A nut is a fastener for a screw drive or threaded connection. They differ from other parts by a threaded hole. Together with a bolt (screw) it forms a screw pair. Nuts that are screwed onto a stud or bolt make up a bolted joint. Most often, hexagonal nuts are made in factories. They are specially made for a wrench. Also on sale you can still find nuts with "lamb" ledges, square shape, round knurled and other shapes. They are made from automatic steel. For this, special machines are used.
When buying it, make sure that the square that supports the glasses is the size of your regular rattle. If not, you will have to buy new glasses or at least one adapter. Of course, it is important that the nuts on the motorcycle are tight. However, contrary to what many people believe, it is not good to press "to death" everything you put in: for example, the cylinder head must be perfectly level, with the same pressure on the joint and block in its entire contour. If this is not the case, you can eventually warp and cause a compression leak or a mixture of oil and water inside the engine, resulting in "shredding".
It is worth noting that the nuts also differ in strength class. So, for nuts made of carbon alloyed or non-alloyed steels, a strength class of 4-6, 8-10 is established. For nuts having a normal height (more than 0.8d), strength class 12 is set. Those nuts that have a height of 0.5d-0.8d have a strength class of 04-05. The shape of the nut is also different. There are winged open and closed ones (defined by GOST 3032-76), hexagonal crowned round, hexagon slotted (defined by GOST 6393-73, 11871-80). There are lower hex nuts, especially high, high and normal height. Hexagonal castle nuts, slotted and hex nuts can be lightweight (with small outer dimensions), as well as normal (photo 1).
For this, it is not only important to tighten with the force that the manufacturer indicates to you, if you do not follow the order that sends you. If there is no set order, always in a cross: if you start with a screw, the next one to tighten is not the one next to it, but the one in front. Continue what you have at an angle with this one and then before this third.
Combination pipe wrench
The truth is that many mechanics have a bad habit of using torque gauges only in stocks, pulleys and a little more: the truth is that this is very important. But if you take the workshop book, you will see that almost all the threads of the bike are tightened, and they are, and they are all "in place" because the bike will last longer and work better: no more friction causing friction required screws, bolts, broken excessive force or loose nuts that they went through. In fact, if you could see the mechanics of the world, you would see that they hardly use anything else to tighten their nuts.
Hex nuts are the most common. Castellated and slotted nuts are used when it is necessary to lock the nuts with cotter pins. For fastening different parts round nuts are used, well, for connections that need to be constantly assembled and disassembled, it is best to use wing nuts, which can be easily tightened without even using a special wrench. By the way, if you need to use a large number of nuts, it is more expedient to take lightweight ones, since they will save a lot of weight. When it can be seen that the shank of the bolt is underloaded in tension, it is best to use low nuts. To protect the thread from wear, as well as crushing during frequent unscrewing and heavy loads, use extra high or high nuts (photo 2). 
The size of the nut should be understood as the distance that is formed between the parallel faces. Dimensions are regulated by GOST. So, nuts of accuracy class A, hexagonal low, increased accuracy have the dimensions specified in GOST 5929-70. The size of hex nuts of accuracy class A is specified in GOST 5916-70. In other state standards - GOST 5916-70, 5915-70, the dimensions of nuts of accuracy class B, hexagonal low and hexagonal are given. All dimensions can be viewed in the tables given in GOST (photo 3). 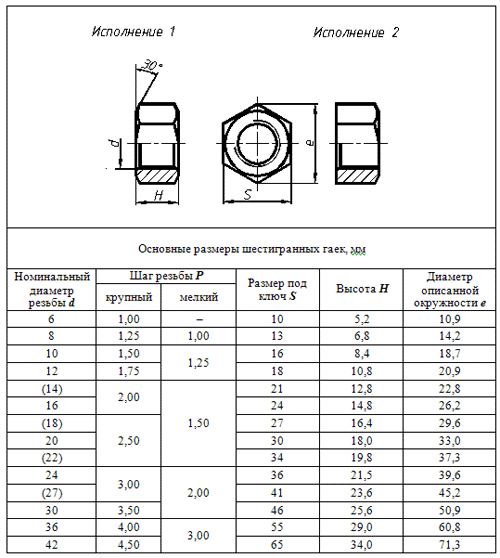
The most popular nut, as already mentioned, is a hex nut. Such nuts differ in size: M 6, M 8, M 10, M 12, M 16, M 24, M20, M30, M27, M 36, M 52, M 48, M 42. keys. Today there are fifteen types of such keys. There are on sale gas, end, cap, open-end, adjustable, balloon, combined, hexagonal and candle, designed for spark plugs (photo 4). 
Wrench sizes also vary. The size of the thread will play a role for the nut, so they can be M1.6 - M110. The distance between the jaws of wrenches ranges from 3.2 millimeters to 155 millimeters. The length of the handle can be from one hundred and fifty millimeters to five hundred millimeters. Combination wrenches are popular - on one side are caps, and on the other are open-ended. It is also worth noting that special nuts are used in industry today. These are hex nuts that are used to seal joints, fasten wheels on vehicles (photo 5).
Three types of sockets used in socket wrenches. These are the elements that are connected to the dynamometer and allow tightening, in the photo we have an example wrench 10 connected to different heads according to their width. It always contracts when cold due to the expansion of materials when hot. It is important to make the gesture continuous at the moment of tightening, so we must use turns and elbows, where we do not allow the key to turn completely. If not in use for a long time, it is recommended to store it at minimum torque by turning the knob clockwise until it stops.
The caliper is a handy and easy-to-use measuring tool. Proper use of it allows you to measure linear values in various situations, and for a variety of objects, from tire tread to plastic flexible tubes. How to measure with a caliper - examples and sequence - these issues are discussed further.
Measurements in the design and manufacture of threaded connections
The bolt-nut connection is one of the most common in mechanics. When designing and manufacturing structures, the task of how to measure a bolt with a caliper is often difficult.
Before work, it is worth remembering that the main dimensions of the bolt / nut are the length of the product and the diameter of the thread. Standard bolt any performance in carrying out such measurements is not needed. Another thing is when the bolt is made in artisanal conditions, or it is required to measure the fastener without dismantling the connection. The following situations are possible here:
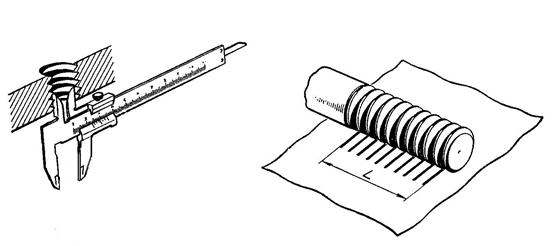
Tread pattern measurements
How to measure the tire tread if you need to assess the degree of wear? A depth gauge will help, which measures along the entire generatrix of the tire tread. It should be taken into account that wear is almost always uneven, and the number of measurements should be at least 3 ... Before measurements, the tire should be thoroughly cleaned of dirt, dust and fragments of small stones stuck inside.
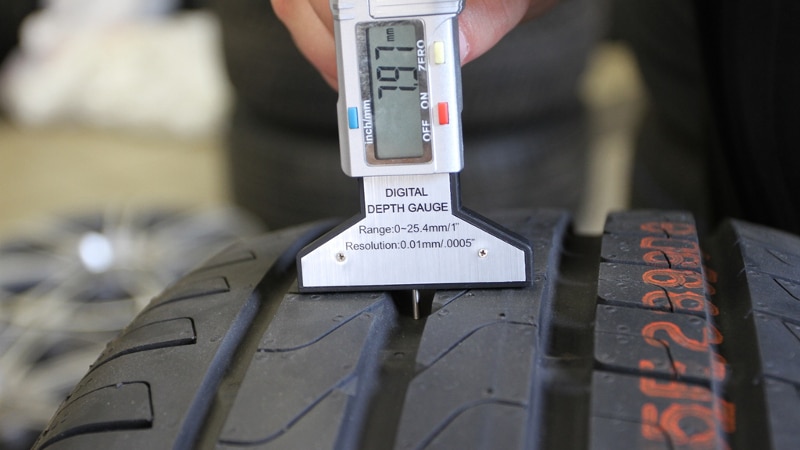

Sometimes you need to solve the problem - how to measure the tire tread with a caliper to determine the degree of wear uniformity. This establishes the wear of the tread tires not only in depth, but also along the radius of the transition from the circumference of the protrusions to the circumference of the depressions. They act like this. The depth of the pattern on the new tire tread is measured, and then the linear size of the visually changed zone on the used part. The difference will determine the degree of wear and help to accept the right decision about changing a wheel.
All measurements are made with a depth gauge, which must be installed strictly perpendicular to the generatrix of the tire tread.

Columbic tread wear measurement
Diameter measurements
How to measure the diameter with a caliper? Distinguish between parts with a constant and variable length section. The latter include, in particular, reinforcing bars. How to measure rebar diameter with a caliper? It all depends on the reinforcing profile, which can be:
- ring;
- crescent;
- mixed.

It is easiest to measure such reinforcement parameters in the second case. First, the height of the protrusions of the profile is determined with external measuring sponges, and then with a depth gauge - the size of the depression. Measurements must be made in two mutually perpendicular directions, since the reinforcement, and even not produced at specialized enterprises, often has an oval cross section. After that, according to the tables of standard reinforcing profiles, the most suitable value is found (special accuracy is not required here). How to measure the diameter of the reinforcement with a caliper if it has a different type of profile? Here, instead of the diameter of the protrusions, the diameter of the protruding part of the sickle-shaped notches is determined, and then they proceed in the same way as in the previous case.

When measuring the internal dimensions of pipes, the internal measuring scale of the tool is used. How to measure the thickness of the pipe with a caliper, especially if the gap is small? It is enough to calculate the difference between the external and inner diameters and divide the result by two.
Linear measurements
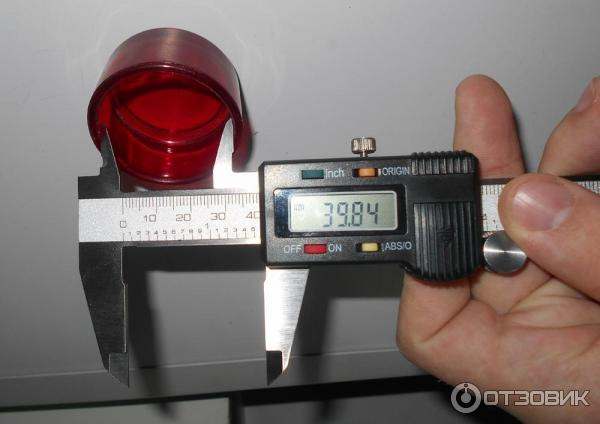
How to measure linear dimensions with a caliper? It all depends on the material of the part / workpiece. For rigid elements, the product is tightly pressed against some base plate, after which the outer measuring jaws of the tool are measured. You must first establish the suitability of the existing type of caliper for work. For example, the main measuring scale on the rod should be longer than the part by less than 25…30 mm (taking into account the own width of the jaws). When using a depth gauge, this value is even smaller, since the length of the frame should also be taken into account (for the most common tools 0-150 mm and an accuracy of 0.05 to 0.1 mm, this parameter is taken at least 50 mm).
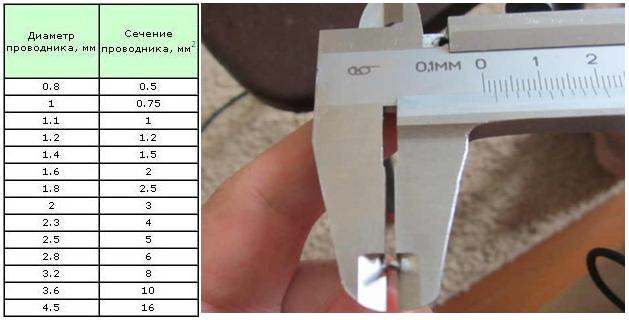
How to measure the cross section of a wire with a caliper? Non-metallic products are flexible, and therefore significantly distort the result obtained in the usual way. Therefore, a rigid steel part (screw, nail, piece of rod) should be introduced into the cambric, after which the diameter of the wire section should be determined with external sponges. Do the same if you want to know inner size wires.
The question - how to measure a chain with a caliper - is often asked by cyclists, since chain wear, defined as the distance between its adjacent links, allows you to decide whether to replace the product. The outer jaws are set at a distance of 119 mm and inserted into the link, after which they are stretched to the sides until further increase in size is impossible (to facilitate work, the chain can be preloaded with a tensile force). The deviation from the original size will show the actual wear, which must then be compared with the maximum allowable.
If you find an error, please highlight a piece of text and click Ctrl+Enter.











How to understand: will the kitten be fluffy?
What kind of light alcohol can be drunk for pregnant women: the consequences of drinking
Why do the legs swell in the ankles and ankles of the feet in pregnant women: causes and methods of treatment
The wedding of Prince Harry and Meghan Markle: scandalous and secret details of the marriage (photo) The future marriage of Prince Harry year NTV
How to close white plums for the winter