fund, the purposes of this part of the capital are not regulated. In this case, paragraph 69 of the “Regulations on Accounting and Accounting in the Russian Federation” may serve as a guide to action, which, in addition to the procedure for distributing funds from the reserve fund among various sub-accounts, lists possible ways of spending it. LLCs can use reserve capital for:
- compensation for losses;
- redemption of bonds;
- redemption of founder's shares;
- increase in the authorized capital.
FOR YOUR INFORMATION! If a JSC or LLC receives foreign investment, its reserve capital must be at least a quarter of the authorized capital, as required by the laws of the Russian Federation.
How is reserve capital reflected in accounting?
As already mentioned, reserve capital is included as an integral part in the equity capital of a legal entity (clause 66 of the Accounting Regulations). Paragraph 69 of the same document stipulates that the reserve fund should be displayed separately in the balance sheet. For this purpose, a special account 82 “Reserve capital” is provided, which is a liability. It displays information about the availability of funds in the reserve fund and their dynamics.
Since funds for the reserve fund are taken from retained earnings, the credit of account 82 will function in correspondence with account 84 “retained earnings, uncovered loss.”
EXAMPLE 1. Supercontract LLC declared in its constituent documents the size of its authorized capital at 50 million rubles. – this figure appeared in the documents after the last meeting of the founders on February 15, 2017. The amount of reserve capital as of this date was 2 million 200 thousand rubles. Net profit according to the final documents of 2016 amounted to 12 million rubles.
The amount of reserve capital, in accordance with the requirements of the law and the Charter of Supercontract LLC, should be 5% of the total equity capital: 50 million rubles. X 5% = 2 million 500 thousand rubles. Annual contributions also amount to the statutory 5%. Thus, the net profit of the previous reporting year will contribute 12 million rubles to the reserve fund. X 5% = 600 thousand rubles.
To achieve the size of the reserve fund provided for by the Charter, 2 million 500 thousand rubles are missing. – 2 million 200 thousand rubles. = 300 thousand rubles. They can be accrued from the net profit of 2016, which was decided by the Board of Founders of Supercontract LLC.
The accounting entry was as follows:
15.02.2017
Debit 84, credit 82 – 300,000 rubles. – “Reserve capital has been formed from net profit.”
If the purpose of replenishing the reserve fund is to increase assets, then such an operation must be reflected again under credit 82, but debit 75 must be used - “Settlements with founders”. You can also open additional subaccounts.
EXAMPLE 2. JSC Trayan, represented by its shareholders, decided to increase the value of its assets by 6,000,000 rubles, contributing the appropriate funds for this. This decision was reflected in the minutes of the meeting of the joint stock company dated March 13, 2017. Some shareholders transferred the necessary money the next day, March 14, 2017, and the last payment was made on March 21, 2017. This is what the final accounting entry will look like:
14.03. 2017 – 21.03.2017
Debit 51, credit 75 – 6,000,000 rub. – money was received for the formation of reserve capital from shareholders.
21.03.2017
Debit 75, credit 84 – 6,000,000 rubles. – reserve capital has been formed through contributions from shareholders.
Target accounting of reserve capital
Since reserve capital (for joint stock companies) can be used exclusively for certain purposes, accounting in each specific case is strictly regulated by the Accounting Rules. The debit of account 82 can be in correspondence with the following accounts provided for in the Account Management Plan:
- 84 “Retained earnings, uncovered loss”;
- 66 “Settlements for short-term loans and borrowings”;
- 67 “Calculations for long-term loans and borrowings.”
Analytical accounting of reserve capital
Unlike accounting, analytical accounting allows you to clarify the areas of use of reserve capital. Reserves formed by enterprises may have different destinations and sources.
- Reserves included in the cost. In accounting, this group of assets is reflected in passive account 96 “Reserves for future expenses.” They are regularly and evenly included in costs, each type of which corresponds to a separate subaccount of this account:
- vacation pay for staff;
- bonuses based on performance results;
- repair of fixed assets;
- warranty repairs and maintenance, etc.
- Reserves included in other income. Initially having different purposes, they are shown in different accounting accounts. When forming them, the amount of the created reserve is subtracted from the cost price, so they will be reflected on the balance sheet at the market value current on the date of entry. These amounts may be written off if they are not used by the beginning of the next accounting period. They are recorded in account 59 “Reserves for depreciation of financial investments.” Such reserves include:
- reserves created by reducing the value of tangible assets - when the market value on the date of entry into the balance sheet is lower than the actual value, the difference forms a reserve;
- depreciation of investing money in securities - the same situation as with tangible assets can also arise with securities (purchasing them on the stock exchange at a cost higher or lower than their nominal value, the difference constitutes a reserve).
- Provisions for problematic debt. Problematic (doubtful) debt is a receivable that has not been repaid within the prescribed period and is not secured by guarantee obligations. Such debts can be identified after taking inventory at the end of the year. First you need to assess the debtor's potential ability to repay the debt. The year following the accounting year is allotted for this, during which the amount of debt will be considered a reserve. After this year, the unpaid debt that was the reserve will be listed as debt (5 years are allowed for this) and then will be written off as a loss.
- Additional capital. When an organization is doing well, its capital increases. There is an opportunity to increase assets, including reserve capital. Additional capital may consist of:
- revaluation of enterprise assets (current and non-current);
- the difference between the actual and nominal price of shares used for the authorized capital;
- differences in exchange rates when contributing shares to the authorized capital, if they were made in foreign currency.
ATTENTION! In accounting, when reflecting the balance on account 58 “Financial investments”, it is necessary to subtract the amounts included in the reserve fund for the depreciation of financial investments.
Such a reserve must be taken into account in account 63 “Reserves for doubtful debts” (creation - by debit, writing off and adding reserve balances - by credit).
For accounting of additional capital, account 83 “Additional capital” (credit) and special sub-accounts are intended. A debit can be account 50 “Cash”, 51 “Cash accounts”, 52 “Currency accounts”, etc.
IMPORTANT INFORMATION! The amount included in the reserve as additional capital is usually not subject to write-off, except in cases of an increase in the authorized capital, a write-down of fixed assets after revaluation, or a negative exchange rate difference.
EXAMPLE 3. OJSC “Potrebitel” received the opportunity to increase its authorized capital by placing additional shares in it. At par value, the increase would have been 300,000 rubles, but when selling by subscription, 320,000 rubles were paid for the shares.
Entries in the accounting of OJSC "Potrebitel":
- debit 75 “Settlements with founders”, subaccount “Settlements for contributions to the authorized capital”; credit 80 “Authorized capital”, subaccount “Announced capital” - 300,000 rubles. — the increase in the authorized capital is reflected;
- debit 80 “Authorized capital”, subaccount “Announced capital”; credit 80 “Authorized capital”, subaccount “Subscribed capital” - 300,000 rubles. - subscription to shares is reflected;
- debit 51 “Current accounts”; credit 75 “Settlements with founders”, subaccount “Settlements for contributions to the authorized capital” - 320,000 rubles. - the receipt of funds for the purchased shares is reflected;
- debit 75 “Settlements with founders”, subaccount “Settlements for contributions to the authorized capital”; credit 83 “Additional capital” - 20,000 rubles. - share premium is reflected (the excess of the actual cost of placing shares over their par value).
Value of reserve capital
Reserve capital or reserve fund (these concepts are used in the same field) has a rather limited scope of application. Its main function is to compensate for certain losses of the organization. The procedure for spending funds from reserve capital does not increase or decrease the assets of a legal entity: it is only reflected in the composition of equity capital.
The reserve fund is an indirect means of saving the finances of an enterprise, because it protects part of the profit from immediate use at the moment of its occurrence, and forces it to “save” this part for a “rainy day” of possible losses, thereby insuring the organization from acute negative consequences.
It is customary for organizations to create various types of reserves from their own funds. Financial reserves play a special role. Among them are especially highlighted:
- Estimated.
- For upcoming expenses.
- Statutory.
The domestic accounting system is trying to increasingly focus on international standards in this matter. Because of this, there is a need to change the financial information that is generated at enterprises in our country.
The new rules for accounting for reserves provide for the presence of five accounts.
For statutory:
- 82 Dedicated to capital with reserves.
Expenses to come:
- 96 Designation of reserves for expenses for the near future.
For a reserve group of valuation type:
- 63. Dedicated to reserves that arise due to doubtful debts.
- 59. In case securities investments depreciate.
- 14. In case the value of any material assets decreases.
The explanations to the balance sheet and reporting indicate all the information that is necessary to clarify the data. You can read about how to correctly prepare consolidated statements in this.
Reserve capital is the property of enterprises in which retained earnings are placed.
The same capital is needed when it is necessary to repurchase shares owned by management, pay off bonds, and cover incurred losses. In other words, This is the amount to cover losses in situations where other sources have exhausted themselves. The organization's reserve capital is formed in accordance with the law.

Purpose and size of the organization's reserve capital
Reserve capital is used in the following areas:
- To buy back shares or pay off purchased bonds.
- To transfer money to creditor accounts with investors when the underlying profit is insufficient.
- To cover losses that were not provided for.
- Capital group payments.
- Payments related to interest.
- To pay taxes. This is relevant if there is no money, but the deadline is already approaching.
- To write off losses.
- When writing off debts recognized as bad.
There are several more rules associated with this concept. Only the owners of the company have the right to set the accumulation period and the minimum amount for reserve capital.
It is best to start forming reserve capital during the period when the company has retained earnings. The presence of reserve capital will guarantee that the enterprise will operate uninterruptedly in any situation. And that the interests of third parties will always be respected.
The organization's reserve capital becomes an important mechanism for stabilizing the company's activities. After all, this direction is always associated with certain risks. Deductions to cash reserves are possible only during a period of confirmed absence of losses.
How is reserve capital formed and accounted for?
This type of capital must be at least five percent of the total savings of the enterprise. The reserve capital is formed through annual contributions until the amount stipulated by the charter has been accumulated. The charter of the same company determines exactly what part of the profit each year must be directed to the formation of reserves.
Shareholders make decisions at general meetings - this is the main document by which accountants formulate and record reserve capital. But the organization of such meetings is usually carried out after the end of the year in a financial sense.
Dates after reporting periods are displayed as usual. This means that on the date the shareholders make a certain decision, any transactions are reflected that assume that profits are only distributed.

How to use the authorized reserve capital account if you need to cover losses?
The use of reserve capital for this purpose is possible only in the event of officially confirmed losses. Only part of it, which is equal to losses, is used to cover expenses.
Here are a few examples of situations:
A reformation was carried out on the enterprises, after which it turned out that account 84 had a debit balance of 100 thousand rubles. 350 thousand rubles was equal to the amount of reserve capital formed by the reporting date.
Only 100 thousand rubles should be allocated to cover the loss.
- The balance of account 84 becomes zero when the posting in the accounting department is completed in full.
- 250 thousand rubles is the amount of reserve capital. It can be used to pay dividends to those who have preferred shares.
- It is unacceptable to pay amounts to those who purchased ordinary shares using funds from these groups.
A right that does not arise solely because of the very fact of having a credit balance on account 84 becomes dividend payments. Separate articles in the rules on JSC say that Dividends cannot be paid or declared in the following cases:
- In the event that the adoption of such a decision will contribute to a decrease in capital, its inconsistency with reserve funds and statutory indicators.
- In the presence of pure reserves, which are no longer sufficient to resolve issues.
- When placing shares with privileges, when the par value exceeds the indicators in the charter.
Drawing up a reserve fund is the responsibility of management at any enterprise. But management has the right to regulate the formation and use of funds from other funds, depending on the desired policy.
An example of calculating an organization's reserve capital
200 thousand – total profit for the reporting period. 500 thousand rubles are in a special fund. Finally, 350 thousand rubles are equal to the company’s obligations associated with the obligation to pay dividends to those who have preferred shares.
When calculating dividends and preparing a report in the accounting department, such transactions are reflected in compliance with the following rules:
1. Debit 84. Credit 75.
200 thousand rubles - to indicate net profit, which is used to receive dividends to holders of preference shares.
2. Debit 82. Credit 75.
150 thousand rubles - the amount from which the special fund is formed is also used to pay those who purchased this type of shares.
But there is another scheme that is not directly prohibited by current legislation:
3. Using the funds in a special fund, it is possible to pay all dividends associated with those who have a certain number of shares of the preferred group. In the same example, we write off the entire amount of 350 thousand, it is written off from the debit of account 82. For other purposes, payments on ordinary shares, we direct the net profit received for a certain period.

Community bonds when forming the authorized capital and redemption rules
Bonds belong to the group of securities, according to the text of Article 143 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation.
An addition needs to be made here. Bonds are paid out of the reserve capital only when there are no other sources of payment. Other expenses usually include the amount representing the difference between the redemption cost and the nominal price, in a larger direction.
This situation can arise only if other miscellaneous expenses stop being generated. This requires the complete absence of any actions related to the conduct of business of entrepreneurs.
- The amounts used to redeem bonds and transactions on them are displayed in Debit 82 and Credit 66 or 67. But not everyone recognizes this option as correct. The placement of bonds is associated with the formation of a credit balance in the loan and credit accounts. Due to the processing described above, the debt may increase.
- Reverse wiring also becomes impossible. For example, Debit 66 (67) and Credit 82. Repayment of debt due to borrowed funds cannot be the reason why reserve capital is increased.
How to buy back shares if they are included in the authorized reserve capital?
Reducing fixed capital is the main purpose for which shares can be repurchased.
But it is not necessary to cancel them after the procedure is completed. And it is not necessary to reduce the authorized capital. You can sell securities to third parties or community members if the organizers at the general meeting make an appropriate decision.
In account 83 of the sub-account “Share Issue Income” it is then necessary to include the difference between such indicators as the redemption price and the nominal value of the paper. But for this account, you can only reduce the credit balance, in accordance with current legislation.
And a small conclusion. Account 82 accumulates only funds that can be used for expenses, the financing of which is reimbursed by net profit. Account 96 takes into account other types of financial assets that serve as reserve funds.
If the amount is taken into account, then it must be set at the moment when the cost of products, of any of its varieties, is formed. For tax purposes, accounting uses the procedure set out in Article 25 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation. Amounts credited to account 82 are not subject to income tax.
The legislation applies the concepts of both reserve funds and capital. However, they mean the same thing. It was capital that was considered, since it is included in the Government Plan, which is aimed at regulating this issue.
How to form and account for reserve capital, see this video:
Account 82 “Reserve capital” is used to account for movements in the organization’s reserve capital.
The account is passive, the reserve is reflected in the account balance.
Account correspondence
The reserve fund is formed at the enterprise at the end of the year, after its closure, based on profit data. The reserve is created on the basis of the amounts of retained earnings remaining at the end of the year.
The creation of reserve capital is mandatory for enterprises that have the legal form of a joint-stock company. For enterprises of other forms, the creation of a reserve fund is possible at the discretion of management.
Reserve capital may include:
- employee corporatization fund;
- reserve fund;
- fund for dividends on preferred shares;
- and others.
This fund is intended to cover the losses of the joint-stock company, as well as for settlements on bonds and shares in the absence of other sources. The reserve fund cannot be spent for any other purposes.
Reserve capital is formed by deductions from net profit. The annual amount of contributions is set by the management of the joint-stock company; this rate cannot be less than 5%.
The capital of the reserve fund is included in the equity capital of the enterprise when reporting.
How is reserve capital formed?
Reserve capital is formed by posting Dt “Retained earnings (loss)” - Kt 82 “Reserve capital”.
An example of formation at the expense of profit
The size of the reserve fund of PJSC Marengo is equal to 5% of the authorized capital. The amount of annual deductions from net profit is 7%.
As of the date of the meeting of the board of directors, the authorized capital was 15,000,000 rubles, net profit - 4,000,000 rubles, the amount of reserve capital - 850,000 rubles.
In accordance with the charter of the joint-stock company, the amount of reserve capital should be 1,000,000 rubles: 20,000,000 * 5%.
The amount of deduction from net profit will be: 4,000,000* 5% = 200,000 rubles. It is necessary to add another 150,000 rubles to the approved amount of the reserve fund. The board of directors decided to transfer 150,000 to the reserve from the net profit received.
The reserve is created by posting:
An increase in the net assets of an enterprise through the contribution of property (property rights) by shareholders of the company can also be reflected as an increase in the reserve fund. Wiring in this case:
An example of formation through the transfer of funds by shareholders
At the meeting, the company participants decided to contribute 10,000,000 rubles to the reserve fund.
Postings were created to reflect this operation:
Use of reserve capital
The use of the reserve fund for the purpose of its purpose occurs by decision of the board of directors of the joint-stock company or its other governing body. At the end of the year, this body has the right to decide to repay the resulting loss from the existing reserve.
Loss Coverage
At the end of 2015, the uncovered loss of Flagman LLC amounted to 375,000 rubles. The governing body decided to cover it from the reserve.
This operation will be reflected by the following transactions:
The reserve fund funds allocated to repay the loss in the current year must be restored in the following periods, so that the amount of the reserve is always no less than the amount stipulated by the charter.
Redemption of bonds and repurchase of shares
From the point of view of maintaining the interests of the enterprise, repaying bonds and buying back own shares at the expense of the reserve cannot be called a good solution. But it can be used in the absence of other sources.
In the first case, the wiring will look like:
Loan accounts are passive, so correspondence with account 82 increases the debt.
Transactions for the repurchase of own shares look like this.
Account 82 “Reserve capital” is intended to summarize information about the state and movement of reserve capital.
Deductions to reserve capital from profits are reflected in the credit of account 82 “Reserve capital” in correspondence with the account “Retained earnings (uncovered loss)”.
The use of reserve capital funds is accounted for as a debit to account 82 "Reserve capital" in correspondence with the accounts: "Retained earnings (uncovered loss)" - in terms of the amounts of the reserve fund allocated to cover the organization's loss for the reporting year; “Settlements for short-term loans and borrowings” or “Settlements for long-term loans and borrowings” - in terms of amounts used to repay the bonds of the joint-stock company.
Account 82 "Reserve capital"
corresponds with accounts
Application of the chart of accounts: account 82
- Audit program
As a contribution to the authorized capital; - journals-orders and statements of accounts 75 ... “Settlements with founders”, 80 “Authorized capital”, 81 “Own ... shares (shares)”, 83 “Additional capital”, 82 “Reserve capital”, general ledger ; -financial statements. RD...
- The procedure for filling out the balance sheet in a general form. Example
Which is taken into account on account 83 “Additional capital”. Additional capital (without revaluation... to be reflected in the line above. Reserve capital. The balance of the reserve fund is indicated on line 1360... assets). Line 1360 "Reserve capital" = Kt 82. Line 1370 "Undistributed...; Authorized capital (share capital, authorized capital, contributions of partners)" is equal to the credit balance of the account.... Line 1360 “Reserve capital” is the credit balance of account 82. In our case, this is...
- The procedure for filling out the balance sheet in a simplified form. Example
Lines In the first line “Capital and reserves” indicate the total... reflected in section. III "Capital and reserves" of the usual form... dividend payments, contributions to the authorized capital, etc. Please note... Dt 50 15,000 Kt 82 10,000 Dt 51,250 ... now the balance sheet liability. Authorized and reserve capital, as well as retained earnings are reflected... on one line “Capital and reserves”. Amount... account credit balance 60 + account credit balance 62 + account credit balance 69 + credit...
- Audit of annual financial statements of organizations for 2018
February 16, 2005 No. 82. Based on the Federal Laws “On... network resources as a backup service, network policies and... funds, statement of changes in capital, statement of cash flows... recalculation, subject to inclusion in additional capital of the organization. Disclosure of data on... the name and characteristics of the balance sheet account No. 40824 “Escrow accounts of individuals, individuals... by shareholders, participants for increasing the authorized capital of a credit organization have been clarified. The amounts indicated...
- The near-term prospects for the ruble have become more dependent on capital flows
Balance of payments accounts - inflow of direct investment and import of capital... increasingly dependent on capital flows - its weakening now... barrel). The traditional deterioration in the current account in the second quarter... to $83.4 billion from $82.4 billion in the first quarter... sales of foreign currency from the Reserve Fund, a decrease in capital outflow from the banking sector... shocks and a sharp increase in capital outflow. “The balance of payments is all... the higher the current account surplus, the higher the capital outflow), we bet on...
Banks account 51 "Current accounts" (instead of accounts 51 "Current accounts" ... capital account 80 "Authorized capital" (instead of accounts 80 "Authorized capital", 82 "Reserve capital...", 83 "Additional capital" ... ; ); to account for financial results...
Account 82 of accounting is a passive account “Reserve capital”, reflects the creation of reserve capital and the purposes for which it is directed. Let's consider the specifics of using account 82 in accounting and examples of business transactions for the formation of a reserve fund and postings to account 82.
Reserve capital is created from the net profit of the organization.
Amount of reserve capital:
- For a JSC there must be at least 5% of the authorized capital;
Amount of contributions to the reserve:
- For JSC, at least 5% of net profit per year;
- LLCs determine the value at their own discretion.
Purposes of using reserve capital:
- Loss coverage;
- Redemption of own bonds;
- Redemption of own shares.
The size of the authorized capital of most LLCs is small and usually amounts to 10,000 rubles. The amount of reserve capital directly depends on the size of the management company and amounts to a small amount of 10,000 rubles. Therefore, reserve capital for most LLCs is of a formal nature and does not solve the problem of covering the organization’s losses.
Account 82 in accounting
The credit balance of account 82 shows the amount of reserve capital available to the organization:
Two types of reserves are created on the account, which are presented in the diagram:

Formation of a reserve fund and posting to account 82
Let us give examples of business transactions for the formation of a reserve fund and postings to account 82.
Get 267 video lessons on 1C for free:
Example No. 1. Additional accrual of the reserve fund in connection with legal requirements
Let’s assume that a private security company (PSC) had a capital account balance as of December 31, 2009:
- Account balance 80 – 10,000 rubles;
- Account balance 82 - 1,000 rubles;
- Account balance 84 – 41,000,000 rubles.
The company's charter provides for the creation of a reserve fund in the amount of 10% of the amount of its authorized capital. The reserve fund has been formed in full.
In December 2009 Amendments were made to the law “On Private Security Activities”, in particular, the authorized capital of a private security company providing armed security services cannot be less than 250,000 rubles.
In January 2010 the organization brought the amount of authorized and reserve capital into compliance with the law.
Postings for the formation of the reserve fund in account 82, made in the organization in January 2010:
The private security company's balance in its authorized and reserve capital accounts as of January 31, 2010 was:
- Account balance 80 – 250,000 rubles;
- Account balance 82 - 25,000 rubles.
Example No. 2. Formation of a reserve fund
Let’s assume that the authorized capital of an LLC engaged in the sale of alcoholic beverages is 1,000,000 rubles. The charter of the LLC provides for the creation of a reserve fund in the amount of 15% of the amount of its authorized capital. The reserve fund is formed by deductions from profits until the fund reaches the specified size. The amount of annual contributions to the reserve fund is 5% of net profit. The organization was registered in the Unified State Register of Legal Entities in 2008.
Table of indicators and calculation of reserve capital:
| Of the year | Profit (+)
Loss (-) |
The amount of reserve capital provided for by the charter | Reserve,
liable to additional accrual |
Credit balance on account 82 at the end of the year | |
| 2008 | -200000 | none | 1000000*5%=150000 | none | |
| 2009 | -320000 | none | none | ||
| 2010 | +200000 | 10000 (200000*5%) | 150000-10000=140000 | 10000 | |
| 2011 | +400000 | 20000 (400000*5%) | 140000-20000=120000 | 30000 | |
| 2012 | +3250000 | 120000 (150000-10000-20000)
(3250000*5%)=162500 162500>150000. 150,000 is involved in the calculation |
120000-120000=0 | 150000 |
Postings to account 82 made in the organization:
| Dt | CT | Sum
(rub.) |
Contents of a business transaction | Document |
| In December 2010 | ||||
| 84 | 82 | 10000 | Contributions to reserve capital | |
| In December 2011 | ||||
| 84 | 82 | 20000 | Contributions to reserve capital | Charter, accounting certificate |
| In December 2012 | ||||
| 84 | 82 | 120000 | Contributions to reserve capital | Charter, accounting certificate |







Presentation on the topic "special theory of relativity"
Why is Rosneft buying TNK-BP Which oil and gas company does TNK own?
Blog of Anatoly Shariy 25.08. How blogger Anatoly Shariy fired the Minister of Information of Ukraine. Conflicts with the Ministry of Internal Affairs
Best International Art Gallery
Chinese Pilot Jao Da